isomers and conformations
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
what are configurational isomers?
stereoisomers that cannot interconvert
what are conformational isomers?
spatial arrangements of molecules through rotations of bonds
what are the features of enantiomers? (3)
non super imposable mirror images of each other
both rotate plane polarised light in equal but opposite directions
other physical and chemical properties are the same
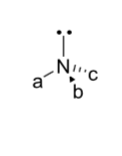
how do chiral amines behave?
not configurationally stable
inversion of lone pair is fast at room temp
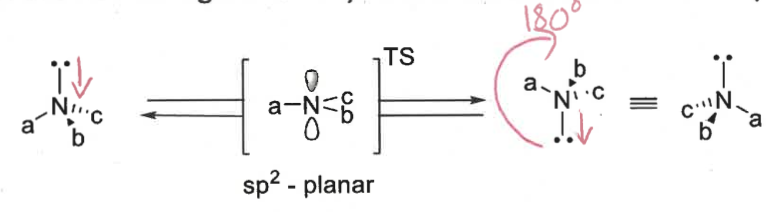
why can phosphines and sulfoxides be isolated as single enantiomers?
they interconvert slower
what is planar vs axial chirality?
planar = planar system with a perpendicular substituent
axial = non planar arrangement of 4 groups about an axis
is this planar or axial chirality?
planar (perpendicular substituent)
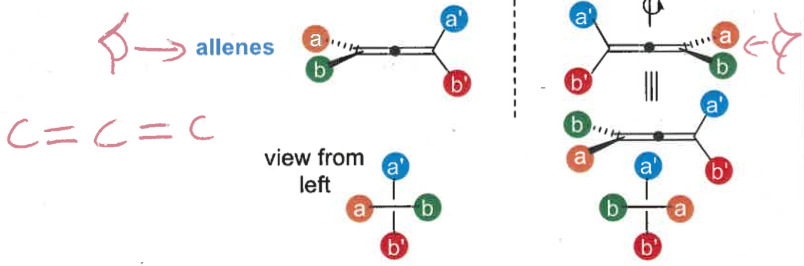
is this planar or axial chirality?
axial
what is atropisomerism? what is type of chirality is this?
restricted rotation around a chiral axis
a type of axial chirality
what are diastereoisomers?
how do their properties compare?
stereoisomers with different configurations at one or more stereo centres
different chemical and physical properties
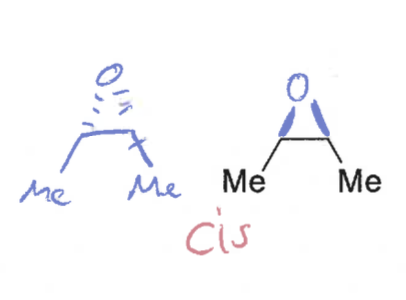
what is the difference between syn and anti (diastereoisomers)
syn = groups on the same face
anti = groups on the opposite face
for compounds with n stereocentres…
how many stereoisomers are there? how many diastereomers?

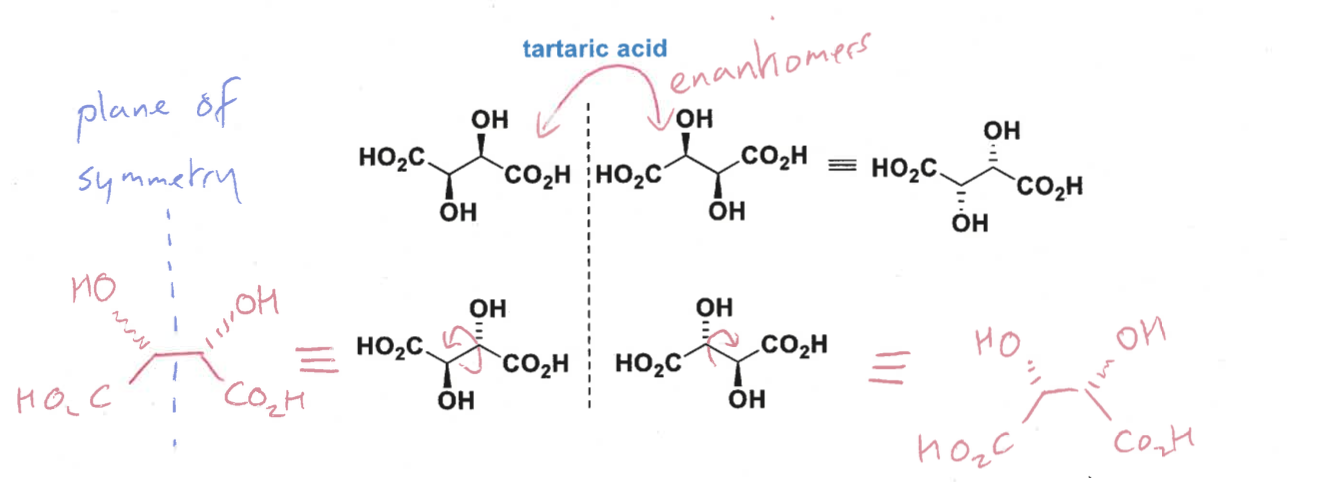
what are meso isomers?
stereoisomers with identical substituents show diastereomers and one is achiral due to a symmetry plane or point of inversion
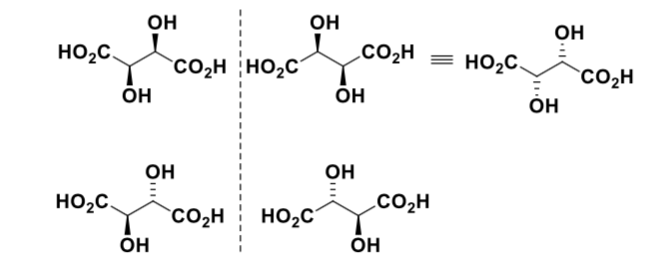
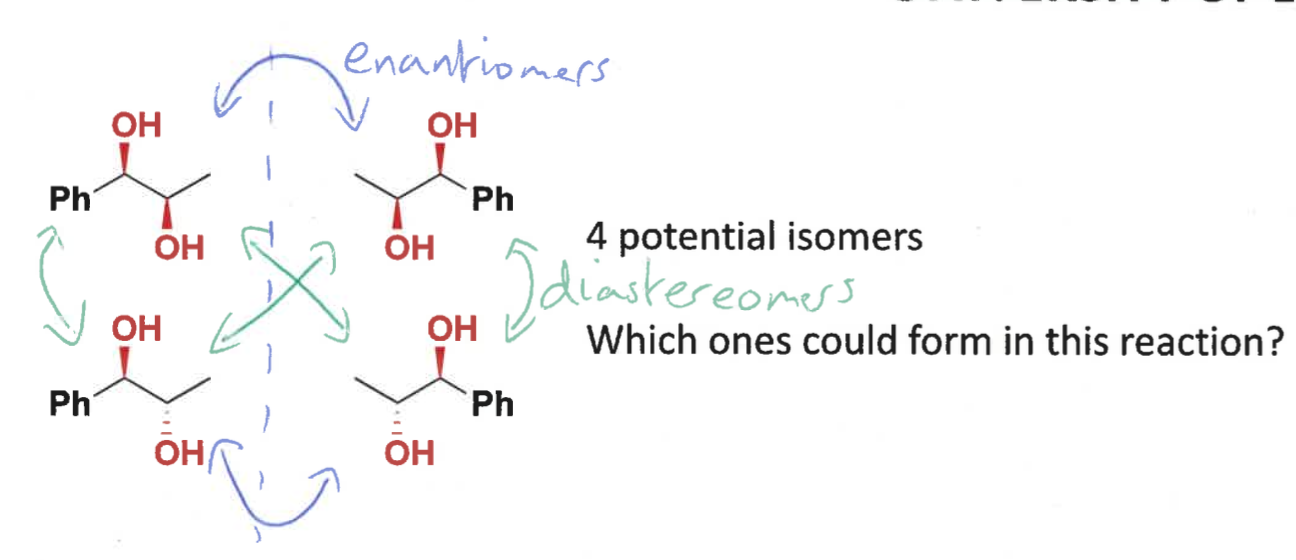
what is the top molecules’ relationship to each other
how are the top and bottom molecules meso isomers?
are there any diastereomers?
top two molecules are enantiomers
not enantiomers to each other as they are achiral
the top and bottom would be diastereomers, except that the bottom molecule is not chiral and has no stereocentres
how to decide whether a geometrical isomer of an alkene is E or Z (Cahn-Ingold)?
assign which end of the double bond is highest in priority
on each carbon, assign the priorities of each group
E = two higher priority groups on opposite sides
Z = two higher priority groups on same side
how to decide whether an enantiomer is R or S (Cahn-Ingold)?
priorities the substituents on the molecules from highest to lowest
redraw the molecule to look down the bond of lowest priority
determine if substituents 1,2,3 are in clockwise or anticlockwise order
R = clockwise
S = anticlockwise
how can the substituents on a molecule be prioritised?
higher atomic number > lower
greater number of higher priority atoms
multiple bonds = 2 or 3 bonds to atom of that atomic mass
if above doesn’t work, move to next atom in ring or chain
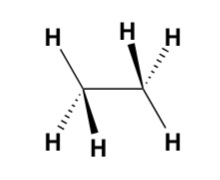
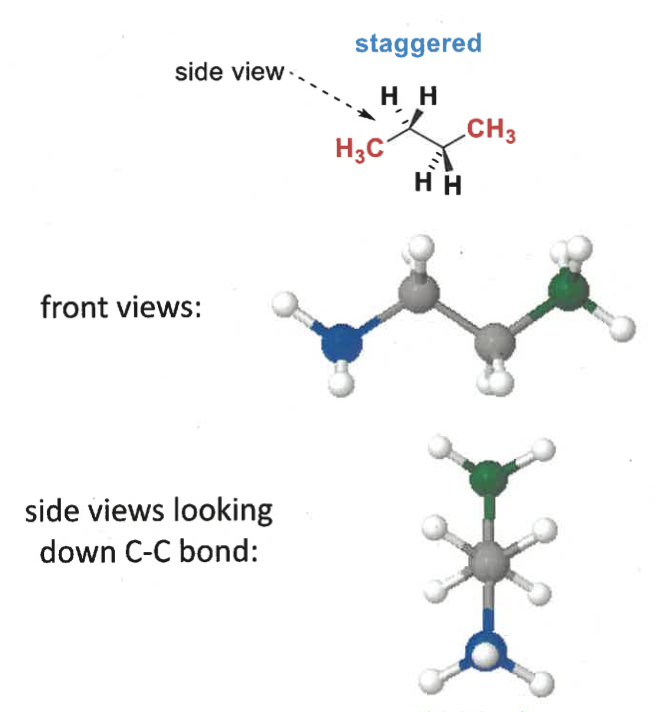
how to determine if a molecule is eclipsed or staggered?
rotate C-C bond so groups with same orientation are both up/down
look down bond
staggered = as far apart as possible
eclipsed = groups line up
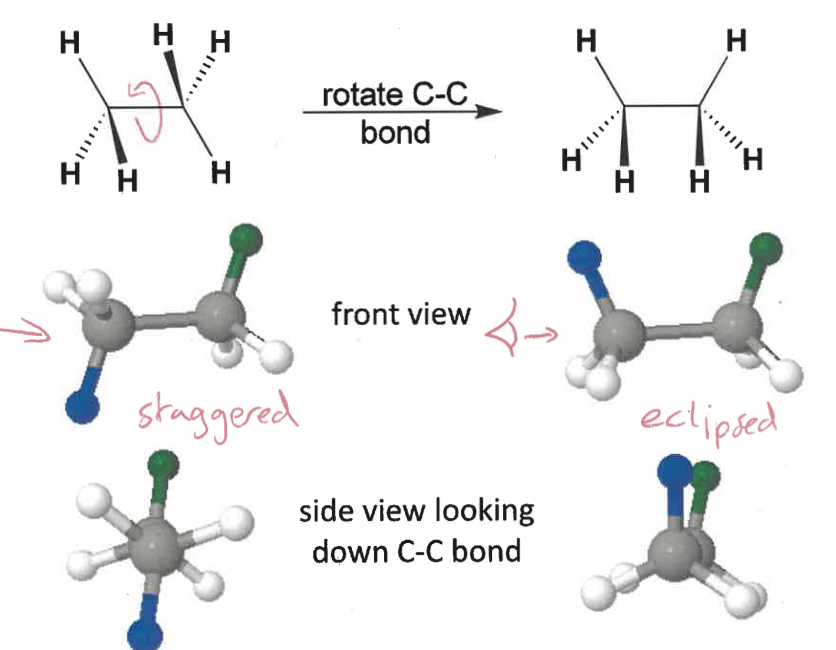
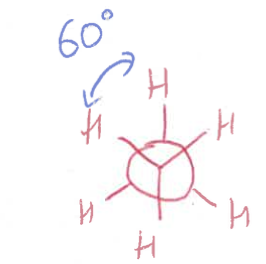
staggered Newman projection
bond angle?
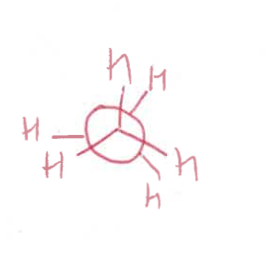
eclipsed Newman projection
why are staggered and eclipsed conformations different energies?
eclipsed = higher due to repulsion of coplanar bonds
staggered = groups as far apart as possible, also hyper conjugative stabilisation
how does the staggered conformation of ethane show hyper conjugative stabilisation?
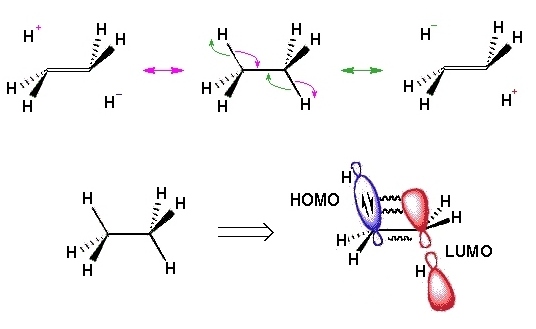
what is the energy diagram as ethane moves through staggered and eclipsed?
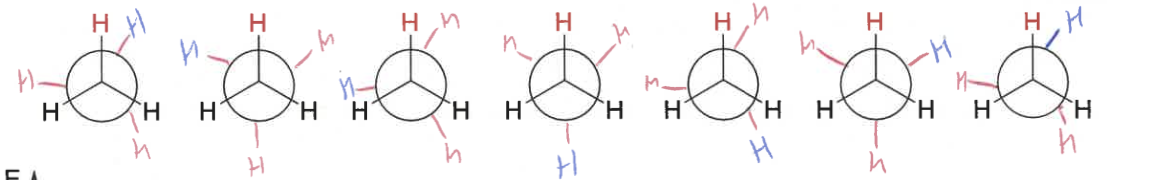
staggered conformation of butane?
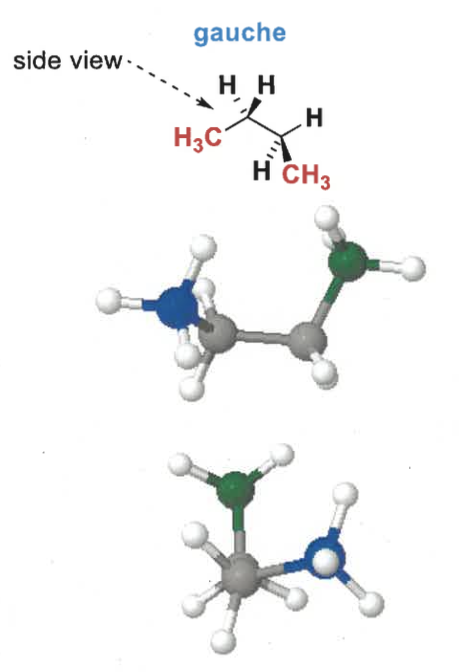
gauche conformation of butane?
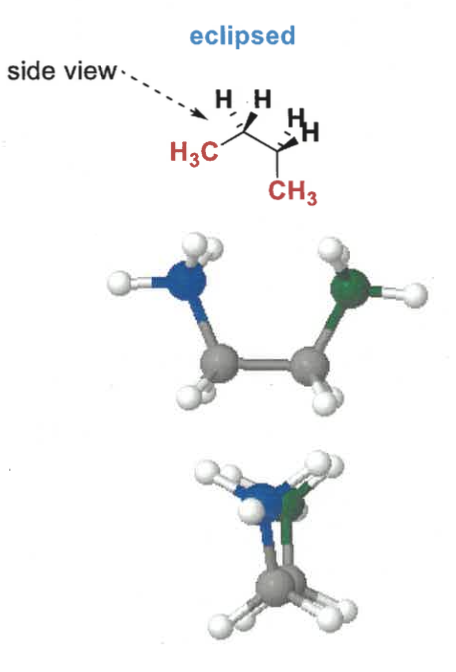
eclipsed conformation of butane?
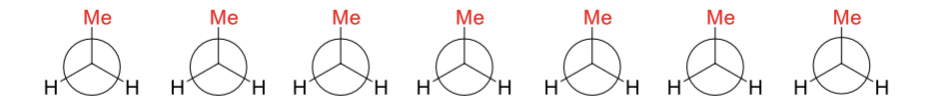
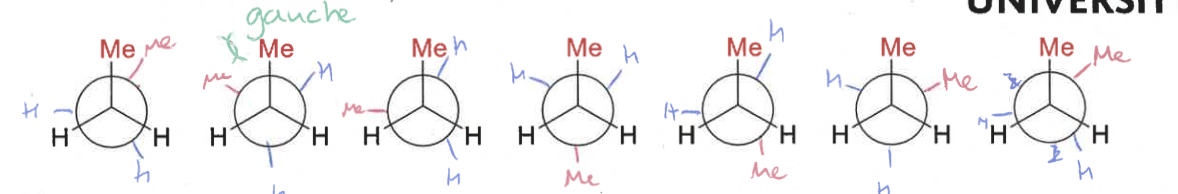
draw butane’s conformations as it rotates
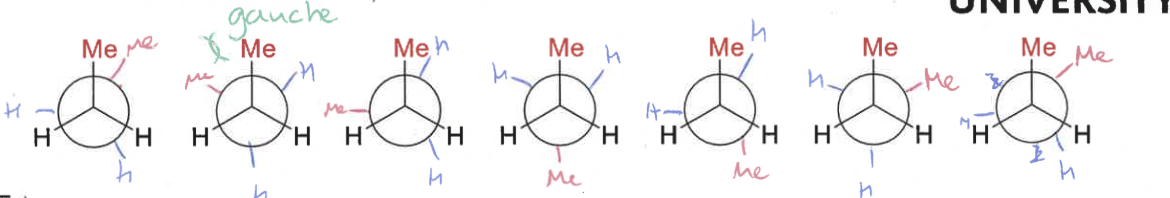
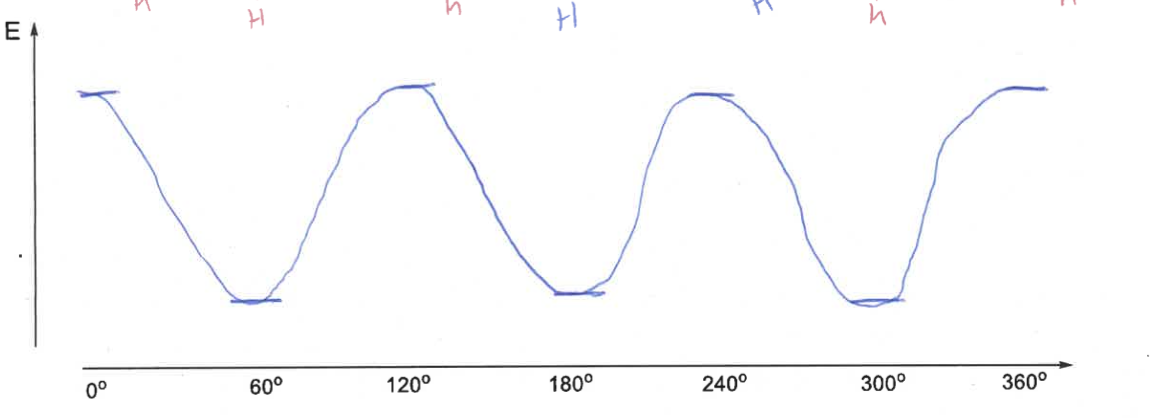
what is the energy diagram as butane moves through its conformations?
explain the shape compared to ethane
methyl groups have larger steric effect than hydrogens
gauche = groups as far apart as possible, also hyper conjugative stabilisation so lower in energy
minimum when methyl groups are antiperiplanar
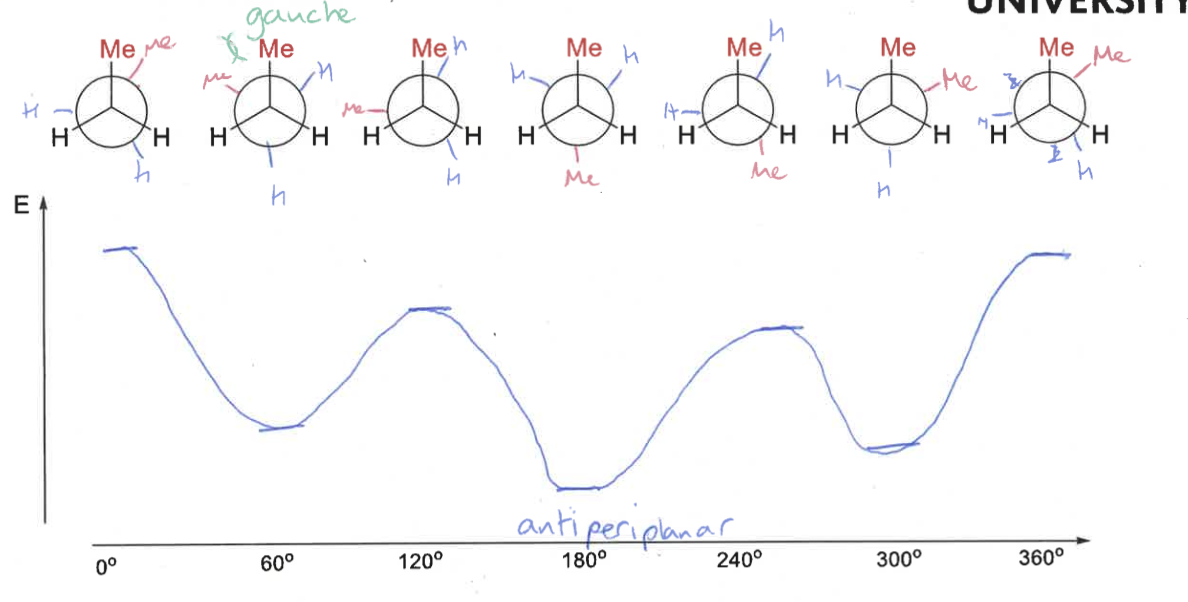
what is the difference between axial and equatorial in 6 membered rings?
axial = atoms above or below the ring
equatorial = atoms to the side of the ring
what do chair and boat conformations look like?
which is more stable
chairs are more stable than boats
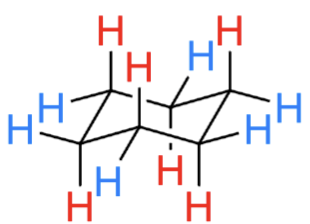
where is there a steric clash?
1,3-diaxial
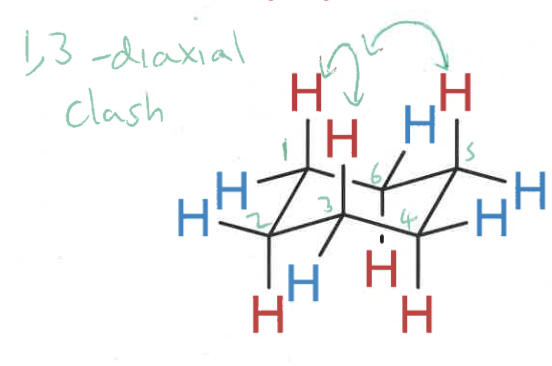
how do chairs change after ring inversion?
orientation of substituents change
all equatorial become axial and all axial become equatorial
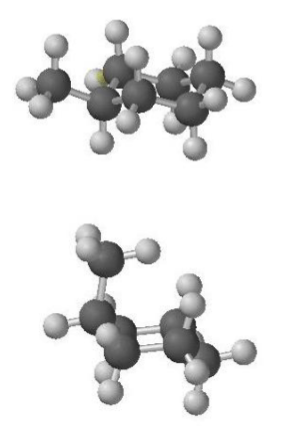
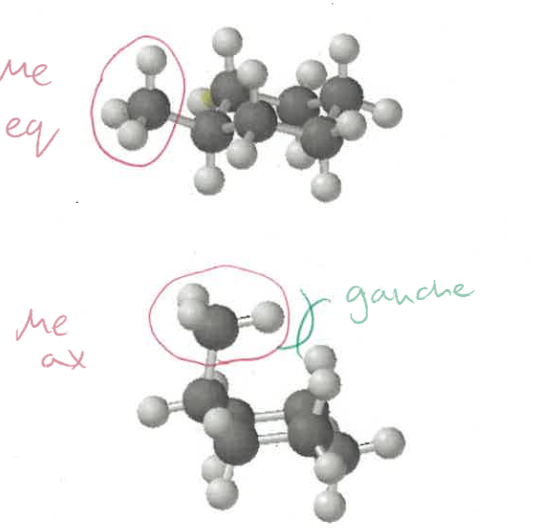
which position are larger groups more stable in (chairs)?
more stable in equatorial
in axial there are 1,3-diaxial, and gauche interactions
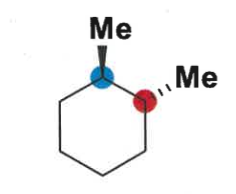
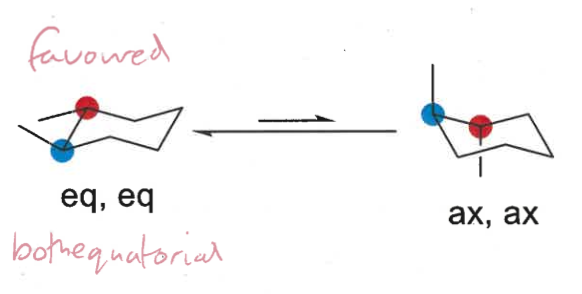
which conformation is favoured in disubstituted cyclohexanes?
largest group or more groups equatorial
draw in chair and decide which conformation is more favoured
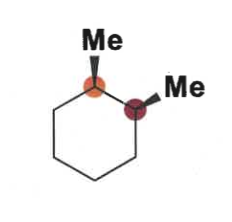
draw in chair and decide which conformation is more favoured
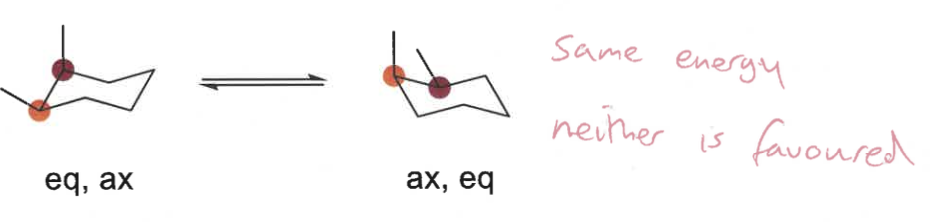
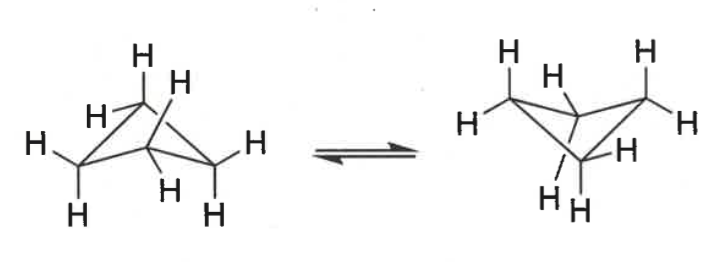
why are smaller rings less stable that cyclohexanes?
rings are more strained
eclipsing interactions = torsional strain
show ring strain in cyclopropane
torsional strain? orbital overlap?
each C-C angle is 60

show ring strain in cyclobutane
how is it better than cyclopropane?
relieves some torsional strain by adopting puckered conformation
show ring strain in cyclopentane
confirmation?
adopt envelope conformation - sawn off chair
eclipsed = more strain on right hand carbon
how does ring strain chain as ring gets bigger?
strain decreases
carbons become more staggered rather than eclipsed
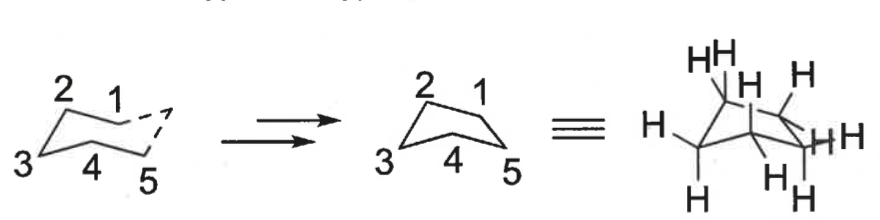
what conformation does cyclohexene adopt?
hybridisation?
contains two sp2 carbons = trigonal planar
adopts half chair conformation
= more strained
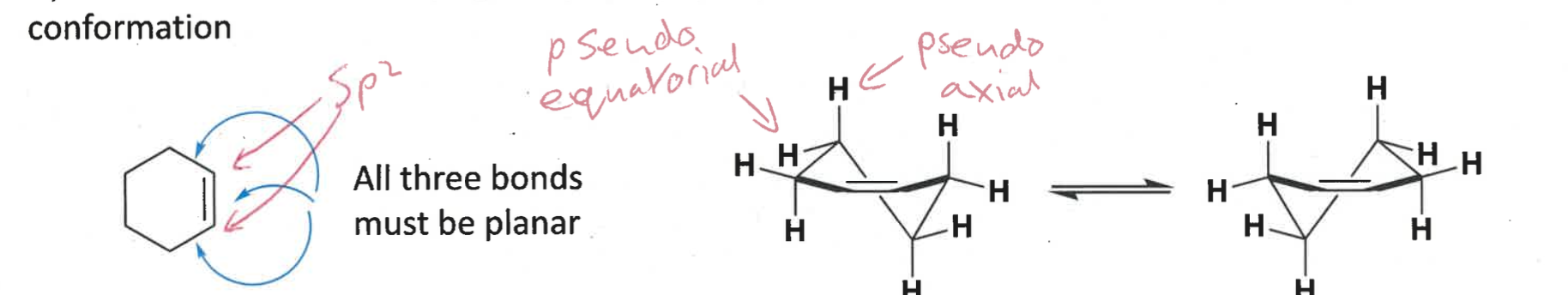
are double bonds attached to cyclohexane ring axial or equatorial?
draw angle
neither
C=O bond intersects axial-equatorial bond ange
show cyclohexene chair ring flip

what is a decalin?
fused cyclohexanes
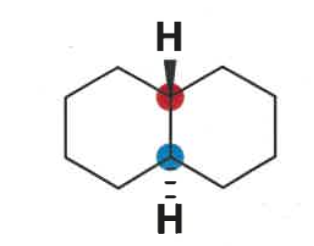
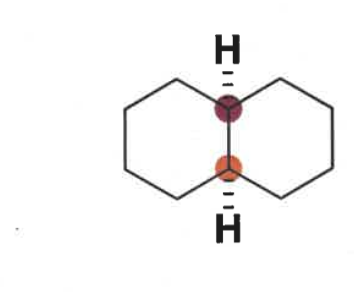
how do trans decalins exist?
draw both conformations
both groups equatorial
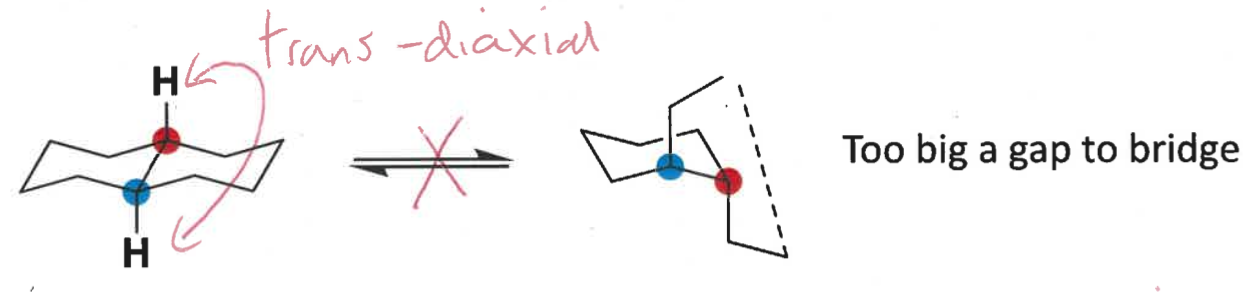
how do cis decalins exist?
draw conformations
can have two - one substituent equatorial and one axial

is a trans or cis decalin more stable?
trans is more stable than cis
cis has 1,3-diaxial clash

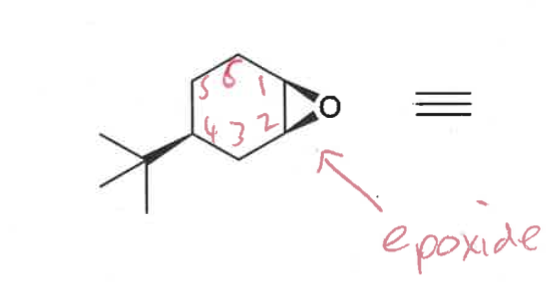
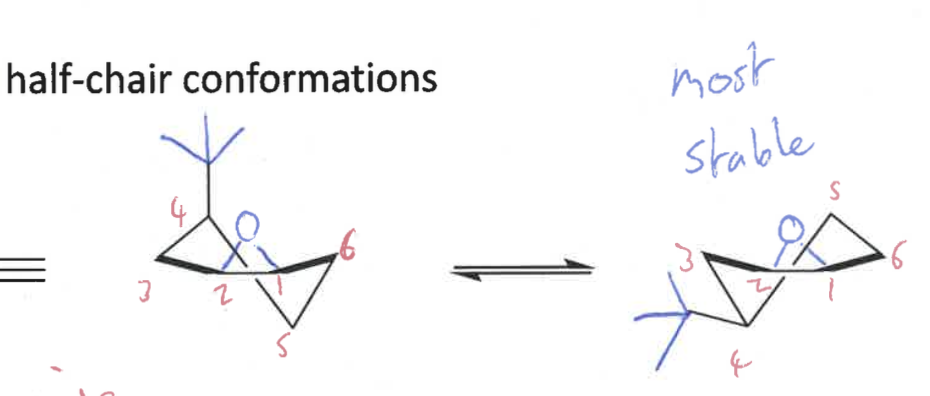
what conformations do epoxides form?
draw conformations - which is most stable?
half chair
pseudo equatorial is most stable
epoxide stays the same even after ring flip
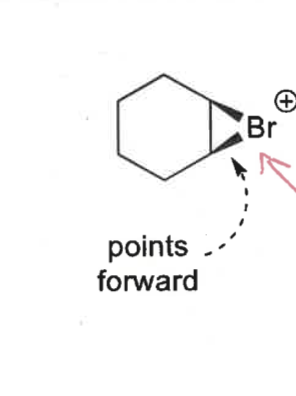
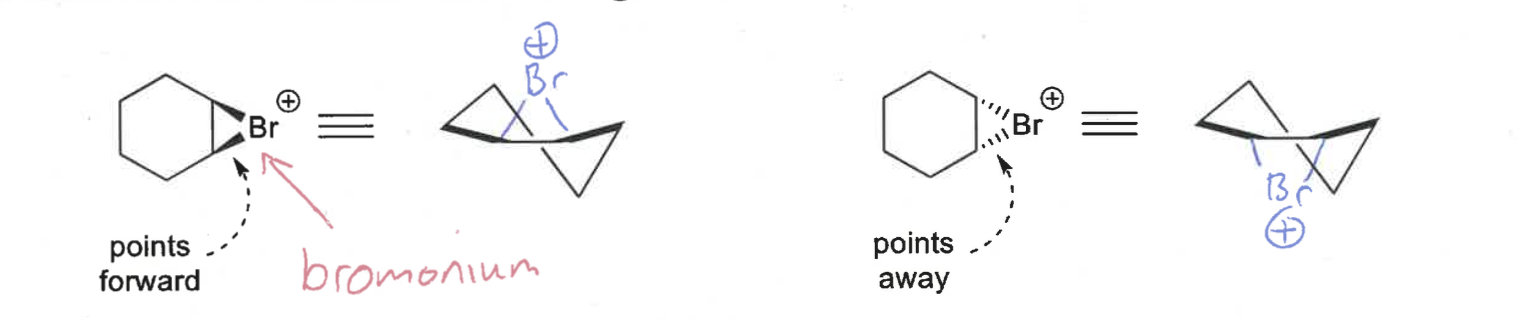
what conformations do bromoniums form?
show for both points forwards and points away
half chair
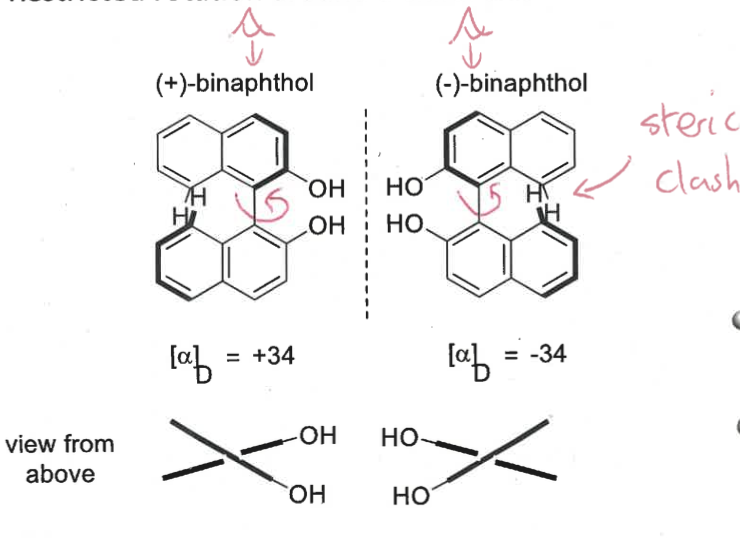
how can enantiomers be described?
as either + or - depending on how they rotate plane polarised light
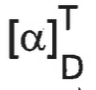
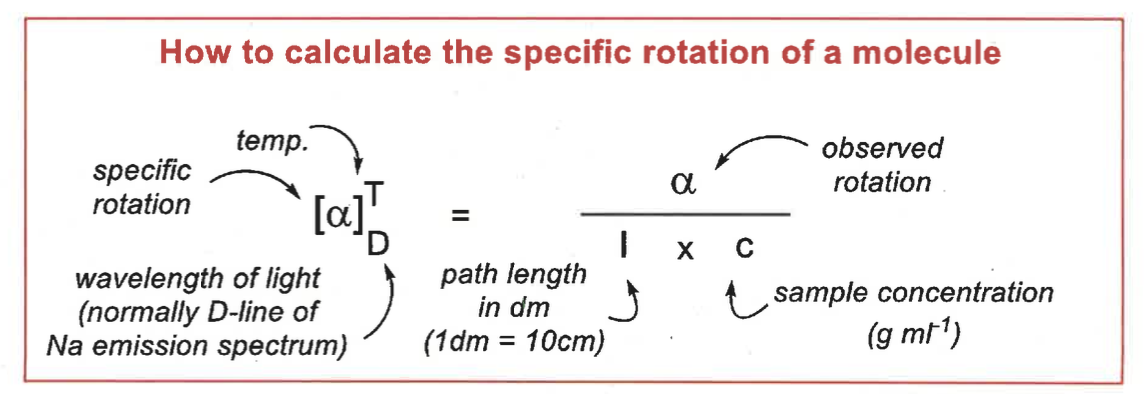
how to calculate specific rotation of molecule
units?
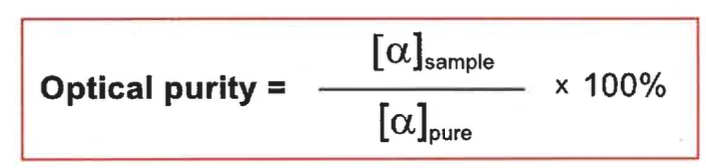
how to calculate optical purity?
what is a disadvantage of this?
you must know the rotation of a pure sample - may not have been prepared before
what are the two ways of referring to a ratio of mixture of enantiomers?
enantiomeric ratio
enantiomeric excess
how to calculate enantiomeric excess?
i

if there is 95:5 ratio of two enantiomers, what is the enantiomeric excess?
95 - 5 = 90% e.e.
5:5 racemic so 90% not cancelled out
how is chiral chromatography performed? what type of chromatographic techniques are used
gas chromatography or high performance liquid chromatography
stationary phase is modified with chiral molecules
diastereomeric environment = one enantiomer is more strongly retained than the other = separated
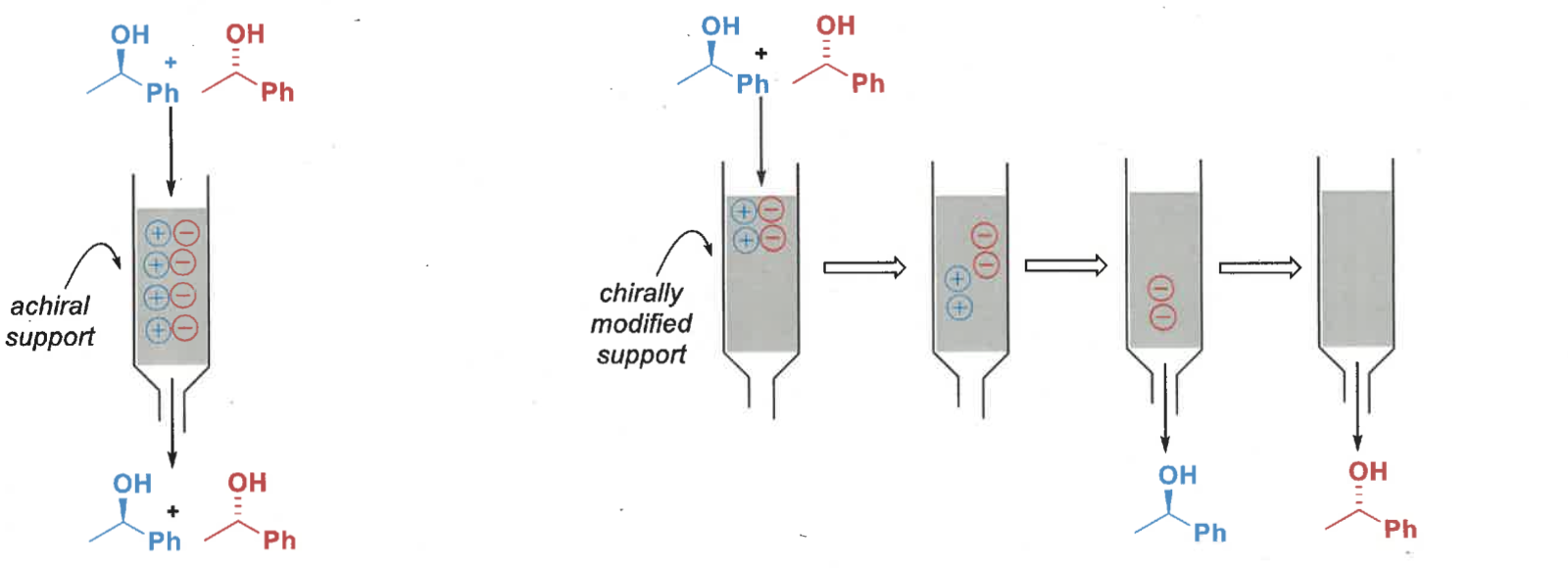
what is the difference between achiral and chiral chromatography?
achiral = enantiomers have same affinity for stationary phase and so pass through at same rate
chiral = different affinity for stationary phase, different chemical environments so pass through at different rates
what are the different H environments in this molecule?
no rotation so not in same environment
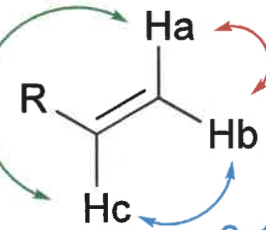
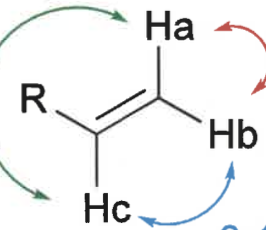
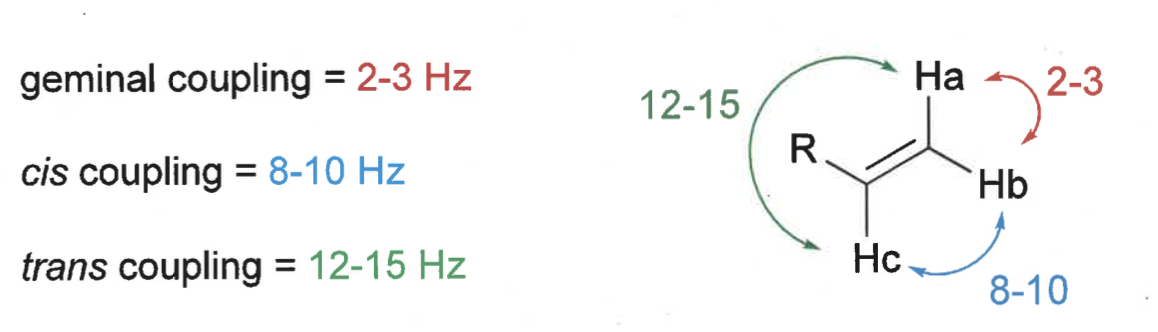
what is trans, cis and geminal coupling constants?
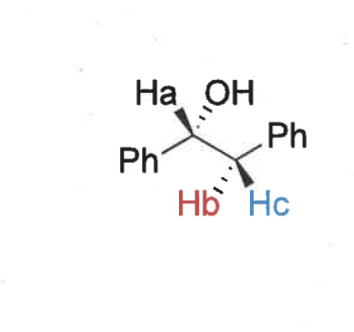
proton environments near a stereocentre are what?
diastereotopic = non equivalent
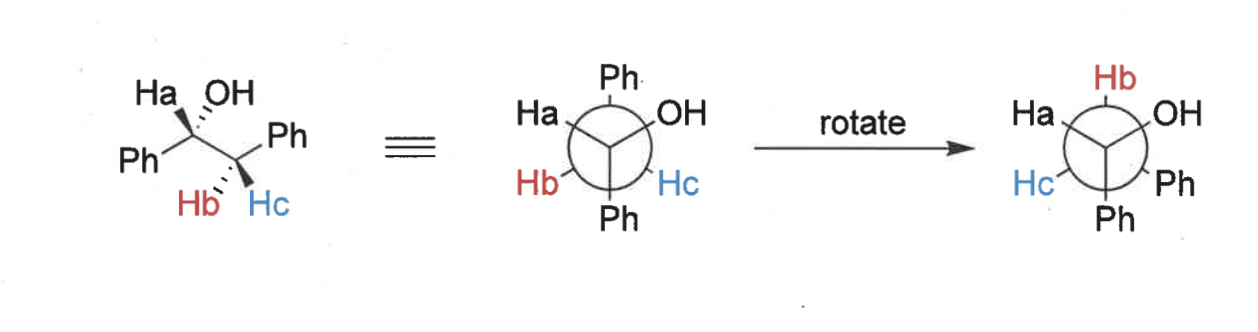
show how these environments are different
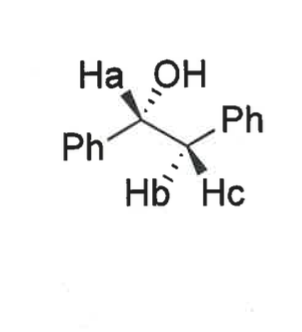
show bond angles of these H’s
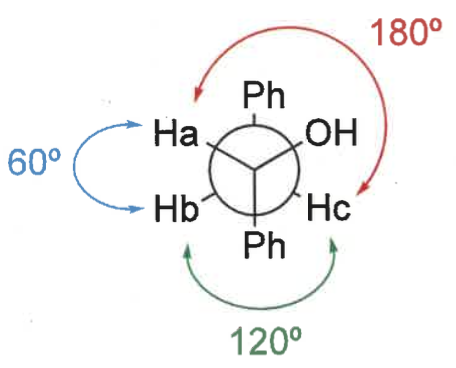
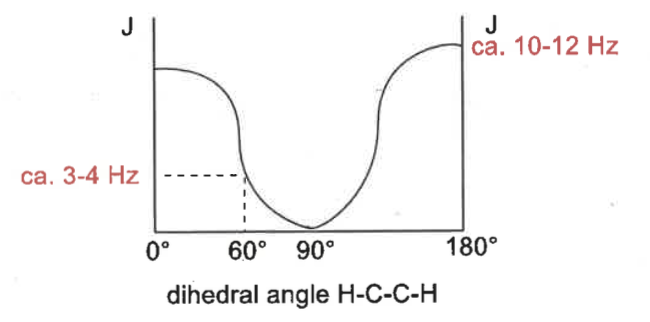
what is the karplus relationship?
show graph
coupling constants (3 bond H-C-C-H) depends on dihedral angle
protons opposite each other means higher coupling constant
120 = 8-12Hz
60 = 3-4Hz
180 = 10-12Hz
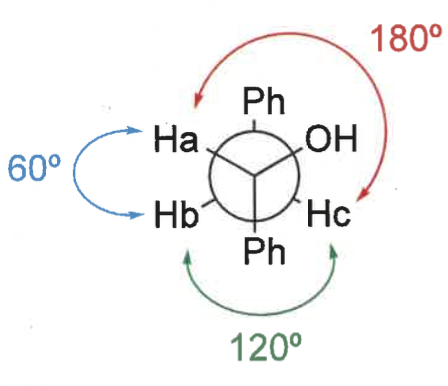
using karplus relationship, what are the J values?

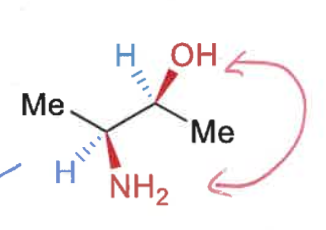
how to draw Newman projections?
draw intermediate sawhorse projection
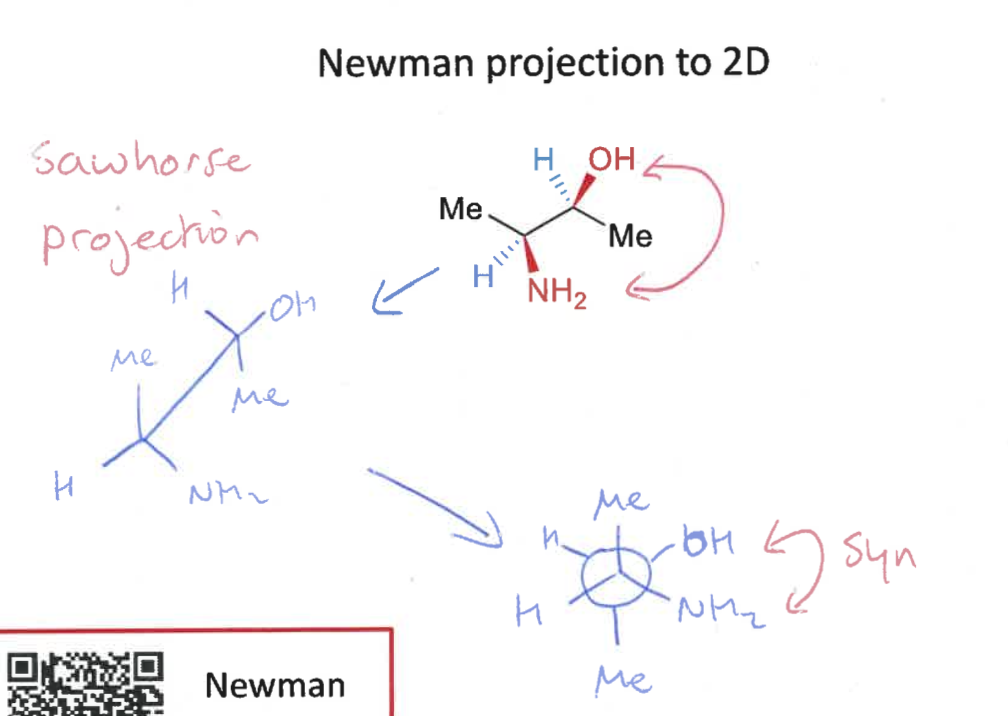
draw 2D of Newman projection
draw intermediate sawhorse projection
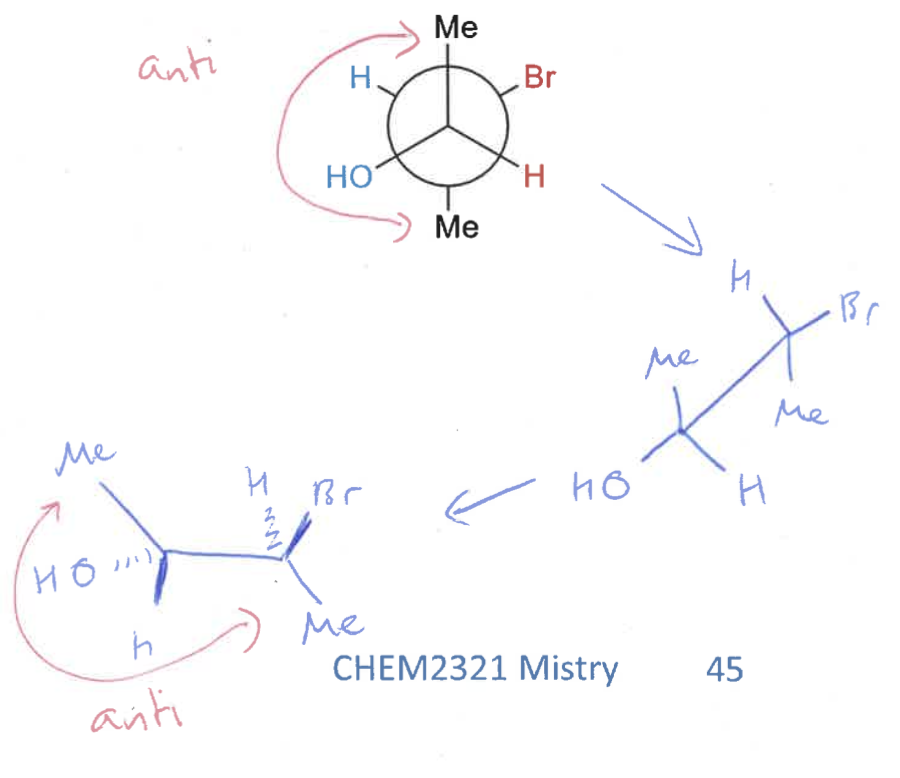
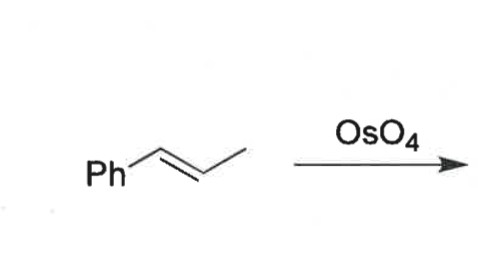
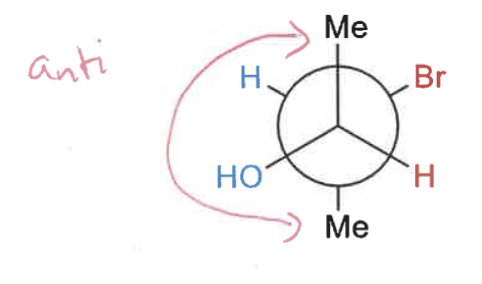
what are the 4 potential isomers that could be formed
what is stereospecificity?
only a certain stereoisomer can be produced due to how the reaction proceeds
what is stereoselectivity?
the reaction has a choose but one stereoisomer is preferred
what is diastereocontrol?
controlling which diastereomer is produced
what is enantiocontrol?
controlling which enantiomer is produced
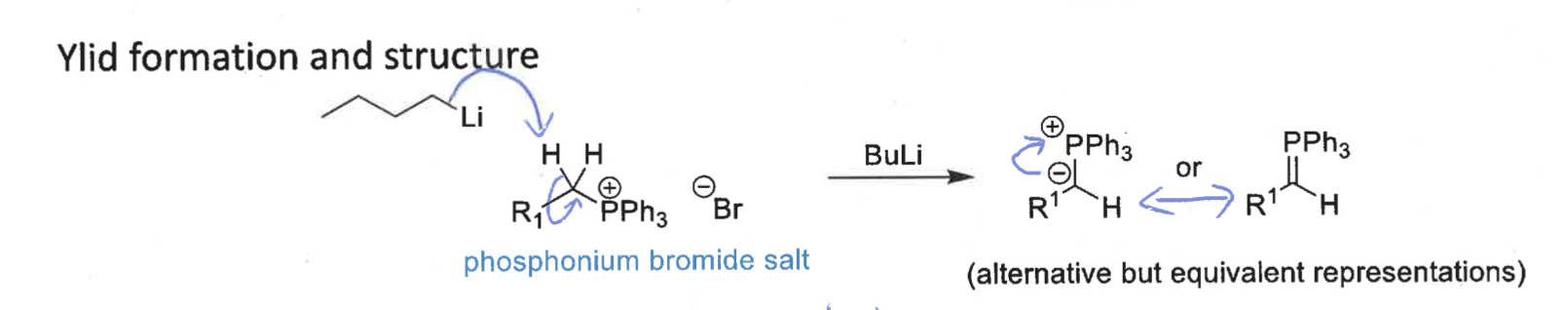
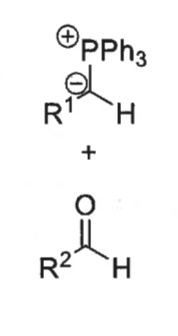
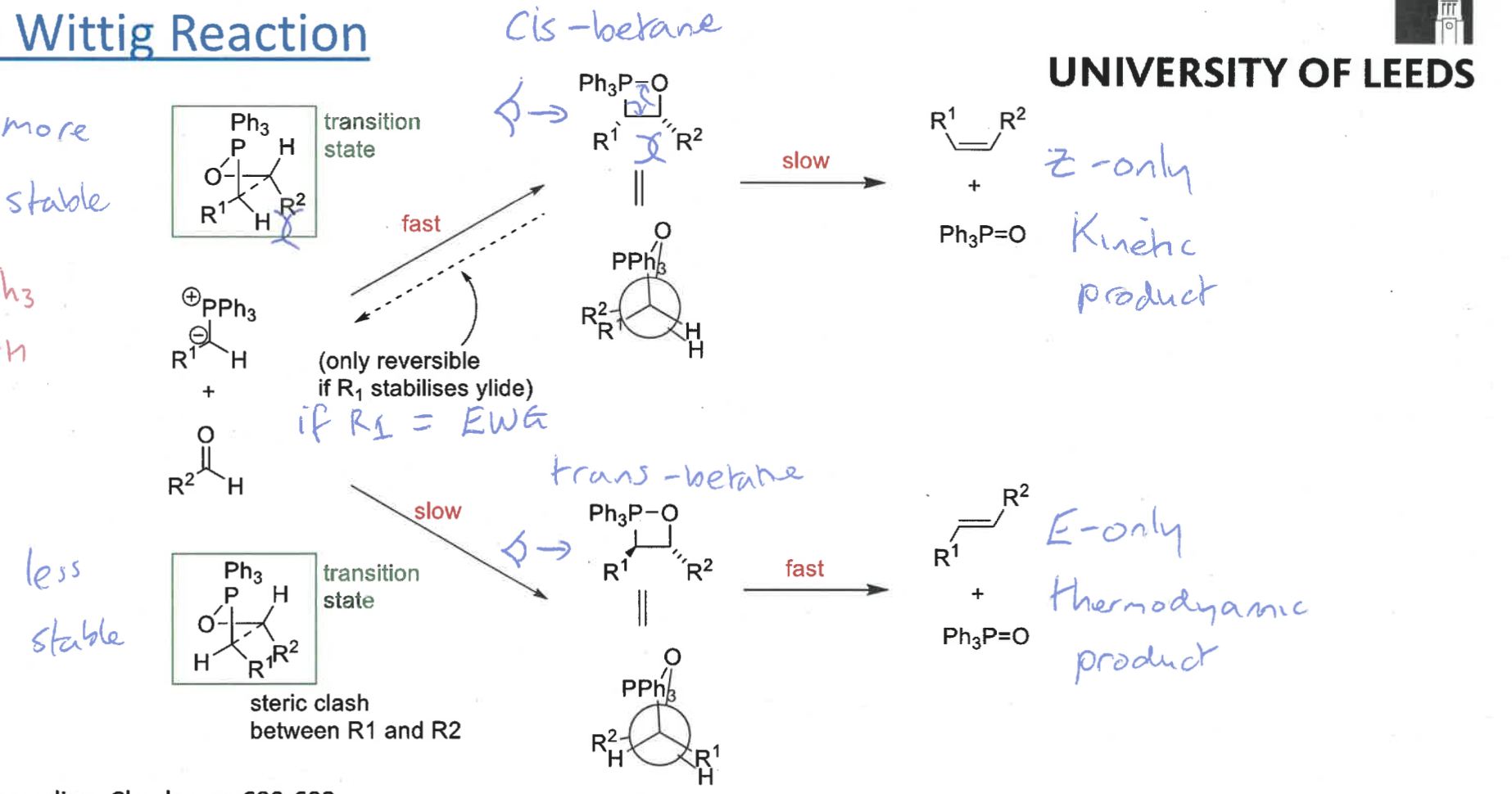
what is a ylid?
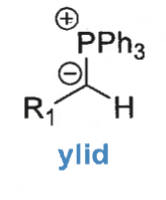
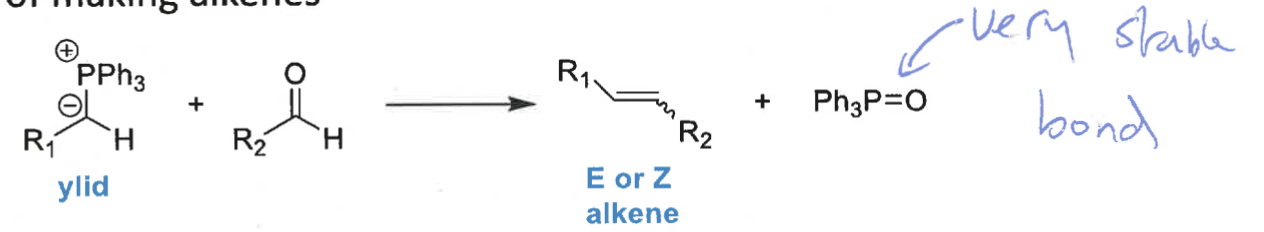
what is the wittig reaction?
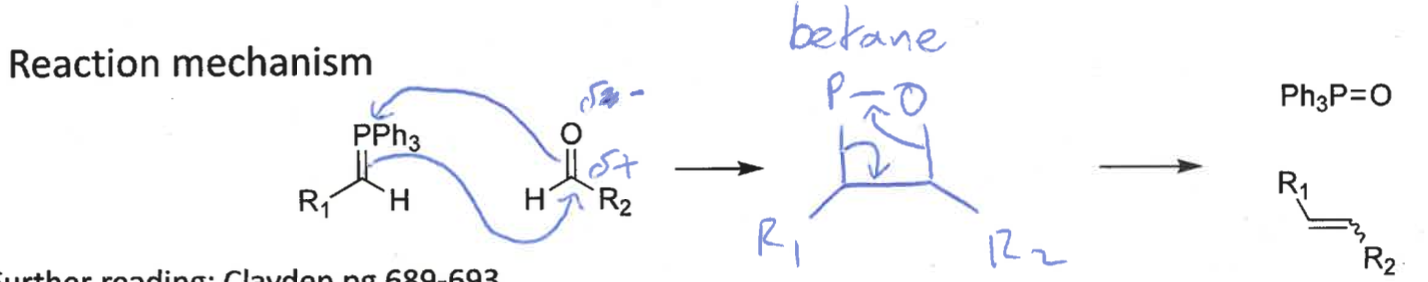
ylid + aldehyde = alkene + Ph3P=O
how is ylid formed?
phosphonium bromide salt + BuLi
what is the reaction mechanism for wittig reaction?
intermediate?
betane intermediate = collapses into products as ring strain
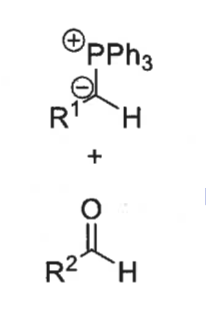
what are the two possible intermediates?
cis and trans betane
draw cis betane and Newman projection
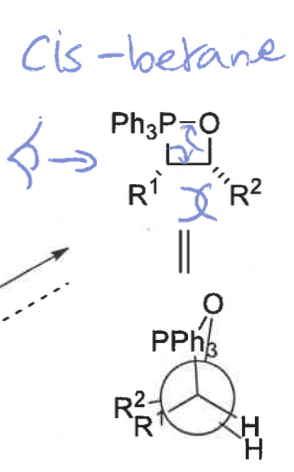
draw trans betane and Newman projection
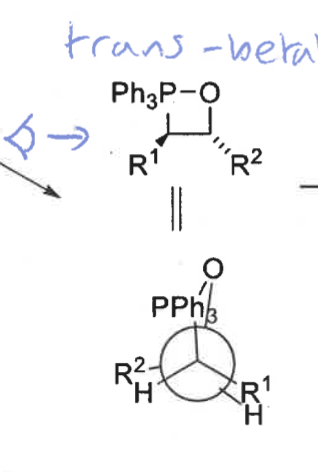
which betane forms fast and slow?
which is reversible?
cis = fast and reversible
trans = slow
when is the cis betane formation reversible?
if R1 is electron withdrawing group so stabilises ylid
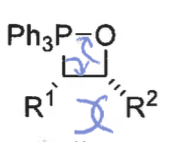
what are the cis and trans betane formation transition states?
which is more stable and why?
cis transition state is more stable - R groups on opposite sides
trans transition state has R groups overlapping = steric clash
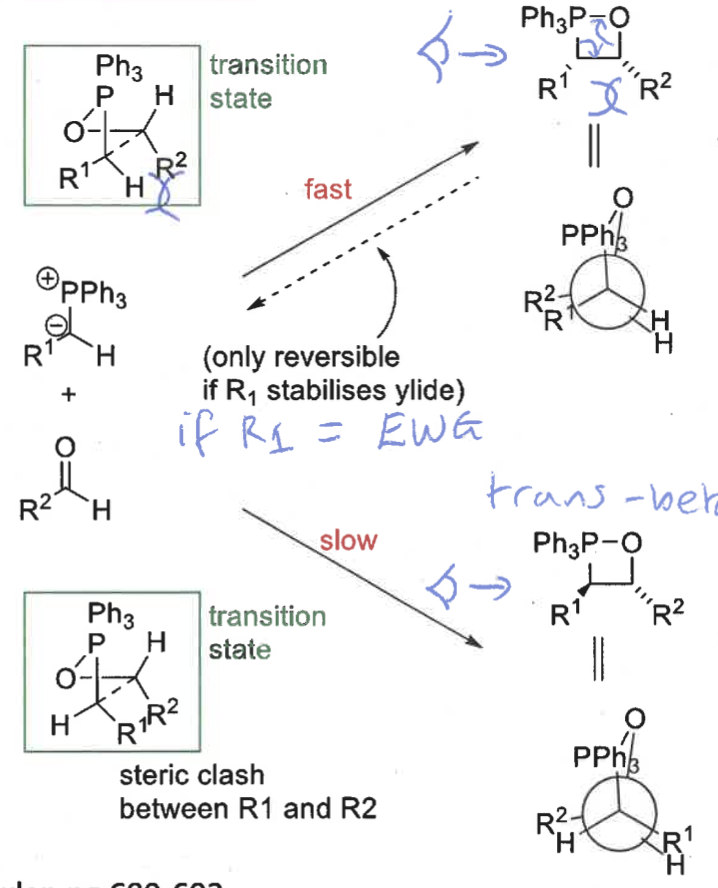
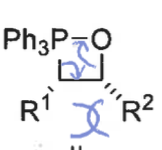
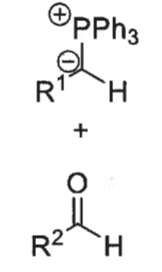
what is the product from the cis betane intermediate? is it fast or slow?
Z isomer only - concerted reaction as no bond rotation
slow formation
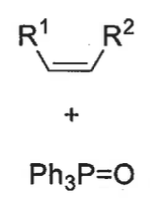
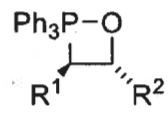
what is the product from the trans betane intermediate? is it fast or slow?
E isomer only
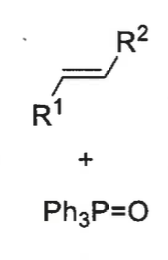
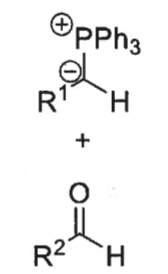
overall ,which is the kinetic and which is the thermodynamic product? why?
Z isomer (from cis betane) is the kinetic as quicker pathway
E isomer (from trans betane) is the thermodynamic product as the trans betane is much more stable and lower energy
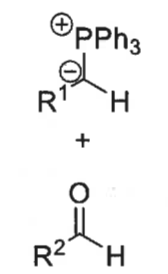
which isomer is formed?
if the R group doesn’t have a stabilising group (EWG), then Z isomer as proceeds through cis route
if there is a stabilising group, it goes to Z and then reverses to make E
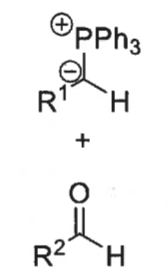
draw the two reaction pathways and show transition states and intermediates
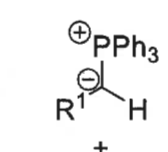
show an example of EWG stabilising ylid
if R1 is ester
electrons delocalised onto C-C bond
stabilises and withdraws electron density
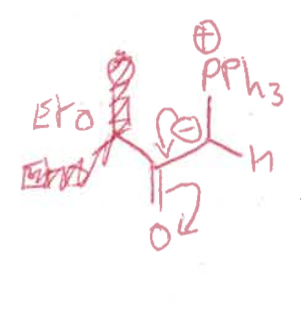
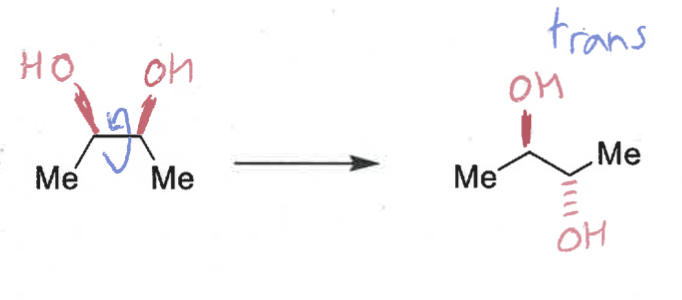
what is the dihydroxylation reaction?
what is special about it
alkene + water using OsO4 catalyst
it is diastereospecific

draw mechanism
which isomer is formed?
cis diol only formed as O is on same face of alkene
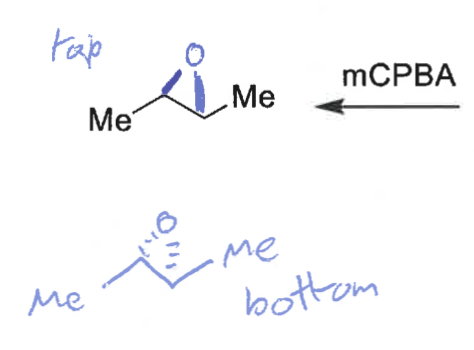
what is special about the epoxidation reaction?
it is diastereospecific
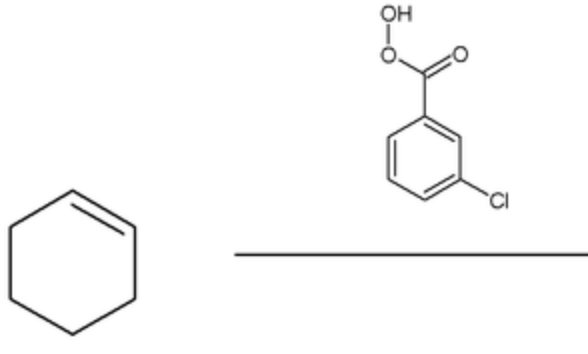
draw mechanism of cyclohexene + mCBPA
which isomer is formed?
cis epoxide formed (bonds on same face)
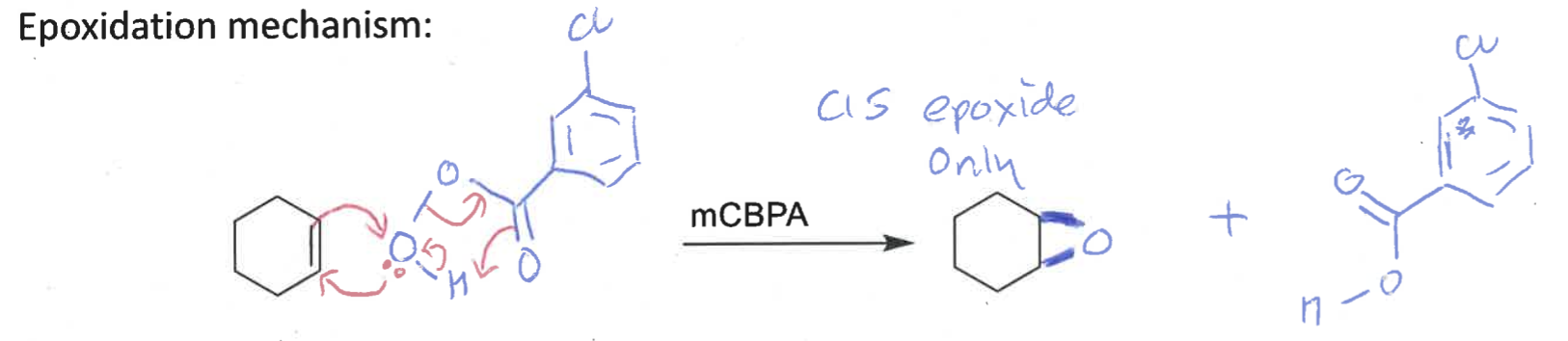
what is mCBPA?
meta-chlorobenzoperacid
what is a peracid?
carboxylic acid with an extra O
why is alkene dihydroxylation and epoxidation diastereospecific?
alkene reacts at both ends at the same time (concerted) so stereochemistry of alkene is preserved
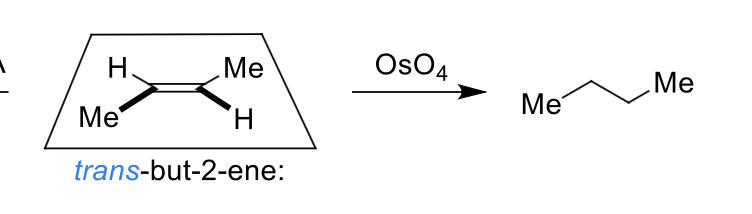
what are the products when OsO4 reacts on the top and on the bottom?
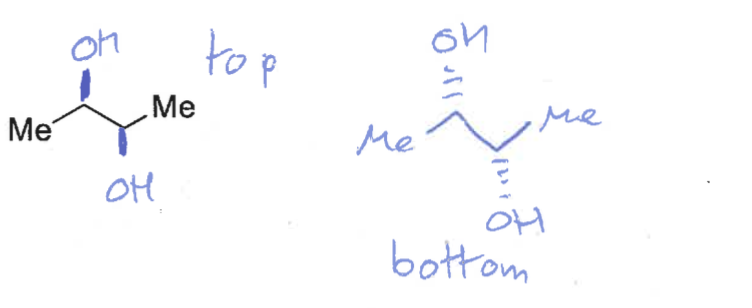
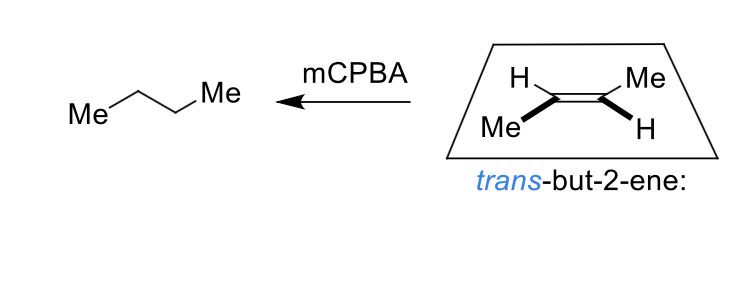
what are the products when mCPBA reacts on the top and on the bottom?
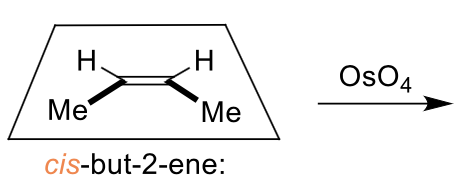
what is the product when OsO4 reacts?
cis has high steric clash so rotates to be trans
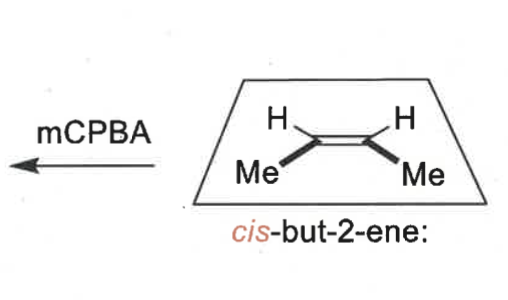
what is the product when mCPBA reacts?
cis product