Nuclear Chemistry
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
All nuclei with atomic numbers greater than ___ are radioactive, most emit alpha particles
83
Isotopes with too many neutrons decay by ___
decay by beta decay
Isotopes with too many protons decay by ___
decay by positron emission or electron capture (positron more likely with smaller atoms)
Stable (“magic”) numbers of protons/neutrons
2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, 126 (neutron only)
Alpha Decay
loss of helium nucleus 42 He, causes atomic number & mass to go down
Mass number
Number of protons + neutrons, top number to the left of an element
Atomic number
Number of protons, bottom number to the left of an element
Beta Decay
loss of an electron, aka beta particle: 0-1 e, atomic number goes up
Gamma radiation
loss of y-ray, represents energy lost
Positron emission
loss of a positron (opposite charge of electron): 01 e, atomic number goes down
Electron capture
Addition of an electron to a proton in the nucleus, add 0-1 e to the atom, atomic number goes down
Nuclear transmutation
Happens when you do something to accelerate a particle to collide it with the nuclide
Particle accelerator
Enormous devices that perform nuclear transmutations, usually using 42 He as the bombarding particles
Transuranium elements
Elements after uranium were discovered by bombarding uranium isotopes with neutrons
Nuclear Equation for Nuclear Transmutation
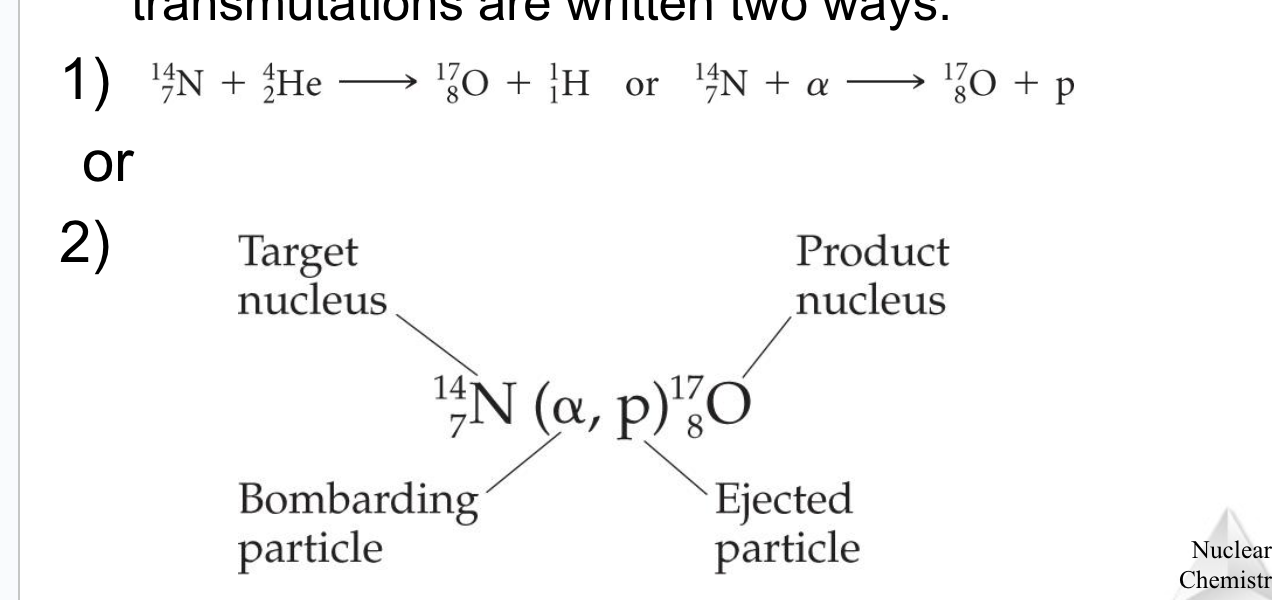
Radioactive decay equation
0.693/k = t1/2 & ln(Nt/N0) = -kt
nuclear fission
heavy nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, releases energy
nuclear fusion
light nuclei fuse into one nucleus, releases energy
nuclear chain reaction
neutrons get bombarded and cause other neutrons to undergo fission
critical mass
minimum mass that must be present for a chain reaction to be sustained
supercritical mass
when more than critical mass is present, causes explosions
fuel rods
provide nuclear reactor with fuel
control rod
block some neutron paths, prevent reactor from reaching supercritical mass