AP Environmental Science- Test 6 Energy
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/160
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
fossil fuels
a fuel derived from biological material that became fossilised millions of years ago
3
New cards
nonrenewable energy resource
an energy source with a finite supply, primarily the fossil fuels and nuclear fuels
4
New cards
nuclear fuel
fuel derived from radioactive materials that give off energy
5
New cards
commercial energy source
an energy source that is bought and sold
6
New cards
subsistence energy source
an energy source gathered by individuals for their own immediate needs
7
New cards
Developed countries only account for only 20% of the world’s population, however use almost _____ of the world’s energy each year.
half
8
New cards
wood was predominant energy source until
1875
9
New cards
from after _ *until the early 1900’s _, _, _, began being more widely used*
1875, coal, natural gas, oil
10
New cards
the 1950’s saw energy generated by _ power plants as well as _.
nuclear, hydroelectricity
11
New cards
1970s saw a decline in *_ and an increase in _*
oil, coal
12
New cards
midwestern and southeastern states prefer
coal.
13
New cards
western and northeastern states prefer
a mix of nuclear energy, natural gas and hydroelectricity.
14
New cards
Northern areas consume more energy during
winter to warm up.
15
New cards
Southern areas consume more energy during
summer to cool down.
16
New cards
energy efficiency
useful work performed relative to the total energy input in a system
17
New cards
efficiency of converting coal into electricity is approximately
35 percent
18
New cards
oil and natural gas together make up _ of overall energy use in the US
64
19
New cards
30% of energy use in the United States is for
transportation.
20
New cards
energy carrier
something that can move and deliver energy in a convenient, usable form for users
21
New cards
primary energy source
coal, oil, natural gas, etc.
22
New cards
secondary energy source
electricity
23
New cards
turbine
a device that can be turned by water, steam, or wind to produce power
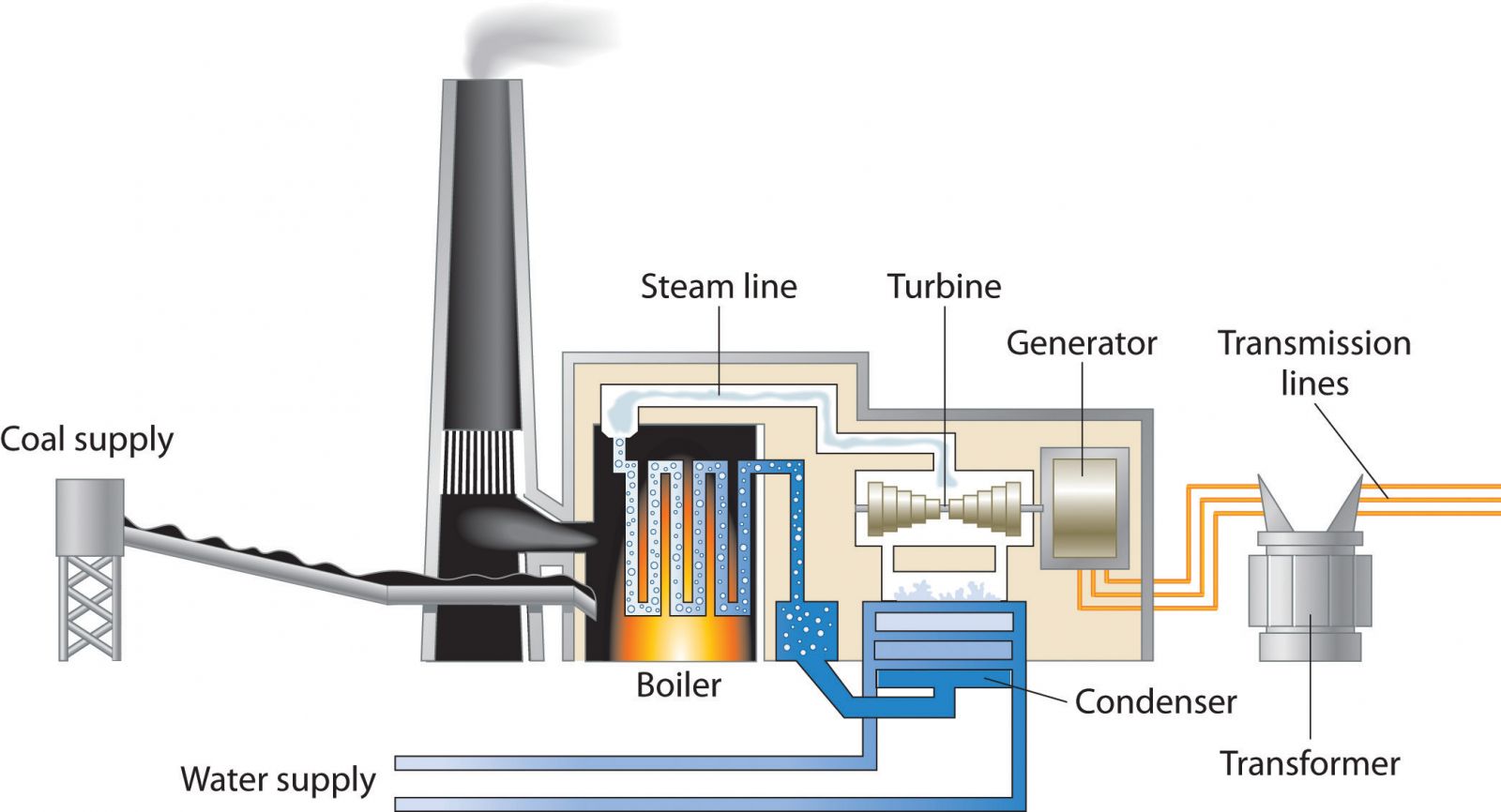
24
New cards
electrical grid
a network of interconnected transmission lines that join together power plants and links them with end users of electricity
25
New cards
combined cycle
a power plant that uses both exhaust gases and steam turbines to generate electricity
26
New cards
capacity
in reference to an electricity-generating plant, the maximum electrical output.
27
New cards
capacity factor
the fraction of time a power plant operates in a year.
28
New cards
cogeneration
the use of a fuel to generate electricity and produce heat.
29
New cards
advantages of coal use
\-used to generate electricity
\
\-easy to exploit by surface mining
\
\-easy to transport
\
\-does not require a lot of refinement for burning
\
\-technological and economic costs are relatively low
\
\-easy to handle
\
\-easy to exploit by surface mining
\
\-easy to transport
\
\-does not require a lot of refinement for burning
\
\-technological and economic costs are relatively low
\
\-easy to handle
30
New cards
disadvantages of coal use
\- surface mining will inevitably lead to subsurface mining which is more technologically demanding and worse for human health
\
\-coal releases sulfur and trace elements into the atmos
\-lignite and anthracite have low percentages of sulfur while bituminous has higher percentages
\
\-leaking of chemical cleaning compounds and ash holding for coal plants
\
\-CO2
\
\-ugly mining process, destroys habitat
\
\-coal releases sulfur and trace elements into the atmos
\-lignite and anthracite have low percentages of sulfur while bituminous has higher percentages
\
\-leaking of chemical cleaning compounds and ash holding for coal plants
\
\-CO2
\
\-ugly mining process, destroys habitat
31
New cards
petroleum
a widely used fossil fuel that occurs in underground deposits, composed of a liquid mixture of hydrocarbons, water and sulfur
32
New cards
crude oil
liquid petroleum removed from the ground
33
New cards
petroleum is formed by
phytoplankton.
34
New cards
coal is formed by
plants.
35
New cards
advantages of petroleum
\-extremely convenient to transport and use
\
\-relatively energy-dense and burns cleaner than coal
\
\-relatively energy-dense and burns cleaner than coal
36
New cards
disadvantages of petroleum
\-oli contains trace elements released to atmos when burned
\
\-oil has to be extracted from under the ground or beneath the ocean
-potential for spills
\
\-transport
-potential for spills
\
\-oil has to be extracted from under the ground or beneath the ocean
-potential for spills
\
\-transport
-potential for spills
37
New cards
petroleum can be refined to produce
tar, asphalt, gasoline, diesel, kerosene, petrochemicals; plastics, lubricants, pharmaceuticals, cleaning solvents
38
New cards
net energy
usable amount of high quality energy available from a given quantity of an energy resource
39
New cards
which has a higher net energy? oil or nuclear?
oil.
40
New cards
net energy efficiency
how much useful energy we get from an energy source
41
New cards
life cycle cost
initial cost of car/appliance + lifetime operating costs
42
New cards
best lightbulbs
LED and CFL
43
New cards
no incandescent bulbs
95% energy wasted
44
New cards
fluorescent light bulbs
contain Hg which can be recycled
45
New cards
LEDs and organic LEDs
lower energy waste percentage
46
New cards
CFL uses _ of the energy of incandescent bulbs
1/4
47
New cards
LED uses _ of the energy of incandescent bulbs
1/6
48
New cards
internal combustion engines waste %
94% waste in fuel
49
New cards
coal burning power plant waste %
66% waste heat
50
New cards
nuclear power used for heat and heating water waste %
83-92%
51
New cards
peak load
amount of electricity needed at the time of highest demand
52
New cards
brownout
lights dim
53
New cards
rolling blackout
take turns losing power to different neighbourhoods
54
New cards
how do people find natural gas and oil?
GIS, satellites, drilling test holes and rock samples, explosion on the surface and measuring seismic waves
55
New cards
sweet crude oil
low sulfur, less corrosive, found in LA, Libya, Nigeria
56
New cards
sour crude oil
high sulphur, corrosive, found in most of middle east
57
New cards
primary recovery
oil extracted by drilling into deposit, oil flows into wells and is pumped to the surface
58
New cards
secondary recovery
increases yield by injecting water into well to force oil into a central well
59
New cards
tertiary recovery
even more oil removed, injecting steam and C02, really expensive
60
New cards
1/2 of the worlds oil reserves are in the
persian gulf region
61
New cards
peak oil
the point at which half of the supply of oil has been used up
62
New cards
1/2 of the worlds natural gas is in
Russia, Iran and Qatar
63
New cards
largest coal reserves found in
US, Russia, China, Australia and India
64
New cards
natural gas is 80-95%
methane.
65
New cards
advantages of natural gas
\-natural gas contains fewer impurities and therefore emits almost no sulfur dioxide or particulates during combustion
66
New cards
disadvantages of natural gas
\-unburned natural gas will leak into the atmosphere (methane) is a potent GHG
\
\-pipelines and tankers can leak
\
\-drilling leads to enviro degradation
\
\-pipelines and tankers can leak
\
\-drilling leads to enviro degradation
67
New cards
oil sands
slow-flowing viscous deposits of degraded petroleum mixed with sand, water and clay
68
New cards
oil sands issues
* have to be surface mined
* require refinements to remove sand
* releases more air pollutants
* mostly found in UTAH and Alberta, Canada, Venezuela, and Russia, and Columbia
* boreal forests damaged during removal
* require refinements to remove sand
* releases more air pollutants
* mostly found in UTAH and Alberta, Canada, Venezuela, and Russia, and Columbia
* boreal forests damaged during removal
69
New cards
bitumen
a degraded type of petroleum that forms when it migrates to the surface of the Earth and is modified by bacteria
70
New cards
CTL
(coal to liquid) the technology to convert coal solid into coal liquid
71
New cards
energy intensity
the energy use per unit of gross domestic product
72
New cards
strip mining
the removal of strips of soil and rock to expose ore
73
New cards
mine tailings
unwanted waste material created during mining including mineral and other residues that are left behind after the desired metal or ore is removed.
74
New cards
open-pit mining
a mining technique that creates a large visible pit or hole in the ground
75
New cards
mountaintop removal
a mining technique in which the entire top of a mountain is removed with explosives
76
New cards
placer mining
the process of looking for minerals, metals, and precious stones in river sediments
77
New cards
subsurface mining
mining techniques used when the desired resource is more than 100 meters below the surface of the earth.
78
New cards
Mining Law of 1872
allowed individuals and companies to recover ores or fuels from federal lands.
\
\-few environmental protection provisions
\
\-few environmental protection provisions
79
New cards
SMCRA (1977)
land has to be minimally disturbed during the mining process and be reclaimed after the mining is completed.
80
New cards
How long did EXXON VALDEZ spill take to clean up?
2 decades
81
New cards
How much oil spilled from the EXXON VALDEZ accident?
42 million liters
82
New cards
Deep Water Horizon oil spill
780 million liters spilled out into the Gulf of Mexico
83
New cards
thermal shock
a dramatic change in water temperature that can kill organisms.
84
New cards
bottom ash
residue collected at the bottom of the combustion chamber in a furnace
85
New cards
fly ash
the residue collected from the chimney or exhaust pipe of a furnace
86
New cards
gravitational settling
a way to remove ash and particulate matter using gravity. the ash falls to the bottom, easier to collect.
87
New cards
a scrubber
removes particulate matter using water mist. mist collects the particles and drops it down where it is collected by a sludge removal system.
88
New cards
nuclear fission
a nuclear reaction in which a neutron strikes a relatively large atomic nucleus, which then splits into two or more parts, releasing additional neutrons and energy in the form of heat.
89
New cards
fuel rods
a cylindrical tube that encloses nuclear fuel within a nuclear reactor
90
New cards
control rods
a cylindrical device inserted between the fuel rods in a nuclear reactor to absorb excess neutrons and slow or stop the fission reaction
91
New cards
Hubbert curve
a bell-shaped curve representing oil use and projecting both when world production will reach a maximum and when the world will run out of oil.
92
New cards
anthracite
is a metamorphic rock.
93
New cards
lignite and bituminous
are sedimentary rocks.
94
New cards
most important energy used in the US
oil
95
New cards
meltdown
when the metal around the uranium melts, releasing radiation called a meltdown
96
New cards
stigma against nuclear energy
\-accidents and radioactivity
97
New cards
bacquerel (Bq)
Unit that measures the rate at which a sample of radioactive material decays; 1 Bq = decay of 1 atom or nucleus per second.
98
New cards
Curie
a unit of measure for radiation; 1 curie = 37 billion decays per second
99
New cards
problem with nuclear waste
it is really difficult to dispose of
100
New cards
nuclear fusion
a reaction that occurs when lighter nuclei are forced together to produce heavier nuclei