7.2 The Nomenclature and Uses of Alkyl Halides
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
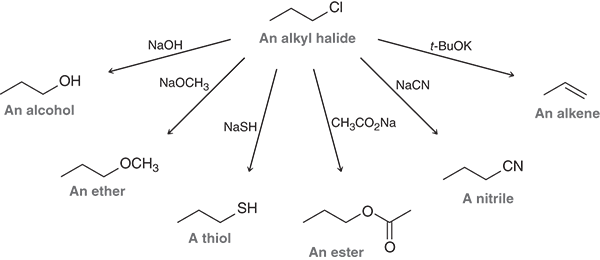
What is the α (alpha) carbon in an alkyl halide
The carbon directly attached to the halogen (Cl, Br, or I)
What is the β (beta) carbon in an alkyl halide?
The carbon next to the α carbon, one carbon away from the halogen
Why is the α carbon important?
It’s electrophilic- the halogen pulls electron density away, making it reactive toward nucleophiles in substitution reactions
Why are β carbons important?
They’re the positions where a base removes hydrogen during elimination reactions to form a π (double bond)
What are γ and δ carbons?
Carbons that are farther away from the halogen, beyond the β position.
An example of all the carbons labeled
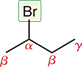
How many positions can an alkyl halide have?
Only one- it’s the carbon directly bonded to the halogen
How are alkyl halides classified?
As primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) based on how many carbons are attached to the α carbon.
What is a primary (1°) alkyl halide?
The α carbon is attached to one other carbon
What is a secondary (2°) alkyl halide?
The α carbon is attached to two other carbons
What is a tertiary (3°) alkyl halide?
The α carbon is attached to three other carbons
An example of primary, secondary, and tertiary carbons
What are the four IUPAC steps for naming alkyl halides?
Identify and name the parent chain.
Identify and name the substituents.
Number the parent chain and assign numbers to substituents.
Assemble the name alphabetically.
How are halogens treated when naming alkyl halides?
Halogens are treated as substituents on the main carbon chain

What are the names of the halogen substituents?
Fluoro (F)
Chloro (Cl)
Bromo (Br)
Iodo (I)
How do you decide where to number the halogen
Number the chain so the halogen gets the lowest possible number.
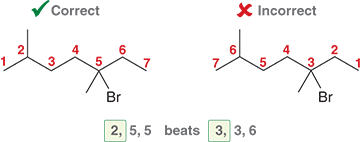
In what order do you list substituents in the final name?
List them alphabetically (ignoring prefixes like di-, tri-, etc.).
When do you need a number for a substituent on a ring?
When the ring has only one substituent- it is automatically carbon 1
Why isn’t bromocyyclohexane caled 1-bromocyclohexane
Because there’s only one substituent , so the position number isn’t needed
When do you need to use numbers a ring?
When the ring has two or more substituents, to show where each one is located
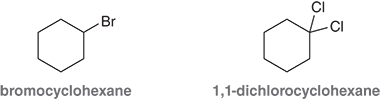
What’s the rule for numbering substituents in a ring?
Give the substituents the lowest set of numbers possible
What must be shown in the name if an alkyl halide has a chiral center?
At the beginning of the name, in parentheses
What does (R) or (S) describe?
The 3D arrangement of atoms around a chiral carbon
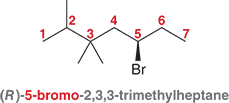
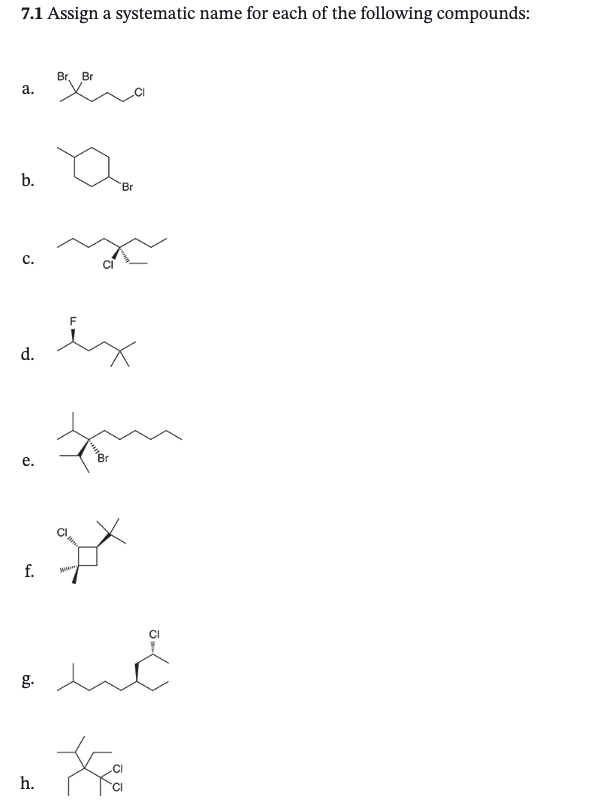
Do these practice questions
Answers in chapter 7.2
What are the two naming systems used for halogenated compounds?
Systemic (IUPAC) and common names
How does the systematic name treat the halogen?
As a substituent on the main carbon- called a haloalkane
How does the common name describe the compound?
As an alkyl group + halide, called an alkyl halide or organohalide
What does “organohalide” mean?
Any organic containing a halogen, including alkyl, aryl, or vinyl halides =
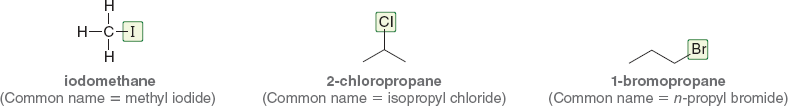
What does the pre-fix “n-” stand for in names like n-propyl bromide?
It means “normal”, indicating a straight, unbranched carbon chain
Is the “n-” prefix used in IUPAC names?
No, it’s only in common names
What’s the common name for 1-bromopropane?
n-propyl bromide
What’s the common name for 1-bromobutane?
n-butyl bromide
What are organohalides?
Organic compounds that contain carbon-halogen bonds; many are toxic and used as insecticides
What does DDT stand for?
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
When and why was DDT developed?
In the late 1930’s as a powerful insecticide to kill mosquitoes that spread diseases like malaria
Why was DDT effective?
It was toxic to insects but had low toxicity to mammals, making it useful for disease control
What environmental issues did DDT cause?
It doesn’t degrade easily, leading to bioaccumulation- buildup of DDT in animals and the environment
How did DDT affect bird populations?
It made eggshells too thin, causing eggs to break, and led to a decline in eagle populations
When was DDT banned in the U.S.
In 1972 by the EPA
When was DDT banned worldwide?
In 2004, due to ongoing health and environmental concerns
What is Lindane used for?
To treat head lice in shampoo, but only as a second choice treatment because of neurotoxicity risks
Why is Lindane use limited?
It can be absorbed through the skin and cause neurotoxicity, especially in babies and young children
What were Chlordane and Methyl Bromide used for?
As fumigants to prevent or treat termite infestations
Why were Chlordane and Methyl Bromide banned in the U.S.?
Chlordane: 1988
Methyl Bromide: 2016
Why do organohalides persist in the environment?
They are very stable compounds that don’t break down easily, leading to bioaccumulation
What are PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls)?
Biphenyl compounds with multiple chlorine atoms attached; very stable and toxic organohalides
Why are PCBs environmentally dangerous?
They presist and accumulate in the environment, causing long-term pollution and health risks
What are PFAS?
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances-highly organohalides known as "forever chemicals” because they degrade slowly
Why are PFAS called “forever chemicals”?
Because they don’t break down easily and accumulate in the environment and the human body
What has been the consequence of PFAS pollution?
Lawsuits and billions of dollars in cleanup costs for contaminated water supplies
What environmental lesson do PFAS, DDT, and PCB’s teach us?
That we must weigh the environmental impact and long-term effects of new chemicals before using them widely.
Are all organohalides synthetic and dangerous?
No — many are natural and safe, produced by plants and marine organisms.
What is the most abundant organohalide in Earth’s atmosphere?
Methyl chloride, produced by evergreen trees and marine organisms.
How do bacteria like Hyphomicrobium and Methylobacterium use methyl chloride?
They consume it and convert it into CO₂ and Cl⁻.
Why do marine organisms like sponges, corals, and seaweeds produce organohalides?
They use them as chemical defenses against predators — a type of natural chemical warfare.
How many new marine organohalides are discovered each year?
Hundreds of new compounds are identified every year.
Are all organohalides toxic?
No — many are safe and have important medical, food, and industrial uses
What are some beneficial uses of organohalides?
They are used in medicine, psychological treatments, and as anesthetics.
What is sucralose?
An artificial sweetener made by replacing three –OH groups in sugar with chlorine atoms; sold as Splenda.
How was sucralose discovered?
By accident in 1976, when a student “tasted” instead of “tested” a chlorinated sugar compound.
How are organohalides used in organic synthesis?
Back:
As starting materials (precursors) for making more complex molecules.
Which types of organohalides are especially useful in synthesis?
Aryl and vinyl halides, which have halogens on aromatic rings or double bonds.