TCA cycle
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Where does the TCA cycle take place?
Mitochondrial matrix
AT this point, what stage is metabolism of glucose at?
Glycolysis done, PDH complex has produced Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA also comes from other mechanisms of breakdown (B-oxidation, amino acid catabolism)
What is the overall putpose of TCA?
Complete oxidation of acetyl units to CO2 and capture energy
What is special about the TCA (what can product intermediates be used for)?
There is no one final product, goes around in cycle
Each intermediate can be siphoned off and used for other processes (catabolic and anabolic)
What type of procses is the TCA cycle?
cyclical pathway
Amphibolic pathway (catabolic and anabolic pathway)
a NET catabolic pathway (more catabolism than anabolism)
How many steps is the TCA cycle? What are phases. Which steps are in which phases
8 steps of the TCA cycle
4 Phases of the cycle
Acetyl Entry (steps 1-2)
Oxidative Phase (steps 3-4)
Substrate-level phosphorylation (step 5)
Regeneration phase (step 6-8)
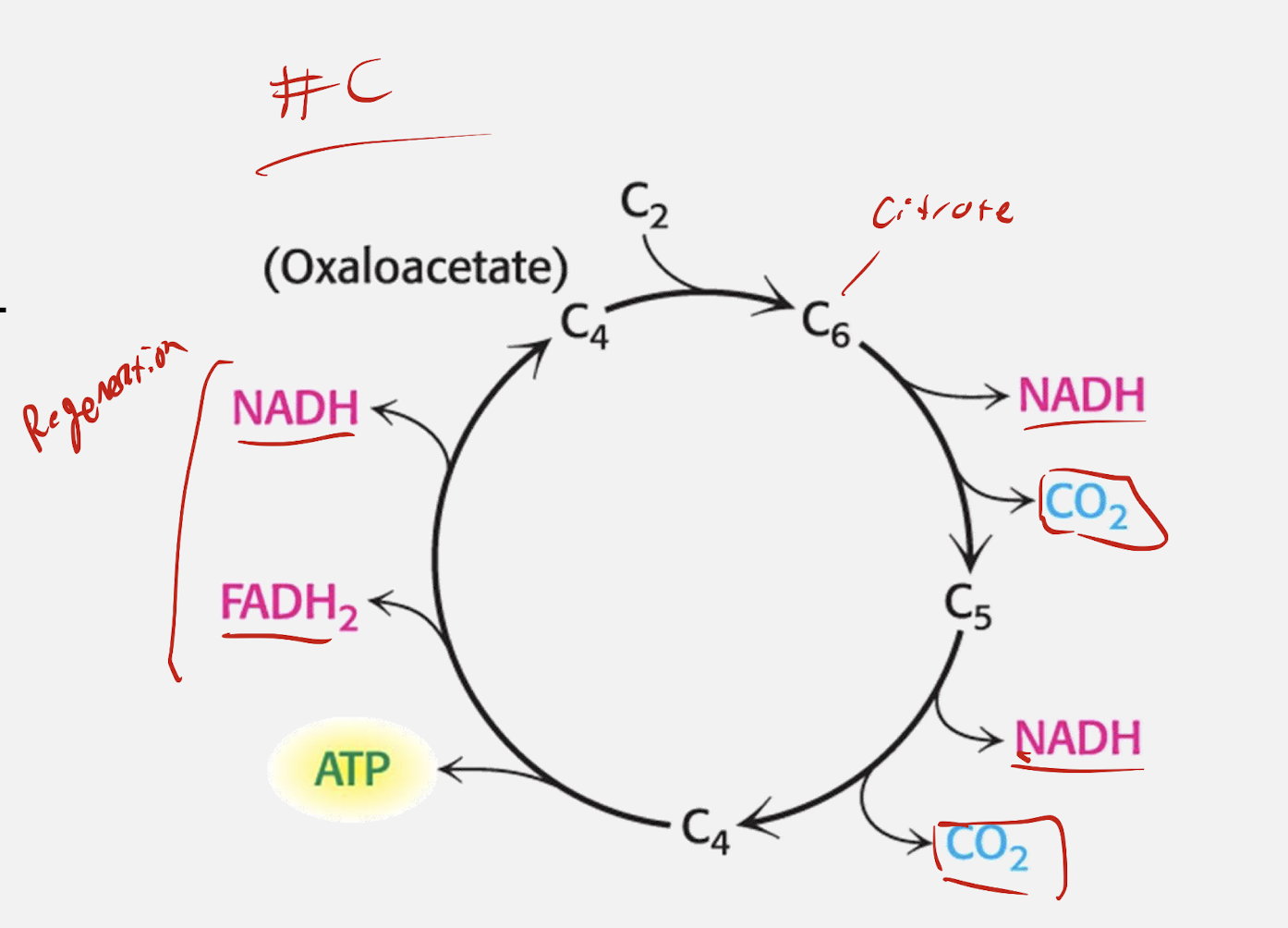
What happens in each phase of the TCA cycle?
Acetyl Entry (steps 1-2)
Acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate → Citrate → Isocitrate
Oxidative Phase (steps 3-4)
Two decarboxylations producing NADH + CO2
Substrate-level phosphorylation (step 5)
Energy Captured as GTP/ATP (an ATP equivalent)
Regeneration Phase (steps 6-8)
Rebuild Oxaloacetate + MORE NADH/FADH2

What is produced from ONE cycle of the TCA? What molecule runs the cycle?
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
2 CO2
ONE acetyl-CoA → ONE cycle of the TCA
For one molecule of Glucose, how many times does the TCA run? What is produced overall?
One glucose → two Acetyl-CoA → TWO cycles of the TCA
6 NADH
2 FADH2
2 GTP/ATP (depends on the tissue, 2 ATP equivalents)
4 CO2
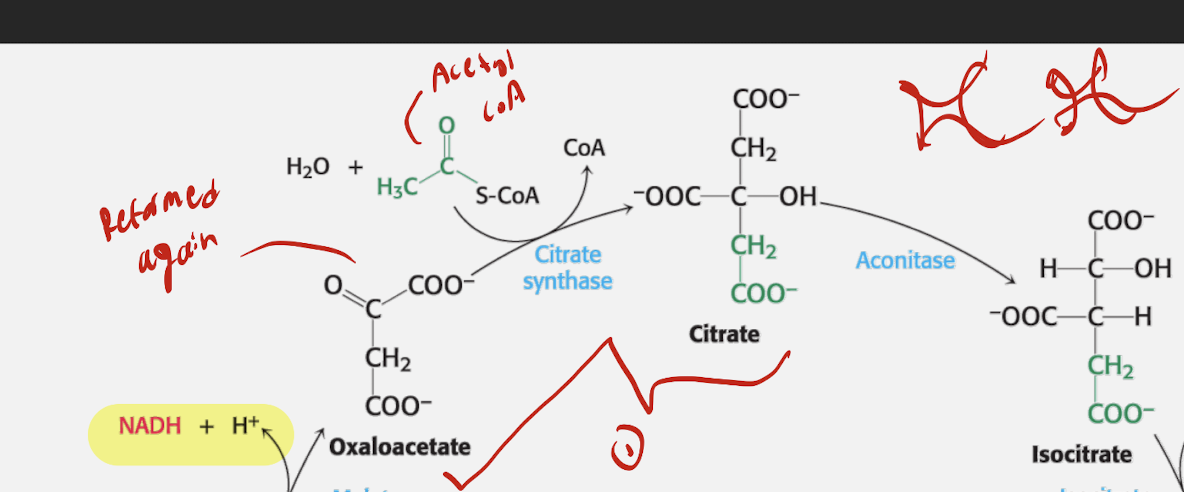
List out all th Enzymes, reactants, and products for each phase of step of the TCA cycle. THIS IS ACETYL ENTRY PHASE
Acetyl Entry Phase
Step 1
Reactant: Oxaloacetate + Acetyl-CoA
Enzyme: Citrate Synthase
Products: Citrate + CoA
Step 2
Reactant: Citrate
Enzyme: Aconitase
Product: Isocitrate
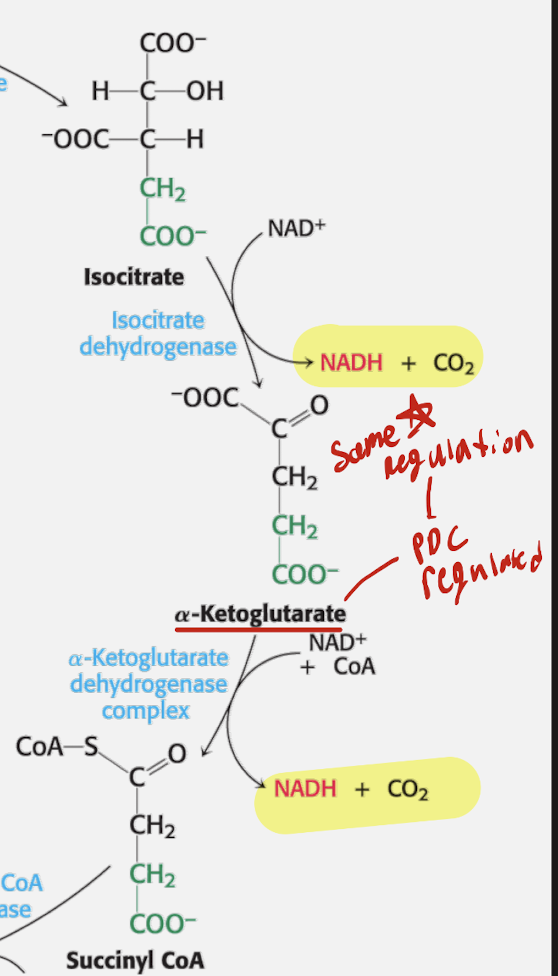
List out all th Enzymes, reactants, and products for each phase of step of the TCA cycle. THIS IS OXIDATIVE PHASE
Oxidative Phase
Step 3
Reactant: Isocitrate + NAD+
Enzyme: Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
alpha-ketoglutarate + NADH + CO2
Step 4
Reactant: alpha-ketoglutarate + NAD+ + CoA
Enzyme: alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
Product: Succinyl CoA + NADH + CO2
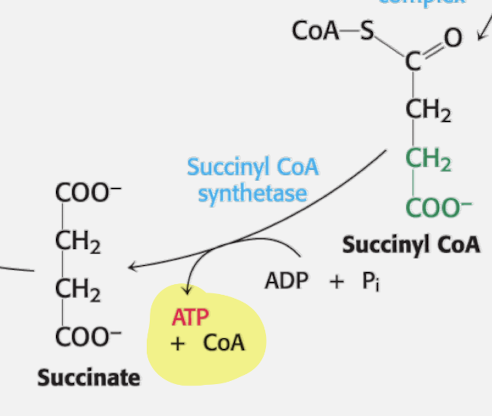
List out all th Enzymes, reactants, and products for each phase of step of the TCA cycle. THIS IS SUBSTRATE-LEVEL PHOSPHORYLATION PHASE
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
Step 5
Succinyl CoA + ADP + Pi
Enzyme: Succinyl CoA
Product: Succinate + ATP + CoA
List out all th Enzymes, reactants, and products for each phase of step of the TCA cycle. THIS IS REGENERATION PHASE
Regeneration Phase
Step 6
Succinate + FAD
Enzyme: Succinate Dehydrogenase
Product: Fumarate + FADH2
Step 7
Reactant: Fumarate + H2O
Enzyme: Fumarase (Fumarate Hydrolase)
Product: Malate
Step 8
Reactant: Malate + NAD+
Enzyme: Malate Dehydrogenase
Product: Oxaloacetate + NADH
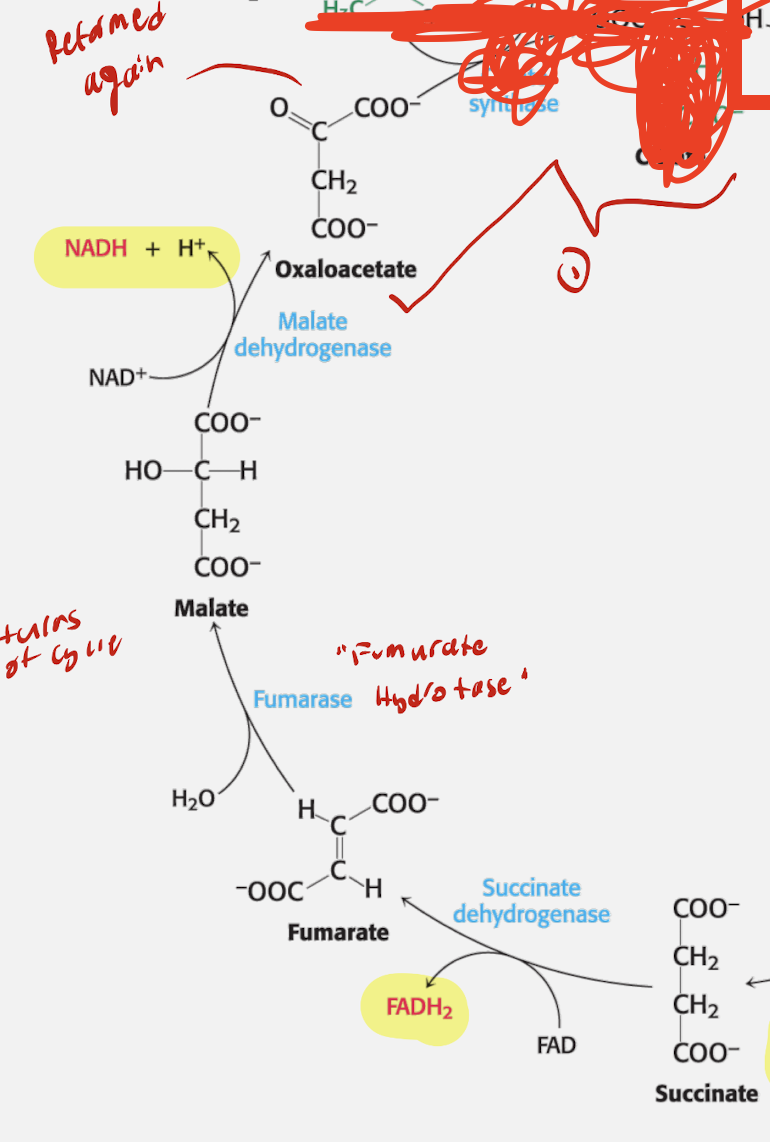
Which Steps produceH NADH and CO2? Which Step produces FADH2? What step produces GTP/ATP? Which steps produce CO2
NADH AND CO2
Step 3.
Isocitrate + NAD+ —Isocitrate Dehydrogenase→ alpha-ketoglutarate + NADH + CO2
Step 4
alpha-ketoglutarate + NAD+ + CoA —alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex→ Succinyl CoA + NADH + CO2
JUST NADH
Step 8
Malate + NAD+ —Malate Dehydrogenase→ NADH + H+
Which Step produces FADH2? What step produces GTP/ATP?
FADH2
Step 6
Succinate + FAD —Succinate Dehydrogenase→ Fumarate + FADH2
GTP/ATP
Step 5
Succinyl CoA + ADP + Pi —Succinyl CoA Synthetase→ Succinate + ATP + CoA
How much ATP does 1 molecule of NADH produce? What about FADH2?
NADH → 2.5 ATP
FADH2 → 1.5 ATP
Per glucose, how much ATP is produced from 1 molecule of Glucose (2 cycles beacuse 2 Acetyl-CoA produced from 2 pyruvate molecules)
6 NADH → 15 ATP (via ETC)
2 FADH2 → 3 ATP (via ETC)
2 GTP = 2 ATP (via substrate-level)
Total = 20 ATP JUST from TCA
For questions about ATP production, what is imporatnt to remember?
One glucose → 2 pyruvate → 2 acetyl-coA → 2 TCA cycles
Direct ATP vs. ATP from NADH/FADH2
Direct: 2 ATP from substrate-level via TCA
Indirect: ATP from NADH/FADH2
DO NOT include ATP from glycolysis or PDH if asking about just “TCA”
What is the mnemonic to remember TCA products?
Can → Citrate (via citrate synthase)
I → Isocitrate (via aconitase)
Keep → alpha-ketoglutarate (Isocitrate dehydrogenase)
Selling → Succinyl CoA (alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenation complex)
Sex → Succinate (Succinyl CoA Synthetase)
For → Fumarate (Succinate Dehydrogenase)
Money → Malate (Fumarase)
Officer → Oxaloacetate (Malate Dehydrogenase)
Does the TCA have a “commitment” step>
no
What are the 3 control points of regulation in TCA?
Step 1 - Citrate Synthase
Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetate —Citrate Synthase→ Citrate
Step 3 - Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Isocitrate + NAD+ —Isocitrate dehydrogenase→ a-ketoglutarate + CO2.+ NADH
Step 4 - alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
a-ketoglutarate + NAD+ —a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex→ Succinul CoA
What is the regulation at step 1
Step 1 - Citrate Synthase
Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetate —Citrate Synthase→ Citrate
Inhibition:
NADH, ATP
Both are indicative of high energy charge which inhibit the cycle
bc no need to make more NADH which would make more energy because we already have high energy
What is the regulation at step 3 (activation and inhibition)
Step 3 - Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Isocitrate + NAD+ —Isocitrate dehydrogenase→ a-ketoglutarate + CO2.+ NADH
Inhibition
ATP NADH
Inhibition: High energy charge slows cycle
Activation
Calcium, ADP
Activation: Low energy charge stimulates cycle
Key fkux control point
What is the regulation at step 4
Step 4 - alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
a-ketoglutarate + NAD+ —a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex→ Succinul CoA
Inhibition
ATP/GTP & NADH (high energy charge), Succinyl CoA (product via negative feedback)
Inhibition of high eneryg charge and of succinyl CoA product prevents overproduction
Wh
What is a pattern that could be noticed with regulation of the TCA?
All regulation takes place in 1st half of cyccle
Inhibiting firrst half inhibits 2nd half since the intermediates aren’t being produced
What is the catabolic reaction that TCA does (the overall rxn)
Acetyl-CoA → CO2 + ATP/GTP + NADH + FADH2
Which intermediates of TCA can be used for Anabolic processes (and what are they)
Citrate: Fatty acid + Sterol synthesis
a-ketoglutarate: Amino Acid synthesis (glutamate), purines
Succinyl-CoA: Heme synthesis
Oxaloacetate: Aspartate, asparagine synthesis
What happens if intermediates of the TCA are removed? What needs to be done after>
Cycle stops (because there is no final carbon product, each reaction relies on an intermediate)
Need anaplerotic reaction to kickstart Cycle again
What is an anaplerotic reaction? What major enzyme does it for the TCA?
Anaplerotic rxn replenishes intermediates
TCA: Pyruvate Carboxylase (from gluconeogenesis) replenishses Oxaloacetate
Pyruvate + CO2 + ATP —Pyruvate Carboxylase→ Oxaloacetate + ADP + Pi
What is pyruvate carboxylase activated by (allosteric activator)
INC Acetyl-CoA → INC Pyruvate Carboxylase activity → INC Oxaloacetate → INC TCA
What are other minor anaplerotic rxn?
Amino acid transamniations
PEP Carboxykinase (reverse direction reaction)
Phosphoenolpyruvate → Oxaloacetate
INC PeP —PEP carboxykinase (in reverse)→ INC Oxaloacetate in Cytoplasm → Transported into Mitochondria cia Malate-Aspartate Shuttle → INC TCA
Why is PEP Carboxykinase not as a major contributor to anaplerotic rxn as Pyruvate carboxylase?
Pyruvate carboxylase takes place in the mitochondria already, so it doesn’t need to be reformed to malate and re transported. Can immediately go into TCA
PEP carboxykinase takes place in cytoplasm so it needs to transport
How does the TCA have diverse fuel input options with carbs, farry acids, and proteins?
All eventually produce acetyl-CoA
Carbs: Glucose → Pyruvate → ACetyl-CoA
via PDH complex
Fatty Acids: B-oxidation → Acetyl-CoA
major fuel sources, during fasting
Proteins: Amino Acids → Acetyl-CoA or other cycle intermediates
Starvation
What Are the products and intermediates of TCA used for?
NADH & FADH2: Energy via ETC to produce ATP
Citrate, a-ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, oxaloacetate for Biosynthesis
CO2 and H2O completly oxidized
How does THiamaine defciciency affect TCA?
Thiamine phosphoryate needed for PDH complex to function
No PDH activity → DEC Acetyl-CoA → DEC TCA
How does Arsenic poisoniing affect TCA?
Arsenic binds to lipoamide → Inhibits a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
Inhibition of a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex causes backup buildup of intermediatess → Cant’ function
How does Cancer Metabolism affect the TCA? What is the specific effect called? How are TCA intermediates used?
Some tumors use TCA differently, called the Warburg effect
TCA intermediates (oncometabolites) succinate and fumarate accumulate
beacuse no oxidative phosphorylation happens. They complete with de-methylating enzymes, preventing cells from expressing p53 gene to combat the cancer
WHat is the warburg effect?
Cancer cells prefer to use glycolysis (anarobic respiration) instead of oxidative phosphorylation (aerobic respiration)
Even though not as efficient, cancer cells want the energy FAST as possible
Since cancer cells do mainly glycolysis and no oxidative, what happens with pyruvate?
Pyruvate accumulates, and is used as the carbon skeleton and building block for carbon structures in the cell