Electron microscopy - part 3 ( Electron/specimen interaction)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Electron Specimen interaction
TEM has a higher resolution (anything reflected is SEM, scanning electron microscopy) (anything transmitted is TEM, Transmitted electron micrsocpy).
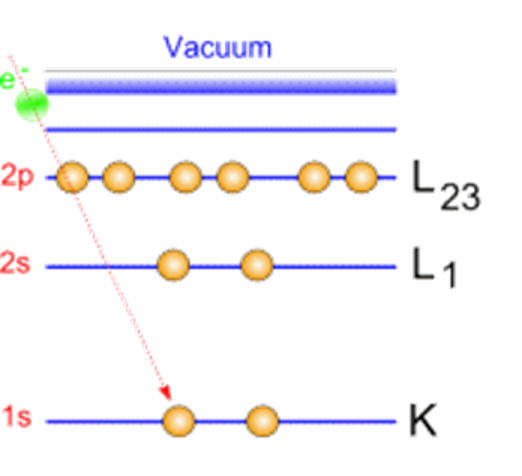
Auger Electron spectroscopy (AES)
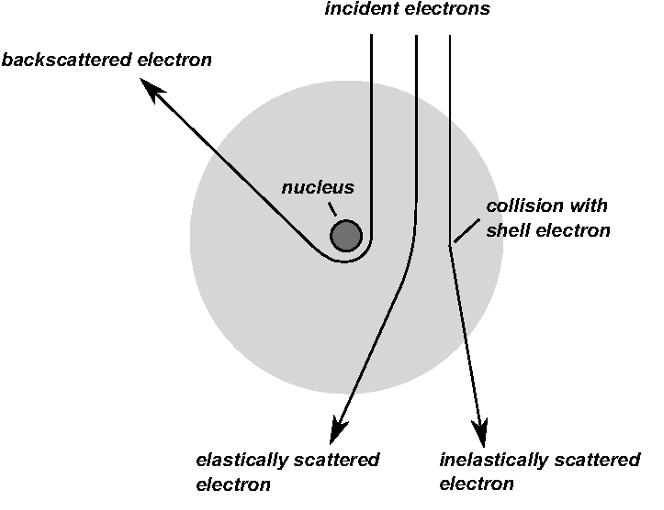
The interaction volume depends on the following factors:
Atomic number of the material being examined.
Accelerating voltage being used.
Angle of incidence for the electron beam.
High Z = cause deceleration of primary electrons.
(Referring to the analysis of gold = 2 and a ½ nanometres)
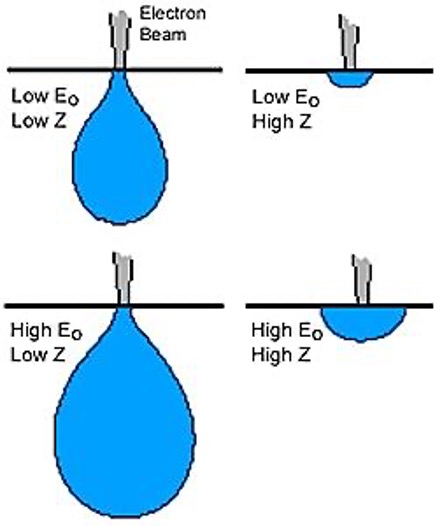
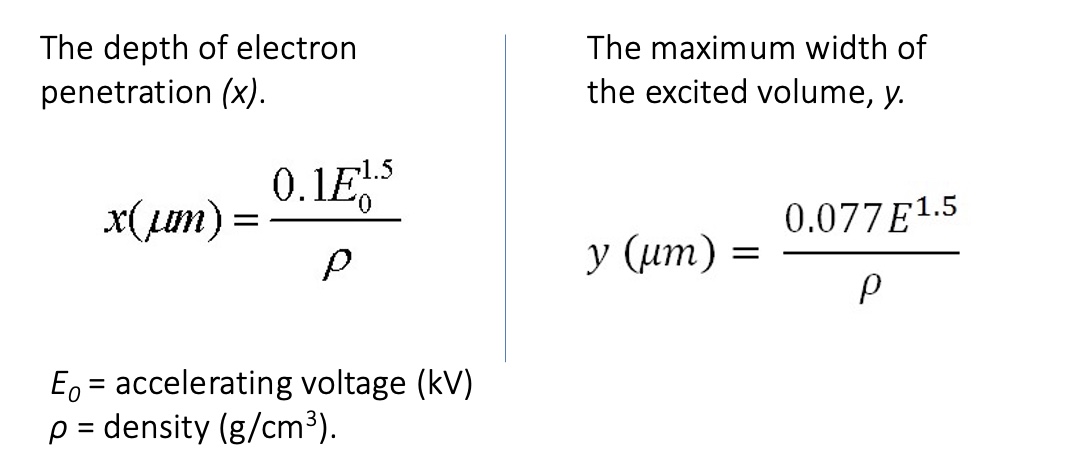
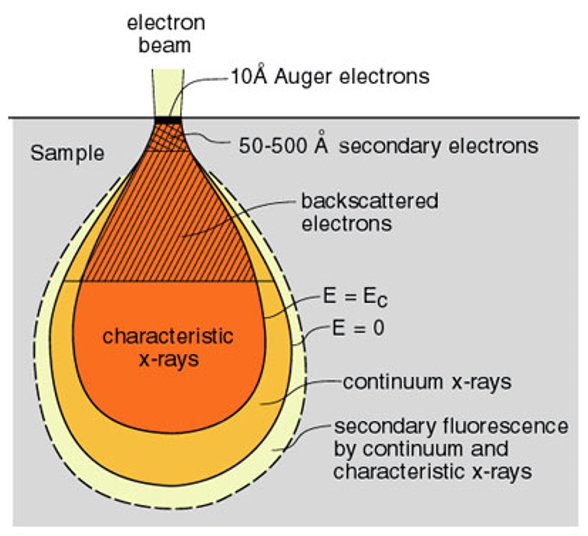
Reaction Volume
The range of an electron, r, the maximum straight-line distance between where an electron enters and its final resting place, for a given Eo is given by:
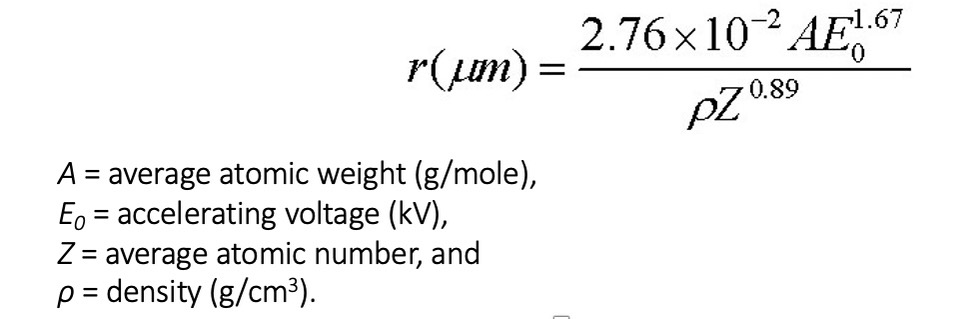
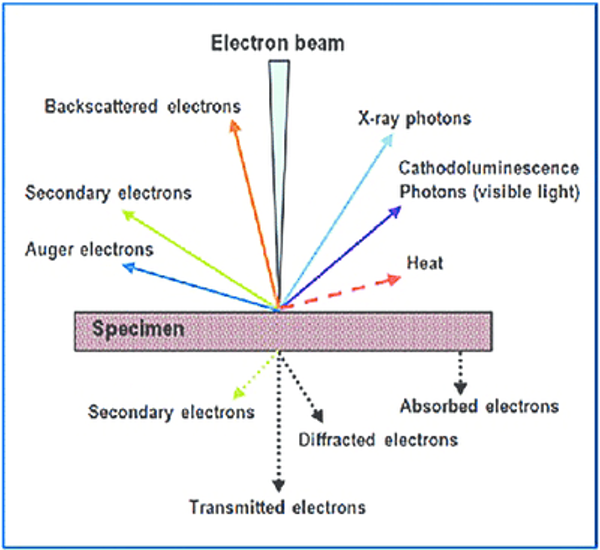
Electron- specimen interaction
Reaction Volume
To observe a medulla in a hair sample on an electron microscope, you need to slice the hair in half.
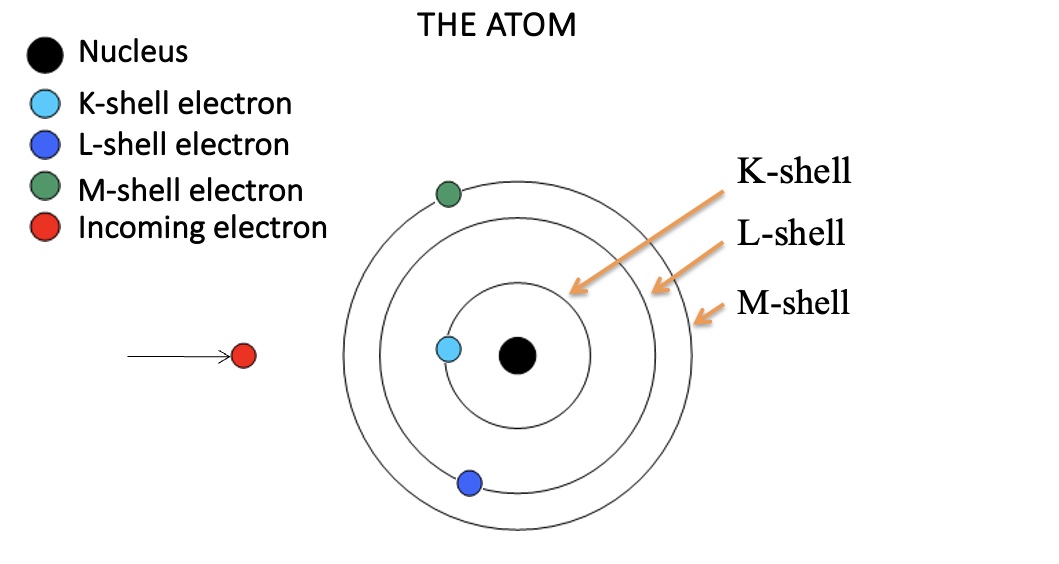
K shell = 1S orbital
(Cover atomic absorption and the Jablonski diagram)

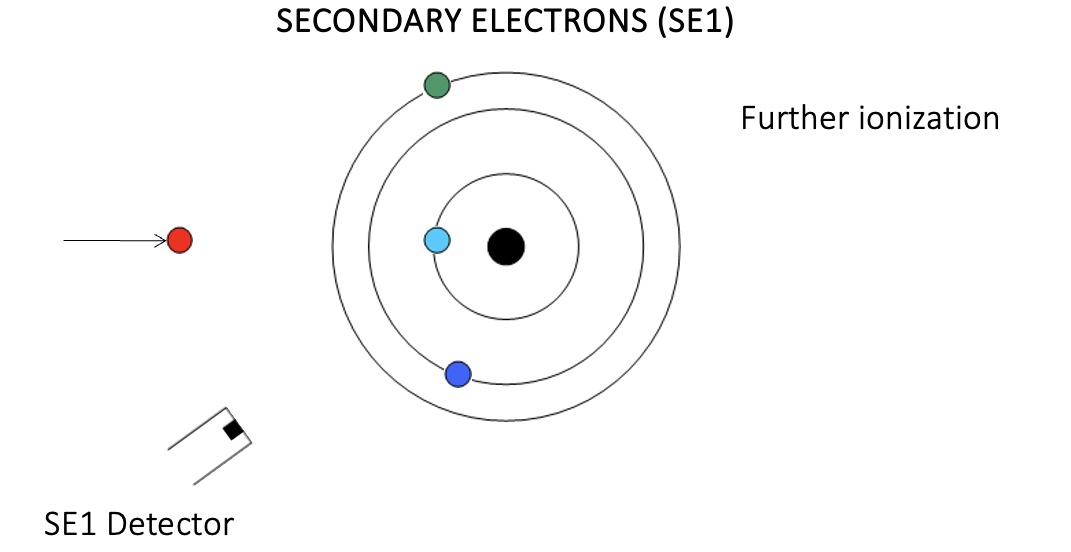
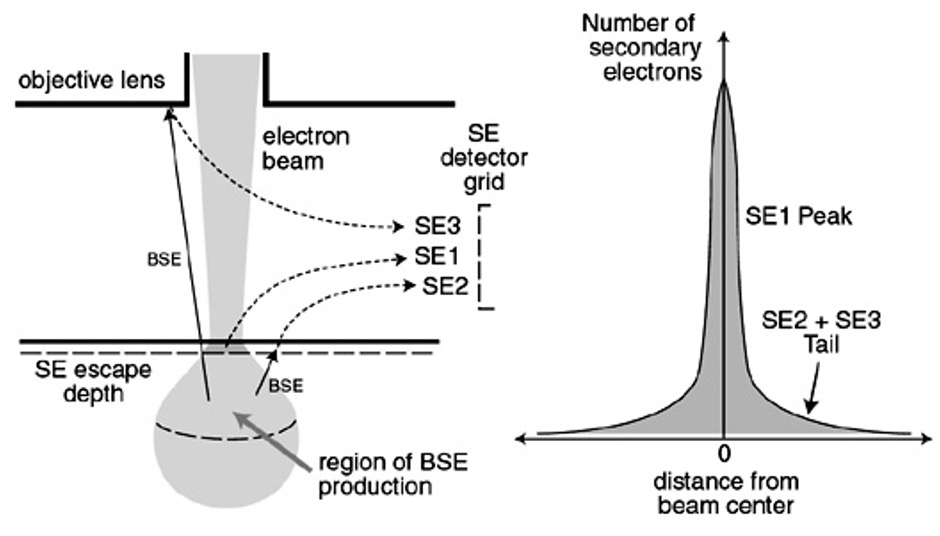
SECONDARY ELECTRONS (SE1)
This ionized electron or SE that leaves the atom has a very small kinetic energy (5eV).
Due to their low energy, 5eV, only SE that are very near the surface (<10 nm) can exit the sample and be examined.
Production of SE is very topography related.
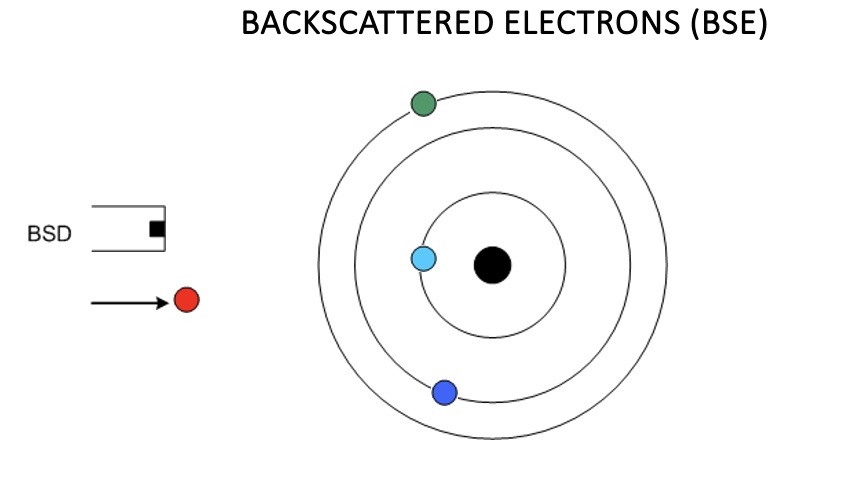
BACKSCATTERED ELECTRONS (BSE)
The production of BSE varies directly with atomic number.
This differing production rates causes higher atomic number elements to appear brighter than lower atomic number elements.
This interaction is utilized to differentiate parts of the specimen that have different average atomic number.
The radius of a hemispherical region (R) from which backscattered electrons are produced is:
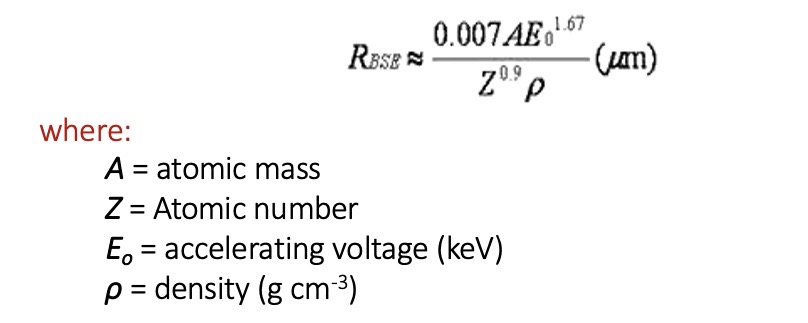
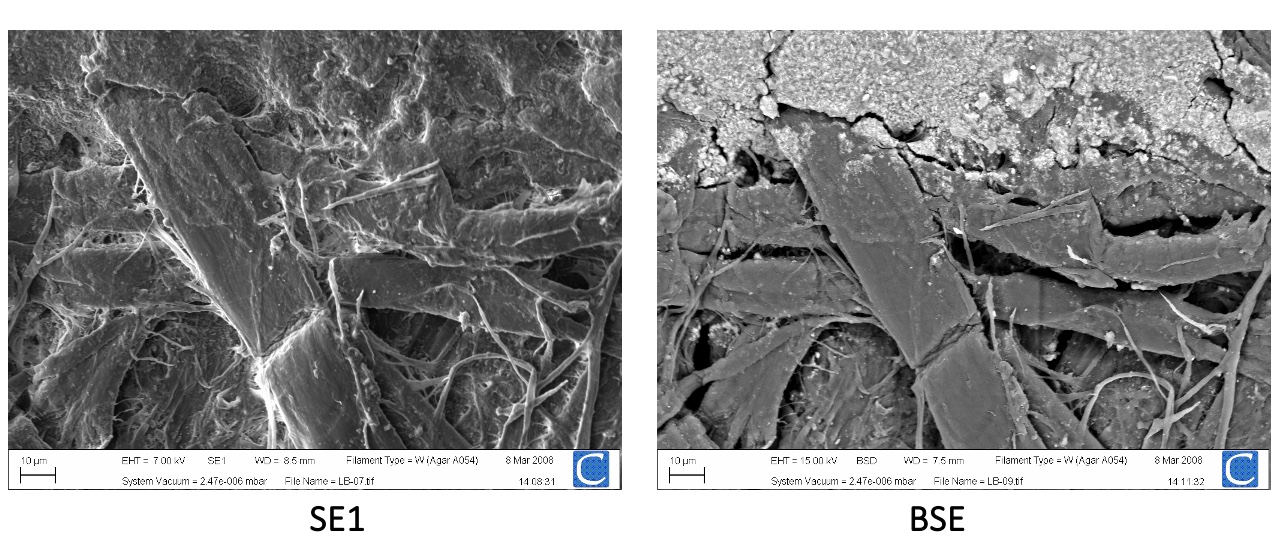
electrons micrograph of money
BACKSCATTERED ELECTRONS (BSE)
SE2- Elastically scattered electrons (BSE) generate SE as they leave the surface.
SE3 - BSE collide with the SEM equipment in range of the specimen to produce SE.
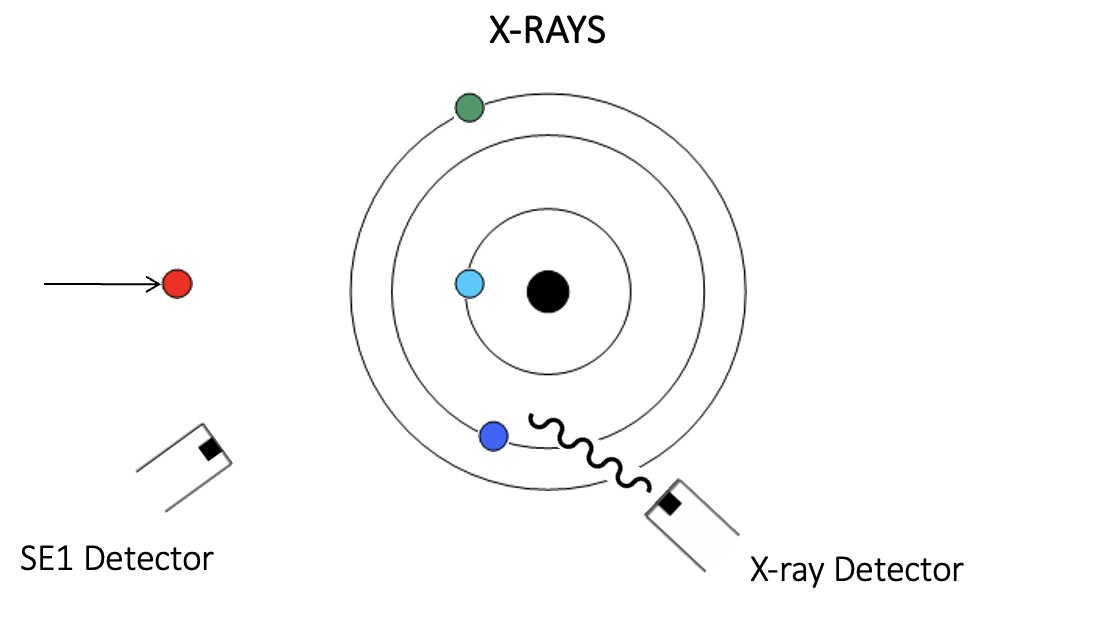
X-rays have a characteristic energy which is unique to the element.
Provide compositional information about the specimen.
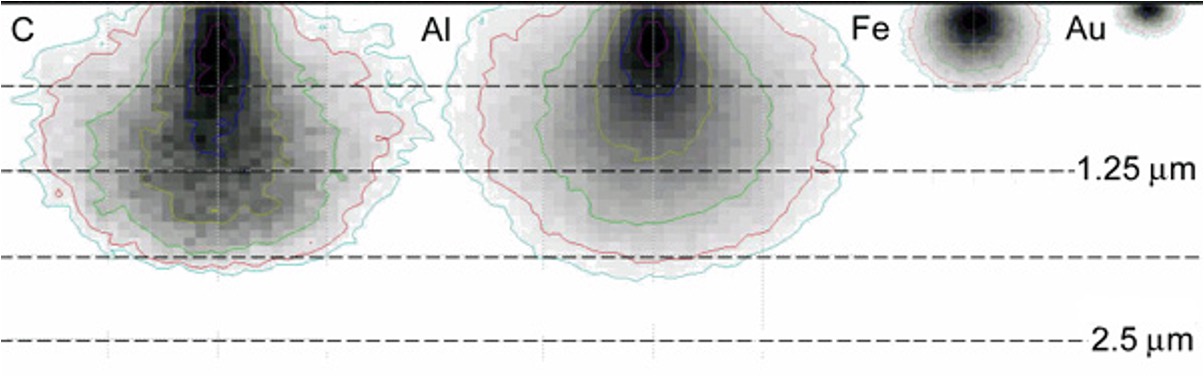
Compositional information of this type collected in a relatively large area (~1-2 µm in diameter).
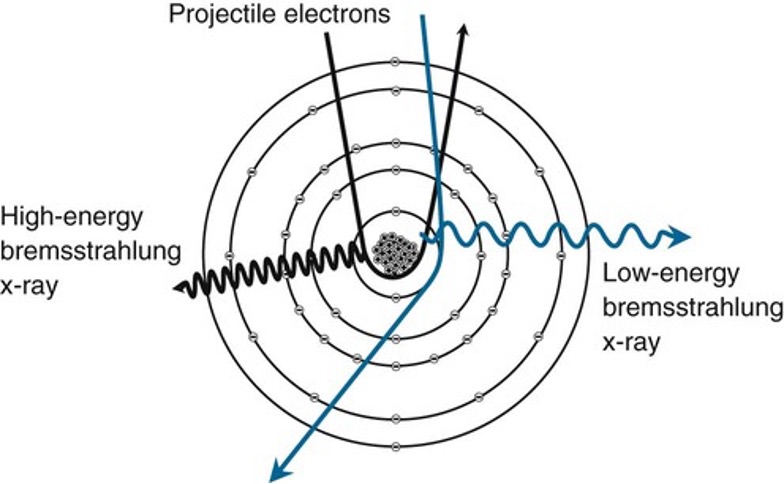
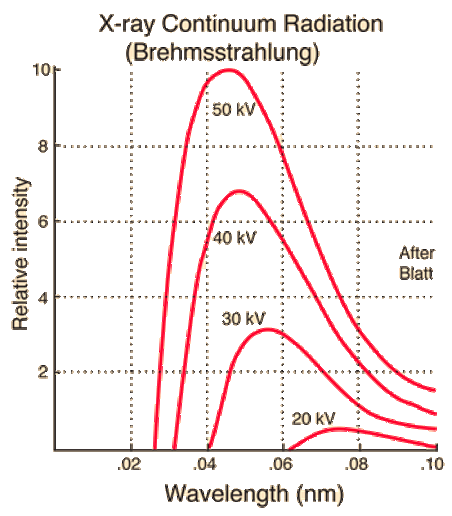
X-RAY - Bremsstrahlung (Braking radiation)
question on X-ray analysis in exam!
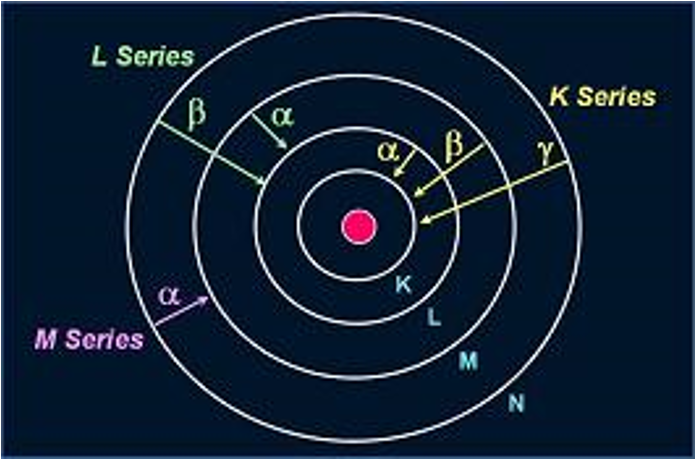
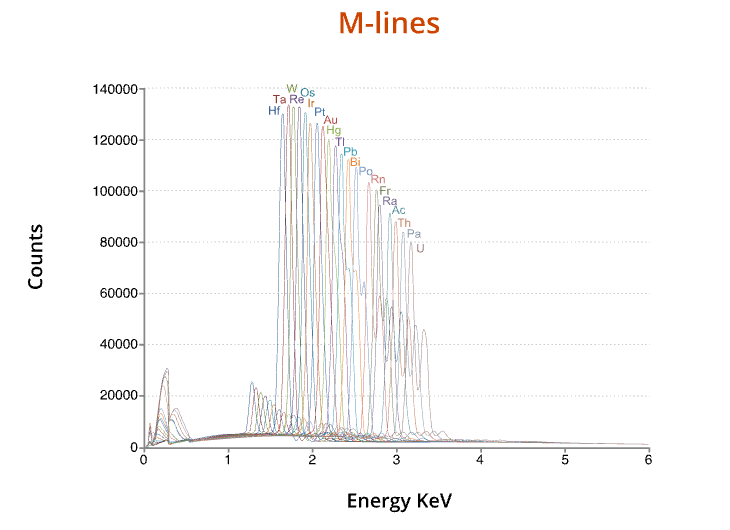
X-ray Lines
EDX = energy dispersive x-ray.
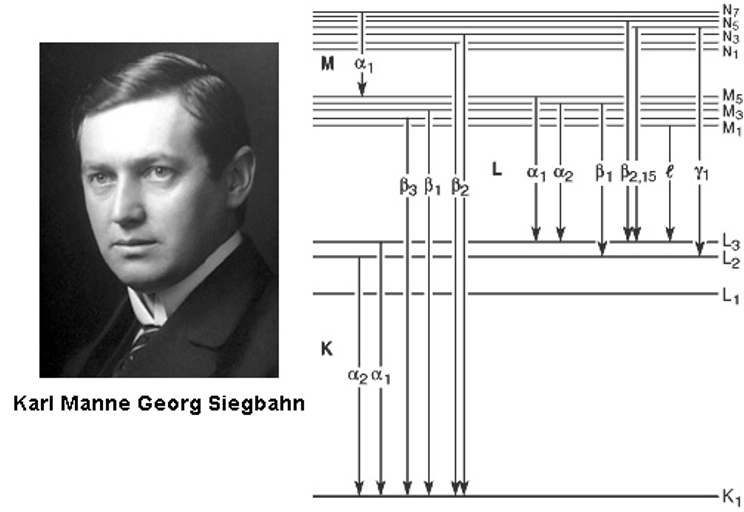
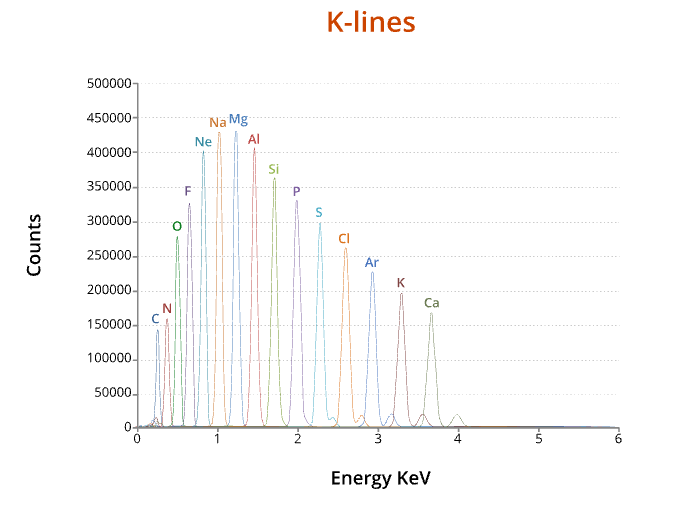
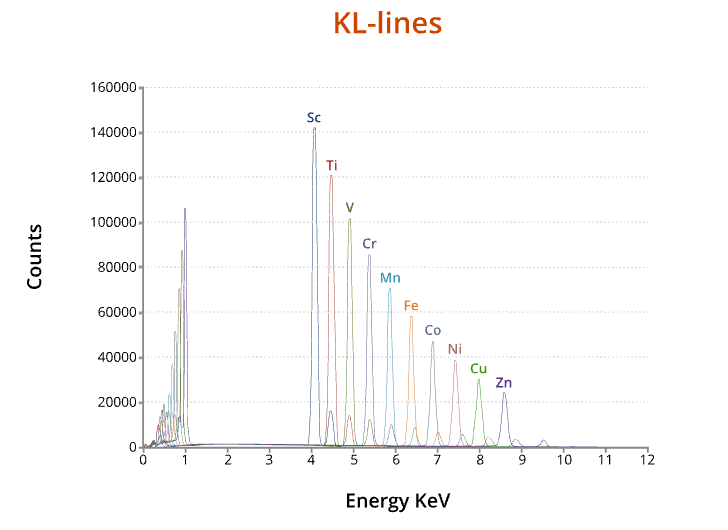
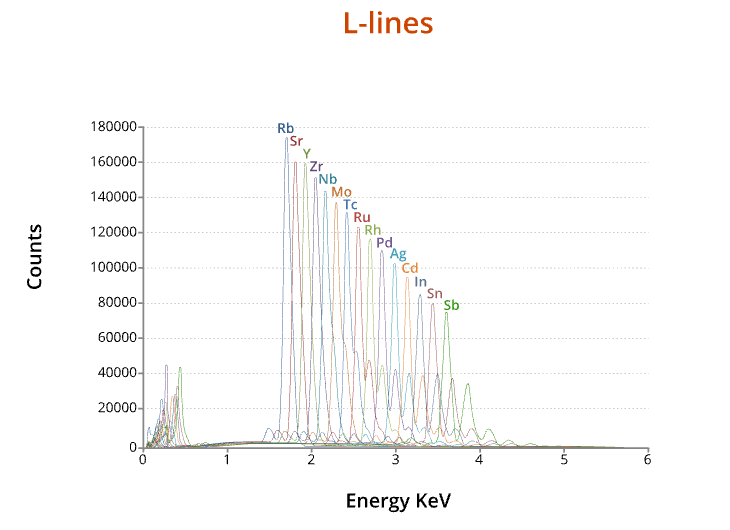
X-ray lines
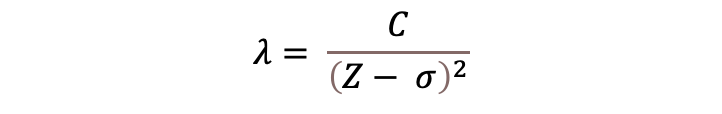
The relationship between atomic number (Z) and characteristic x-ray wavelength (λ) was established by Henry G.J. Moseley in 1914:
where,
C is a constant for a given x-ray spectral line and σ is called the shielding constant.
put equation into straight line (y=mx+c)
= you you plot z as y and x as 1/the root of lambda

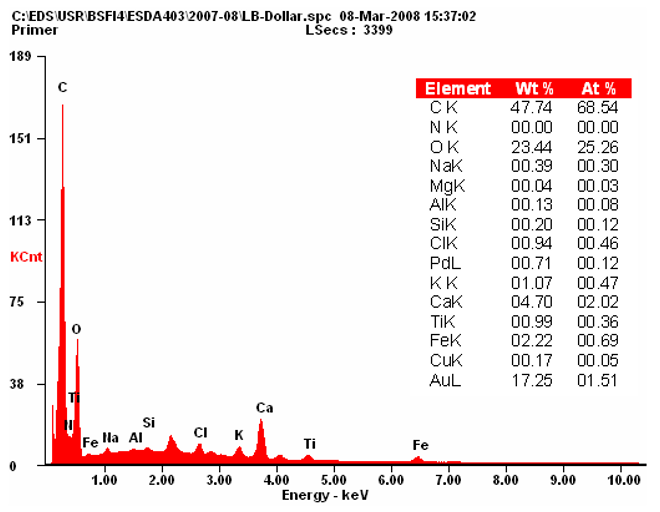
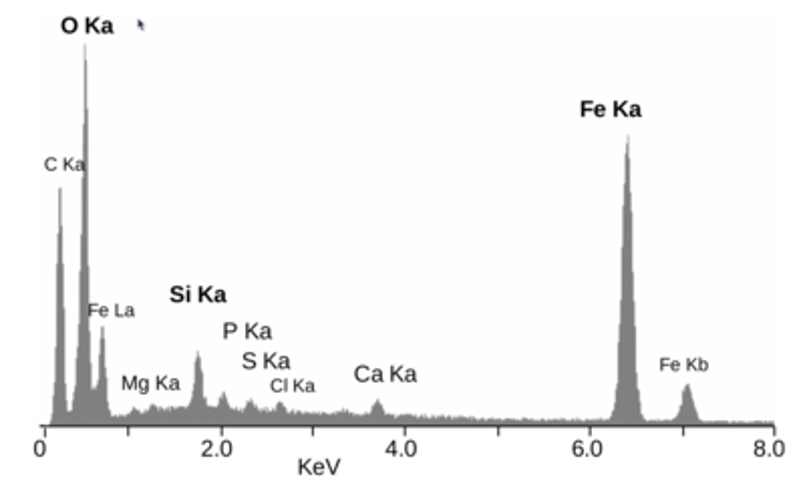
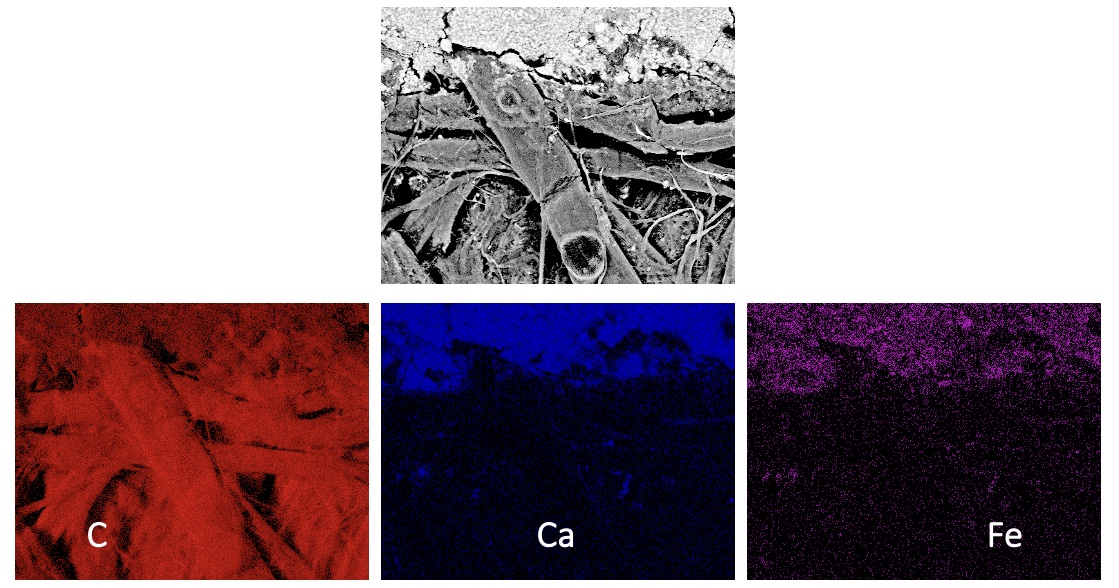
EDX Spectrum
EDX Maps of Money
sample preparation
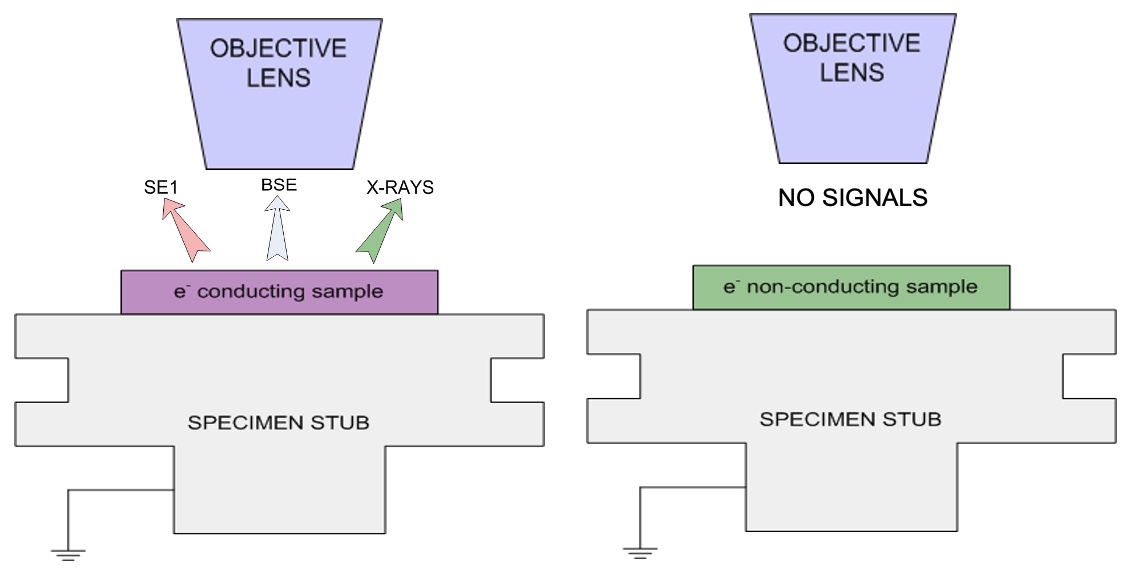
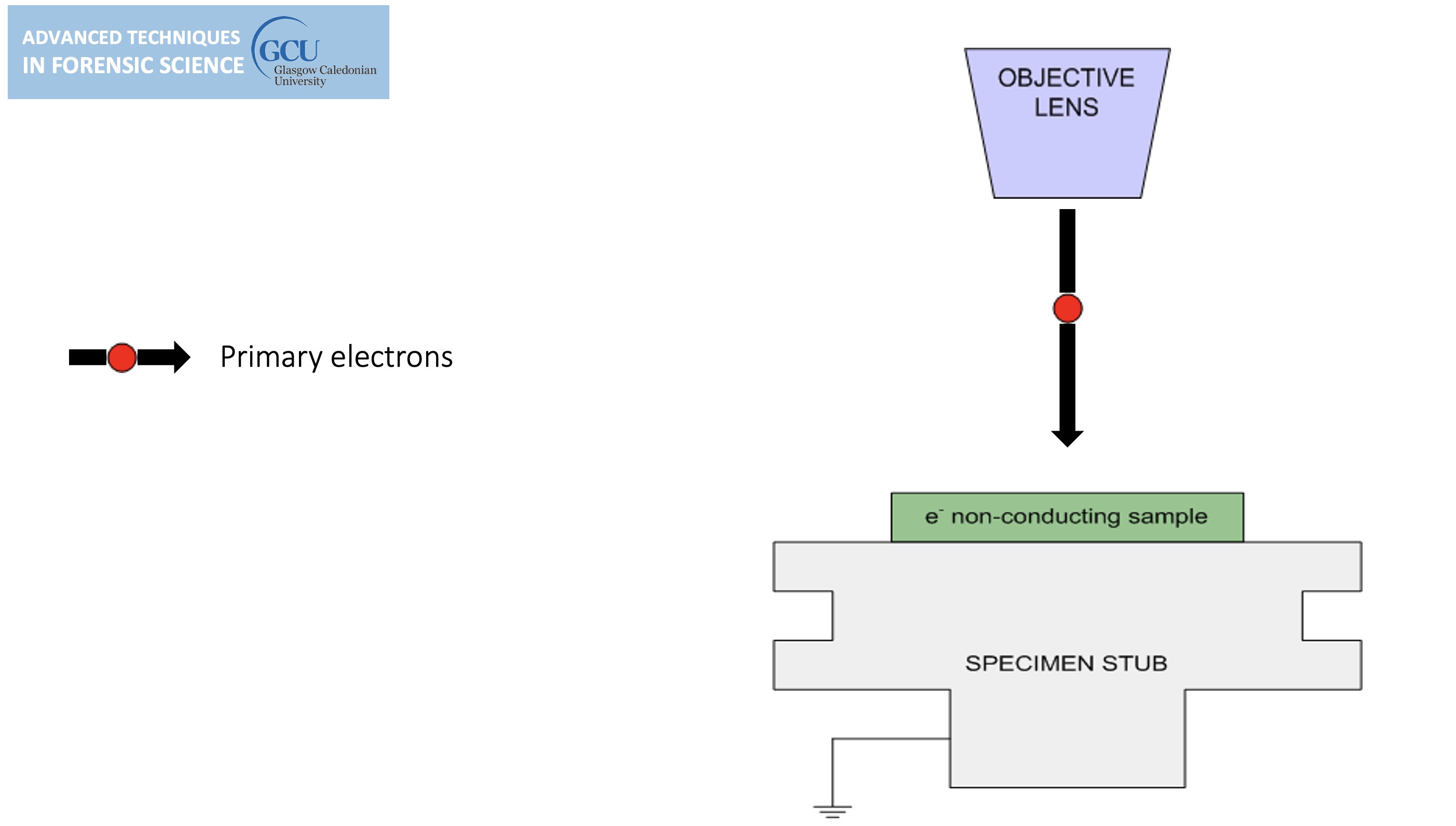
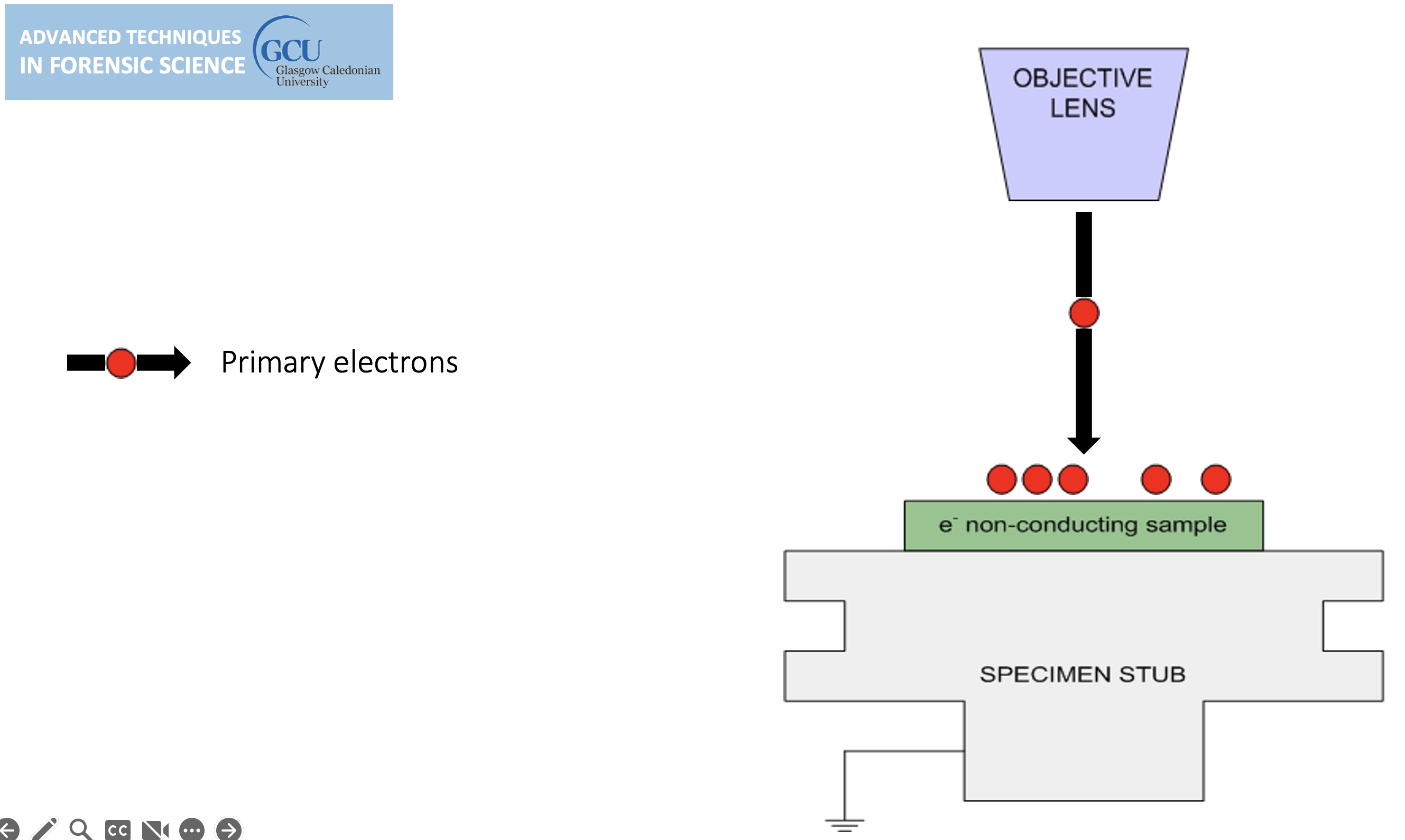
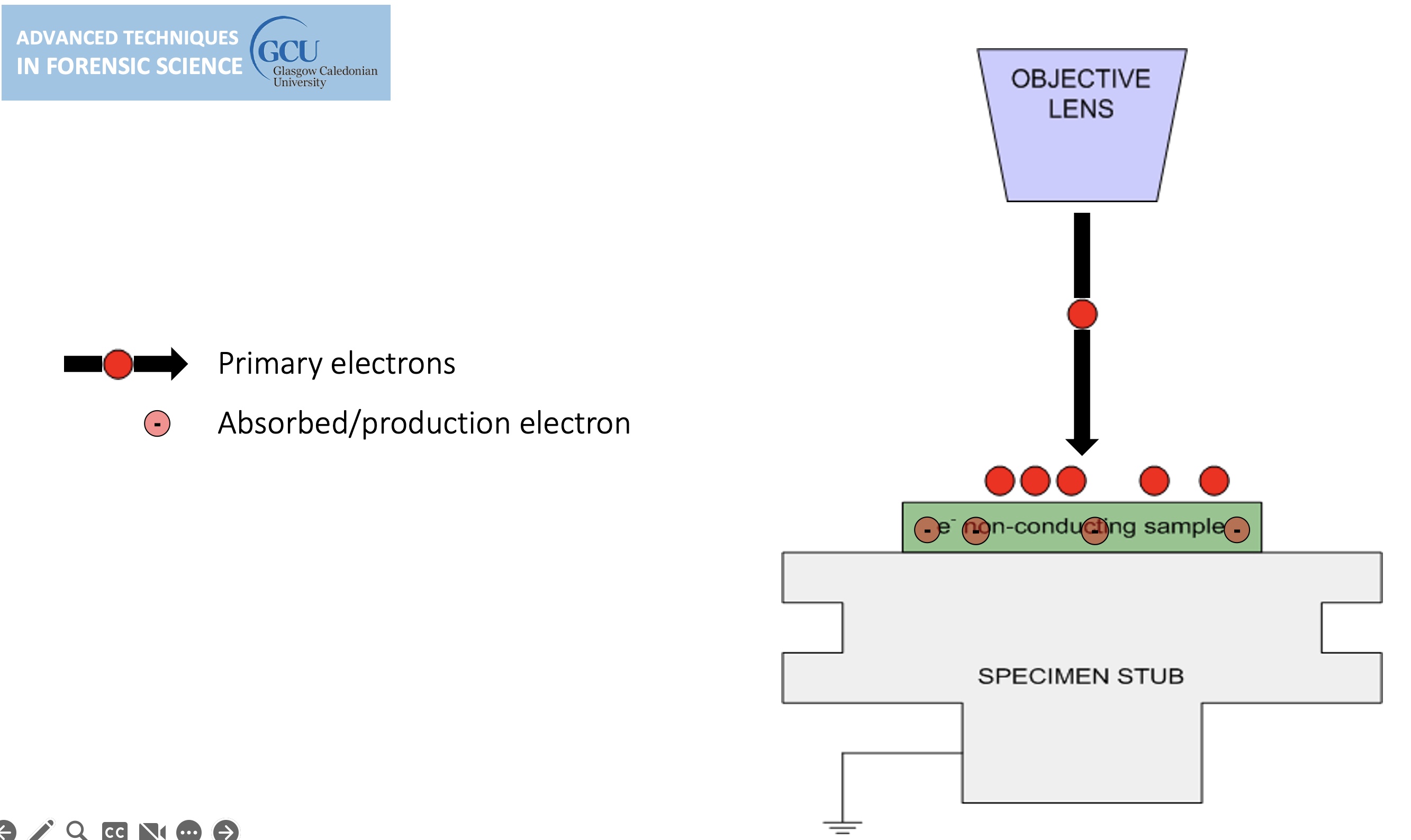
For conventional imaging in the SEM, specimens must be:
Electrically conductive.
Electrically grounded.
Clean.
Non-conductive specimens are usually coated.
ultrathin coating of Au, Au/Pd alloy, Pt, Os, Ir, W, Cr or C (graphite).
Use sputter coating or CVD.

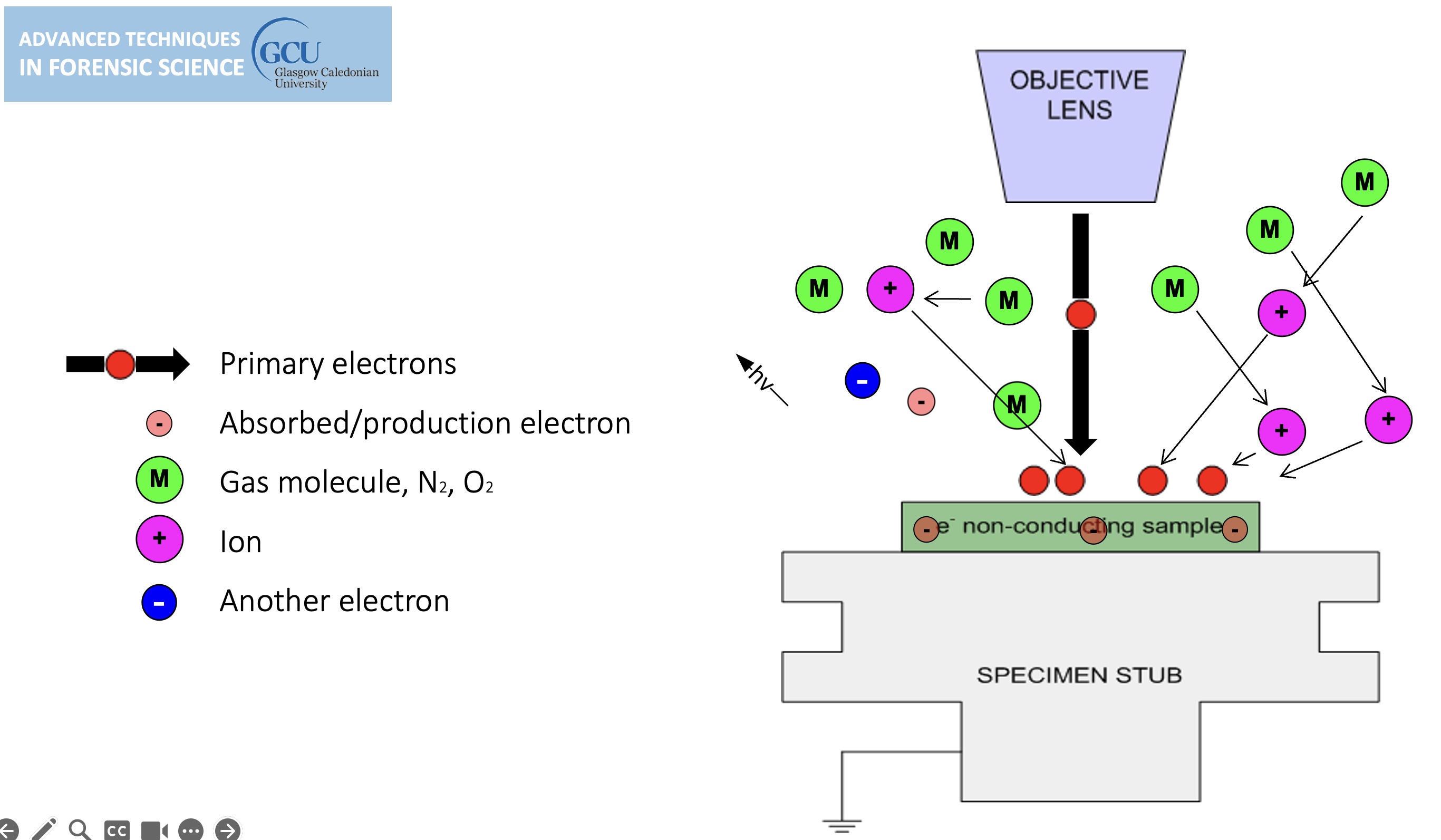
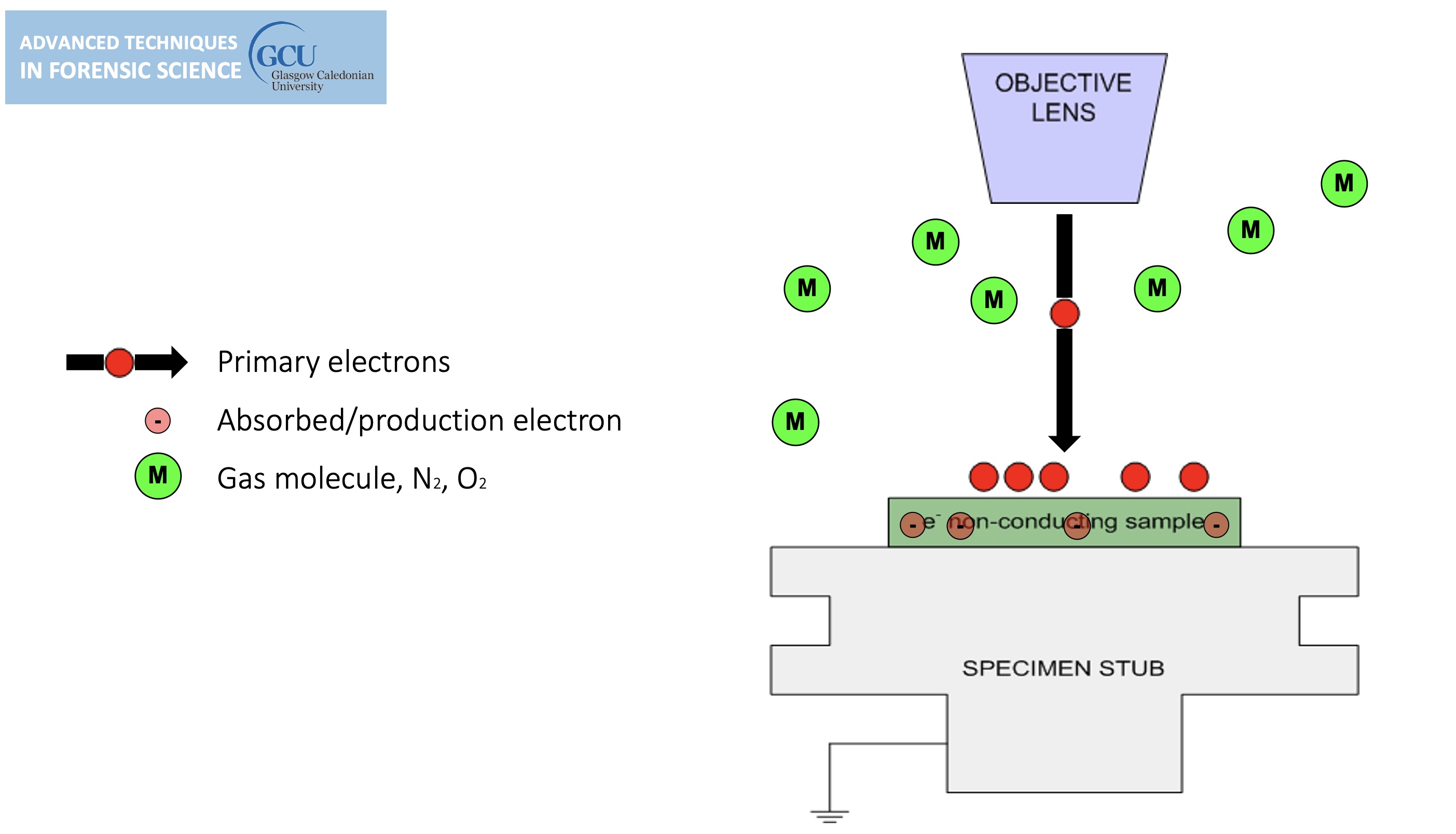
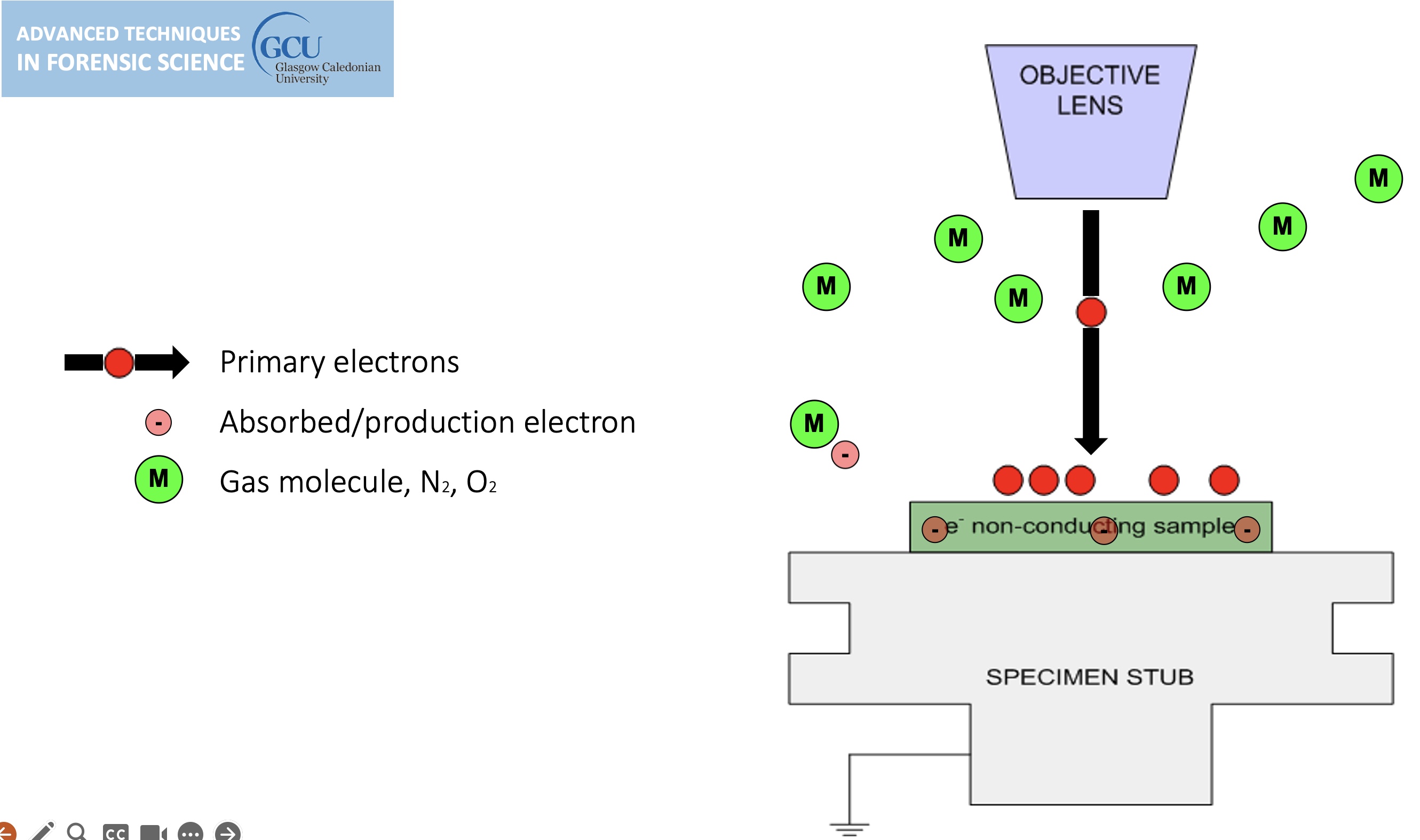
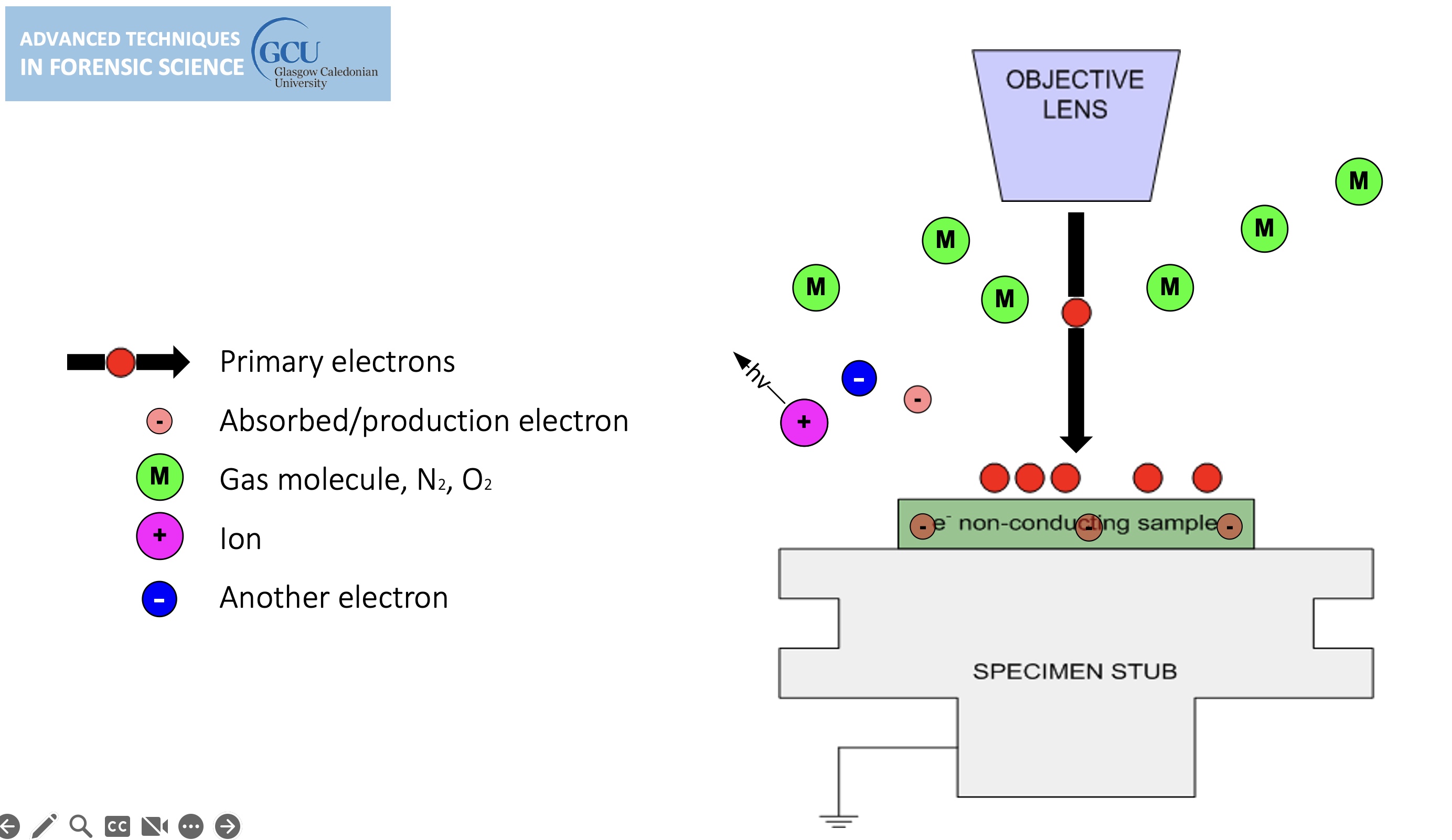
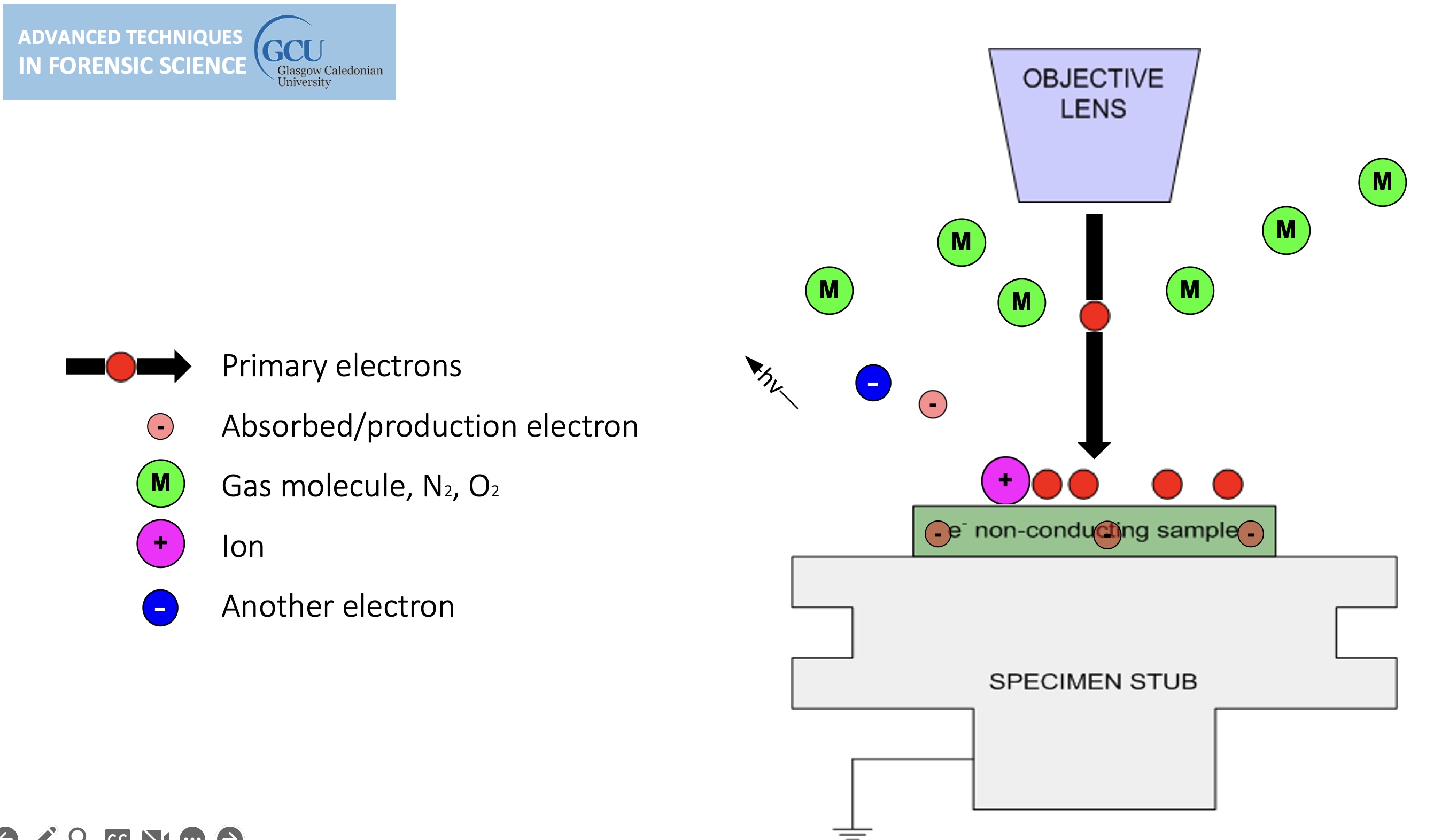
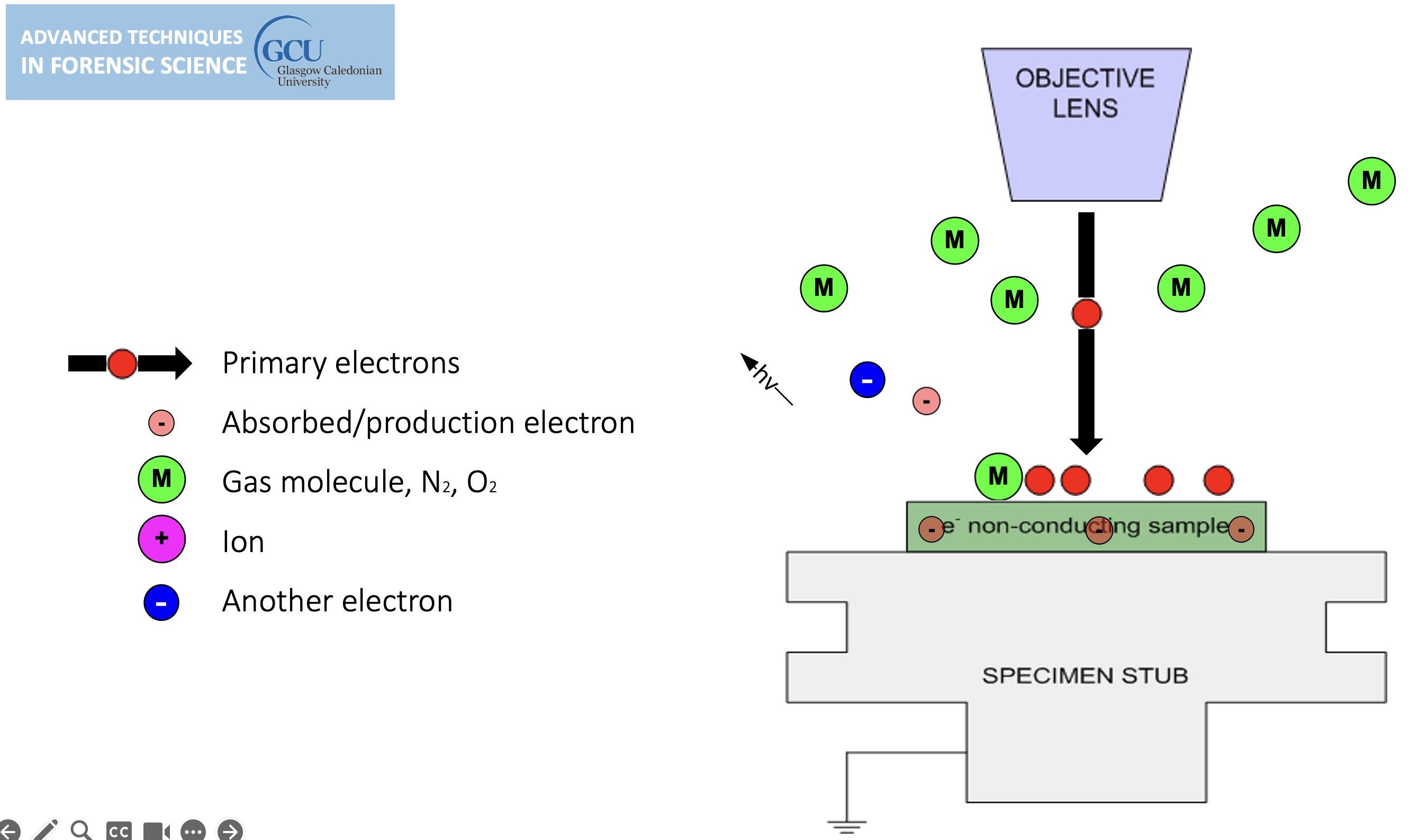
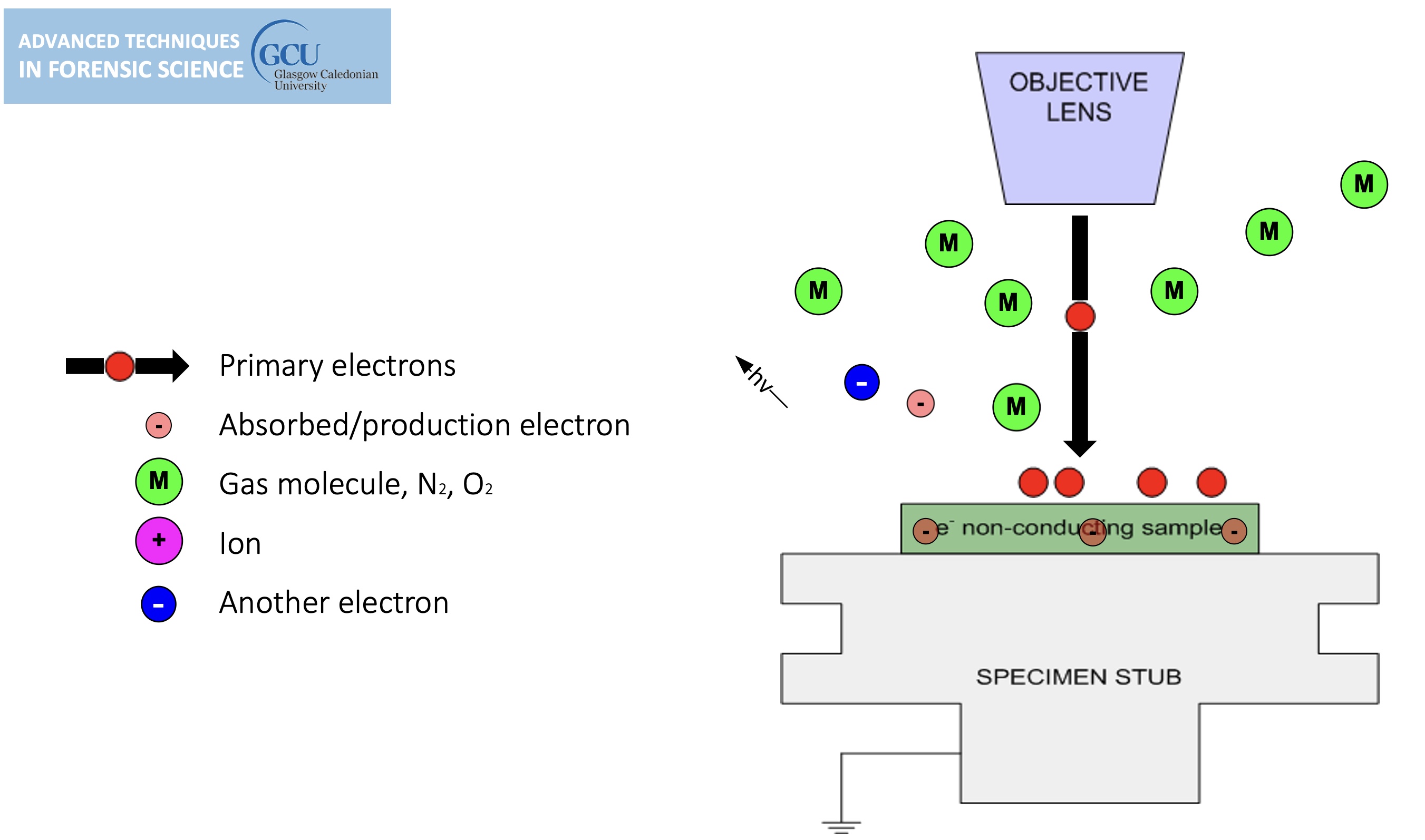
Environmental SEM
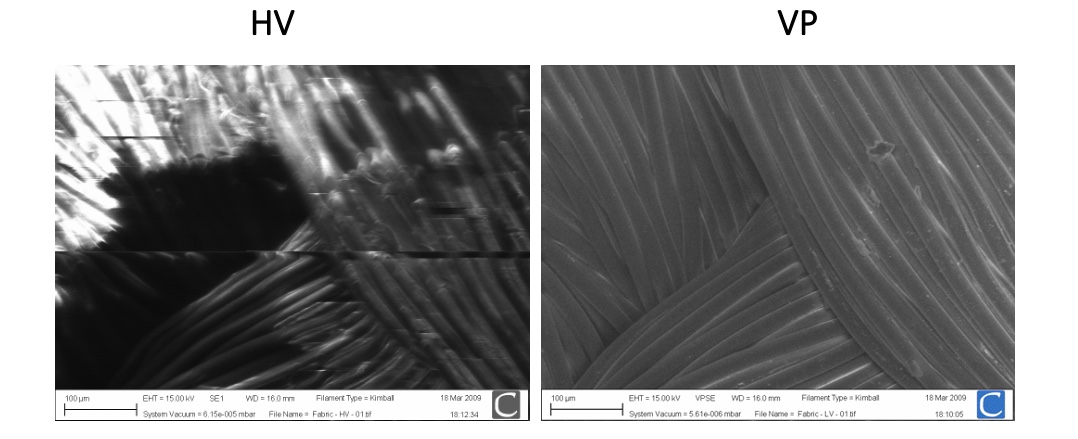
Non-conducting specimens causes the accumulation of electrostatic charge at the surface.
lines in the image are evidence of charging, can be overcome by environmental SEM.
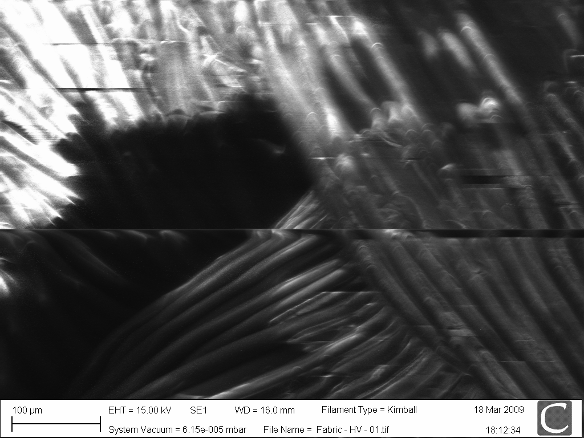
sample charging: extreme cases
Environmental SEM
Environmental SEM instruments place the specimen in a relatively high pressure (low vacuum) chamber.
The high pressure region around the sample in the ESEM neutralizes charge and amplifies the SE1 signal.
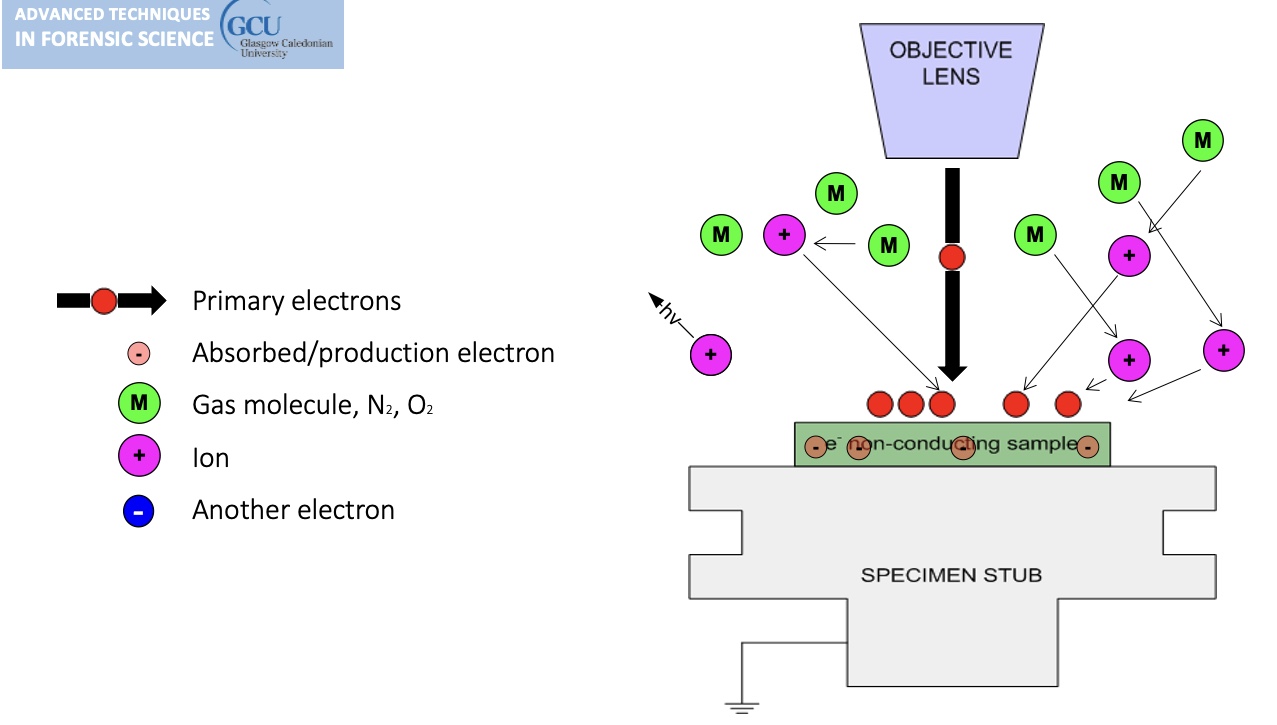
gas is introduced, tiny amount, the ion bumps into gas on its way out, this causes a chemical reaction (ionisation of gas molecule) (light can be generated) (the gas generates a new electron).
cannot do high resolution in environmental mode.
(steps to follow)
Manmade textile
un-coated
Step 1:
step 2:
step 3:
step 4:
step 5:
step 6:
step 7:
step 8:
step 9:
step 10: