L13- OPTIMISING DRUG PROPERTIES TO ENSURE GOOD ORAL BIOAVAILABILITY
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
list some of the requirements for an effective drug molecule
efficacy
must achieve intended therapeutic effect
appropriate size and structure
chemical stability
solubility
suitable logp value ( 1→3) -lipophilicity
explain the importance of logp in drug absorption
a balance is needed between the solubility of a drug and its ability to partition ( go from solid→ aqueous→ lipid→ aqueous )
hydrophilic character is needed to dissolve in the water but if too hydrophilic then it’ll be poor at partitioning into the cell membrane
lipophilic character is needed to allow the drug to partition into the cell membrane but if its too high it’ll affect the drugs solubility and the drug will also struggle to partition back out of the cell membrane-it can they accumulate into the fatty tissue
what are the factors that afftect the lipophilicity and the logp
the chemical structure of the drug- different functional groups have different lipophilic and hydro
more specifically ionisation and hydrogen bonding
what are the majority of drugs ( weak or strong acids/bases )
weak acids and bases
what affects the ionisation of a drug
varying pH of the environment and their own pka ( pka=how easiliy a drug will ionise or not)
explain the difference between ionised and unionised drugs when considering oral drug absorption
unionised drugs- have increased lipophilicity and are more optimal for membrane permeability
ionised drugs- have increased drug absorption and have a reduced membrane permeability
between strong and weak acids/bases, which is better absorbed and why
weak is better absorbed as…
strong acids and bases are less absorbed as only a small percentage of them will remain unionised which the optimum for drug absorption
strong acids and bases exists in mostly the ionised form
what is something that an ionised drug can do to be absorbed though the membrane
it can pair with an ion of the opposite charge to neutralise and pass through
explain the effect of hydrogen bonding on drub absorption
before a drug can be absorbed de-solvation must occur-when a molucule’s loses its bound water molecules before crossing the membrane
the hydrogen bond must be broken before the drug enters the cell membrane
the more of the hydrogen bonds the more energy required to break them
so molecules with more hydrogen bonds are less favourable as more energy is required to allow them desolvate which is needed before they can pass through
when considering molecules proton donors and acceptors which elements are considered
OH AND NH= proton doners
N AND O = proton acceptors
what is lupinskis rule of 5
its a rule that predicts that poor absorption is likely is 2 or more of the criteria regarding:
lipophilicity- logp
size-molecular weight
hydrogen bonding- number of acceptors and donors
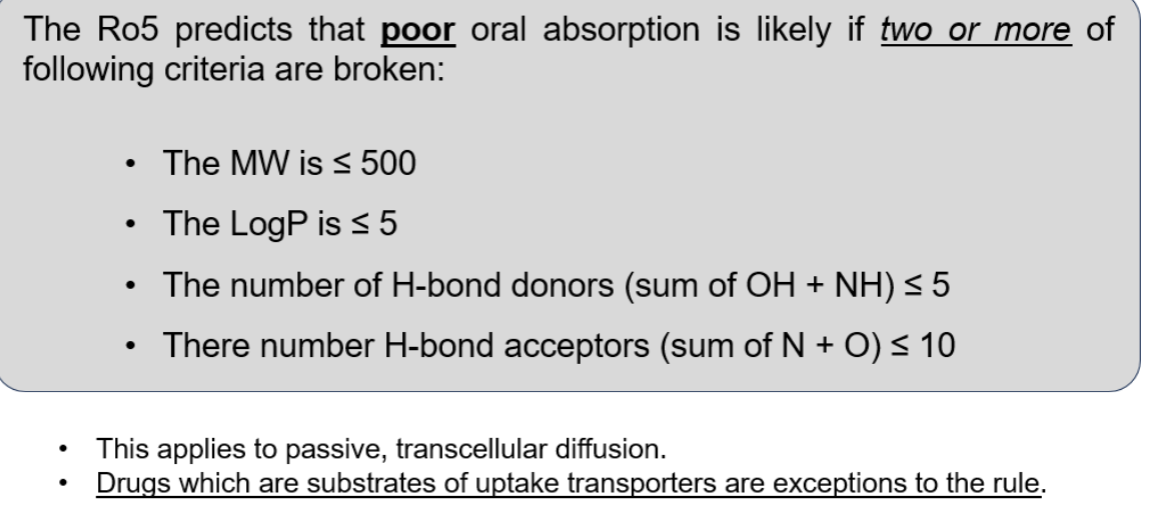
what are the exceptions to the rule
drugs which are substrates of transporters
as the rule only applies for passive diffusion
also the rues just act as a guide as some drugs break the rules but are still well absorbed
explain other rules/ factors that could affect/ decide the likehood of a drug being absorbed
verbers rules- it sates that the number of rotational bonds should be less than or equal to 10 as the more roattional bonds the more conformational forms and this incares the chances of finding the optimum
also the total polar surface area needs to be less than or equal to 140A2
what are things that can be done to increase how well a drug is absorbed
modify the polarity to change the logp
this can be done by including ionisable groups to increase solubility
change the pka of functional groups to increase lipophilicity
reduce the number of hydrogen acceptors and donators
pro drug strategies- making the drug more lipophilicity by adding functional groups that are later cleaved off
explain the pro-drug approach of increasing a drugs absorption
this includes taking a drug that is quiet hydrophilic and making it more lipophilic so that it can diffuse across the membrane
they are modified with lipophilic groups after absoption metabolic process within the cells remove the groups to reveal the parent drugs