Ch. 7 attribution of pop. affinity + Sydney Garcia Guest Lecture
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
anth exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
biological essentialism
belief that behavioral traits like intelligence, criminality, or the propensity to aggression are linked to racial categories, and are both innate and predetermined
Linnaeus
taxonomy, 4 human varieties, 1st to associate physical descriptions with social qualities “intelligence, temperament,”
Blumenbach
continued Linnaeus’ work, correctly believed that environment impacts variation, still associated (-) traits with POC, 5 racial groups in hierarchy
Morton
OG polygenist, measured cranial capacity to associate intelligence with whiteness –provided rationale for slavery and eugenics.
Hrdlicka
physical anthropology collections at Smithsonian, museum of us in SD, propagated racial categories that became foundational to physical anthropology
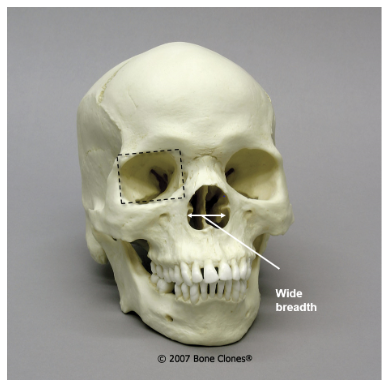
ancestry?
African
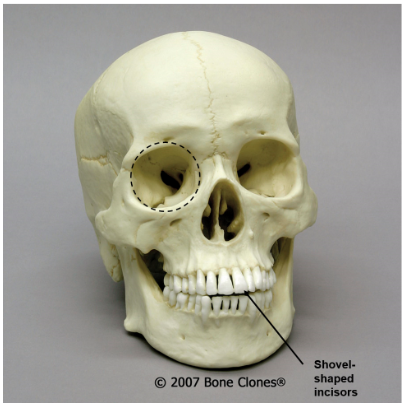
ancestry?
Asian: rounded eye orbit, shovel-shaped incisors
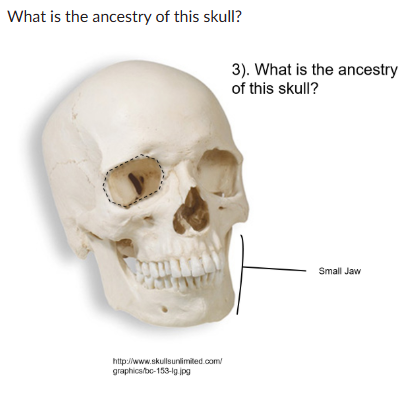
ancestry?
European: angular eye orbit, small jaw
ancestry?
Asian: rounded eye orbit, large jaw, shoveled incisors, low nose bridge
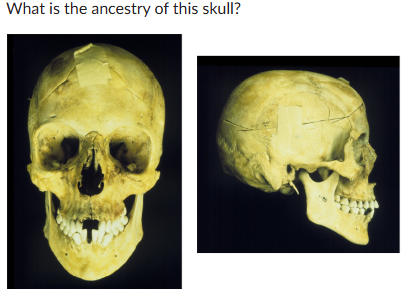
ancestry?
European: angular eye orbit, small jaw, high nose bridge, spatulate incisors
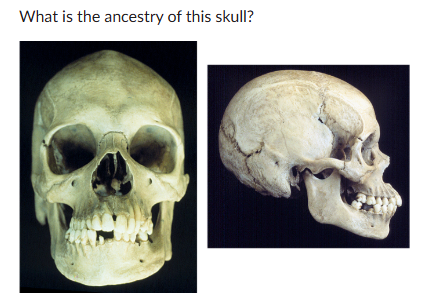
ancestry?
African: wide nasal aperture
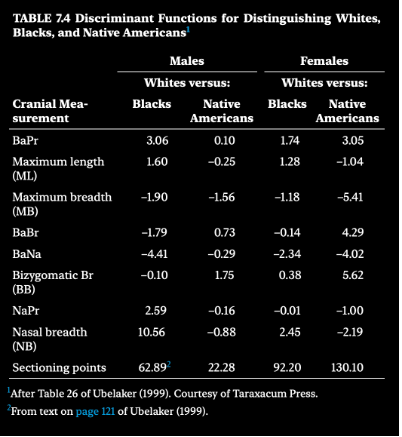
ancestry? multiply each cranial measurement with corresponding coefficients.
Add all 8 final values together
over 22.28: native american
under 22.28: white
Native American
what is race?
a social construct, clusters of phenotypes linked to geographic region and other phenotypes
what is ethnicity?
more specific, most used when self-identifying, culture, heritage, group identity. linked to geographic origin
what is nationality?
legal category based upon location of birth/ long term residence
what is ancestry?
focused on genetics and adaptations for environments. connection to a geographic region of phenotypes.
why was the concept of race created?
mid 1600s
tied to the shift from indentured servants that could ‘buy’ their freedom (white and black) to enslavement for life (only black)
Native Americans/ Indigenous peoples were labeled as “Indian” because of
rights to land. seizure of indigenous land.
Polygenist
human races had separate origins, and are separate species
what do forensic anthropologists use to determine ancestry?
anthroposcopy and osteometry
anthroposcopic methods
observing visually discernible differences in skeletal architecture between groups
osteometric methods
measurement of skulls and bones, comparison of measurements from known groups to unknown individuals using stats
anthroposcopic features
nose, face, vault, jaws, teeth
white/european
high, narrow nose
angular eye orbit/droopy
straight postbregma
small jaw
spatulate incisors
black/african
low, wide nose
rectangular eye orbit
sometimes depressed postbregma
large jaw
spatulate incisors
asian
low, medium nose
rounded eye orbit
straight postbregma
large jaw
shoveled incisors
interorbital width
european: narrow
african: wide
suture pattern
straighter: european and african
zigzag: asian or native american
T/F: anthroposcopic traits help determine skin color, eye color, hair texture
false
cline
gradual variation in a particular trait across a geographic region
population affinity
an individual’s skeletal/genetic affinity to specific, geographically defined populations
ancestry vs population affinity
‘african’ vs ‘west african’ example
ancestry links to socially constructed categories like race
race often groups population that may not share common genetic history
pop. affinity can link to precise populations
FORDISC
Forensic anthropologists input various skeletal measurements from human remains. the program then compares these measurements against a database of known population samples to calculate how closely the remains match different groups in terms of their skeletal characteristics.
DFA (discriminant function analysis)
assess ancestry based on cranial measurements
used through FORDISC or 3D-ID
goal of craniometrics
to identify the most probable biological affinity of an unknown individual, not to subdivide the entire human species into discrete racial categories
Antenor Firmin
Haitian, equality of races, variation due to environment, mixing was good for species survival
franz boas
Jewish American, four field approach, cranial shape experiments to show environment caused a change in just one generation
caroline bond day
biracial, studies on her family to discredit anti miscegenation propaganda
montague cobb
African American, disproved that Black people had lower intellect than white ppl, 1st AA with PhD in anthropology