Required Practical: Investigating Reflection & Refraction
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
How many pieces of equipment are required in the practical: Investigating Reflection & Refraction
7
list the pieces of equipment required in the practical: Investigating Reflection & Refraction
ray box
mirror with stand
protractor
sheet of paper
pencil
ruler
perspex box
purpose of the ray box?
to provide a narrow beam of light to reflect in the mirror
purpose of the mirror with stand?
to provide a reflective surface
purpose of the protractor?
to measure the light beam angles
purpose of the sheet of paper?
to mark with lines for angle measurement
purpose of pencil?
to draw lines on paper
purpose of the perspex block?
to refract the light beam
what is the resolution of measuring equipment
Protractor = 1°
Ruler = 1 mm
what is the aim of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
To investigate specular reflection off a smooth surface
what is the independent variable of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Independent variable = angle of incidence, i
what is the dependent variable of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Dependent variable = angle of reflection, r
what are the control variables of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Control variables:
Distance of ray box from mirror
Width of the light beam
Same frequency / wavelength of the light
how many steps are there to the method of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
10
step 1 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram
step 2 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
In the middle of the paper use a ruler to mark a straight line of about 10 cm long
step 3 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Use a protractor to draw a 90° line that bisects (cuts in half) the 10 cm line
step 4 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Place the mirror on the first line as shown in the diagram above
step 5 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Switch on the ray box and aim a beam of light at the point where the two drawn lines cross at an angle
step 6 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Use the pencil to mark two positions of the light beam:
A point just after leaving the ray box
The point on the reflected beam about 10 cm away from the mirror
step 7 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Remove the ray box and mirror
step 8 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Use a ruler to join the two marked positions to the point where the originally drawn lines crossed
step 9 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Use the protractor to measure the two angles from the 90° line. The angle for the ray towards the mirror is the angle of incidence, and the other the angle of reflection
step 10 : Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Repeat the experiment three times with the beam of light aimed at different angles
list all the steps to the method of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram
In the middle of the paper use a ruler to mark a straight line of about 10 cm long
Use a protractor to draw a 90° line that bisects (cuts in half) the 10 cm line
Place the mirror on the first line as shown in the diagram above
Switch on the ray box and aim a beam of light at the point where the two drawn lines cross at an angle
Use the pencil to mark two positions of the light beam:
A point just after leaving the ray box
The point on the reflected beam about 10 cm away from the mirror
Remove the ray box and mirror
Use a ruler to join the two marked positions to the point where the originally drawn lines crossed
Use the protractor to measure the two angles from the 90° line. The angle for the ray towards the mirror is the angle of incidence, and the other the angle of reflection
Repeat the experiment three times with the beam of light aimed at different angles
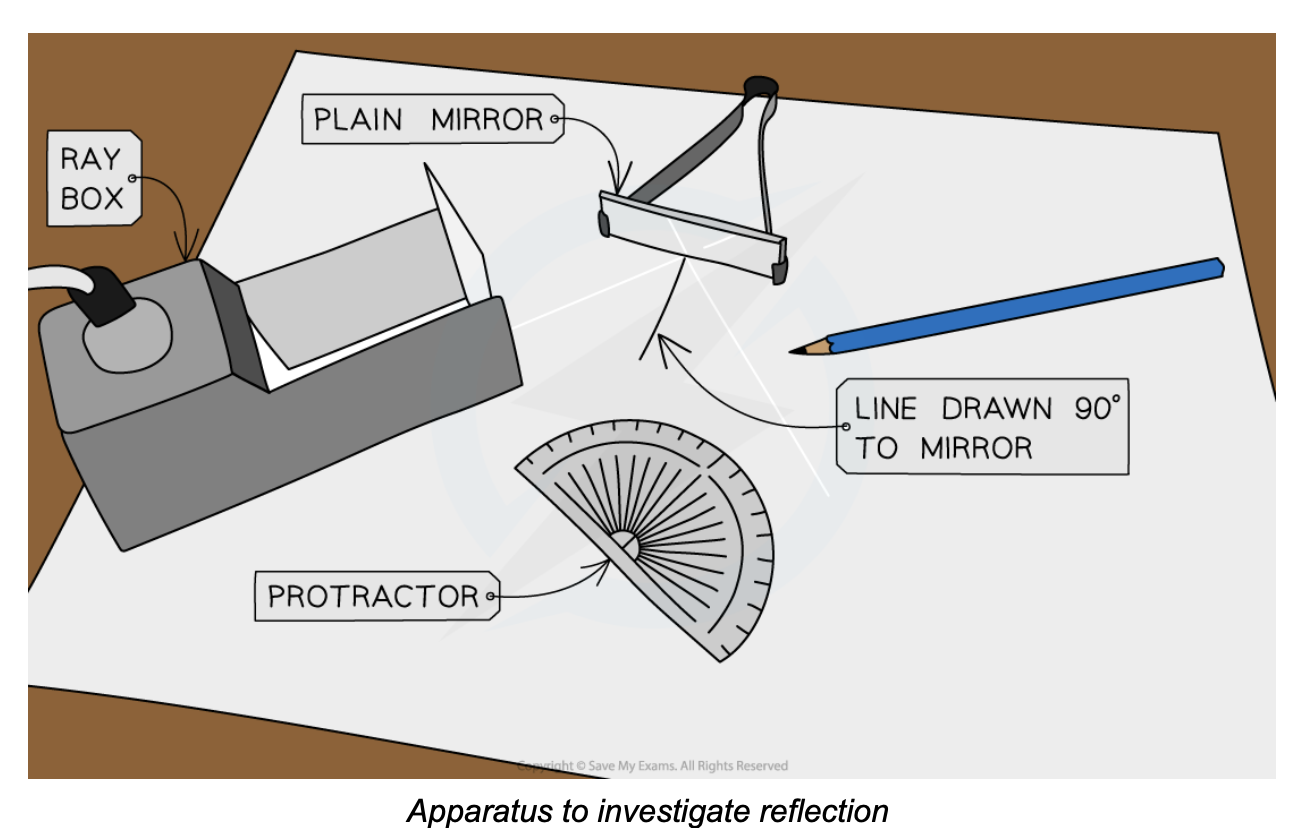
what variables would you include in a results table?
angle of incidence → angle of reflection
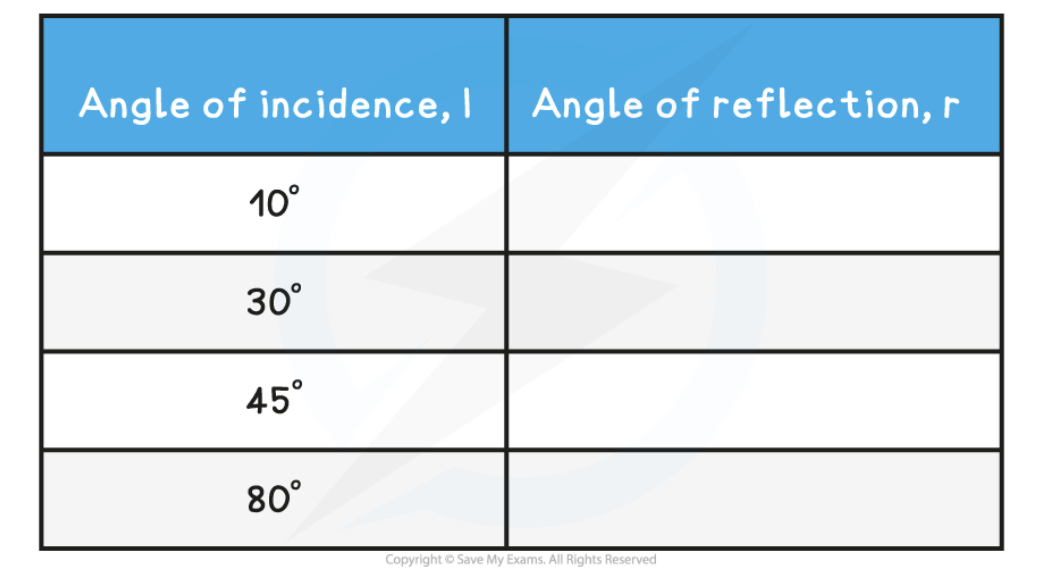
analyse the results of Experiment 1: Reflection of Light in a Mirror
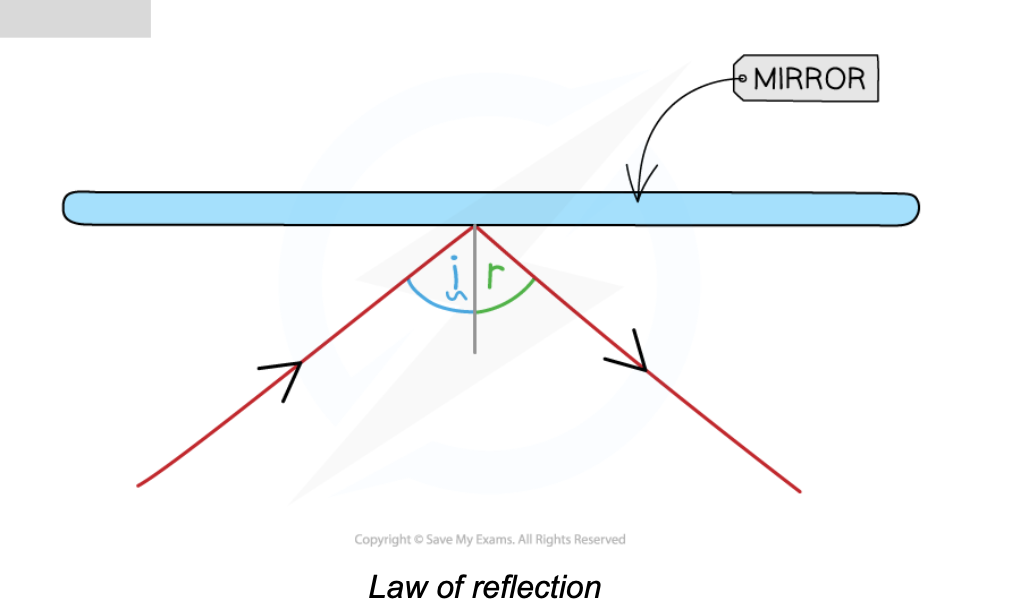
The law of reflection states:
i = r
Where:
i = angle of incidence in degrees (°)
r = angle of reflection in degrees (°)
If the experiment was carried out correctly, the angles should be the same, as shown below:
what is the aim of Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
To investigate the refraction of light by a perspex block
what is the independent variable of Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Independent variable = angle of incidence, i
what is the dependent variable of Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Dependent variable = angle of refraction , r
what are the control variables of Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Control variables:
Use of the same perspex block
Width of the light beam
Same frequency / wavelength of the light
how many steps are there to the method Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
6
step 1 : Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Place the glass block on a sheet of paper, and carefully draw around the block using a pencil
step 2 : Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Switch on the ray box and direct a beam of light at the side face of the block
step 3: Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Mark on the paper:
A point on the ray close to the ray box
The point where the ray enters the block
The point where the ray exits the block
A point on the exit light ray which is a distance of about 5 cm away from the block
step 4 : Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Draw a dashed line normal (at right angles) to the outline of the block where the points are
step 5 : Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Remove the block and join the points marked with three straight lines
step 6 : Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
Replace the block within its outline and repeat the above process for a ray striking the block at a different angle
what would be the variables in Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block
angle of incidence → angle of refraction
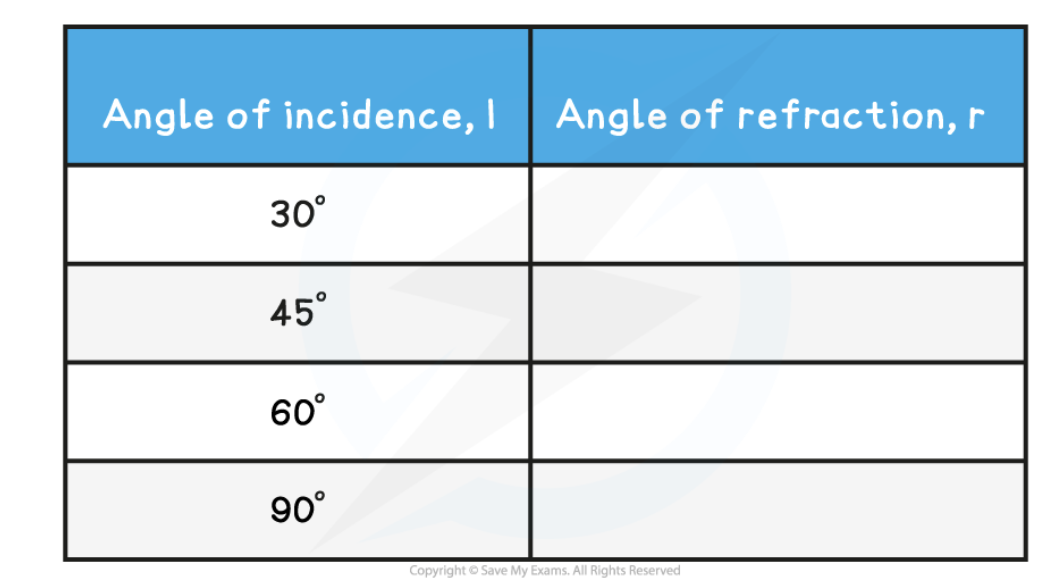
analyse the results of Experiment 2: Refraction of Light By A Perspex Block (5)
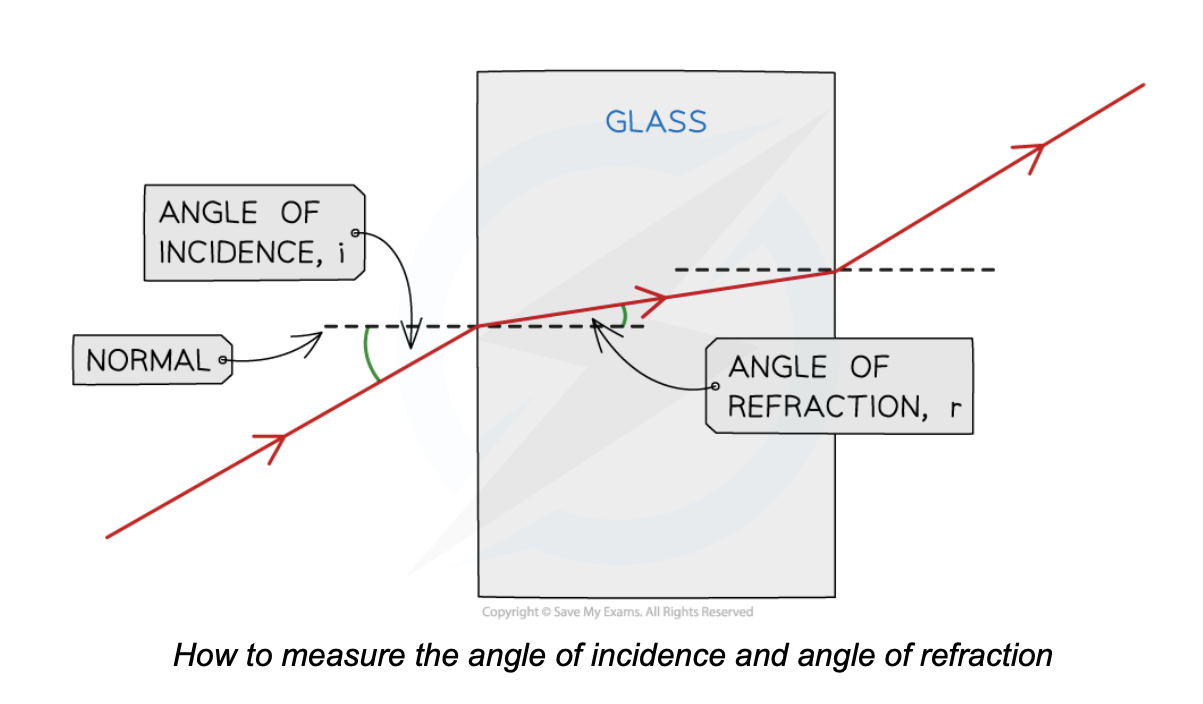
i and r are always measured from the normal
For light rays entering perspex block, the light ray refracts towards the central line:
i > r
For light rays exiting the perspex block, the light ray refracts away from the central line:
i < r
When the angle of incidence is 90° to the perspex block, the light ray does not refract, it passes straight through the block:
i = r
If the experiment was carried out correctly, the angles should follow the pattern, as shown below:
identify and rectify the systematic errors (2)
An error could occur if the 90° lines are drawn incorrectly
Use a set square to draw perpendicular lines
If the mirror is distorted, this could affect the reflection angle, so make sure there are little to no blemishes on it
identify and rectify the random errors (2)
The points for the incoming and reflected beam may be inaccurately marked
Use a sharpened pencil and mark in the middle of the beam
The protractor resolution may make it difficult to read the angles accurately
Use a protractor with a higher resolution
list 3 of the safety considerations
The ray box light could cause burns if touched
Run burns under cold running water for at least five minute
Looking directly into the light may damage the eyes
Avoid looking directly at the light
Stand behind the ray box during the experiment
Keep all liquids away from the electrical equipment and paper
Take care using the mirror
Damages on the mirror can affect the outcome of the reflection experiment