FTM Lecture 4: Tonicity and Osmolarity
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the 2 ways in which water transport can occur across membranes?
1- Simple diffusion - ie water moves from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration
2- Aquaporins- water channels that allow a flux of water across membranes depending on osmotic gradients
Practice Q1

Ans: D

What will be the water concentration in a compartment with high solute concentration? low solute concentration?
High solute concentration= low water concentration
Low solute concentration= high water concentration
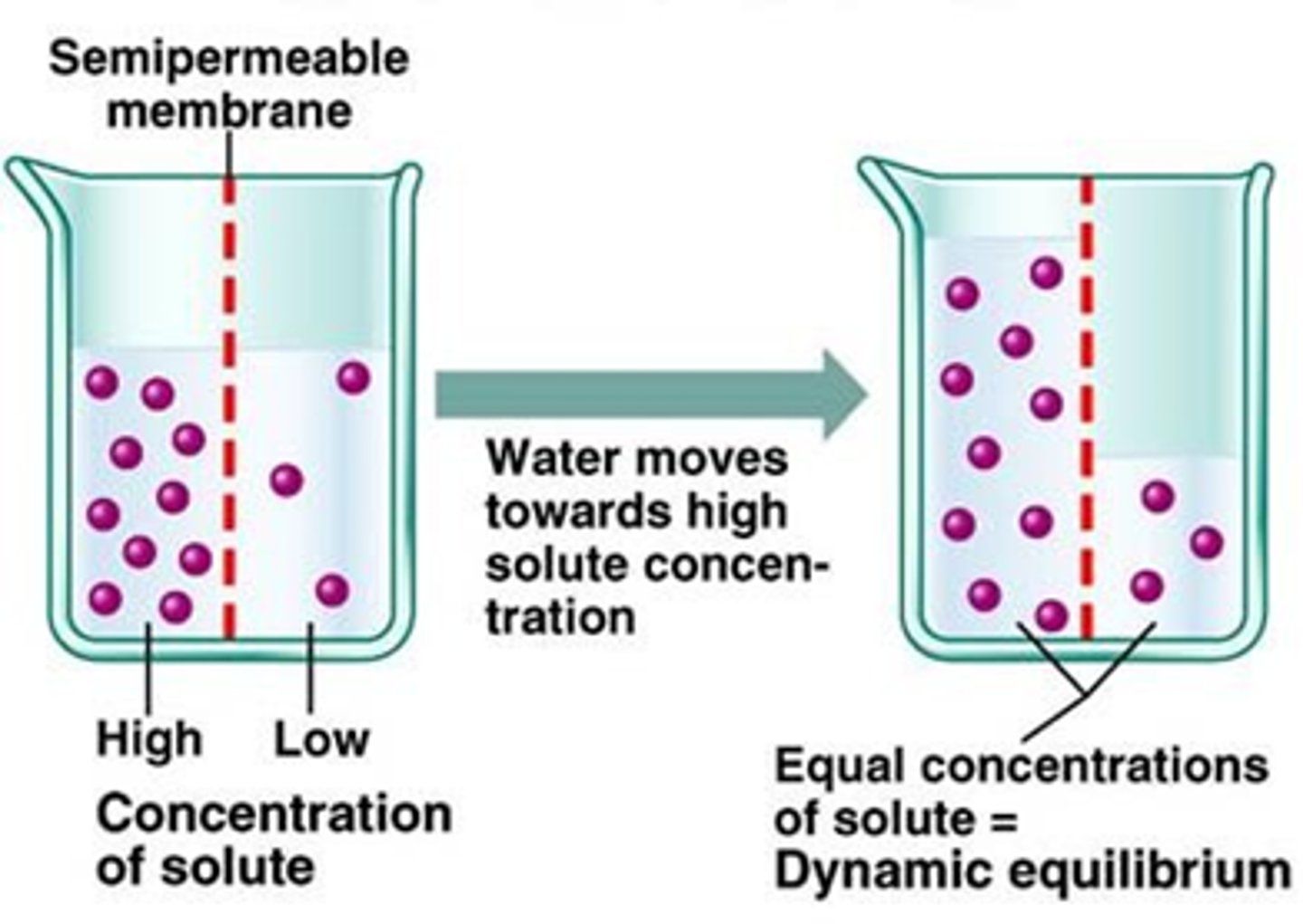
Water can move across membranes down its concentration gradient from .... to .... ?
An area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration until equilibrium is reached
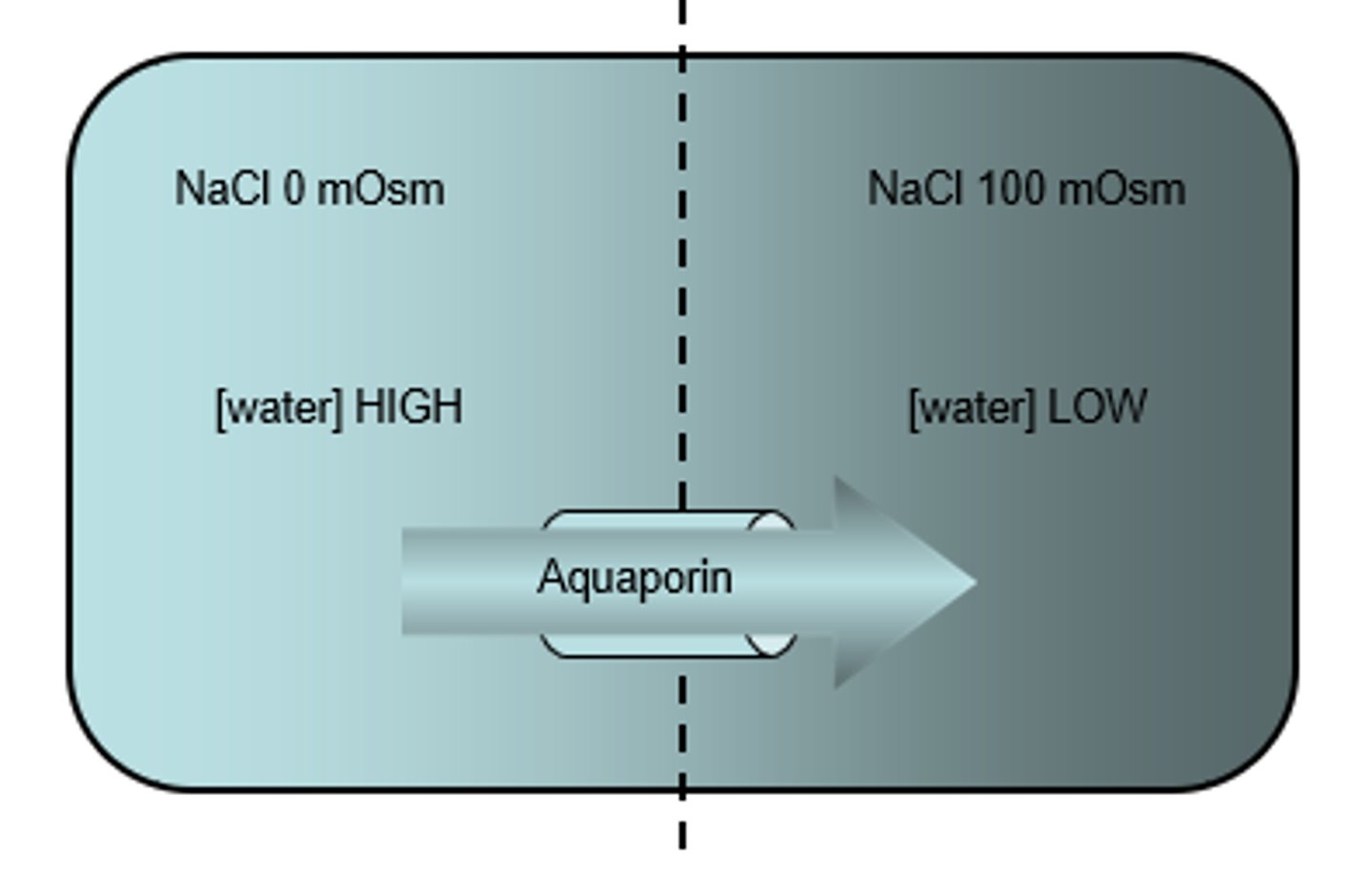
What is the function of Aquaporins?
Allows passage of water across the membrane thus increasing the net flux of water across the membrane
What are the 2 major driving forces for movement of water in the body?
1- Osmotic pressure
2- Hydrostatic driving forces
T or F
Hydrostatic forces across membranes at the cellular level are 0
True
since membranes cannot withstand large hydrostatic forces water movement is governed by solute concentration→ This is not true of solute transport across vasculature Pressures matter!!
What equation is used to calculate osmotic pressure of a solution? Variables?
Van't Hoff equation
pie = osmotic pressure (atm)
n = Number of particles produced by a molecule (e.g. NaCl - 2 particles) (mmol/L)
R = Gas constant (0.082 L-atm/mol-K)
T = Temperature (Kelvin)
C = Concentration (mol/L)
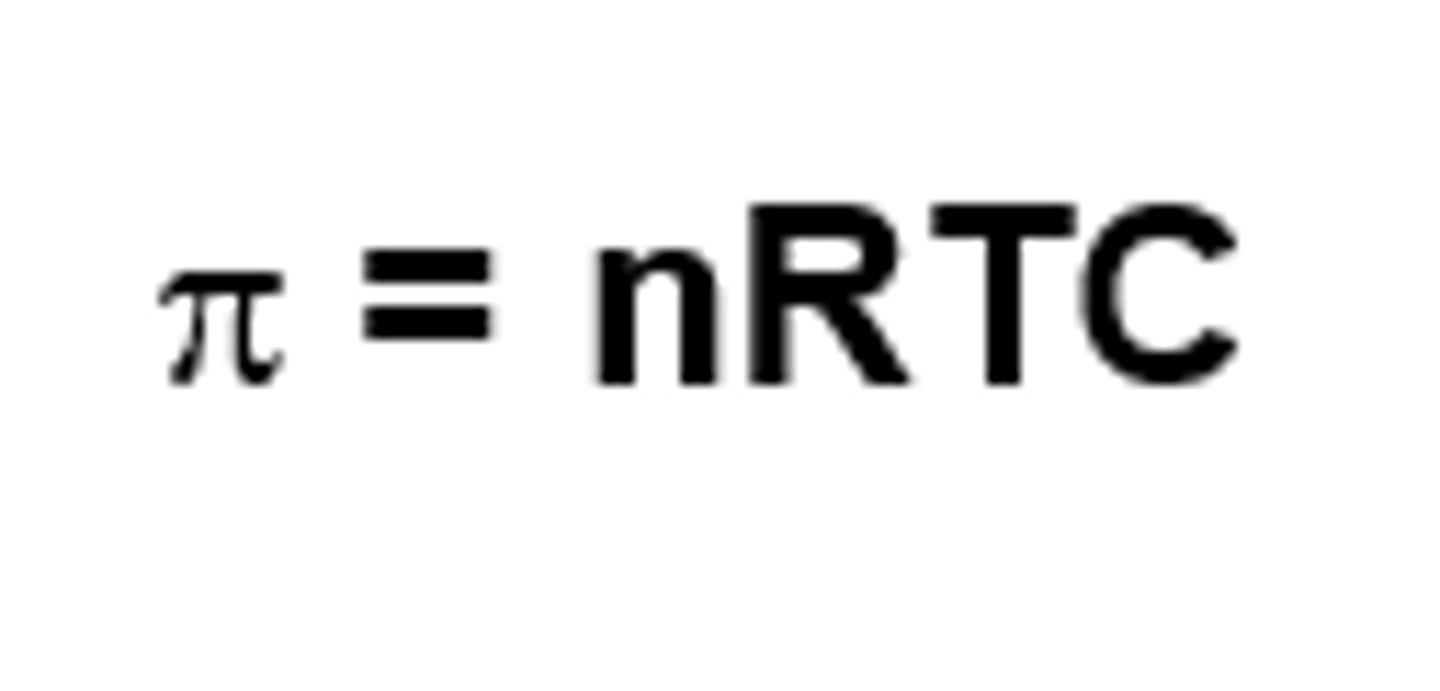
How is effective osmotic pressure calculated?


What is Water flux?
The difference in osmotic pressure between 2 compartments can provide a driving force for water to flow
What is the formula used to calculate Water flux?
Jv = Volume of water flux
Kh = Hydraulic conductivity
(permeability to fluid)
A = Area
Sigma = Reflection coefficient
Ci = Concentration of total solutes inside the cell
Co = Concentration of total solutes outside the cell
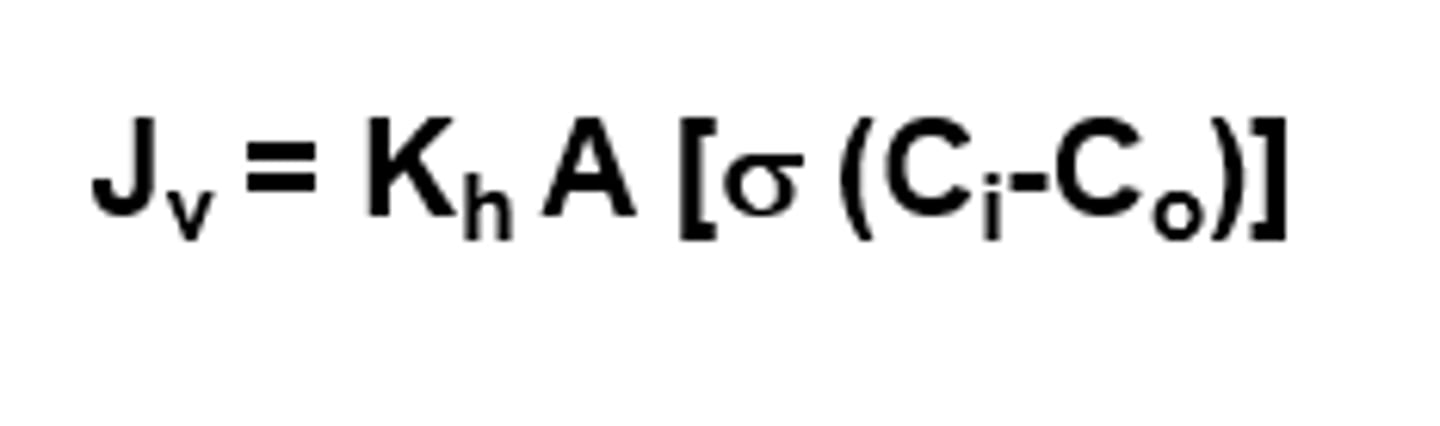
What is Osmosis defined as? Water will flow from ... to ... ?
Flow of water between two solutions separated by a semi-permeable membrane caused by a difference in solute concentration
Water will flow from an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity
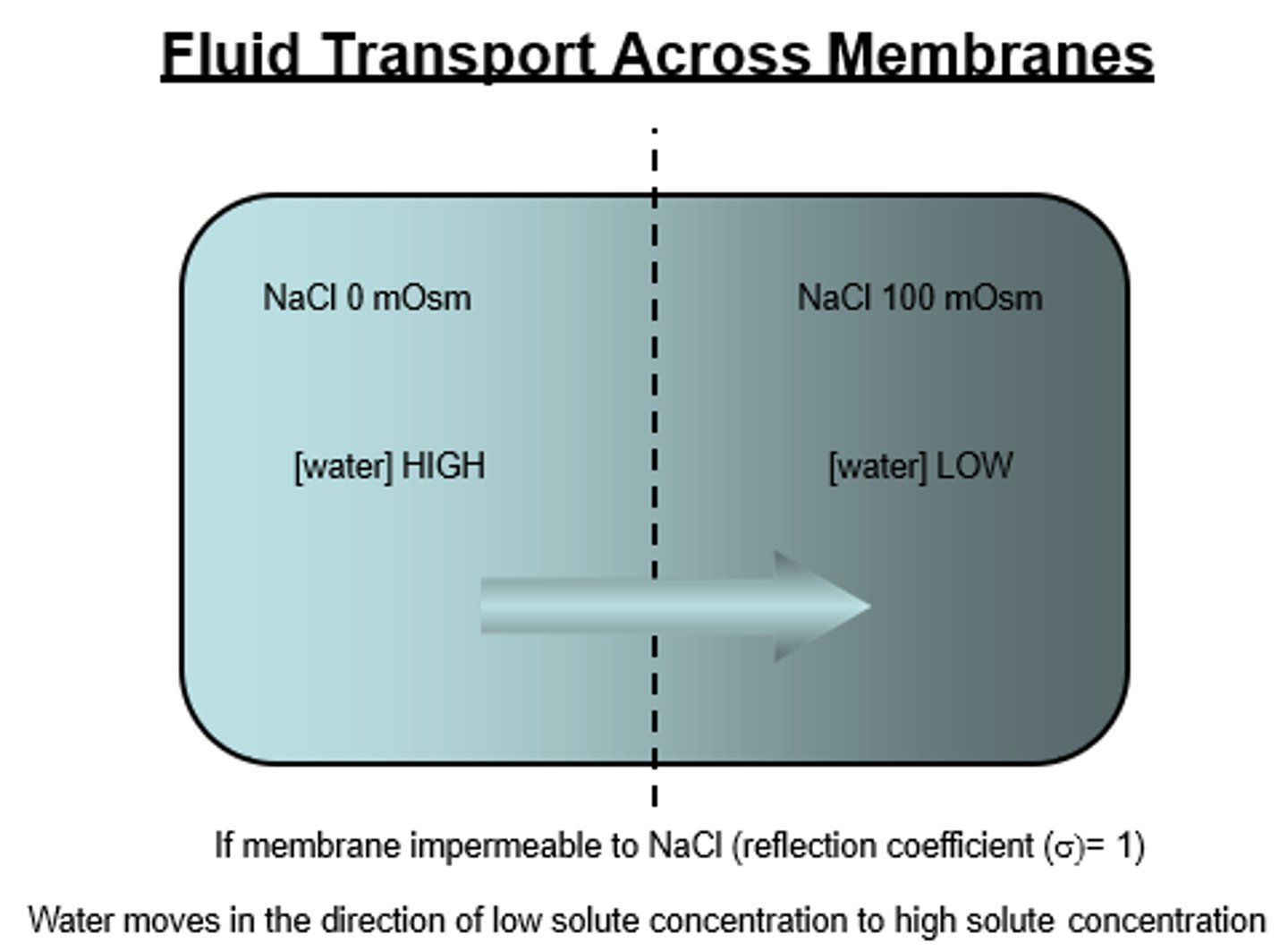
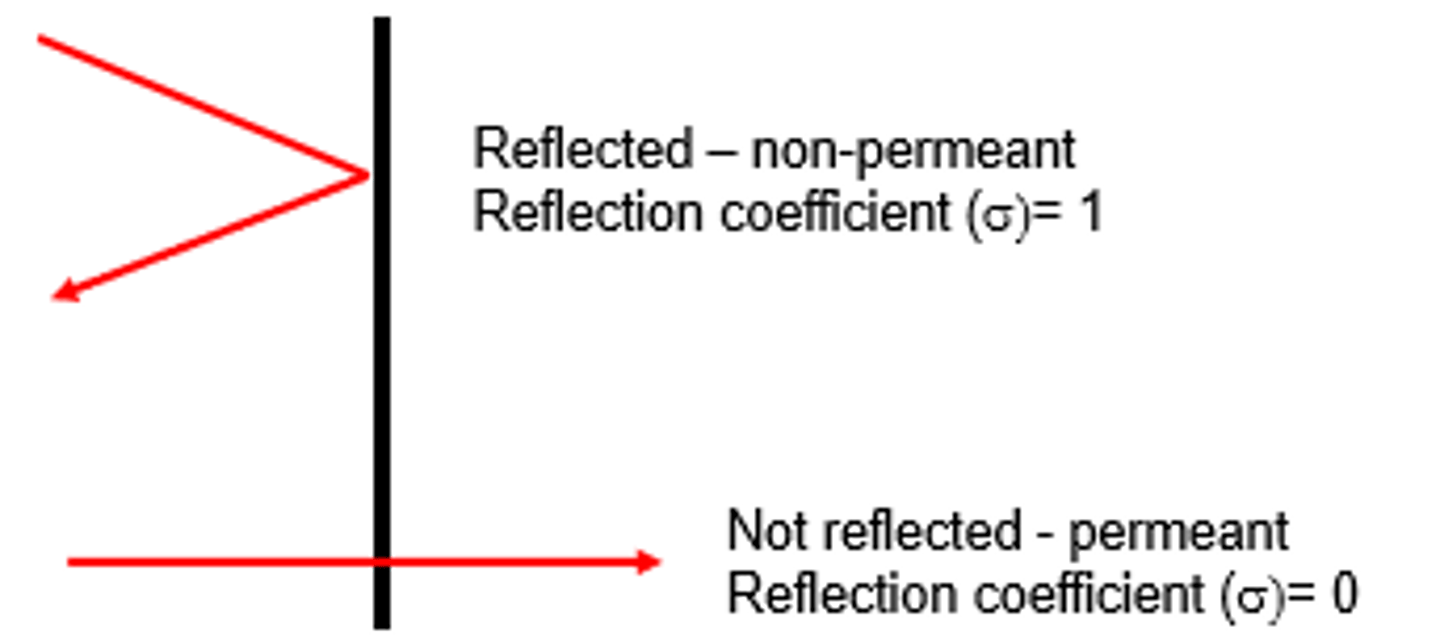
What does it mean if a solute has a reflection coefficient of 1 (reflected- non permeant)? Does it exert an osmotic pressure for water flow?
That means that the solute is totally impermeable and cannot cross the plasma membrane
Yes
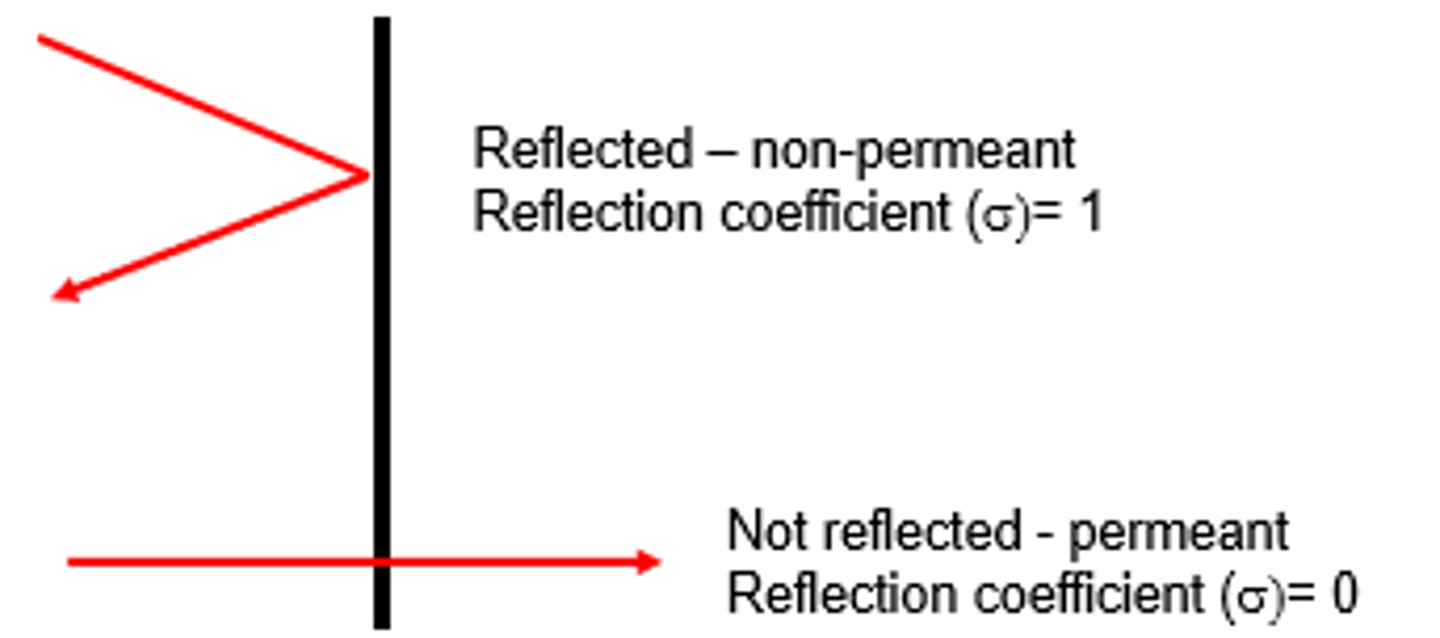
What does it mean if a solute has a reflection coefficient of 0 (not reflected-permeant)? Does it exert an osmotic pressure for water flow?
That means the solute is totally permeable
No, it exerts no osmotic pressure difference between 2 compartments, and therefore does not contribute to water flow
What is Osmolarity defined as? How is it calculated?
Total concentration of all particles in solution

What is Tonicity defined as?
Concentration of only the osmotically active particles
Tonicity of a solution describes the volume change of a cell at
equilibrium
Only what type of particles can contribute to tonicity and can cause changes in cell volume?
Impermeable particles
What are Penetrating solutes defined as? examples?
Solutes that can enter the cell
eg: Glucose, Urea and Glycerol
What are Non-Penetrating solutes defined as? examples?
Solutes that cannot enter the cell
eg: NaCl, KCl and Sucrose
What type of solutes ultimately determine the tonicity of a solution?
Non-penetrating solutes
A solution is considered Isoosmotic if? Hyperosmotic? Hypoosmotic?
Isoosmotic: if total osmotic pressure of the solution is equal to that of the cell
Hyperosmotic: if the solution has greater osmotic pressure than the cell
Hypoosmotic: if the solution has less osmotic pressure than the cell
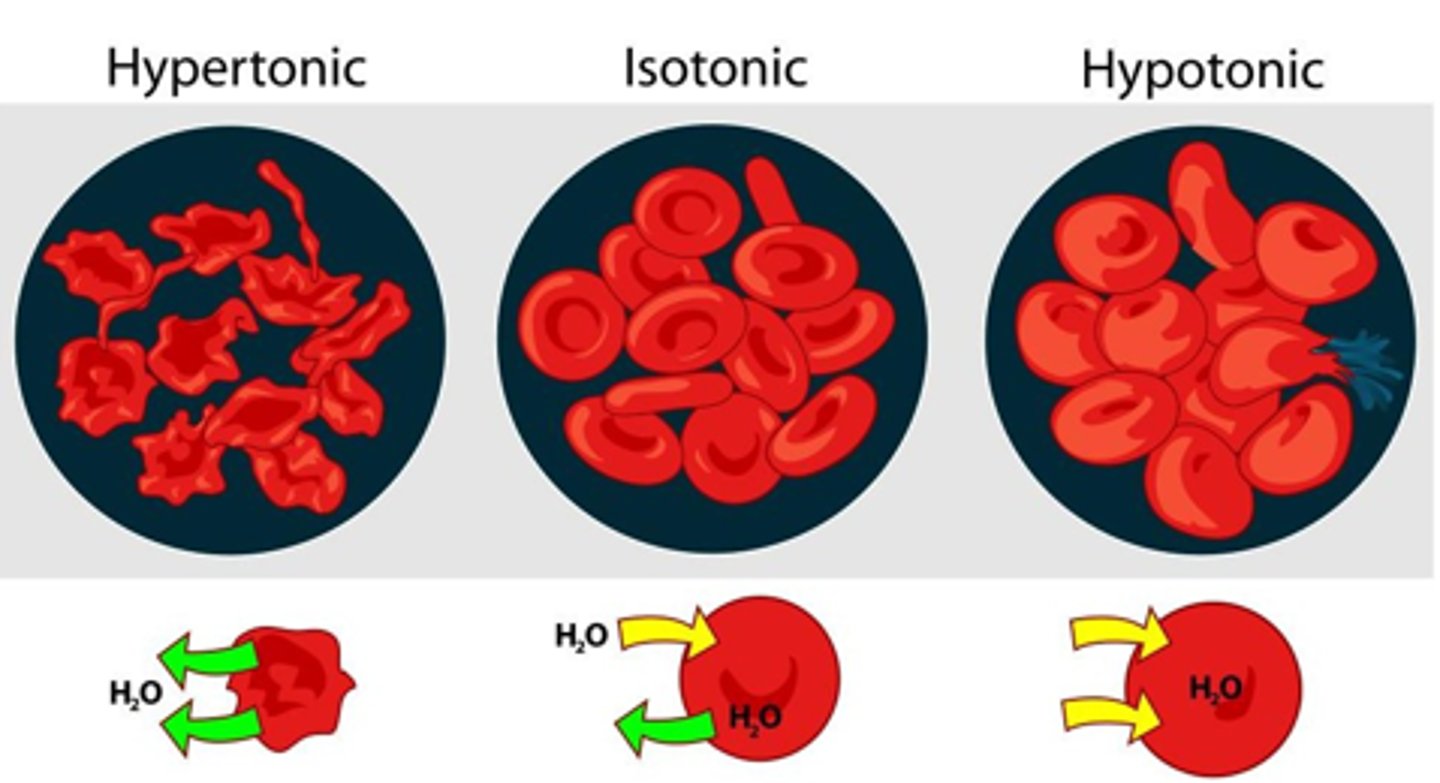
When is a solution considered Isotonic? What is the concentrations of non-penetrating on either side of the membrane in this case?
If at equilibrium no change occurs to cell ie it does not shrink or swell
the non-penetrating solute concentrations on both sides of the cell membrane are the same
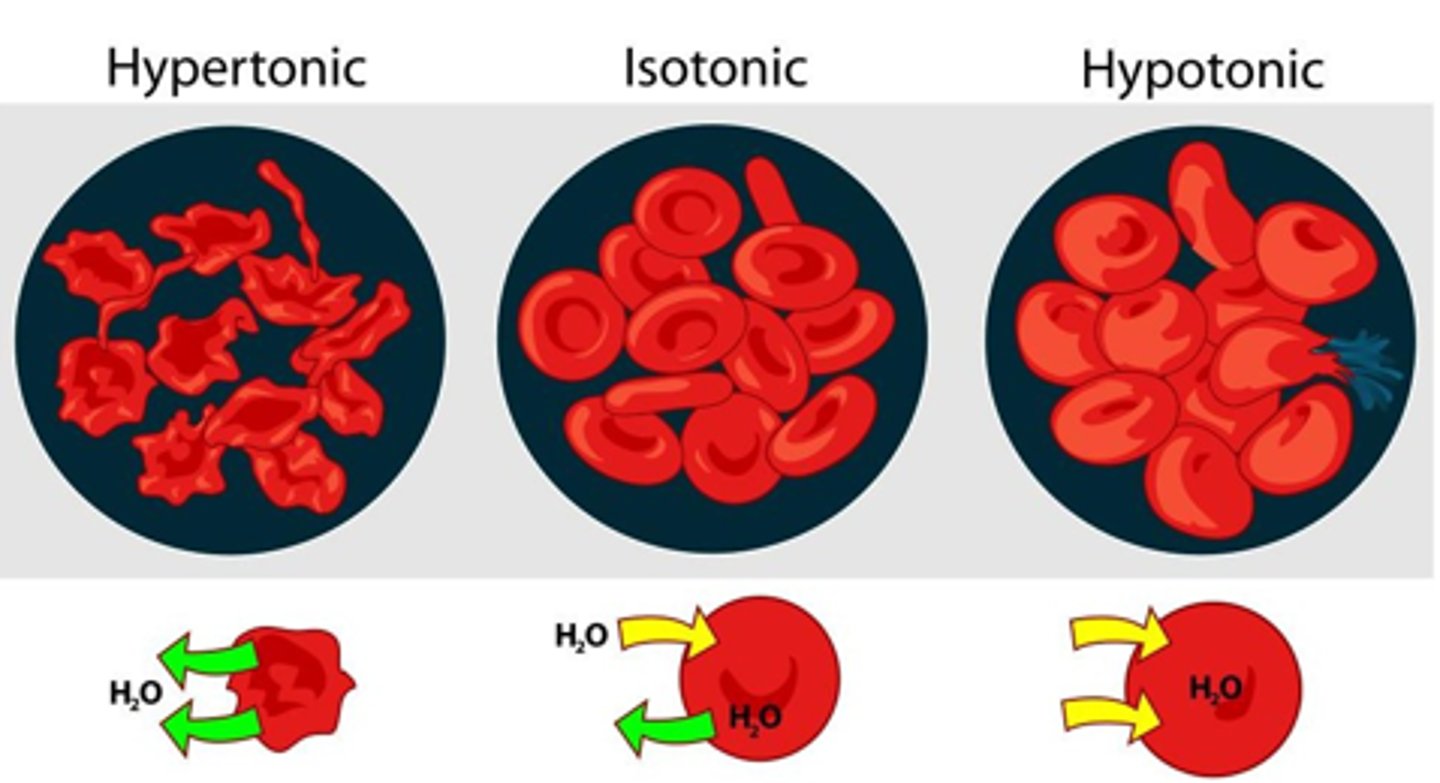
When is a solution considered Hypertonic? What is the concentrations of non-penetrating on either side of the membrane in this case?
If it causes the cell to shrink
Non-penetrating solute concentration is higher outside of the cell as compared to inside
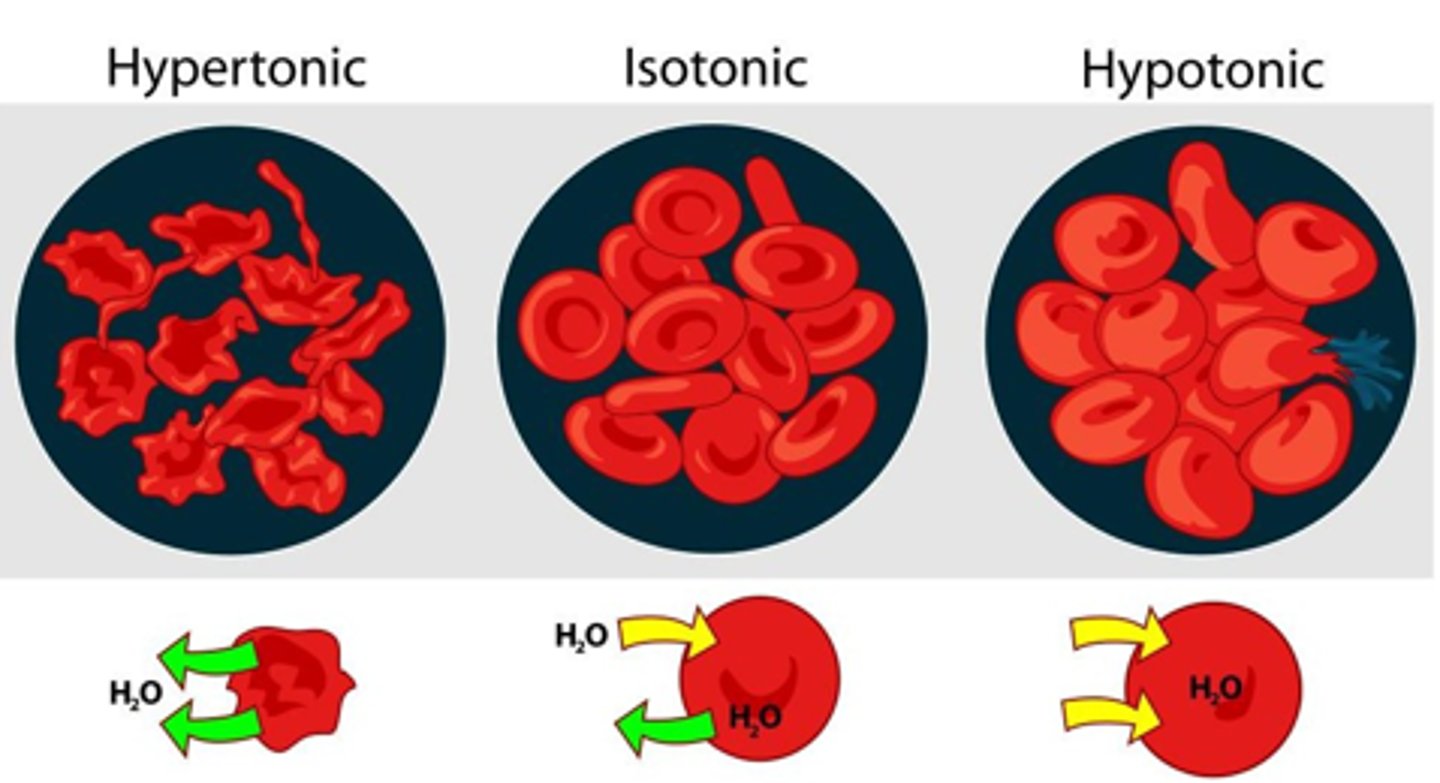
When is a solution considered Hyportonic? What is the concentrations of non-penetrating on either side of the membrane in this case?
If it causes the cell to swell
Non-penetrating solute concentration is higher inside of the cell as compared to outside
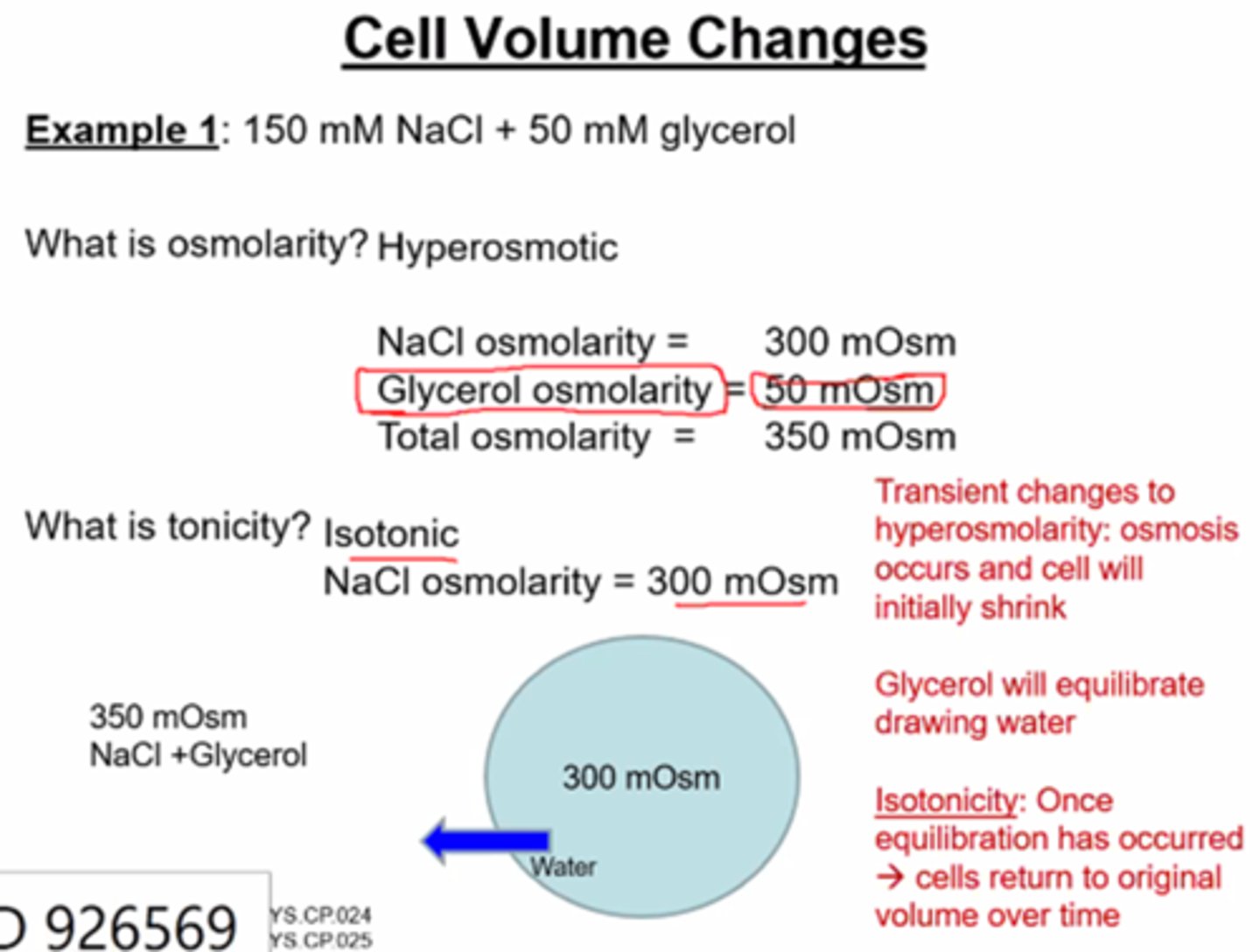
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 1
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 2
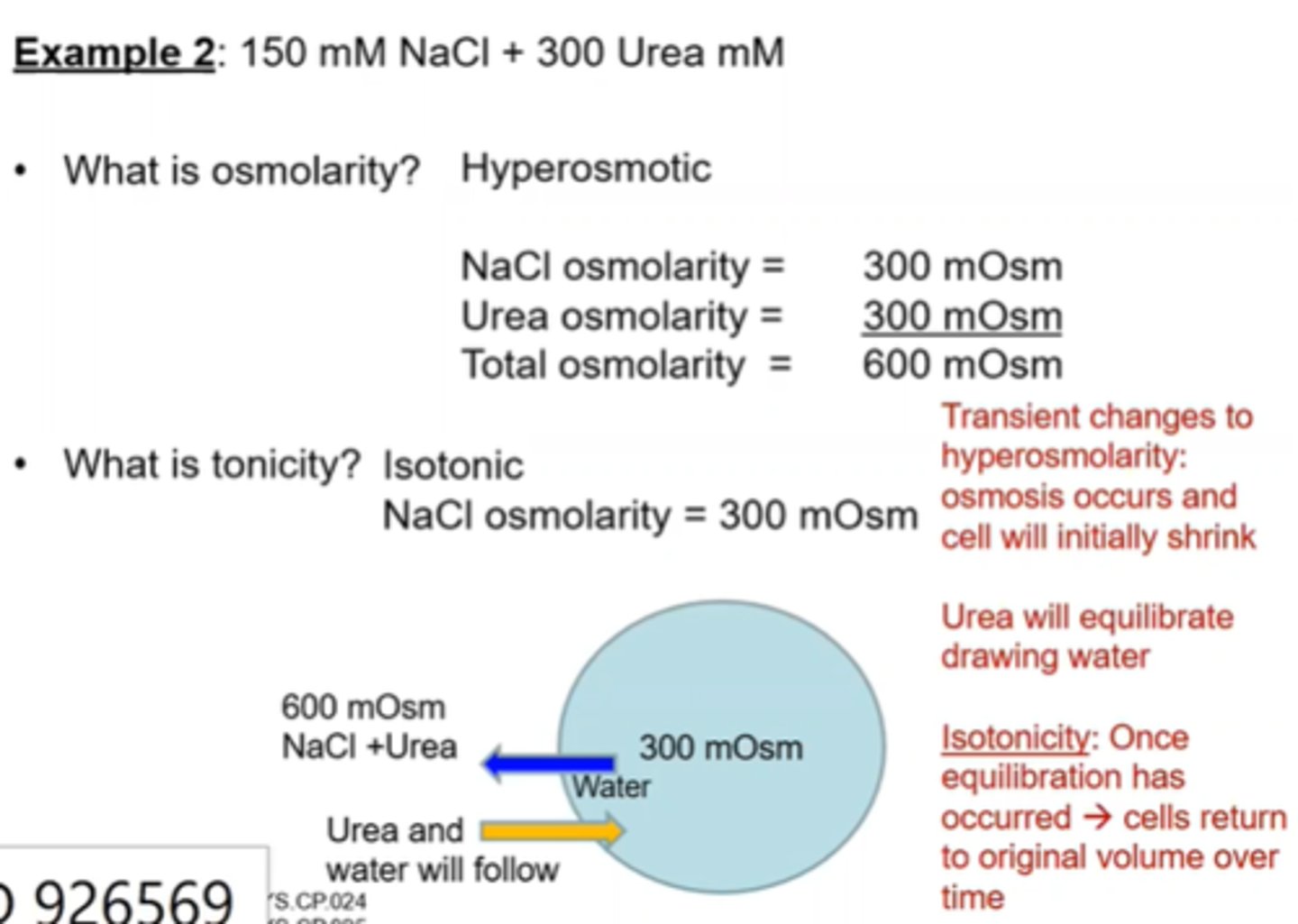
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 3
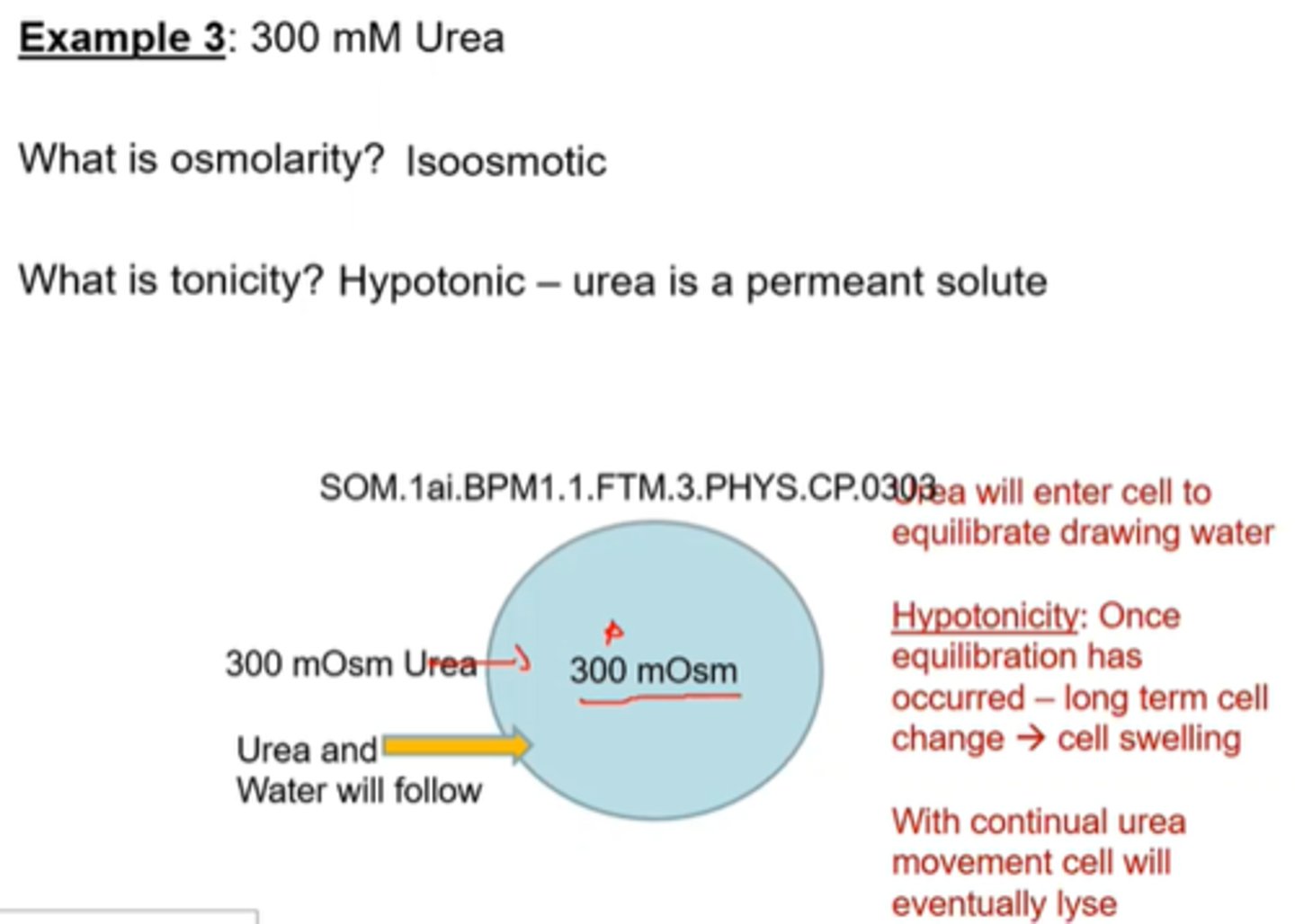
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 4

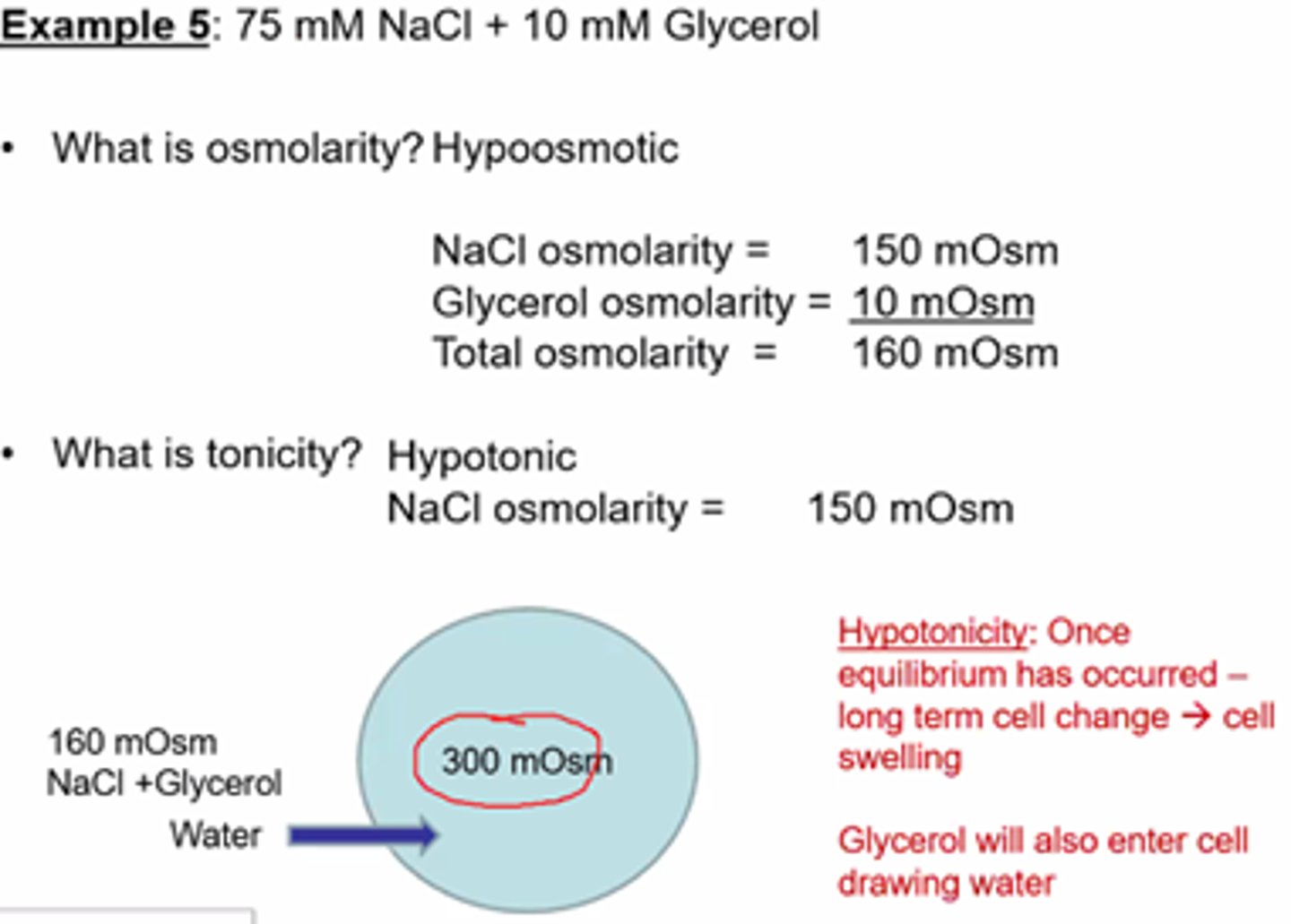
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 5
Practice Qs format example
1- Osmolarity?
2- Tonicity?
3- Direction of water flux?
4- Cell volume after equilibration
5- Does cell shrink/swell or no change?
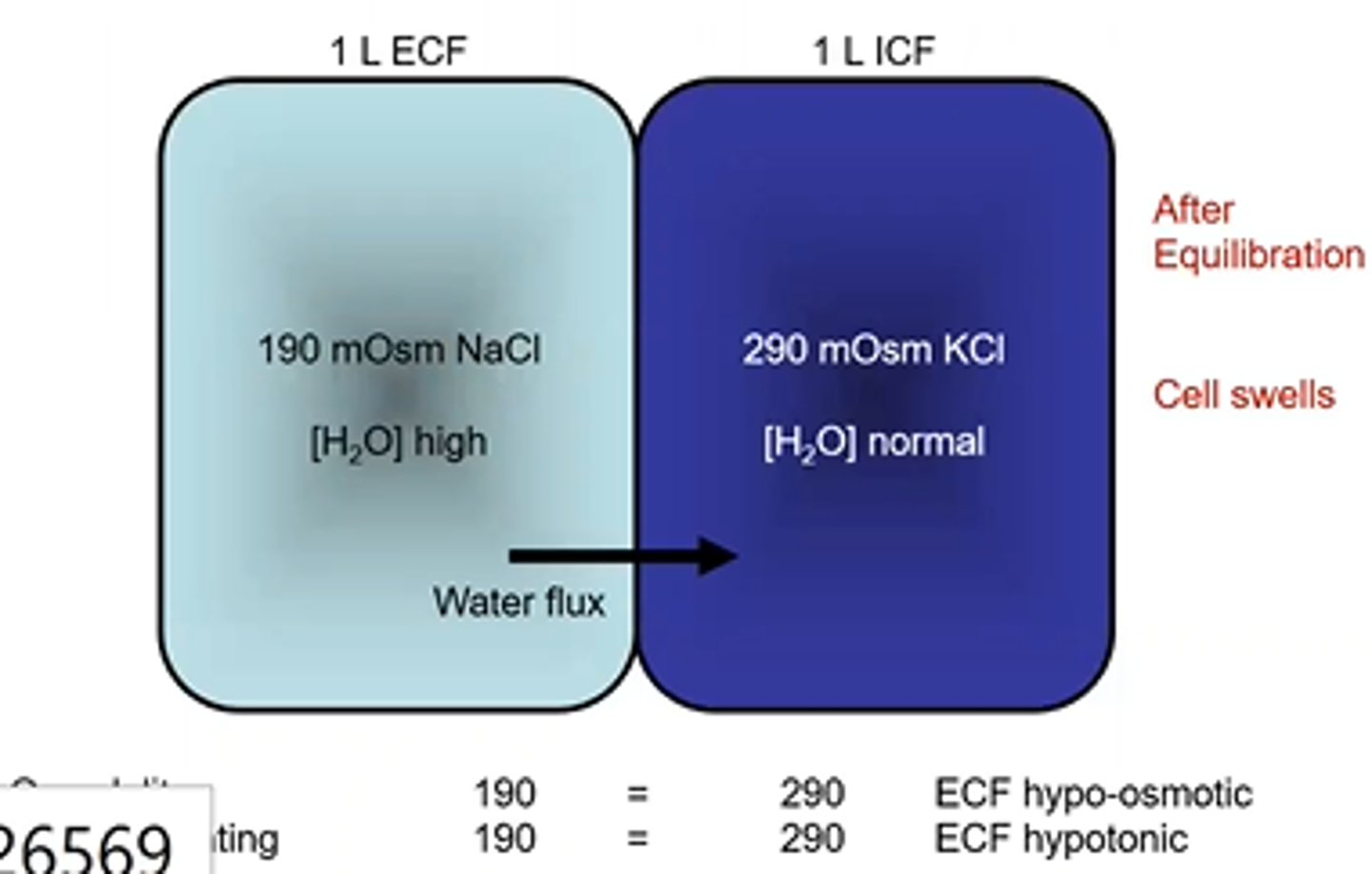
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 6
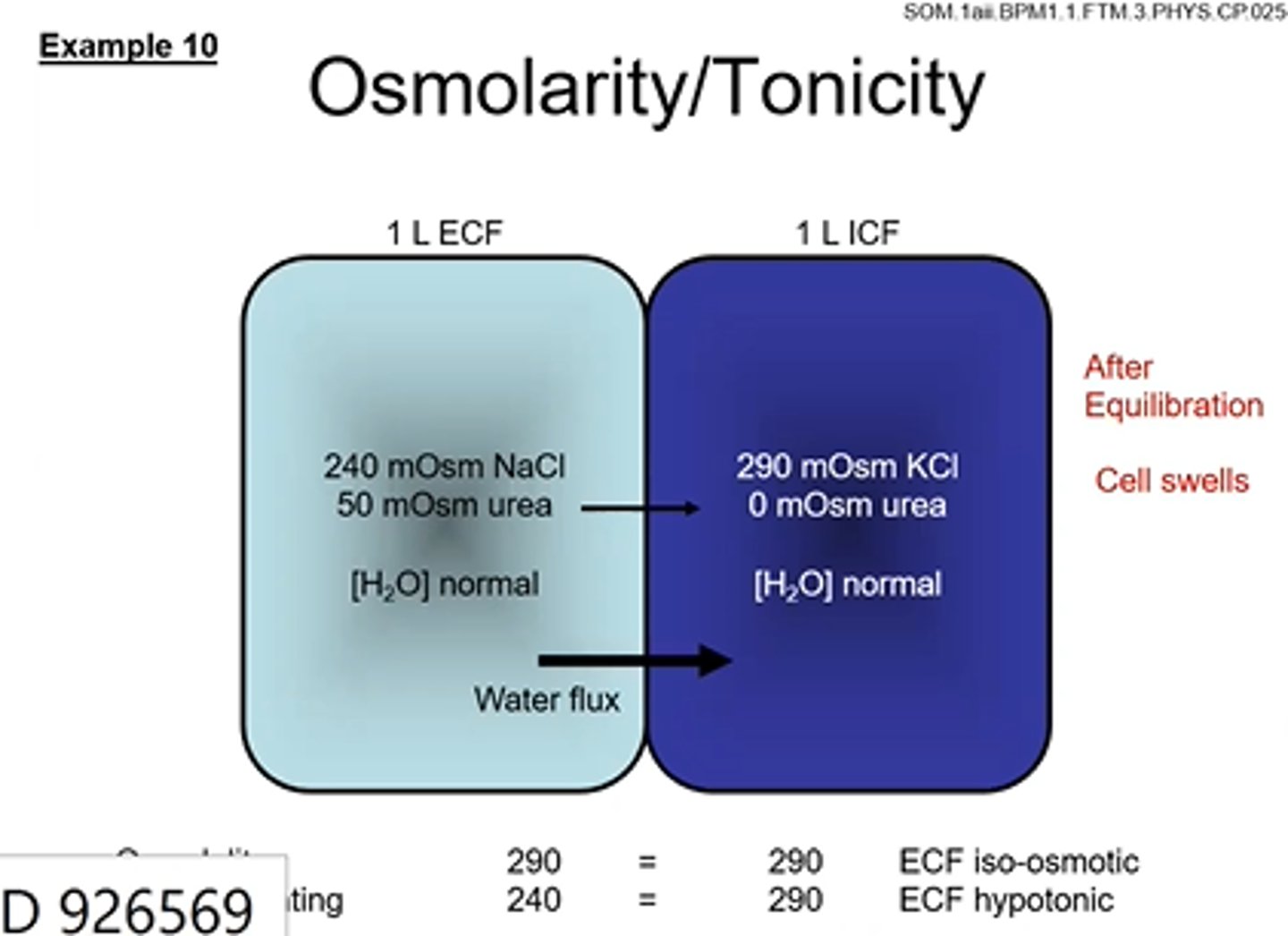
Osmolarity = 290
Tonicity = 290
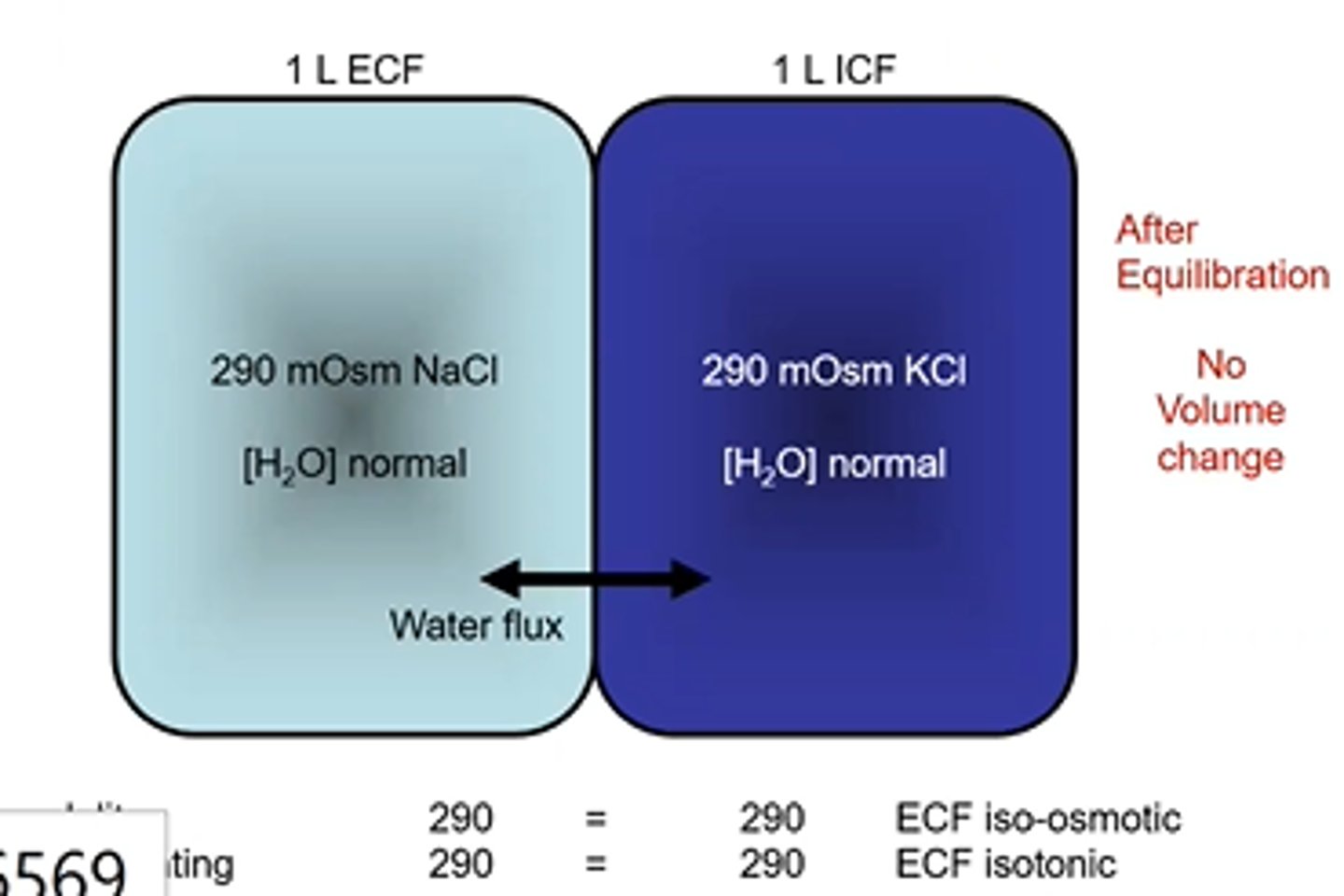
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 7
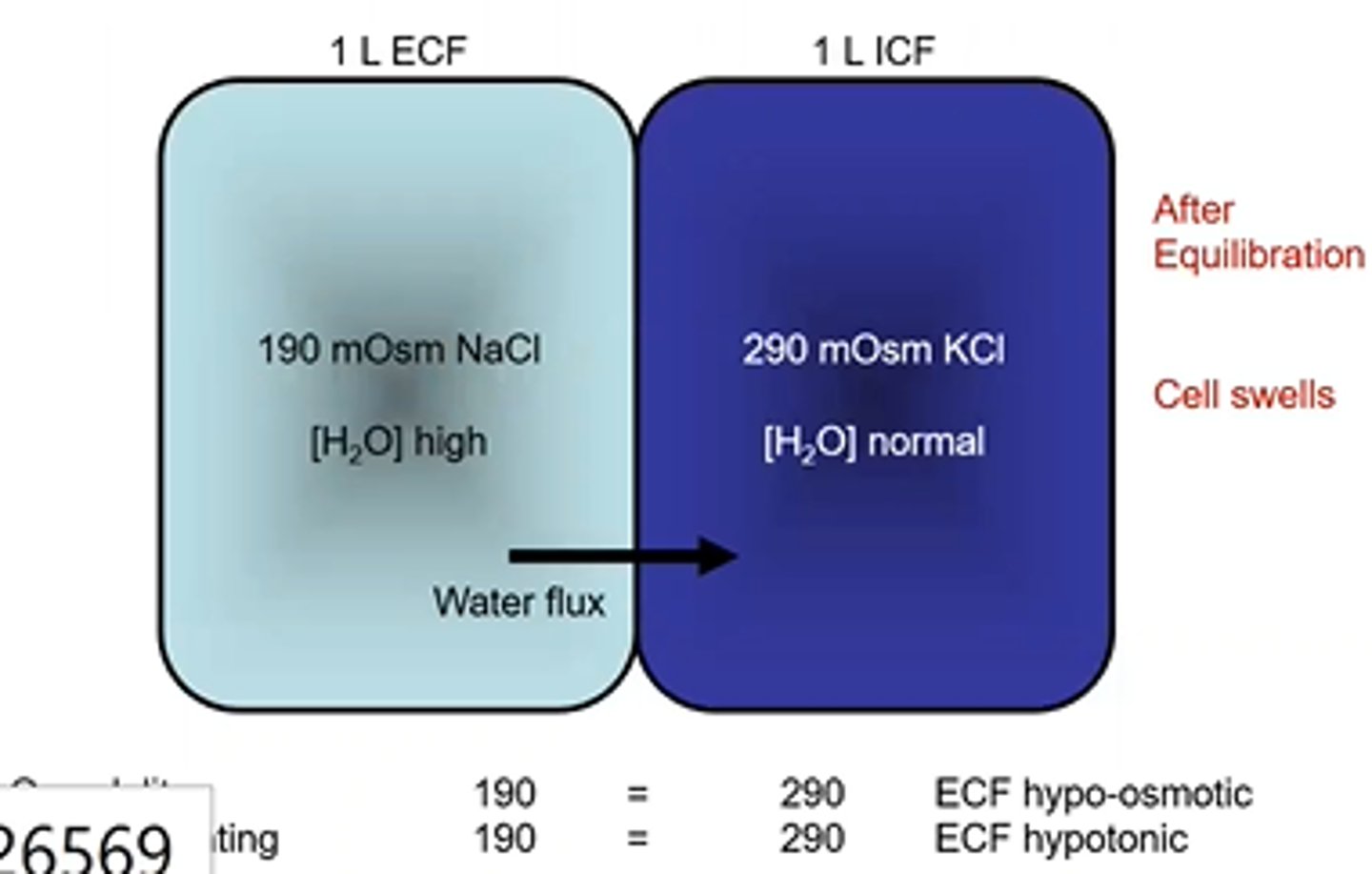
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 8
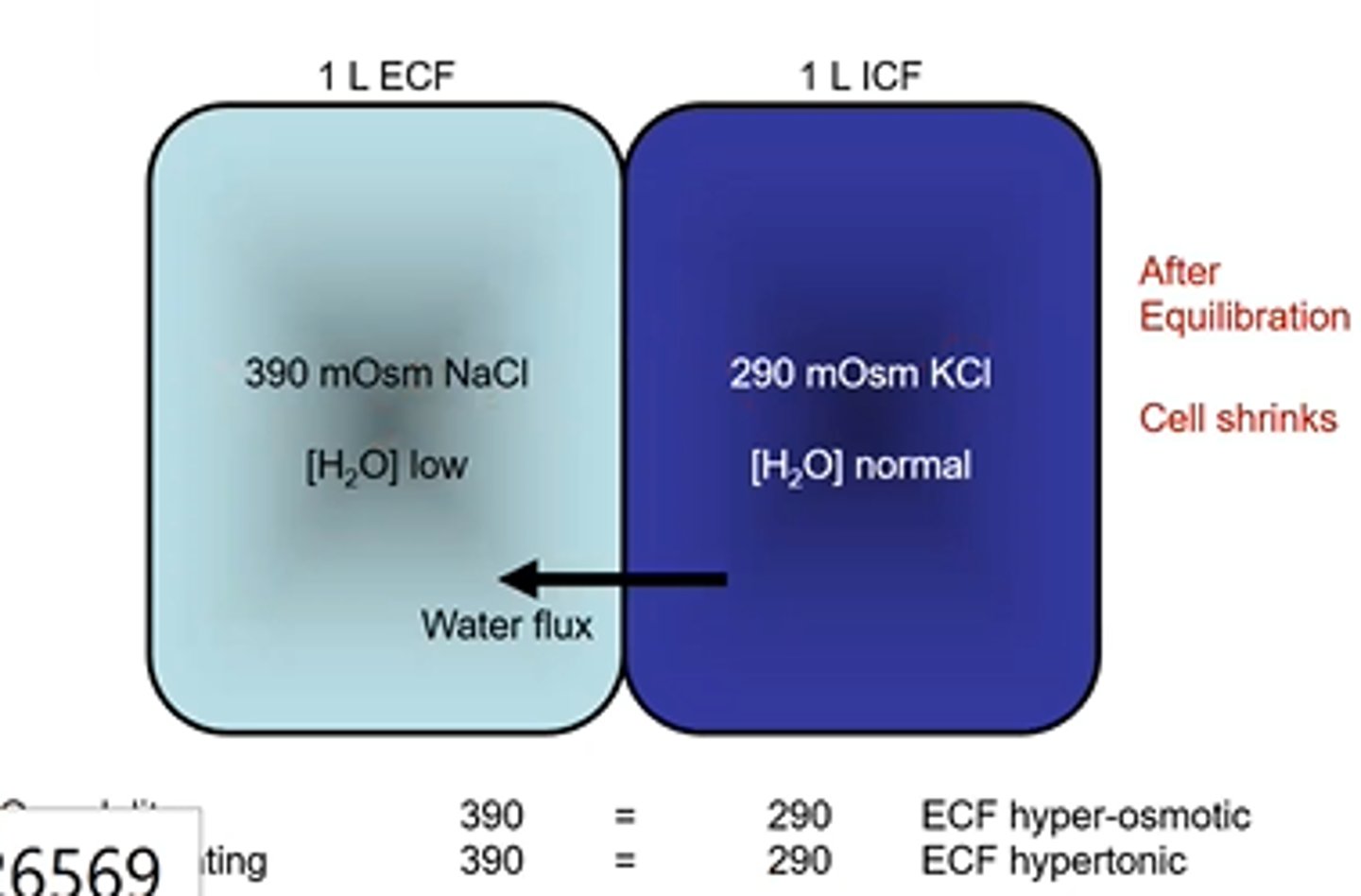
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 9
Osmolarity = 390 mOsm
Tonicity = 290 mOsm
Water flux direction: no volume change
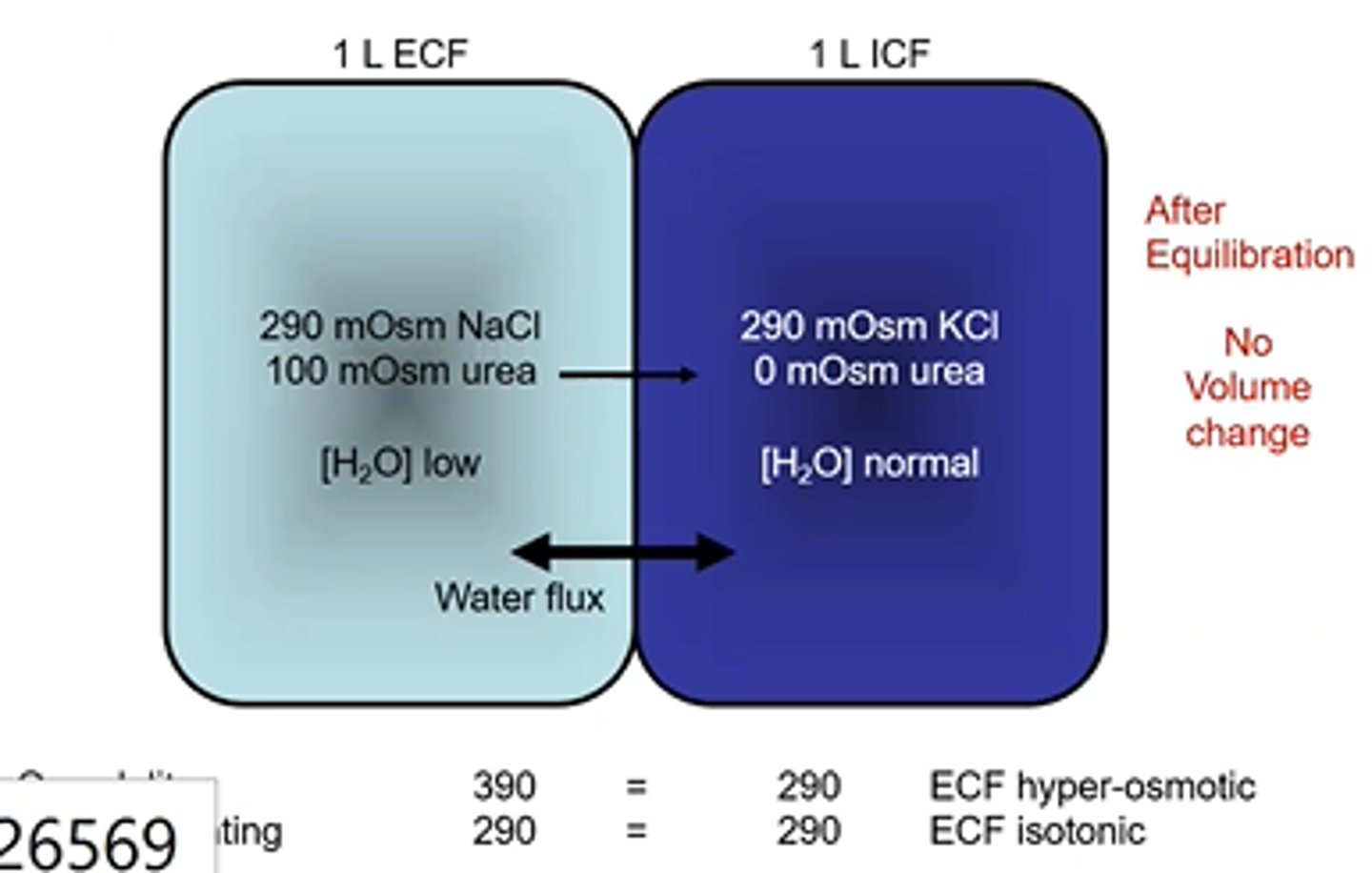
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 10
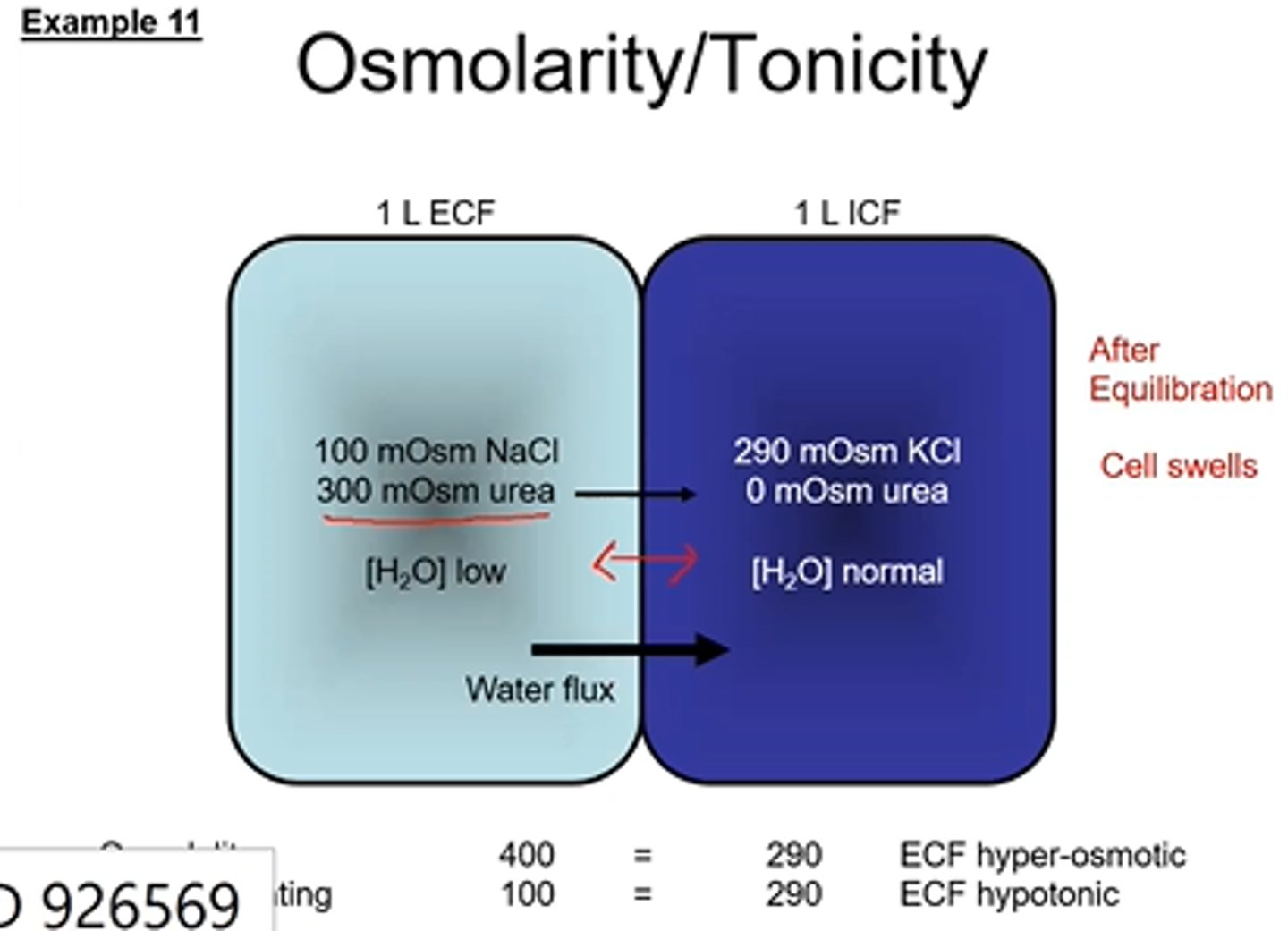
Cell Volume changes- Osmolarity and Tonicity example 11
What effects do Isotonic IV solutions have ? Hypotonic? Hypertonic?
Isotonic- No volume changes
Hypotonic- Donate water to cell
Hypertonic- Sequester water from cell
What is the tonicity of 5% Dextrose in water IV solution?
Isotonic
but physiologically hypotonic
What is the tonicity of 10% Dextrose in water IV solution?
Hypertonic
What is the tonicity of 0.45% Saline in water IV solution?
Hypotonic
What is the tonicity of 0.9% Saline in water IV solution?
Isotonic
What is the tonicity of 3% Saline in water IV solution?
Hypertonic
What is the tonicity of:
5% Dextrose in 0.225% Saline
5% Dextrose in 0.45% Saline
5% Dextrose in 0.9% Saline
Ringers solution
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypertonic
Isotonic
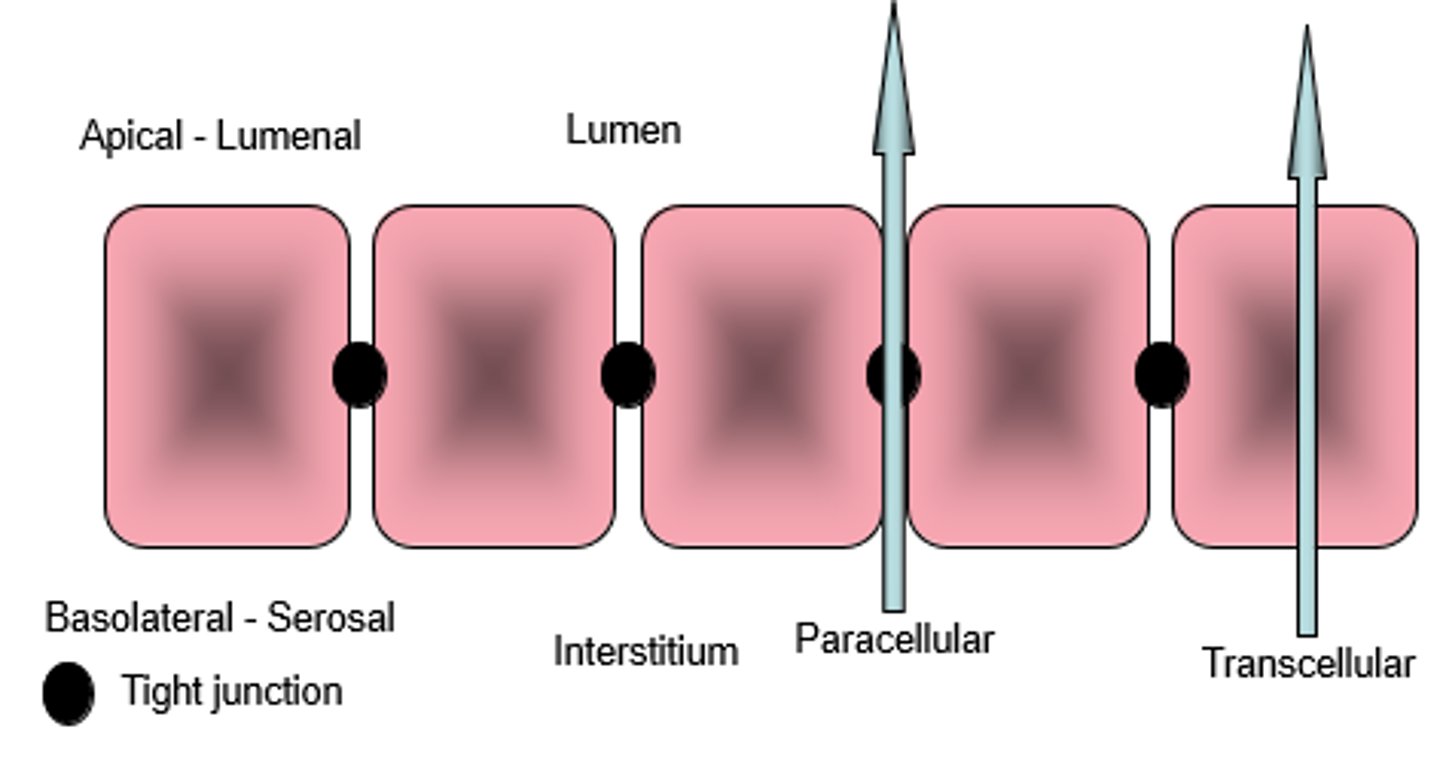
What are the 2 ways water can move across membranes from the basolateral side to apical side and vice versa?
1- Paracellular movement
- movement of water between the cells, is determied by how tight or leaky the epithelia or endothelia are
2- Transcellular movement
- movement of water across epithelial cells
Practice Q2

Ans: I
Osmolarity = 1402 + 203= 340 mOsm= hyperosmotic
Tonicity= 340 mOsm= hypertonic

Summary