ALKENES ☆*: .。. o(≧▽≦)o .。.:*☆
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
GENERAL FORMULA
CnH2n
All alkenes molecules have at least one C=C double covalent bond
this makes them unsaturated
because alkenes are unsaturated
they can make more bonds with extra atoms in addition reactions
there are 2 pairs of electrons in C=C
this gives them a high electron density meaning alkenes are pretty reactive
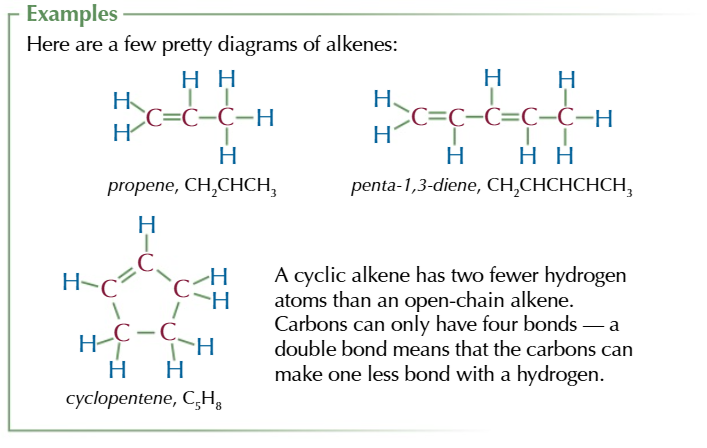
CYCLIC ALKENE GENERAL FORMULA
CnH2n-2
electrophilic addition reactions occur because of alkene high electron density
which means they can be easily attacked by electrophiles
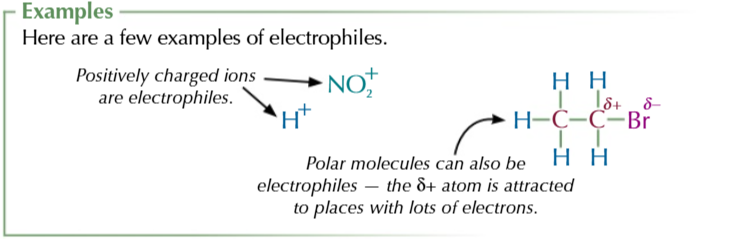
electrophiles
electron pair acceptors, normally positively charged
ethene + X-Y (electrophile) general formula
CH2CH2 + X-Y → CH2XCH2Y
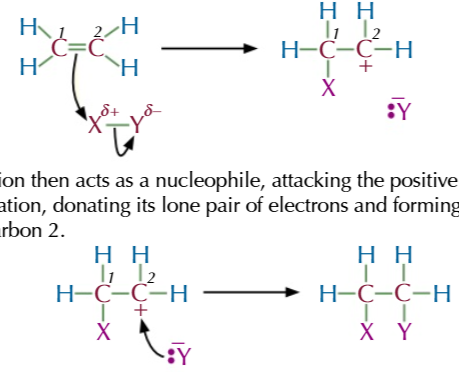
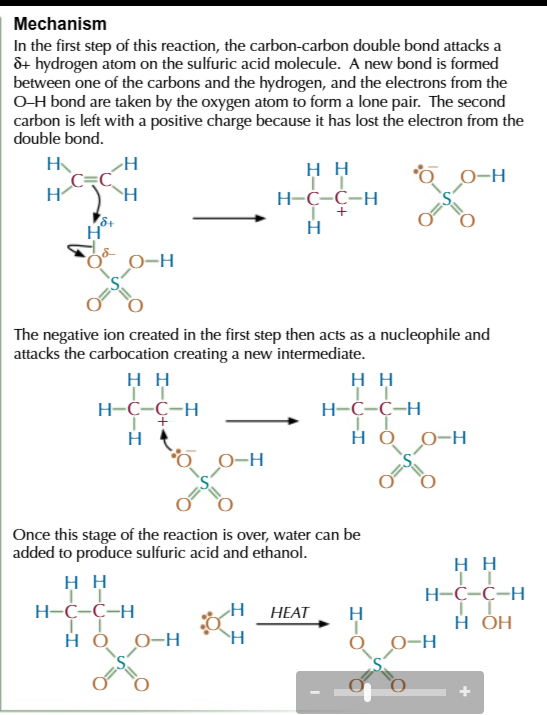
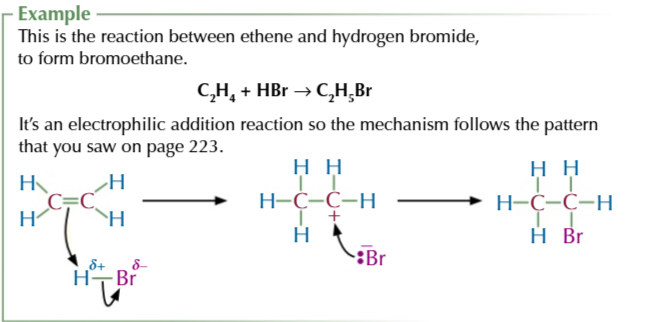
electrophilic addition steps:
bonds in an electrophile are either already polarised OR polarised by the electrons in the C=C bond
the electrons from C=C attack the δ+ atom creating a new bond between carbon 1 and the δ+ atom
this breaks the bonds between the electrophile and the electrons are taken by the δ- atom to form a negative ion with a lone pair of electrons
carbon 2 is left with a positive charge since the double bond broke and carbon 1 took the electrons to form a bond with δ+ atom
this forms an intermediate carbocation
the negative ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the positive carbon 2 to form a bond

test for unsaturation
alkene + bromine water → colour change from orange to colourless
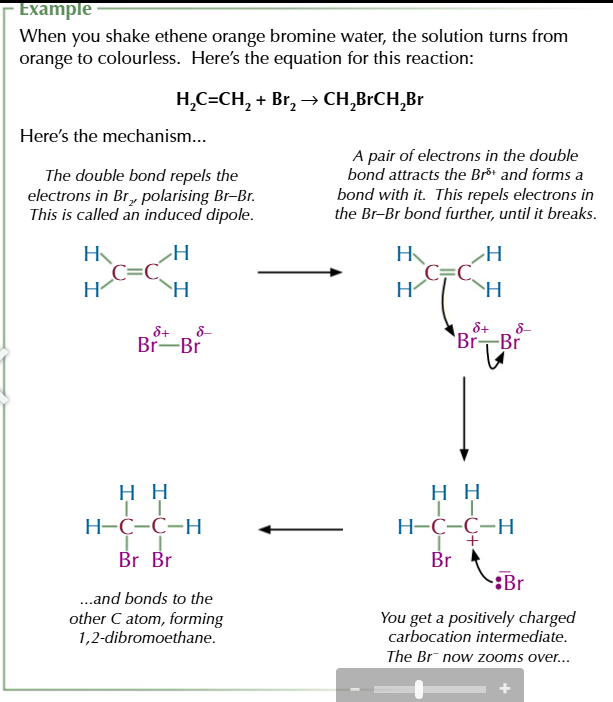
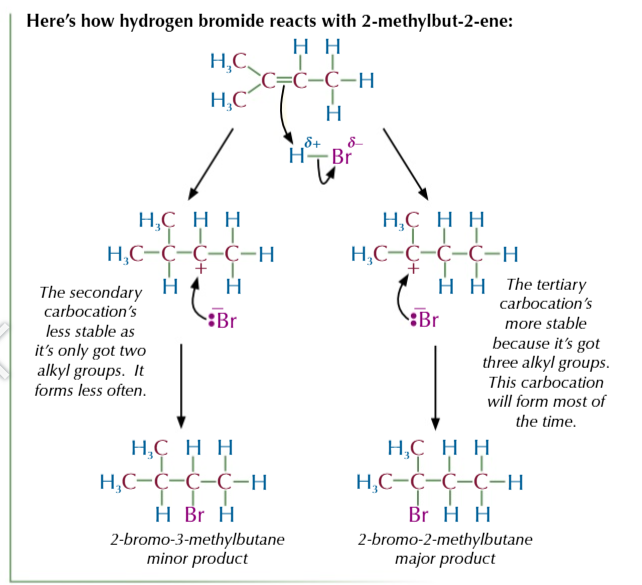
alkene + hydrogen halide (electrophilic addition) → halogenoalkane
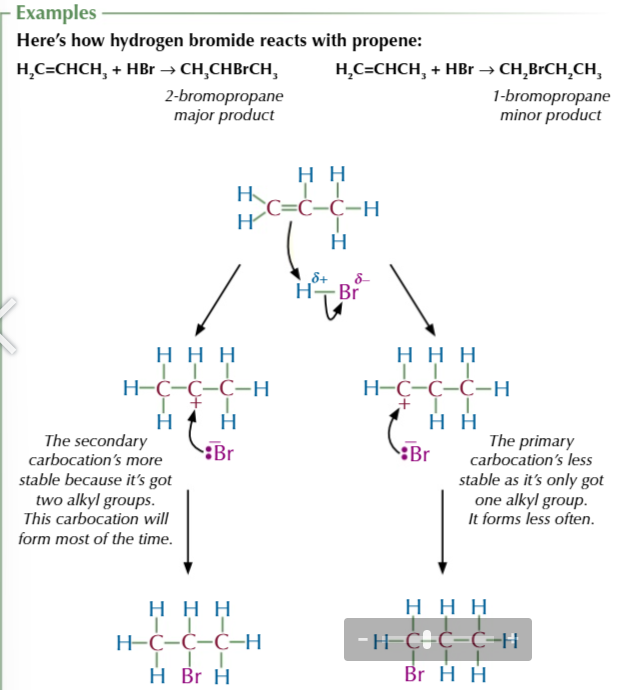
the amount of product formed depends on the stability of the carbocation
the more stable the carbocation the more product formed
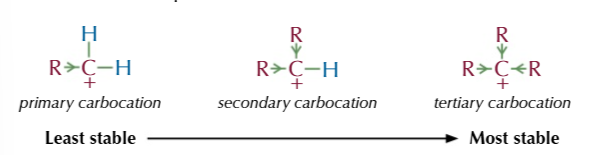
the more alkyl groups the more stable the carbocation
BECAUSE alkyl groups feed electrons towards the positive charge and
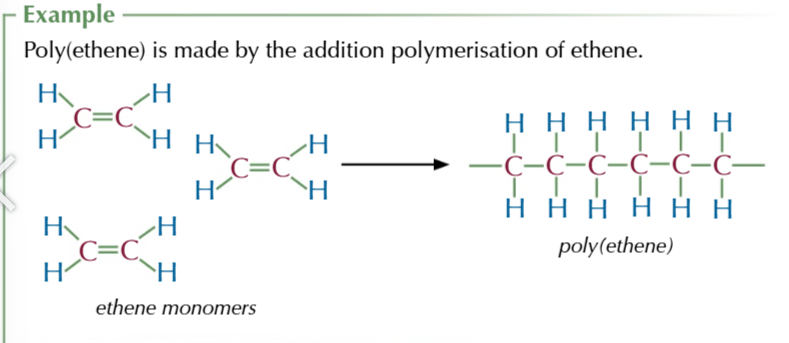
polymers
a long chain of small repeating units, monomers,
natural polymers
DNA
synthetic polymers
polyethene
addition polymers are made from
the double bonds of alkenes opening up to create a long chain
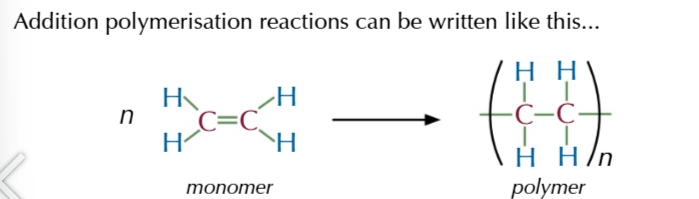
where n stands for the number of repeating units in the polymer
you can also use substituted alkenes as monomers in addition polymerisation
a substituted alkene is an alkene with a hydrogen atom replaced for something else
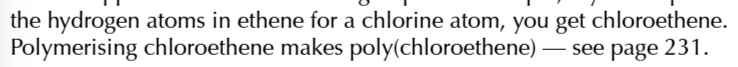
To find the monomer used to form an addition polymer
take the repeating unit and remove unnecessary side bonds and add a double bond
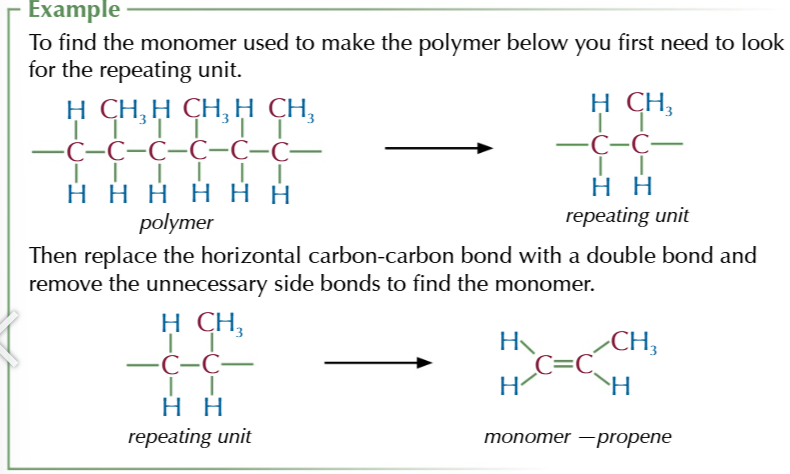
nomenclature of addition polymers
poly(X), where X is the name of the monomer
if the monomer has a number in it then you but a brackets around it
poly(but-2-ene)
if the monomer does NOT have a number then you don’t need brackets
polypropene
alkene monomers are unsaturated
but alkene addition polymers are saturated
polyalkenes are chemically inert because
monomers are unsaturated
the main carbon chain of polyalkenes is saturated
the main carbon chain of polyalkenes is non-polar
monomers within a polymer chain have strong covalent bonds
however weak intermolecular forces which affects the polymer’s properties
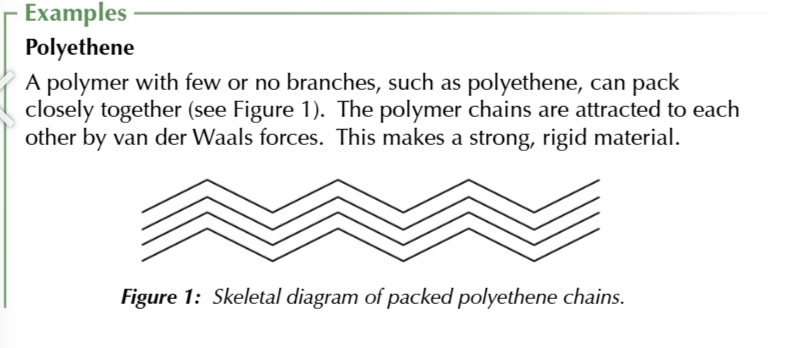
longer chains with fewer branches have stronger intermolecular forces
making these polymer materials stronger and more ridgid
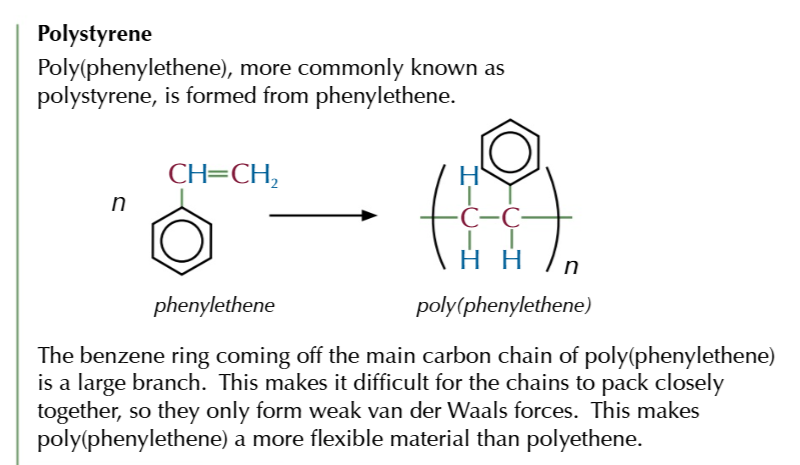
poly(chloroethene)/ polyvinyl chloride/ PVC
an addition polymer formed from chloroethene monomers
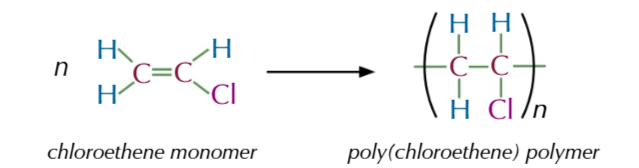
covalent bonds between the chlorine and carbon atoms are polar
because chlorine is more electronegative, creating a permanent dipole-dipole force BETWEEN polymer chains
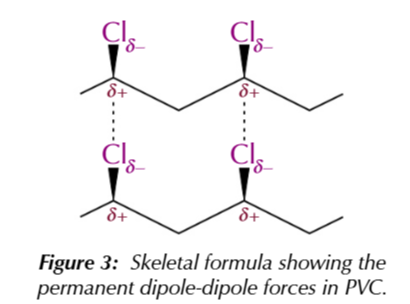
the permanent dipole-dipole force makes PVC hard but brittle material
PVC is used to make drain pipes and window frames
plasticisers
chemicals added to modify polymer properties
adding a plasticiser makes polymer chains bendier
because they get between the polymer chains and push them apart
plasticisers reduce the strength of the intermolecular forces between the chains
so they can slide around more making them flexible
plasticised PVC is more flexible so has more uses
electrical cable insulation
flooring tiles
clothing