US Imperialism
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, economically, or socially.

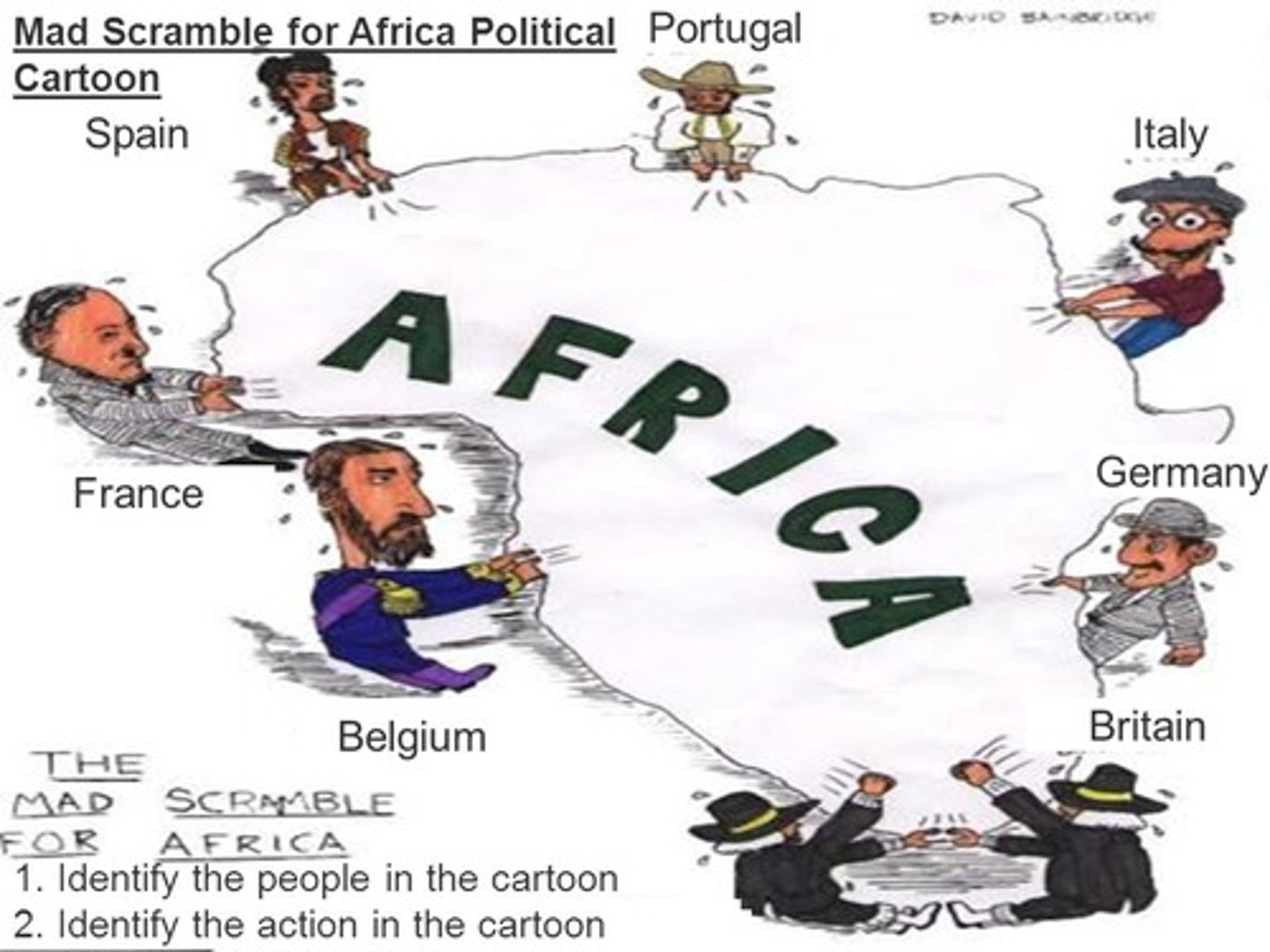
Reasons for Imperialism
-Resources
-New markets
-Strong Military
-Social/Darwinism/White Man's Burden/Cultural Superiority
Foreign Policy
A nation's overall plan for dealing with other nations

Diplomacy, Money, Free Trade
Positive Foreign policy tools

Tariffs, Sanctions, Boycott, Embargo, War
Negative foreign policy tools
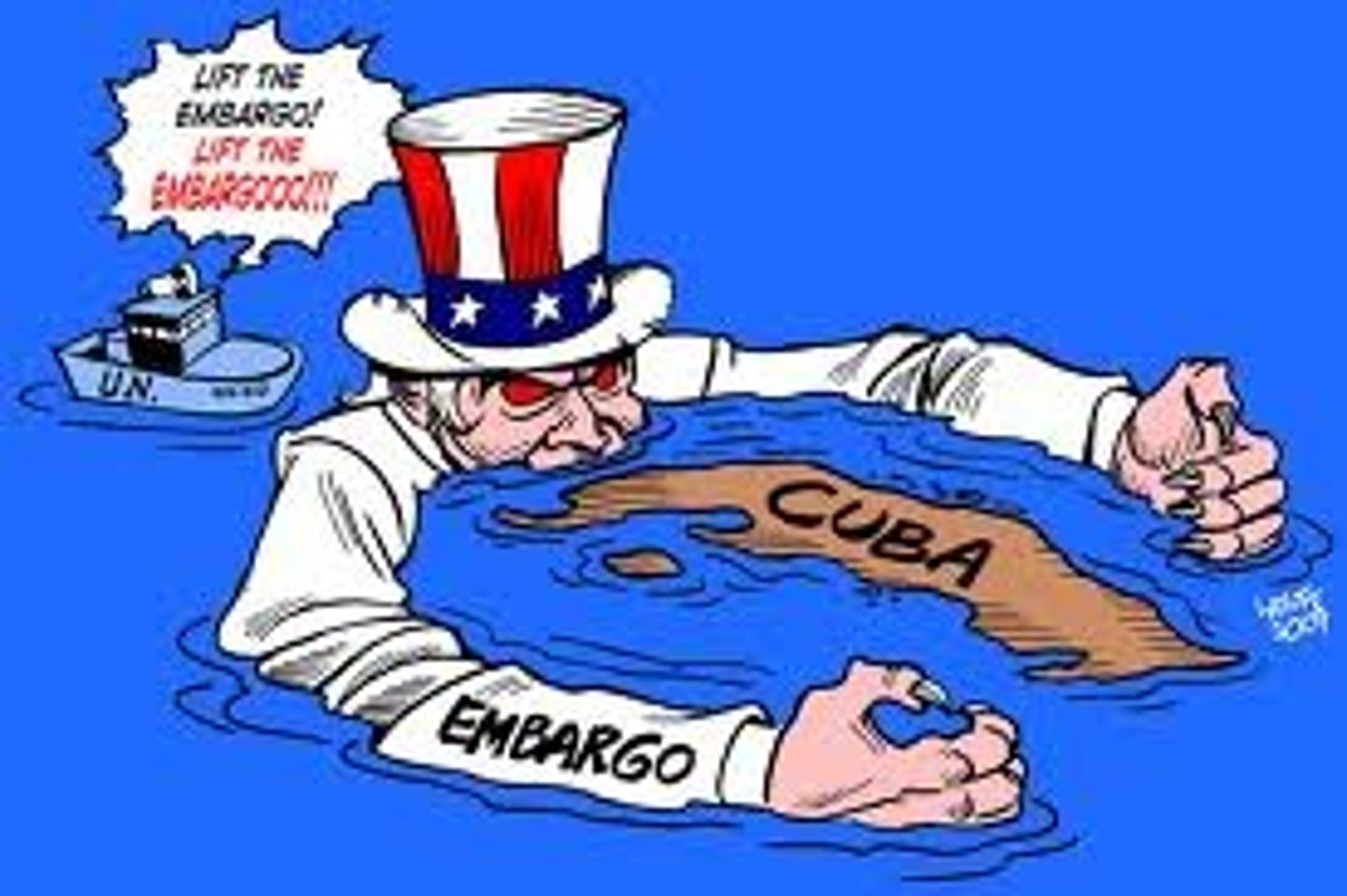

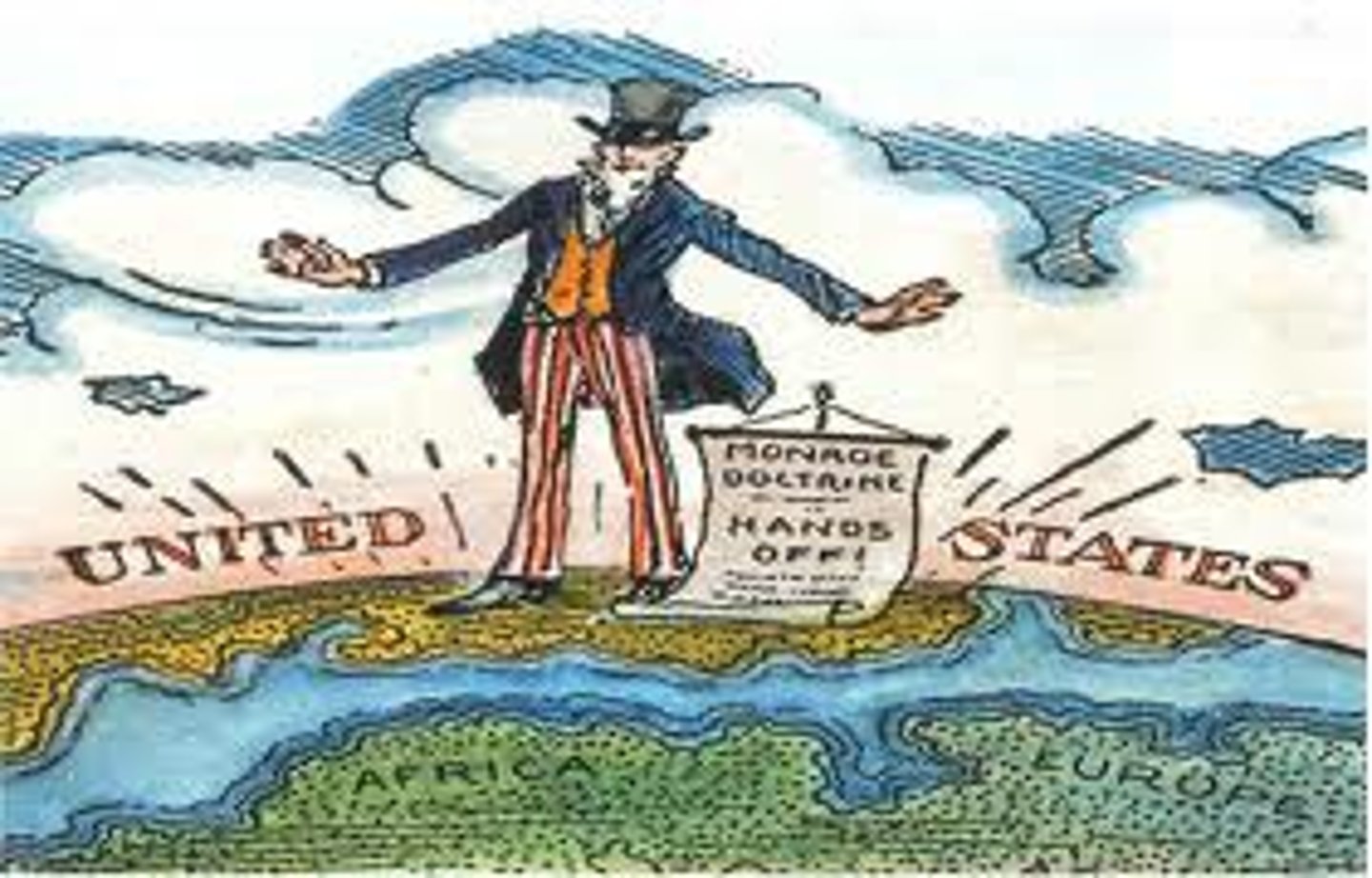
Monroe Doctrine
A statement of foreign policy which proclaimed that Europe should not interfere in affairs within the United States or in the development of other countries in the Western Hemisphere.

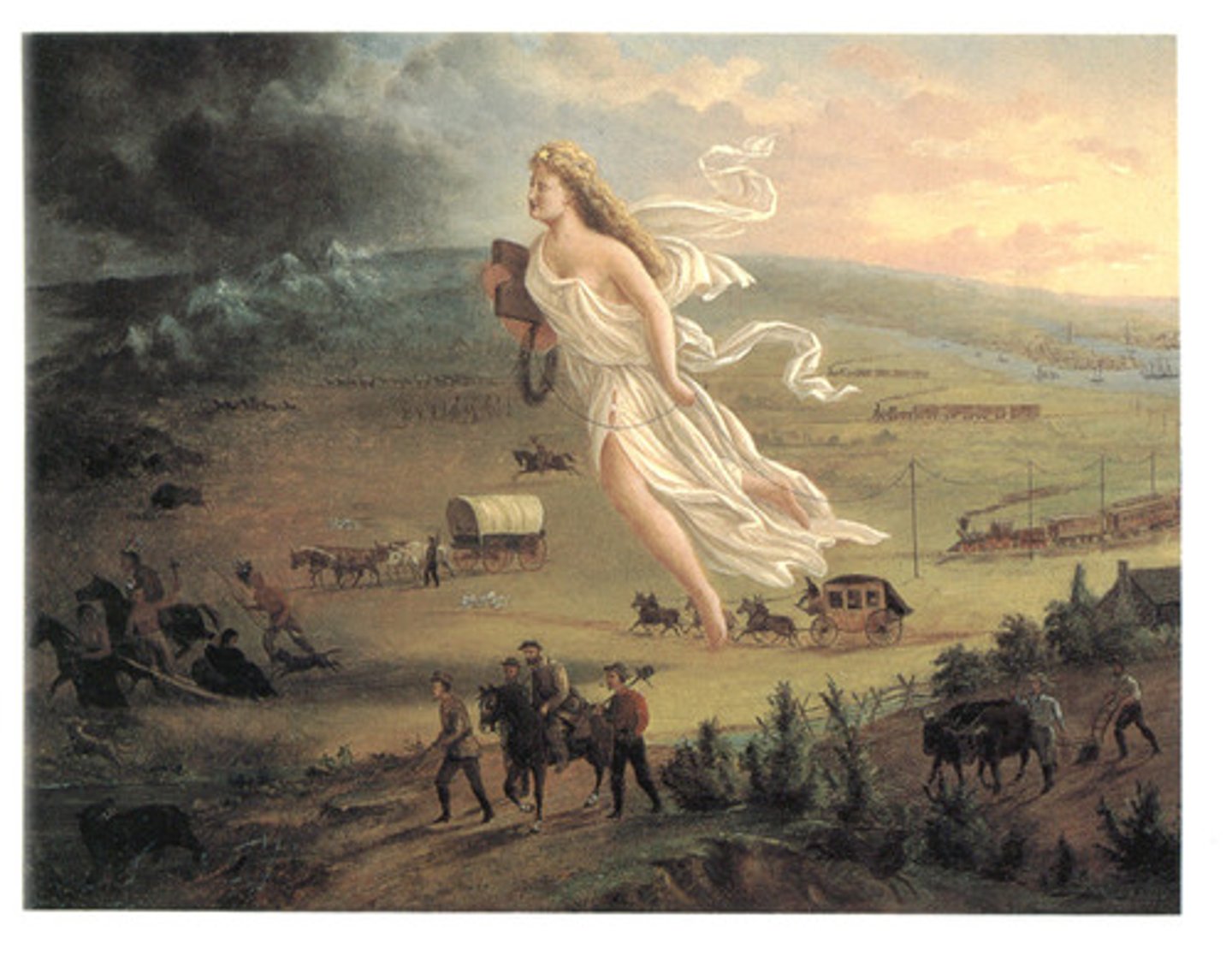
Manifest Destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.

Social Darwinism
The belief that only the fittest survive in human political and economic struggle.

Yellow Journalism
William Randolph Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer published sensational stories and used this form of journalism to promote the Spanish-American War.

Alaska Purchase (1867)
Russia sold it to Seward for $7.2 million
Many people didn't see the value in it + called it "Seward's Folly/ Icebox"
Hawaii
U.S. businessmen overthrew Queen Liliuokalani in 1893, William McKinley convinced Congress to annex these islands in 1898.

USS Maine
U.S. Battleship that exploded in Havana Harbor Cuba in 1898; Evidence suggests an internal explosion, however Spanish military was framed by Yellow Journalism; The incident was a catalyst for the Spanish American War

Roosevelt Corollary
Established the principle that the United States has the right to act as the "policeman of the Western Hemisphere" and intervene in the internal affairs of Latin American nations.

Big Stick
Roosevelt's philosophy - In international affairs, ask first but bring along a big army to help convince them. Threaten to use force, act as international policemen

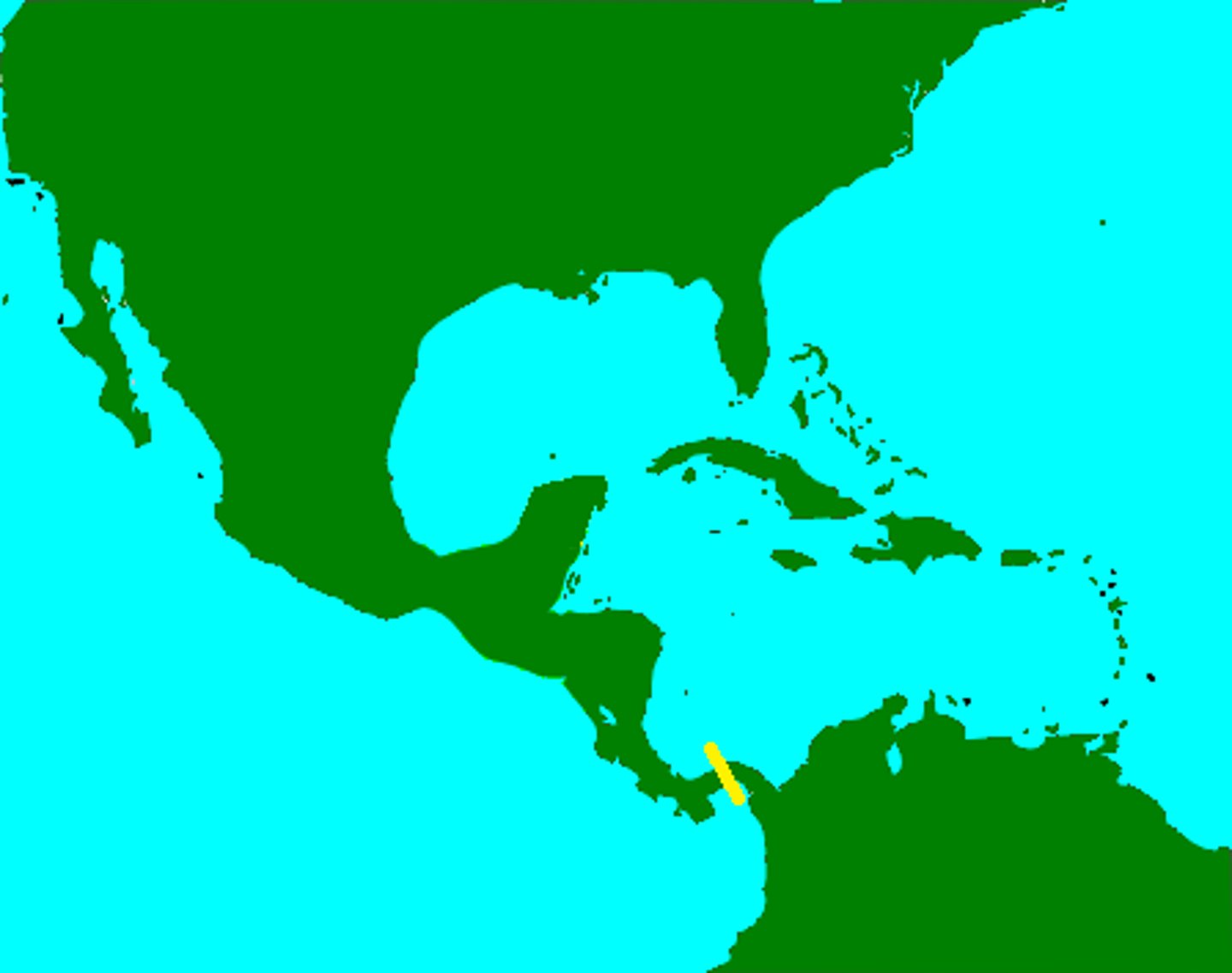
Panama
Country the U.S. essentially created since Colombia wanted too much money for the area where the canal was being built.

Panama Canal
A canal that crosses the isthmus of Panama connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Built by the United States between 1904 and 1914.
Open Door Policy
Statement of U.S. foreign policy toward China. Issued by U.S. secretary of state John Hay (1899), the statement reaffirmed the principle that all countries should have equal access to any Chinese port open to trade.
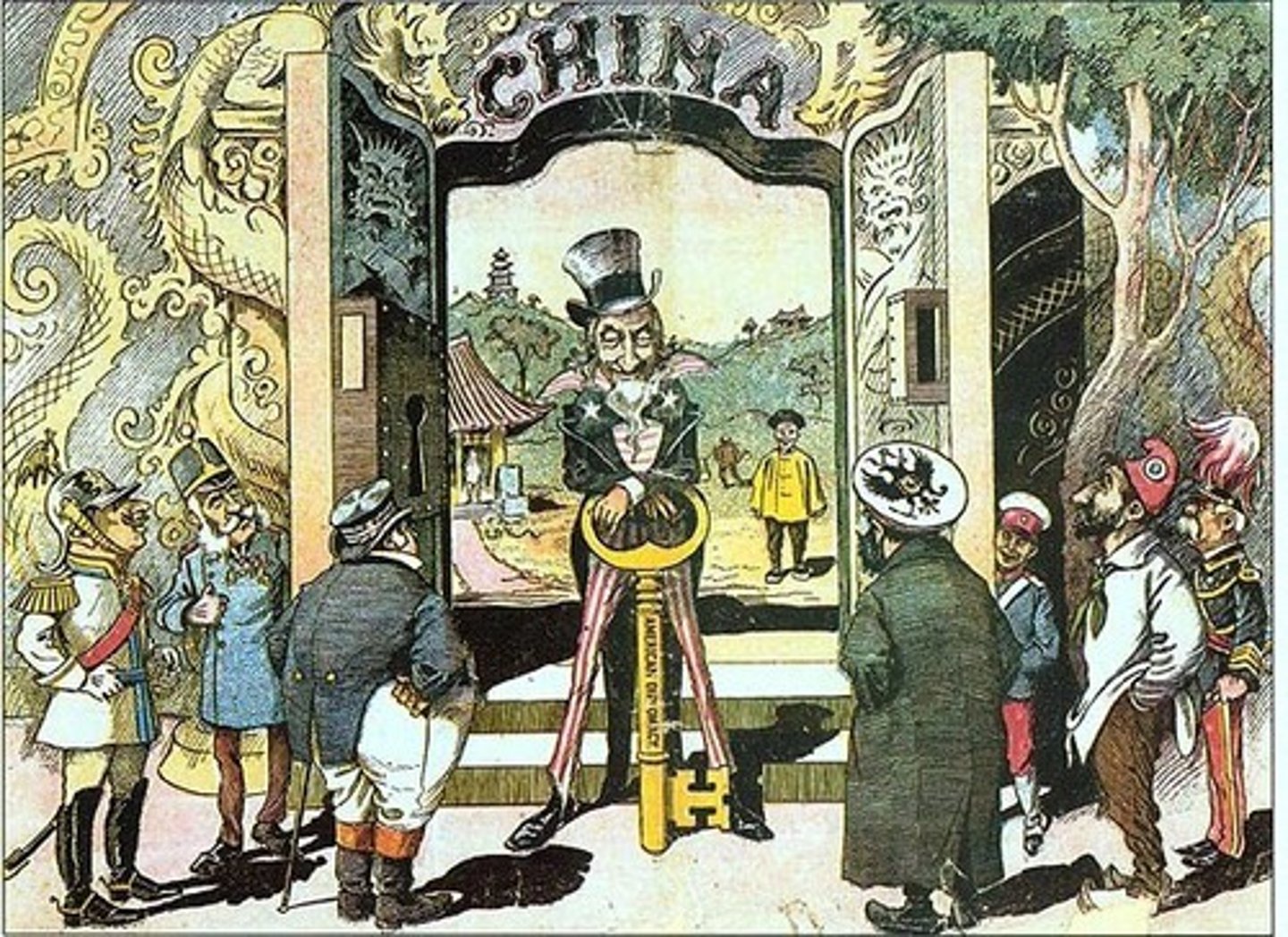

China
The reason we wanted in China was to sell goods to their many people.

Boxer Rebellion
Secret Chinese group that led an uprising against foreign intervention in 1900.

Dollar Diplomacy
William H. Taft's foreign policy of using economic means to influence other countries.

Anti-imperialists
Anti-American, undemocratic; hypocritical (We fought a revolutionary war to break away from "mother" country b/c we did not like being ruled... now we are doing the same); Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, Samuel Gompers (AFL), Speaker of the House, Thomas Reed (resigns in protest).

Racism
Prejudice based on the color of one's skin. During Imperialism, the idea that the inferior indigenous people needed saving.
White Man's Burden
The duty of white people to bring civilization to the less industrialized countries and people.
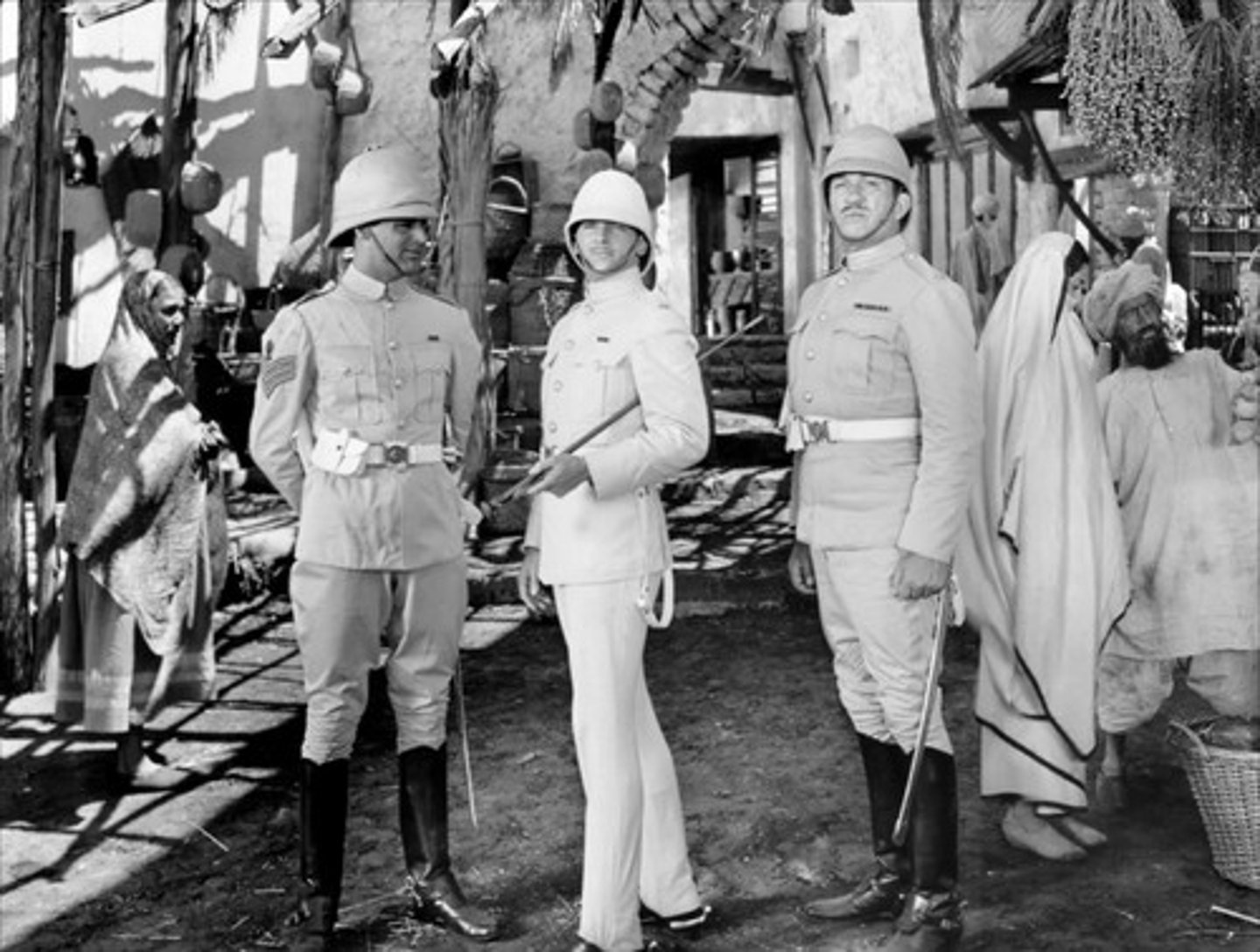

Philippines
The United States established control over the Philippines following the Spanish-American War, leading to a controversial period of colonial governance and uprising against American rule.

Venezuela
Current country in South America U.S. foreign policy interests include economic and political involvement, particularly in oil production and regional stability.
