Biology Year 10
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
249 Terms
Cells structures and Organelles
What are cells?
The building blocks of life
How does each cell know what to do?
DNA tells the cells what proteins to make
Characteristics of cells
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
DNA
Genetic material
Ribosomes
Synthesize proteins
Prokaryotes
No nucleus
No organelles
single cell
DNA
cell
membrane
Eukaryotes
Nucleus
Multicellular
Organelles
DNA
Cell
membrane
Organelles in animal cells———
Cell membrane
• – Selectively controls what enters and leaves the cell; provides protection and support.
Golgi apparatus
Packages proteins transport inside and outside the cell.
Centrosome
Essential for proper cell division.
Vacuole
• Stores water, nutrients, and waste products
Mitochondrion
Generates energy (ATP) through cellular respiration
Nucleus
Stores genetic material (DNA) and controls all cell activities
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Synthesizes lipids
Lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes to break down waste materials
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like fluid that fills the cell.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Covered in ribosomes; synthesizes and transports proteins.
Ribosome
Builds proteins from amino acids
Nucleolus
Produces ribosomes inside the nucleus.
Nuclear membrane
Surrounds the nucleus, controlling movement of molecules in and out.
What is DNA
•Molecule that contains genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism
DNA structure
The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T)
The sequence of the bases along the backbones
serves as instructions for assembling protein and RNA molecules
DNA sequences control
protein production
Mutations
Occur in base sequence and can alter cell function
Genetic Information
• DNA stores instructions for growth, development, functioning, and reproduction.
Protein Synthesis
• DNA codes for proteins via transcription and translation.
Heredity
DNA passes traits from parents to offspring.
Cell Regulation
DNA controls cell activities by regulating gene expression.
Mutation & Evolution
DNA mutations create variation, driving evolution
Cell division
•For an organism to grow, repair and reproduce the cells that make up the organism have to increase in number




How does DNA replicate


DNA replication
DNA unwinds
Base pairing- DNA polymerase adds new complementary nucleotides
Joining-DNA ligase helps seal DNA fragments to form one long strand
DNA — Genes — chromosomes
How can DNA replicate
•For DNA to be easily replicated or undergo transcription, the DNA needs to be stored inside the nucleus in an organised way


Chromosomes

Genes

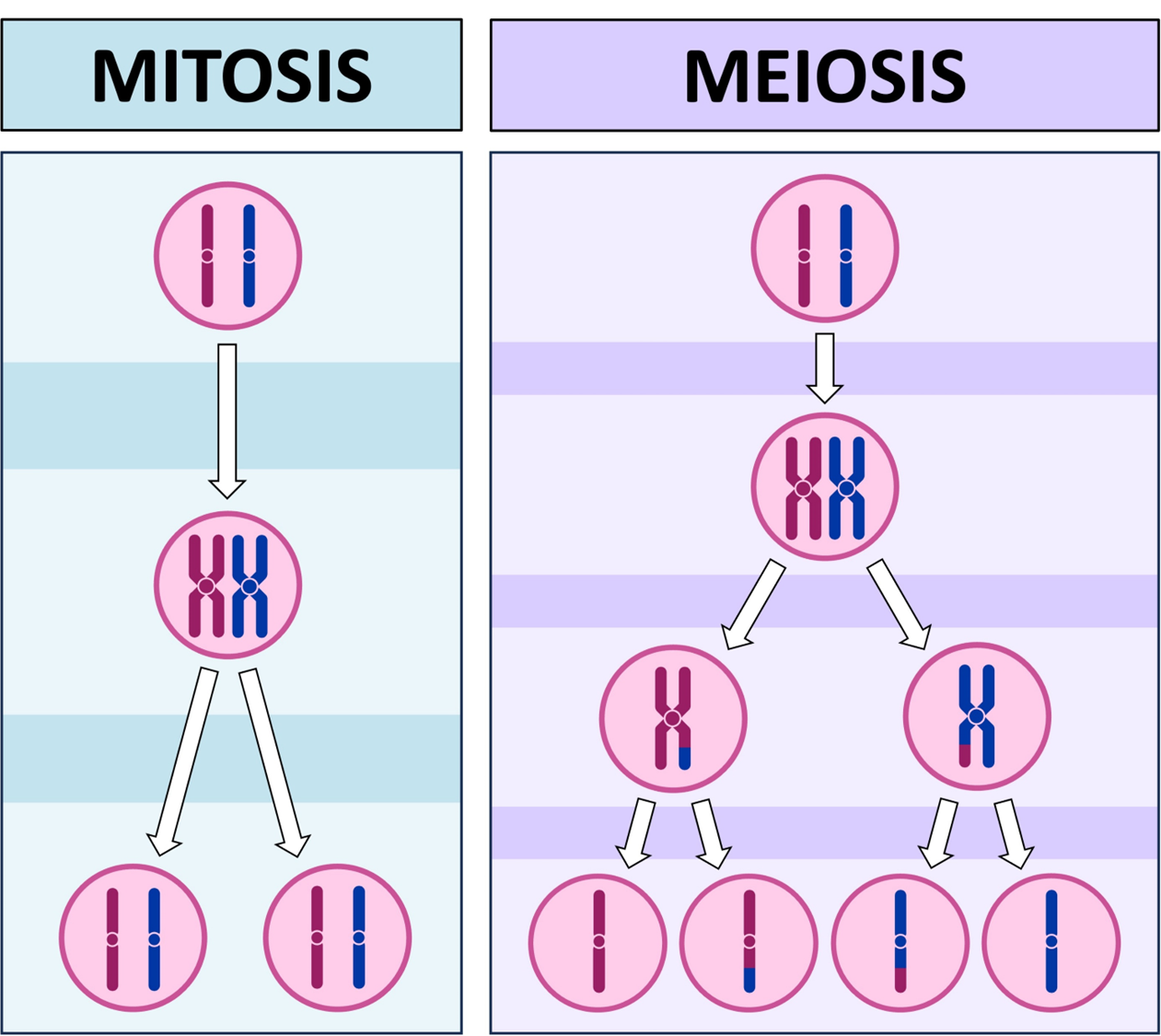
Mitosis

Importance of Mitosis

Somatic Cells
•Body cells that contain the normal number of chromosomes
Skin cells, brain cells, bone cells etc.
Chromosome number: contain two copies of each chromosome
Gametes
Chromosome number: contain one copy of each chromosome

Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the joining of a sperm and ovum (egg cell) it results in the formation of a zygote (fertilised egg)
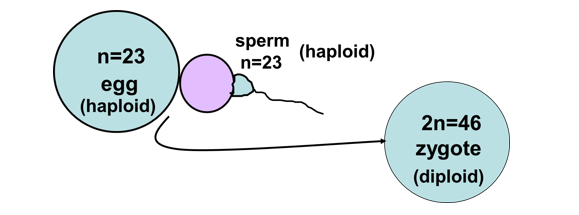
Meiosis

Meiosis vs Mitosis
Prokaryotes
Before nucleus (bacteria)
Eukaryotes
true nucleus (animal and plant cells)
ribose
sugar
nucleic
nucleotides (buildings)
Phosphate backbone
What determines genetic traits
the sequences of bases
Gene
makes protein that builds the wall in a mitochondria
Cell division
for an organism to grow, repair and reproduce, each cell copies itself
Why is process of replication important?
Mitosis steps
Interphase- DNA duplication before mitosis (genetic material is being duplicated)
Prophase- before (getting ready to make the split) 1 allele for brown hair one for blonde
Metaphase- the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell (pulled in by centrioles and the spindle fibres are like ropes)
Anaphase- chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cells (spindles help move chromosomes to the two ends)
Telophase- Chromosomes are at the complete opposite ends, so two nuclei (each side 46 chromosomes)
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis (separates the cell into two creating two identical daughter cells) organelles of the cell have also been seperated (mitochondria)
Condensed DNA creates
Chromosomes, which are made of proteins and DNA
Chromosomes are kept together by
centromeres
Meiosis
Prophase 1: Crossing over (they transfer genetic information)
Metaphase 1: Middle, the chromosomes will line up in the middle of the cell in pairs
Anaphase 1: pulled away by spindle fibres
Telophase: Two cells
Prophase 2:
Metaphase 2: they are in single line
Anaphase 2: away
Telophase 2: split the cytoplasm
Relationship between DNA, Chromosomes and Genes
DNA is the molecule that carries genetic information. it coils around proteins to form chromosomes Genes are sections of DNA on chromosomes that code for specific traits.
DNA
Double Stranded
Bases A, T, C, G
Sugar: Deoxyribose
Function: stores genetic information
Location: DNA
RNA
Single stranded
Bases: A, U, C, G
Sugare: RIbose
Function: carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis
Locations: nucleus and cytoplasm
Asexual Reproduction

Crossing Over

Random Fusion of gametes

Maternal Allels come from…
mothers egg
Paternal Allelel
Fathers Sperm
Maternal and Paternal Allele
come together during fertilisation to form offspring genotype
Karyotypes

Homologous Chromosomes

Allele
Different forms of the same gene
Genotype
the combination of alleles that a person has in their DNA
Phenotype
the physical expression of a genotype
Homozygous
Having identical alleles for a gene
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a gene
Hemizygous
Having only one allele for a gene instead of wo (e.g. males in X-linked genes)
4 types of bases

how many chromosomes found in each autosomal (body) human cell

Natural Selection

Spontaneous mutations

Gene FLow

Covergent evolution

Reproductive isolation can occur through…

Geographical isolation

Vestigial structures

Comparative DNA sequencing
Asexual
Mitosis
sexual
Meiosis (different from parent, think about mice and their colours)
Types of Asexual reproduction
+Budding- bud and parent are IDENTICAL
+Binary fission- •Cell divides into two identical daughter cells
•Unicellular organisms (bacteria, protists
+Vegetative propagation- taking a part of a plant makes a new plant
+Fragmentation- •Single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.
•Flatworms
Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual reproduction
QUICK AND ENERGY EFFICENT AND large amounts of offsping produced DISADVANTAGES LIMITED VARIATION MEANING POPULATION IS VULNERABLE TO CHANGES IN THE ENVIRONMENT OR TO DISEASE (DON’T HAVE THE GENE THAT WILL HELP THEM SURVIVE)
Offspring is the result of sexual reproduction
Gametes and Meiosis
Sexual reproduction pros and cons
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION PRO: VARIATION AND ADAPTATION
CONS: TAKES TIME (INTENSIVE) AND ENERGY
+NEED TO FIND A MATE
Asexual

sexual
