Fuels + Heats of Reactions - Chp 21
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Organic chemistry
is the study of the compounds of carbon
Hydrocarbon
is a compound that contains carbon and hydrogen only
Fossil fuels
fuels that were formed from the remains of plants and animals that lives millions of years agp
Saturated compound
is one in which there are only single bonds between the carbon atoms in the molecule
What are the prefixes for a carbon chain length from 1-10?
meth- 1 carbon
eth- 2 carbons
prop - 3 carbons
but- 4 carbons
pent - 5 carbons
hex- 6 carbons
hept- 7 carbons
oct- 8 carbons
non- 9 carbons
dec- 10 carbons
What is the suffix for the Alkane family?
-ane
What is the suffix for the Alkene family?
-ene
What is the suffix for the Alkyne family?
-yne
What is the suffix for the Alcohol family?
-anol
What is the functional group for the Alkane family?

What is the functional group for the Alkene family?
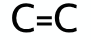
What is the functional group for the Alkyne family?
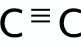
What is the functional group for the Alcohol family?

What is the general term of the Alkane family?
CnH2n+2
What is the general term of the Alkene family?
CnH2n
What is the general term of the Alkyne family?
CnH2n-2
What is an Alkyl group?
A type of side chain consisting of an alkane from which a hydrogen atom is removed: methyl CH3, ethyl C2H5 and propyl C3H7
What is paraffin oil?
paraffin oil is another name for kerosene, which is a commonly used fuel for central heating
paraffin is the old name for alkanes, meaning that they have little reactivity
paraffin oil consists mainly of alkanes, hence its name
Write an equation for the combustion of alkanes in excess oxygen:
alkane + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat
Homologous series
is defined as:
- a series of compounds of similar chemical properties
- showing gradations in physical properties
- having a general formula for its members
- each member having a similar method of preparation
- each member differing from the previous member by a (CH₂) unit
Explain the gradation of physical properties of the Alkanes and Alkenes
the first few 3-4 are gases, the next 11-12 are liquids and the rest are waxy solids
as the molecules increase in size, the Van der Waal’s forces between them also increase, due to the greater number of electrons in the electron clouds
therefore the bigger the molecule, the stronger the intermolecular forces between them, creating a more solid compound
Draw and name the 3 structural isomers of butene:
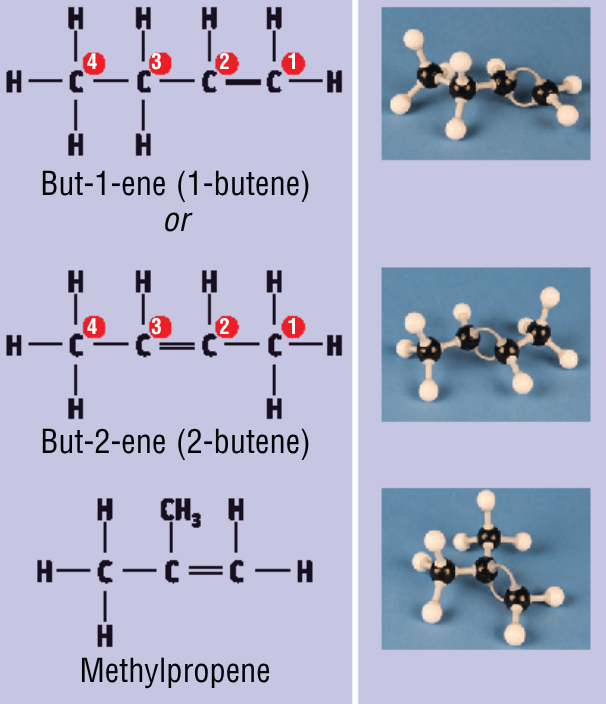
Structural isomers
are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
Why is ethene so important?
it is the starting material from which other substances, particularly plastics, are made
is also produced naturally by fruits as they ripen
When is a carbon described as being planar?
when there is a double or triple bond
When is a carbon described as being tetrahedral?
when there is a single bond
Write a balanced equation for the formation of ethene?
C2H5OH —Al2O3→C2H4 + H2O
Key steps + observations in the procedure for the preparation of ethene:
some ethanol is poured into a boiling tube, and glass wool is added to soak up the ethanol and holds it in place at the end of the boiling tube
a small heap of aluminium oxide (alumina) is place midway along the boiling tube
the aluminium oxide is gently heated by the Bunsen burner, the ethanol is not heated directly as it would vaporise and pass over the aluminium oxide too quickly without being dehydrated to form ethene
bubbles of displaced air from the apparatus are allowed to escape for a short time before 5 test tube and a glass jar of ethene are collected
once finished, the apparatus is raised so that the delivery tube is no longer in the water, and only then is the Bunsen burner turned off; this prevents suck back
What safety precautions are taken when preparing ethene?
stopper on the boiling tube must be air tight, and the Bunsen burner must not be allowed near the mouth of the boiling tube as any gas that escapes is flammable
suck back occurs when the Bunsen burner is turned off before the delivery tube is removed from the water
the alcohol vapour in the boiling tube cools, creating a vacuum, and the water is sucked back to fill the space
the cold water can cause the hot boiling tube to crack or shatter
to avoid suck back, raise the apparatus in order to remove the delivery tube from the water before turning off the Bunsen
Describe the tests on ethene?
physical properties
it is observed that ethene is a colourless gas with a sweetish smell
collected over water, therefore it must be insoluble in water otherwise it would have dissolved; it is only soluble in organic solvents such as cyclohexane and chloroform
combustion
stopper is removed from a test tube and a lit wax taper is held at the mouth of the test tube
a yellow-luminous, slightly smoky flame is observed
when gas has stopped burning some limewater is added to the test tube, which is then stoppered and shaken
limewater turns milky due to the production of CO2
tests for unsaturation
bromine water is added to a test tube of ethene, which is stoppered and shaken
colour change from yellow-orange to colourless is observed
bromine bonds with the very reactive alkene to form a new colourless compound
acidified potassium permanganate is added to a test tube of ethene, which is stoppered and shaken
colour change from purple to colourless is observed
Write an equation for the reaction when ethene burns in air:
C2H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2O
Write an equation for the reaction between limewater and carbon dioxide:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3↓ + H2O
Applications of ethyne:
oxyacetylene welding and cutting
carbide lamps on bikes lit by dripping ethyne onto calcium dicarbide, and this lamp is still used by cave explorers
What is the old name of ethyne?
acetylene
Describe the colour of calcium dicarbide?
grey-brown or sandy, due to the presence of impurities
What impurities can be found in calcium dicarbide?
calcium sulfide CaS
calcium phosphide Ca3P2
calcium nitride Ca3N2
Key steps + observations in the procedure for the preparation of ethyne:
using a spatula, some calcium carbide is placed in a Buchner flask, it must not be touched as moisture from the hand could start the reaction
water is added slowly using a dropping funnel
fizzing takes place in the Buchner flask, a white solid calcium hydroxide is formed and the Buchner flask becomes warm, as an exothermic reaction is occurring
the ethyne gas is bubbled through acidified copper sulfate solution, to remove impurities of hydrogen sulfide, phosphine and ammonia as ethyne does not dissolve
bubbles of gas start to come through the delivery tube, a few test tubes of the gas are collected, the first few are discarded as they only contain displaced air
What safety precautions are taken when preparing ethyne?
since ethynes an explosive misture with air, no naked flam should be brought near the gas preparation apparatus, and all tests should be performed away from the apparatus
after the ethyne is collected the apparatus should be dismantled to ensure no more ethyne is produced
Describe the tests on ethyne?
physical properties
it is observed that ethyne is a colourless gas with a sweetish smell, but if impurities are still present, it will not smell nice
insoluble in water; it is only soluble in organic solvents such as cyclohexane and chloroform
combustion
lid is removed from the gas jar and a lit taper is held at the mouth of the gas jar
a more yellow-luminous, smokey flame and great deal of soot is observed
the soot is a result of unburnt carbon, due to lack of sufficient oxygen to burn it completely
tests for unsaturation
bromine water is added to a test tube of ethyne, which is stoppered and shaken
colour change from yellow-orange to colourless is observed
bromine bonds with the very reactive triple bond to form a new colourless compound
dilute acidified potassium permanganate is added to a test tube of ethyne, which is stoppered and shaken
colour change from purple to colourless is observed
the very reactive triple bond reacts with the potassium permanganate to produce a colourless product
Write an equation for the complete combustion of ethyne in excess oxygen:
2C2H2 + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O
Describe an experiment which describes the solubillity properties of gases:
the syringe on the left is filled with 100cm3 of the gas being studied
the gas is slowly bubbled into water
the syringe on the right collects any gas which does not dissolve
methane, ethene and ethyne are all insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents
Unsaturated compound
is one that contains one or more double or triple bonds between the carbon atoms in the molecule
Aliphatic compound
an organic compound that consists of open chains of carbon atoms and closed chain compounds (rings) that resemble them in chemical properties
Aromatic compounds
compounds that contain a benzene ring structure in their molecules
What puzzled chemists about Benzene?
Reactivity - benzene is an unsaturated compound and was expected to a highly reactive compound, but it was found to be very unreactive
Bond lengths - the bonds between carbons did not alternate between double and single bonds, but rather the bond lengths were all identical and between the length of a single or double bond
What was the explanation Benzene’s unusual characteristics?
electrons were delocalised, and freely shared between the cabrons
What is Methylbenzene used for? Why is it used instead of Benzene?
it is a good organic solvent/non-polar solvent
Benzene is highly toxic and carcinogenic
Fractional Distillation
the separation of crude oil into different hydrocarbon compounds based on their boiling points
Describe the process of fractional distillation
crude oil is heated in a furnace near the bottom of the fractionating column; this keeps the temperature high at the bottom
hot vapour moves up along the column
the temperature decreases as you ascend the tower
as the crude oil rises up the tower, the fractions will reach a temperature that is just below their boiling point and turn into liquids which are collected in trays
the heavier hydrocarbons will condense first, while the lighter hydrocarbons will rise higher and condense higher up the tower
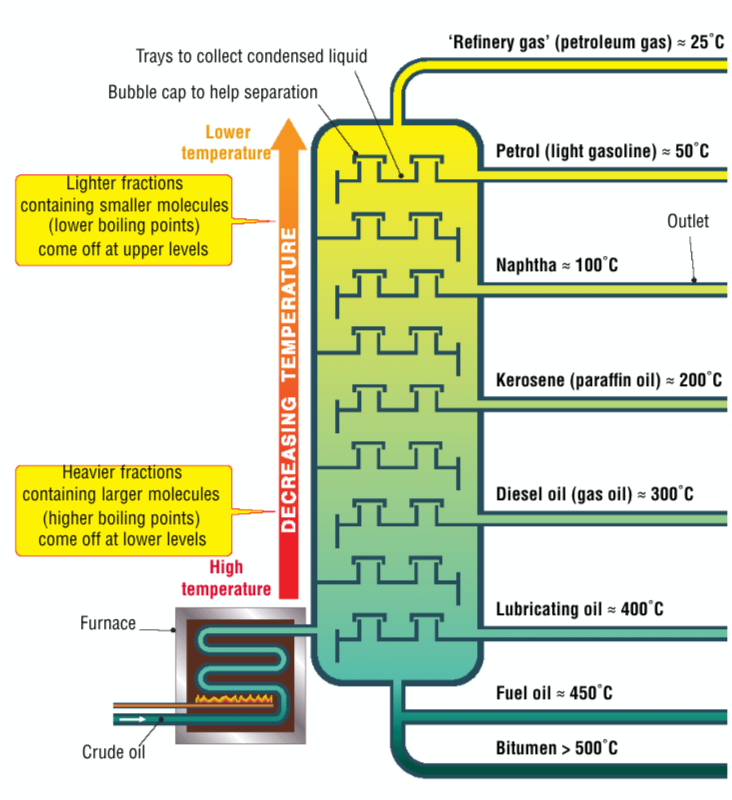
What are the different fractions + length of carbon chain + their uses?
refinery gas - cooking - C1 - C4
light gasoline petrol - C5 - C10
naphtha - petrol + petrochemical industry - C7 - C10
kerosene - aircraft fuel
gas oil - diesel cars
lubricating oil - lubricates machines
fuel oil - large ship fuel
bitumen - road tar - greater than C35
What is LPG?
Liquid petroleum Gas - mixture of propane and butane, liquefied under high pressure
What are the residual fractions?
fractions left over when the more volatile fractions boil off; include lubricating oi, fuel oil and bitumen
Does natural gas have a smell?
no, which is dangerous
mercaptans are organic sulphur compounds that are added to natural gas so that leaks can be detected
Describe how an internal combustion engine works
a mixture of petrol and air is drawn into the cylinder
the mixture is compressed and ignited by a spark
gases produced by the explosion drive the piston down
this rotates the crankshaft causing the wheels to turn
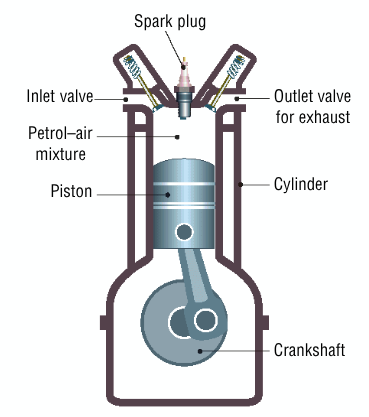
Auto ignition
Is premature ignition (explosion) of the petrol-air mixture before normal ignition of the mixture by a spark takes place
Octane number
Of a fuel is a measure of the tendency of the fuel to resist knocking
What are the reference compounds for assigning octane numbers + what are their octane numbers?
heptane - octane number of 0
2,2,4-trimethylpentane (iso-octane) - octane number 100
What are the factors/structural features which affect octane number?
Chain length - the shorter the chain the higher the octane number
Degree of branching - the more branched the chain the higher the octane number
Straight-chain/Cyclic structures - cyclic compounds have a higher octane number
Name the additive that was first used to reduce knocking + why its use was discontinued?
tetraethyl lead
healthy hazards from poisonous lead pollution
poison the metal catalyst in the catalytic converter of the car
What other ways can the octane number of a fuel be increased?
Isomerisation - changes straight chain compound into their isomers, if they are heated in the presence of a suitable catalyst the chain will break and fragments will rejoin to form a branched isomer of the original compound
Catalytic Cracking - long chain compounds are split into shorter chain molecules, heavy hydrocarbons are heated in the presence of a suitable catalyst and are broken down into saturated products (used to make petrol) and unsaturated products (feedstock for polymer industry)
Adding Oxygenates - an oxygenate refers to any fuel containg oxygen in its molecules, which increases octane number, it also produces less pollution when they burn and thus are cleaner fuels
Dehydrocyclisation - straight chain hydrocarbon is heated in the presence of a suitable catalyst, the chain is converted into a ring structure, involves the removal of a hydrogen molecule in the form of H2 gas
How can hydrogen gas be manufactured?
Steam reforming - reaction of methane with steam in the presence of a suitable catalyst
Electrolysis of water - this can be expensive due to the high cost of electricity
Dehydrocylisation
What is the equation for steam reforming?
CH4 + H2O → 3H2 + CO
Catalytic cracking
Is the breaking down of long-chain hydrocarbon molecules by the action of heat and catalysts into short chain molecules for which there is greater demand
Heat of reaction
Is the heat change when the numbers of moles of reactants indicated in the balanced equation for the reaction react completely
Heat of combustion
Of a substance is the heat change when one mole of the substance is completely burned in excess oxygen
Heat of neutralisation
Is the heat change when one mole of H+ ions from an acid reacts with one mole of OH- ions from a base
Heat of formation
Of a compound is the heat of change that takes place when one mole of a compound in its standard state is formed from its elements in their standard states
Kilogram calorific value
Of a fuel is the heat energy produced when 1kg of the fuel is completely burned in oxygen
Describe the steps involved in using a bomb calorimeter:
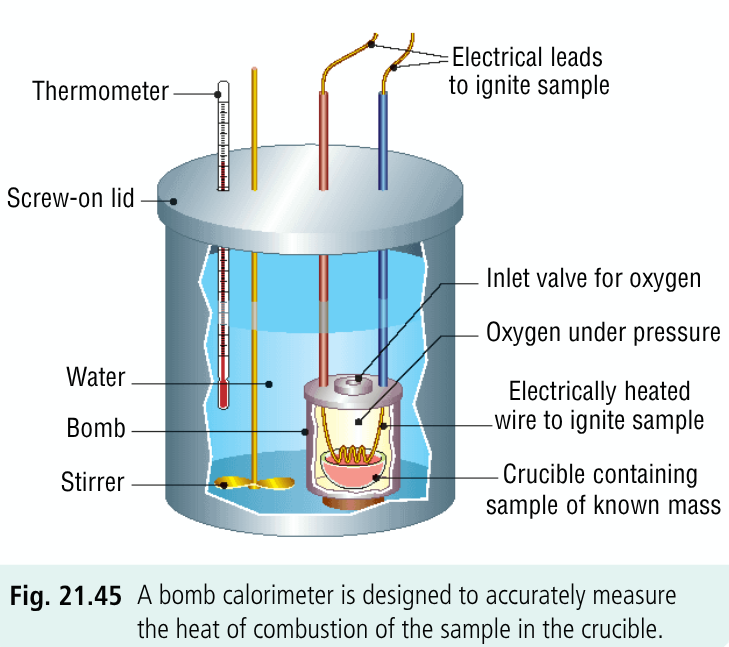
a known mass of the substance whose heat of combustion is being measured is placed in the crucible inside the bomb
bomb is filled with oxygen under pressure; oxygen is in excess to ensure the substance will burn completely
bomb is placed in a known quantity of water contained in the bomb calorimeter
substance is ignited electrically using an ignition coil of wire
Bond energy
Is the average energy required to break one mole of a particular covalent bond and to separate the neutral atoms completely from each other
Hess's law
states that is a chemical reaction takes place in a number of stages, the sum of the heat changes in the separate stages is equal to the heat change if the reaction is carried out in one stage
What is the difference between Exothermic and Endothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions produce heat
Endothermic reactions heat is taken in
Key steps + observations when determining the heat of reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide:
Using a graduate cylinder, a known volume of hydrochloric acid solution is place in a polystyrene cup, and the same volume of sodium hydroxide is placed in a second polystyrene cup: these volumes and concentrations are recorded
Both solutions are allowed to stand until they are at the same temperature, and the temperature of each is recorded
the sodium hydroxide is quickly added to the hydrochloric acid and care is taken to avoid any loss of liquid due to splashing, as this would change the volume used and result in inaccurate results
a lid is immediately placed on the polystyrene cup to avoid heat loss
the solution is stirred continuously to ensure the temperature is constant throughout the solution
the maximum temperature is observed/a rise in temperature is observed
the data gathered is then used to calculate the heat of reaction
Why is an increase in temperature observed when determining the heat of reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide?
the rise in temperature is caused by the heat given out in the reaction, meaning it is an exothermic reaction
What formula is used to calculate the heat of neutralisation/heat of reaction?
△H = mc△T or △H = C△T
What is the difference between calculating heat of neutralisation when a monoprotic acid is used vs when a diprotic acid is used?
Heat of neutralisation involves just one mole of H+ ions reaction
But one mole of a diprotic acid gives two moles of H+ ions
Thus the heat of neutralisation calculated must be halfed so that it is only per one mole of H+ ions
Law of Conservation of Energy
states that energy cannot be created or destroyed bu can only be converted from one form of energy to another