BIOLOGY: EDEXCEL IAL UNIT 1 - PAST PAPER QUESTIONS
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
1
New cards
Bonding in unsaturated lipids
have double bonds between C atoms and between C and O atoms.
2
New cards
method of amniocentesis and how its used to detect CF.
1) amniotic fluid removed (from amniotic sac of the mother) / eq.
2) {fetal/embryonic} cells present in amniotic fluid /{fetal / embryonic} cells needed.
3) DNA can be analysed/ eq.
4) to detect {defective/eq} gene(s) (in sample)/ eq.
2) {fetal/embryonic} cells present in amniotic fluid /{fetal / embryonic} cells needed.
3) DNA can be analysed/ eq.
4) to detect {defective/eq} gene(s) (in sample)/ eq.
3
New cards
method of chorionic villus sampling and how its used to detect CF.
1) placental tissue removed (from the womb of the mother) / eq.
2) fetal cells present in {placenta/placental tissue / chorionic tissue} / fetal cells are needed.
3) DNA can be analysed / eq.
4) to detect {defective / eq} gene(s) (in sample) / eq.
2) fetal cells present in {placenta/placental tissue / chorionic tissue} / fetal cells are needed.
3) DNA can be analysed / eq.
4) to detect {defective / eq} gene(s) (in sample) / eq.
4
New cards
benefits, to a pregnant woman, of prenatal testing.
1) it gives information about abnormalities in the fetus/eq.
2) {opportunity for choice/eq} OR {consider termination/eq} OR time for {preparation/treatment/eq}.
2) {opportunity for choice/eq} OR {consider termination/eq} OR time for {preparation/treatment/eq}.
5
New cards
risks, to a pregnant woman, of prenatal testing.
1) possibility of miscarriage due to procedure/eq.
2) potentially a healthy baby would be lost/eq} / {risk to mother / eq}.
OR
3) idea of a false positive/negative result.
4) a wrong decision made.
OR
3) damage/harm to the fetus.
4) subsequent health issues/miscarriages/eq.
2) potentially a healthy baby would be lost/eq} / {risk to mother / eq}.
OR
3) idea of a false positive/negative result.
4) a wrong decision made.
OR
3) damage/harm to the fetus.
4) subsequent health issues/miscarriages/eq.
6
New cards
Ethical and social issues relating to the use of prenatal testing.
1. idea that fetus is living
2. abortion is wrong/murder/eq.
3. who has the right to decide id tests should be performed/eq.
4. implications of medical costs/disagreements over the next step.
5. who has the right to make the decision for the fetus/ fetus has rights.
6. the fetus is being denied the opportunity to live/ fetus has a right to live.
7
New cards
Describe the roles of the atrioventricular valves during the cardiac cycle.
1) valves separate atria from ventricles.
2) opens during atrial systole/contraction / eq.
3) so that blood can pass through to the ventricles / eq.
4) closed during ventricular systole/contraction / eq.
5) to prevent back flow into atria + to maintain pressure in ventricles.
6) open during diastole.
7) so that ventricles can start to fill up as atria are filling.
2) opens during atrial systole/contraction / eq.
3) so that blood can pass through to the ventricles / eq.
4) closed during ventricular systole/contraction / eq.
5) to prevent back flow into atria + to maintain pressure in ventricles.
6) open during diastole.
7) so that ventricles can start to fill up as atria are filling.
8
New cards
Suggest reasons for the difference in the maximum pressures of the left and right ventricles.
1) pressure in left is higher than right.
2) left ventricles pumps blood all around body / eq.
3) right ventricles pumps blood to lungs / eq.
4) if blood from right ventricle at high pressure there would be damage to lungs/capillaries / eq.
5) lots of muscle/thick wall of left ventricle.
2) left ventricles pumps blood all around body / eq.
3) right ventricles pumps blood to lungs / eq.
4) if blood from right ventricle at high pressure there would be damage to lungs/capillaries / eq.
5) lots of muscle/thick wall of left ventricle.
9
New cards
Define causation
when a change in one variable is responsible for a change in another variable.
10
New cards
define correlation
relationship between 2 variables such that a change in one of the variables is reflected by a change in the other variable / eq.
11
New cards
define gene
a section of DNA/ sequence of bases that codes for a polypeptide / eq. and occupies a particular locus on a chromosome.
12
New cards
define allele
different/variant form of a gene.
13
New cards
define recessive allele
allele that is only expressed in the phenotype of an organism if the dominant allele is not present / eq.
14
New cards
define homozygous
alleles of a particular gene are the same / eq.
15
New cards
amylose is an example of a:
polysaccharide
16
New cards
The three dimensional structure of a protein is held together by:
. disulphide bridges.
. hydrogen bonds.
. ionic bonds.
. hydrogen bonds.
. ionic bonds.
17
New cards
What blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
pulmonary artery.
18
New cards
Define activation energy
1) energy needed for a reaction to occur.
2) by causing bonds to break/weaken/form.
2) by increasing the number of collisions / eq.
2) by causing bonds to break/weaken/form.
2) by increasing the number of collisions / eq.
19
New cards
Explain why it is necessary to measure the initial rate of reaction when investigating the effect of enzyme concentration on the rate of reaction.
1) there should be enough substrate molecules to saturate the enzyme.
2) to endure that the substrate is not a limiting factor / eq.
2) to endure that the substrate is not a limiting factor / eq.
20
New cards
Factors that increase the risk of CVDs
1) genetics.
2) diet.
3) increasing age.
4) male.
5) high BP.
6) smoking.
7) inactivity/lack of exercise.
2) diet.
3) increasing age.
4) male.
5) high BP.
6) smoking.
7) inactivity/lack of exercise.
21
New cards
advantages of the human circulatory system
1) blood flows {faster/at higher pressure/eq} (to the body).
2) blood flows {slower/at lower pressure/eq} to the lung.
3) idea that this reduces risk of damage to lungs.
4) correct ref. to more efficient {exchange/ transport} of gases / eq.
2) blood flows {slower/at lower pressure/eq} to the lung.
3) idea that this reduces risk of damage to lungs.
4) correct ref. to more efficient {exchange/ transport} of gases / eq.
22
New cards
Describe the structure of an enzyme.
1) ref to an enzyme as a protein.
2) ref. to {3D/tertiary/globular} structure.
3) ref. to named bonds (holding structure in place).
4) between the R groups.
5) ref. to active site.
6) idea of specificity of active site.
2) ref. to {3D/tertiary/globular} structure.
3) ref. to named bonds (holding structure in place).
4) between the R groups.
5) ref. to active site.
6) idea of specificity of active site.
23
New cards
Describe the blood clotting process.
1) idea that there is a cascade of events (leading to blood clotting).
2) ref. to thromboplastin (starting the cascade).
3) ref. to conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
4) idea that {thromboplastin/thrombin} is {an
enzyme / a catalyst} ;
5) ref. to conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin.
6) ref. to formation of mesh of {fibres/fibrin}.
7) ref. to requirement of {calcium ions/ Ca2+ / vitamin K} ;
8) ref. to {platelets/blood cells} getting trapped (in the mesh) ;
2) ref. to thromboplastin (starting the cascade).
3) ref. to conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
4) idea that {thromboplastin/thrombin} is {an
enzyme / a catalyst} ;
5) ref. to conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin.
6) ref. to formation of mesh of {fibres/fibrin}.
7) ref. to requirement of {calcium ions/ Ca2+ / vitamin K} ;
8) ref. to {platelets/blood cells} getting trapped (in the mesh) ;
24
New cards
Suggest why cells from mouth swabs or blood samples are used rather than gametes
1) idea that these cells are {easy/painless } to collect.
2) idea that a relatively {large amount of DNA / large number of cells} can be collected.
3) they {contain diploid cells/have (23) pairs of chromosomes}.
4) cells {are genetically identical/have same DNA / have same alleles}.
5) any {recessive allele/mutated (CF) gene} will be present in them / eq.
6) idea that if the gametes were tested they may not contain the {recessive allele/mutated (CF) gene} (as they are haploid).
2) idea that a relatively {large amount of DNA / large number of cells} can be collected.
3) they {contain diploid cells/have (23) pairs of chromosomes}.
4) cells {are genetically identical/have same DNA / have same alleles}.
5) any {recessive allele/mutated (CF) gene} will be present in them / eq.
6) idea that if the gametes were tested they may not contain the {recessive allele/mutated (CF) gene} (as they are haploid).
25
New cards
Explain why it is necessary to test for several different recessive alleles in the screening for CF.
1) cystic fibrosis results from one of a number of possible mutations (of this gene) /eq.
2) idea that testing for only one will miss other recessive alleles.
2) idea that testing for only one will miss other recessive alleles.
26
New cards
Explain why the probability of having a child with CF is low and not zero when both parents aren't carriers.
1) ref. to false negatives/eq.
2) idea that the screening programme does not test for all the possible mutations that can cause cystic fibrosis.
3) idea that a mutation may occur in the formation of the gametes.
4) idea of mutation in both gametes.
5) idea that a mutation may occur after fertilisation.
2) idea that the screening programme does not test for all the possible mutations that can cause cystic fibrosis.
3) idea that a mutation may occur in the formation of the gametes.
4) idea of mutation in both gametes.
5) idea that a mutation may occur after fertilisation.
27
New cards
Explain why family members of CF carriers are offered genetic screening.
1) idea that any other family member could be a carrier.
2) idea that informed choices can be made about having children (if they know that they are carriers).
2) idea that informed choices can be made about having children (if they know that they are carriers).
28
New cards
Function of semilunar valves
1. prevents back flow of blood into heart ventricles.
2. during diastole/atrial systole.
29
New cards
Explain why a mammalian heart is divided into a right side and a left side
1) idea that it keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate.
2) idea that this results in as much oxygen as possible being carried to the tissues/cells.
3) reference to need for different pressures in each side.
2) idea that this results in as much oxygen as possible being carried to the tissues/cells.
3) reference to need for different pressures in each side.
30
New cards
Risk of using antihypertensives
blood pressure falls too low / coughs / swelling of ankles / impotence / tiredness / constipation / headache / confusion / depression / excessively low heart rate / allergy / stroke / provoked type II diabetes / frequent urination / fainting / dizziness / vomiting / dry mouth / breathing difficulties / irregular heart rate / chest pain / hives / rash / dehydration / reduced circulation effects / low potassium / blurred vision / eq.
31
New cards
Explain the meaning of the term primary structure.
1) sequence of amino acids
2) joined by peptide bonds.
2) joined by peptide bonds.
32
New cards
Explain the importance of the primary structure of an enzyme to its function.
1. idea that primary structure determines (three-dimensional) folding/ eq.
2. reference to types of amino acids determine types of bonds formed.
3. reference to position of amino acids determines position of {bonds / correctly named bond}.
4. idea that {shape/position/eq} of active site is determined by position of amino acids.
5. reference to shape of active site being correct to bind to substrate.
6. reference to {amino acids/R groups} involved in {chemical reaction/ eq}.
7. reference to {globular/soluble/enzyme} molecules being {relatively short/small/made up of relatively few amino acids}.
8. reference to {globular/soluble proteins/enzyme} having relatively high number of {polar/ small {amino acids/R groups}.
9. reference to {polar R groups/eq} facing outwards.
33
New cards
Roles of mRNA in protein synthesis.
1. reference to mRNA as a copy of the {genetic code/DNA}.
2. holds the information of the protein (being synthesised)/eq.
3. moves out of the nucleus/to ribosomes/ eq.
4. idea that it acts as a template/has the instructions for translation.
34
New cards
Describe the process of protein synthesis that occurs in the cytoplasm.
1. correct reference to translation.
2. binds to an amino acid/takes the amino acid to the ribosome/mRNA.
3. reference to tRNA being specific to amino acid.
4. holds the amino acid in place/eq.
35
New cards
Explain the effect of ethanol on the permeability of beetroot cell membranes.
1) idea that ethanol causes the membrane to be{disrupted/ eq}.
2) idea that this is due (phospho)lipids dissolve in ethanol.
3) idea that (membrane) proteins denatured by ethanol.
4) comment on the disruption of the vacuole membrane/eq.
5) idea that {betalain/pigment}can escape from the {cell/ vacuole /eq } when the membrane is disrupted.
2) idea that this is due (phospho)lipids dissolve in ethanol.
3) idea that (membrane) proteins denatured by ethanol.
4) comment on the disruption of the vacuole membrane/eq.
5) idea that {betalain/pigment}can escape from the {cell/ vacuole /eq } when the membrane is disrupted.
36
New cards
Explain why water is an effective molecule for transporting other molecules around living molecules.
1) Idea that water is a solvent.
2) idea that water is {slightly charged/dipole/polar/ eq}.
3) idea that polar molecules/ions/eq. can dissolve in water.
4) idea that water is viscous/fluid/ eq.
5) idea of water as a liquid assists mass flow.
6) correct reference to cohesion/adhesion.
2) idea that water is {slightly charged/dipole/polar/ eq}.
3) idea that polar molecules/ions/eq. can dissolve in water.
4) idea that water is viscous/fluid/ eq.
5) idea of water as a liquid assists mass flow.
6) correct reference to cohesion/adhesion.
37
New cards
Suggest why a faulty atrioventricular valve could lead to symptoms of breathlessness and lack of energy.
1) valve does not shut properly/eq.
2) some backflow of blood (from ventricle to atrium) / eq.
3) during ventricular systole/ when ventricles contract / eq.
4) idea of lower blood pressure.
5) idea of less efficient supply of oxygen.
6) idea that blood pressure in lungs increases.
2) some backflow of blood (from ventricle to atrium) / eq.
3) during ventricular systole/ when ventricles contract / eq.
4) idea of lower blood pressure.
5) idea of less efficient supply of oxygen.
6) idea that blood pressure in lungs increases.
38
New cards
Explain how the circulatory system in mammals enables efficient gas exchange.
1) idea that mass flow generated by heart.
2) idea that moving blood helps to maintain a concentration gradient.
3) idea that a steep/eq. concentration gradient gives a fast/eq. rate of diffusion.
4) idea of network/lots/e. of capillaries.
5) large surface area of capillaries/eq.
6) idea that large surface area increases the rate of diffusion.
7) idea that capillaries have very thin walls.
8) idea that diffusion is fastest over small distances.
9) idea that no organs/cells/tissues are far away from blood/capillaries cover alveoli/eq.
10) idea that efficiency is related to double circulation.
2) idea that moving blood helps to maintain a concentration gradient.
3) idea that a steep/eq. concentration gradient gives a fast/eq. rate of diffusion.
4) idea of network/lots/e. of capillaries.
5) large surface area of capillaries/eq.
6) idea that large surface area increases the rate of diffusion.
7) idea that capillaries have very thin walls.
8) idea that diffusion is fastest over small distances.
9) idea that no organs/cells/tissues are far away from blood/capillaries cover alveoli/eq.
10) idea that efficiency is related to double circulation.
39
New cards
Explain why the combination of a high \n fat diet and low activity levels may lead to CVD.
1. idea of energy imbalance.
2. idea of individual becoming overweight / obese / eq.
3. idea of increased blood pressure.
4. idea of obesity leads to diabetes a CVD risk factor.
5. idea of increased (blood) cholesterol / LDL
levels / LDL to HDL ratio.
6. idea of damage to endothelium / overloading of receptors.
7. formation of atheroma / plaque /atherosclerosis } / eq.
8. idea of loss of elasticity of artery / narrowing of lumen / eq.
40
New cards
State what is meant by the term template for the synthesis of mRNA.
1. idea that the RNA nucleotides attach to this strand.
2. idea of nucleotide / base sequence that directs the synthesis of complementary sequence / mRNA / eq.
41
New cards
Differences between the processes of replication and transcription of DNA.
Replication:
1. uses DNA nucleotides.
2. uses DNA polymerase.
3. ref. to semi conservative.
4. copies both DNA strands.
5. makes DNA double helix.
\
Transcription:
1. uses RNA nucleotides.
2. uses RNA polymerase.
3. not semi conservative.
4. cops only 1 DNA strand.
5. makes single RNA strand.
1. uses DNA nucleotides.
2. uses DNA polymerase.
3. ref. to semi conservative.
4. copies both DNA strands.
5. makes DNA double helix.
\
Transcription:
1. uses RNA nucleotides.
2. uses RNA polymerase.
3. not semi conservative.
4. cops only 1 DNA strand.
5. makes single RNA strand.
42
New cards
Explain the meaning of the term recessive allele.
1) idea that both of these alleles need to be present in order for the recessive phenotype to be expressed.
2) different form of a gene / eq.
3) same locus /position / eq.
4) different base sequence / eq.
2) different form of a gene / eq.
3) same locus /position / eq.
4) different base sequence / eq.
43
New cards
How is temperature controlled in an investigation?
heat shield.
44
New cards
Explain why people with CF can have breathing difficulties.
1) produces {thicker / stickier / more viscous / eq} mucus.
2) blocking { trachea / bronchi / bronchioles / airway / eq} / eq.
3) cilia are unable to move mucus out of lungs / eq.
4) idea of reduced flow of {air / oxygen } to alveoli.
5) idea of reduced concentration gradient for {oxygen / carbon dioxide} (in alveoli).
6) idea of loss of surface area / elasticity / eq.
7) idea of reduced gaseous exchange.
8) trapped bacteria may result in more respiratory infections / eq.
2) blocking { trachea / bronchi / bronchioles / airway / eq} / eq.
3) cilia are unable to move mucus out of lungs / eq.
4) idea of reduced flow of {air / oxygen } to alveoli.
5) idea of reduced concentration gradient for {oxygen / carbon dioxide} (in alveoli).
6) idea of loss of surface area / elasticity / eq.
7) idea of reduced gaseous exchange.
8) trapped bacteria may result in more respiratory infections / eq.
45
New cards
Explain the effect of the conc. of an enzyme on the initial rate of reaction of enzyme substrate complexes.
1) idea that enzyme lowers activation energy / provides alternative reaction pathway.
2) idea that the higher concentration of enzyme means that more active sites are available.
3) more chance of a collision between {enzyme / active site } and substrate.
4) reference to enzyme
2) idea that the higher concentration of enzyme means that more active sites are available.
3) more chance of a collision between {enzyme / active site } and substrate.
4) reference to enzyme
46
New cards
Explain how the information in a pedigree diagram suggests a disorder/disease is due to a ... allele.
Talk about:
1) how many people it has affected.
2) specific people and what their genotypes might be.
2) expand on point using pedigree.
3) the number of offspring with disorder/disease .
4) couples and their genotypes and what phenotypes they bring about in their children.
1) how many people it has affected.
2) specific people and what their genotypes might be.
2) expand on point using pedigree.
3) the number of offspring with disorder/disease .
4) couples and their genotypes and what phenotypes they bring about in their children.
47
New cards
Explain the ways in which the structures of amylose and glycogen make them suitable for energy storage.
1) contain glucose / eq.
2) idea that they are compact so large {numbers of glucose / amylose / glycogen } molecules can fit into a small volume (large amounts of energy in small volume).
3) insoluble therefore does not affect osmosis / eq.
4) large molecules therefore remains in cells / too big to diffuse out or into cells / eq.
2) idea that they are compact so large {numbers of glucose / amylose / glycogen } molecules can fit into a small volume (large amounts of energy in small volume).
3) insoluble therefore does not affect osmosis / eq.
4) large molecules therefore remains in cells / too big to diffuse out or into cells / eq.
48
New cards
Explain how rapid gas exchange takes place in a mammal.
1) idea that large surface area provided by alveoli.
2) idea that large surface area provided by capillary network.
3) idea that concentration gradient maintained by ventilation of / air flow in / eq. the lungs.
4) idea that concentration gradient maintained by circulation / mass flow / eq. of blood.
5) idea that diffusion pathway is small because alveoli have a thin wall.
6) idea that diffusion pathway is small because capillaries have a thin wall / are in contact with alveoli / are only one cell thick / eq.
7) idea that air is warmed because lungs are in core of body.
8) warmer air enables faster movement / diffusion / eq. of gases / eq.
9) reference to respiratory pigment / haemoglobin / red blood cells / eq. to carry oxygen.
2) idea that large surface area provided by capillary network.
3) idea that concentration gradient maintained by ventilation of / air flow in / eq. the lungs.
4) idea that concentration gradient maintained by circulation / mass flow / eq. of blood.
5) idea that diffusion pathway is small because alveoli have a thin wall.
6) idea that diffusion pathway is small because capillaries have a thin wall / are in contact with alveoli / are only one cell thick / eq.
7) idea that air is warmed because lungs are in core of body.
8) warmer air enables faster movement / diffusion / eq. of gases / eq.
9) reference to respiratory pigment / haemoglobin / red blood cells / eq. to carry oxygen.
49
New cards
Explain how the structure of an artery is related to its function.
1) smooth endothelium lining to reduce friction (between wall and blood) / eq.
2) thick elastic wall to allow stretch and recoil /eq.
3) collagen layer to provide strength / withstand high blood pressure / eq.
4) smooth muscle in wall to enable artery to change diameter / eq.
2) thick elastic wall to allow stretch and recoil /eq.
3) collagen layer to provide strength / withstand high blood pressure / eq.
4) smooth muscle in wall to enable artery to change diameter / eq.
50
New cards
Explain why mammals need a blood circulation system.
1) mammals have a large volume to surface area ratio.
2) mammals have high nutrient / oxygen requirement.
3) heart and circulation provides a bulk / mass transport system.
4) that overcomes the limitations of diffusion.
2) mammals have high nutrient / oxygen requirement.
3) heart and circulation provides a bulk / mass transport system.
4) that overcomes the limitations of diffusion.
51
New cards
Suggest why BMI is used.
1) idea that height has an impact on body mass.
2) BMI is related to both mass and height.
2) BMI is related to both mass and height.
52
New cards
Suggest why CVD is expressed as incidence per 1000.
to allow comparison between groups of different sizes / eq.
53
New cards
Explain what is meant by the term fluid mosaic.
1) randomly arranged / scattered / eq. proteins in the bilayer.
2) phospholipids forming the bilayer are free to move.
2) phospholipids forming the bilayer are free to move.
54
New cards
Explain why a triplet code is required for the synthesis of protein.
1) only four bases.
2) need to code for 20 / more than 16 amino acids.
3) three bases is the minimum number that provides sufficient combinations to code for each amino acid.
2) need to code for 20 / more than 16 amino acids.
3) three bases is the minimum number that provides sufficient combinations to code for each amino acid.
55
New cards
Explain how Meselson and Stahl confirmed the semiconservative mechanism of DNA replication.
1. Meselson and Stahl's experiment was designed to distinguish between different types of replication.
2. at the start of the experiment cells were grown in a medium with heavy nitrogen / 15N.
3. only a heavy DNA band was observed.
4. the cells were then transferred to a medium with light nitrogen / 14N.
5. after one round of replication an intermediate DNA band was observed.
6. after two rounds of replication intermediate and light bands were observed.
7. showing that replication was semiconservative / one strand of original DNA and one strand of newly synthesised DNA.
56
New cards
Explain the meaning of the term semi-conservative replication.
1. idea that new DNA is synthesised.
2. idea of a new DNA contains original strand and new strand.
57
New cards
Compare and contrast exocytosis and endocytosis.
SIMILARITIES:
º both used to transport large particles / large
quantities of material (1)
º both involve (phospholipid) membrane vesicles (1)
DIFFERENCE:
º exocytosis is export and endocytosis is import of
material (1)
º both used to transport large particles / large
quantities of material (1)
º both involve (phospholipid) membrane vesicles (1)
DIFFERENCE:
º exocytosis is export and endocytosis is import of
material (1)
58
New cards
Compare and contrast the structures of glycogen and starch.
SIMILARITIES:
º both polysaccharides / formed from many (alpha) glucose monomers (1)
º joined by glycosidic bonds (1)
DIFFERENCES:
º starch is composed of two polysaccharides, glycogen only one (1)
º amylose is a {straight / helical} chain, amylopectin and glycogen are both branched molecules (1)
º both polysaccharides / formed from many (alpha) glucose monomers (1)
º joined by glycosidic bonds (1)
DIFFERENCES:
º starch is composed of two polysaccharides, glycogen only one (1)
º amylose is a {straight / helical} chain, amylopectin and glycogen are both branched molecules (1)
59
New cards
State what is meant by the term gene.
sequence of BASES of DNA that code for a polypeptide
60
New cards
Explain why each codon for the DNA genetic code must contain at least three bases.
º enough codons needed for 20 different amino acids (1)
º four bases are used in the genetic code (1)
º triplet code provides enough / 43 / 64 possible codons (1)
º four bases are used in the genetic code (1)
º triplet code provides enough / 43 / 64 possible codons (1)
61
New cards
The CFTR protein coded for by this mutation has one missing amino acid compared to the functioning protein. \n \n Explain how this mutation results in a non-functioning CFTR protein.
º there will be a different sequence of R groups (1) \n \n º therefore the CFTR protein has a different tertiary structure (1) \n \n º because of different {types of / position of} bonds between the R groups (1) \n \n º therefore the movement of chloride ions through the cell membrane is affected (1)
62
New cards
Explain why people with cystic fibrosis may develop lung infections.
º because of reduced water transport from cells (1) \n \n º cilia lining airways are unable to move mucus (1) \n \n º therefore microorganisms get trapped in the mucus (1) \n \n º mucus provides suitable growth conditions for growth of microorganisms (1)
63
New cards
Describe the roles of RNA in the synthesis of collagen. \n \n Collagen is an insoluble, fibrous protein.
º an mRNA molecule codes for each of the polypeptide chains in collagen (1). \n \n º mRNA carries a copy of the genetic code for collagen out of the nucleus to ribosome (1). \n \n º each tRNA carries its own specific amino acid to the ribosome. \n \n º anticodon on tRNA binds to codons on the mRNA (1). \n \n º tRNA holds the amino acid in place while peptide bonds form (1). \n \n º reference to start and stop codons on mRNA (1).
64
New cards
Explain how the primary structure of collagen determines its properties.
º insoluble because there are hundreds of amino acids (1).
\
º insoluble because there are many hydrophobic R groups (1). \n \n º strong because of the triple helix (1). \n \n º therefore there are many repeating amino acid sequences (1). \n \n º many small R groups so that the triple helix can form (1)
\
º insoluble because there are many hydrophobic R groups (1). \n \n º strong because of the triple helix (1). \n \n º therefore there are many repeating amino acid sequences (1). \n \n º many small R groups so that the triple helix can form (1)
65
New cards
Roles of mRNA.
º copy of the genetic code.
\
º copy of the protein being synthesised. \n \n º moves to ribosome. \n \n º template for translation.
\
º copy of the protein being synthesised. \n \n º moves to ribosome. \n \n º template for translation.
66
New cards
Assess 2 graphs...
1) general correlation.
2) the individual pieces of data.
3) pieces of data in each graph that stands out.
4) application of your own knowledge to explain data.
2) the individual pieces of data.
3) pieces of data in each graph that stands out.
4) application of your own knowledge to explain data.
67
New cards
describe the location of the elastic fibres and explain its function.
1) middle layer of wall of vessel/eq/tunica media / in the muscle layer.
2) ref. to allows stretching/recoil/ description.
3) to prevent damage of the aorta/eq. /to maintain the pressure of the blood / eq.
2) ref. to allows stretching/recoil/ description.
3) to prevent damage of the aorta/eq. /to maintain the pressure of the blood / eq.
68
New cards
Give one reason why many mammals have a circulatory system.
idea that it overcomes limitations of diffusion / it is involved in transport / heat transfer.
69
New cards
Explain why glucose and galactose are classed as monosaccharides.
1) reference to consisting of C, H and O / eq.
2) no glycosidic bonds / one sugar unit.
3) idea of ratio of C:H:O is 1:2:1.
2) no glycosidic bonds / one sugar unit.
3) idea of ratio of C:H:O is 1:2:1.
70
New cards
describe the structure of a fibrous protein.
1) fibrous proteins are long / contain many amino acids.
2) amino acid sequence is repetitive / eq.
3) idea of limited folding.
4) polypeptides lie parallel to each other.
5) idea of bonds linking chains together.
2) amino acid sequence is repetitive / eq.
3) idea of limited folding.
4) polypeptides lie parallel to each other.
5) idea of bonds linking chains together.
71
New cards
Suggest why enzymes can break down substrates quickly.
1) enzymes are catalyst.
2) reference to lowering / eq. activation energy.
3) without being used up in the reaction / eq.
4) idea that once reaction is complete, the enzyme detaches from products.
5) and can then bind to another substrate.
2) reference to lowering / eq. activation energy.
3) without being used up in the reaction / eq.
4) idea that once reaction is complete, the enzyme detaches from products.
5) and can then bind to another substrate.
72
New cards
Explain how water is involved in the transport of molecules in living organisms.
1) Dipole nature of water.
2) Hydrogen bonding.
3) Transport of polar molecules.
2) Hydrogen bonding.
3) Transport of polar molecules.
73
New cards
Suggest how triglycerides are transported in the blood.
1) triglycerides are insoluble (in water) / eq.
2) as lipoproteins / as LDL / as HDL.
3) formed into vesicles / micelles.
2) as lipoproteins / as LDL / as HDL.
3) formed into vesicles / micelles.
74
New cards
blood clots form only when requires because the clotting factors used are...
present in an inactive form in the blood.
75
New cards
Explain why statins reduce the risk of CVD.
1) statins inhibit the synthesis / production of cholesterol in the liver.
2) reducing (total) blood cholesterol levels.
3) raises HDL levels / increases HDL : LDL ratio / lowers LDL.
2) reducing (total) blood cholesterol levels.
3) raises HDL levels / increases HDL : LDL ratio / lowers LDL.
76
New cards
Suggest how cholesterol affects membrane fluidity.
1) combines with fatty acid tails.
2) holds / pulls the fatty acid chains together.
3) reducing movement of the phospholipid / fatty acid tails.
2) holds / pulls the fatty acid chains together.
3) reducing movement of the phospholipid / fatty acid tails.
77
New cards
Explain the meaning of the term gene mutation.
1) alteration in DNA.
2) change in base sequence. / eq.
2) change in base sequence. / eq.
78
New cards
What is meant by the term relative risk?
1) the chance / probability of an event.
2. in one {group / person} compared to another ;
2. in one {group / person} compared to another ;
79
New cards
Suggest the health advice that could be given to someone with an obese BMI.
1) individuals should take regular / more exercise.
2) reduce energy intake.
3) reduce BMI to less than 25.
2) reduce energy intake.
3) reduce BMI to less than 25.
80
New cards
Explain one way in which the structure of a capillary is related to its function.
1) thin walls / walls consist of single layer of flattened cells / eq.
2) idea of allowing rapid diffusion.
OR
3) gaps between cells in the wall.
4) to allow exchange (of materials) / increase permeability.
2) idea of allowing rapid diffusion.
OR
3) gaps between cells in the wall.
4) to allow exchange (of materials) / increase permeability.
81
New cards
Describe the relationship between mass and surface are of alveoli.
1) as mass increases demand for oxygen increases / eq.
2) surface area of alveoli increases to allow for increased gas exchange / eq.
2) surface area of alveoli increases to allow for increased gas exchange / eq.
82
New cards
Explain why a pH buffer should be used in the investigation to measure the initial rate of reaction of an enzyme.
1) controlling pH.
2) otherwise pH would change as the fatty acid was used up.
3) (changes in pH) affect the shape of the active site.
4) (changes in pH) change ionic bonds within the enzyme.
5) (changes in pH) change the rate of reaction.
2) otherwise pH would change as the fatty acid was used up.
3) (changes in pH) affect the shape of the active site.
4) (changes in pH) change ionic bonds within the enzyme.
5) (changes in pH) change the rate of reaction.
83
New cards
Describe the structure of the cell membrane.
1. reference to phospholipid bilayer.
2. correct orientation and structure of the phospholipids in the bilayer.
3. phospholipids have polar / hydrophilic heads and non- polar / hydrophobic tails / eq.
4. proteins in the membrane.
5. idea of at least two different locations of proteins e.g. extrinsic, intrinsic, transmembrane.
6. reference to glycoproteins / glycolipids / lipoproteins
7. reference to cholesterol within the membrane.
84
New cards
Explain the term genotype.
genotype is the combination of / pair of / two / all alleles present (in an organism).
85
New cards
Explain the term phenotype
phenotype is the observable feature.
86
New cards
Describe how the primary structure of a protein results in a protein with a 3D structure.
1) primary structure is the sequence of amino acids.
2) idea that amino acids each have different R groups.
3) idea that bonds form between R groups.
4) bonding determines the folding of the polypeptide.
2) idea that amino acids each have different R groups.
3) idea that bonds form between R groups.
4) bonding determines the folding of the polypeptide.
87
New cards
Explain how a genetic pedigree diagram could show how a recessive gene is inherited.
1) parents and offspring for each generation identified.
2) phenotype(s) identified.
3) for /recessive condition two normal/unaffected parents may have {one or more / some / eq. offspring that are affected.
2) phenotype(s) identified.
3) for /recessive condition two normal/unaffected parents may have {one or more / some / eq. offspring that are affected.
88
New cards
The sequence of events in the cardiac cycle is..
atrial systole --> ventricular systole --> atrial diastole --> ventricular diastole.
89
New cards
Explain why long term exercise reduced the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
1) low blood pressure.
2) low heart rate.
3) heart/cardiac muscle is stronger.
4) not overweight.
5) changes LDL/HDL ratio/lowers cholesterol.
2) low heart rate.
3) heart/cardiac muscle is stronger.
4) not overweight.
5) changes LDL/HDL ratio/lowers cholesterol.
90
New cards
Describe how sucrose is formed from monosaccharides.
1) glucose and fructose.
2) joined by condensation reaction / water produced.
3) forming a glycosidic bond/link.
2) joined by condensation reaction / water produced.
3) forming a glycosidic bond/link.
91
New cards
describe the structure of starch
1) (many) glucose molecules joined by glycosidic bonds /links.
2) amylose and amylopectin.
3) amylose is linear / is unbranched / is helical / has 1,4 bonds.
4) amylopectin is branched / has 1,4 and 1,6 bonds.
2) amylose and amylopectin.
3) amylose is linear / is unbranched / is helical / has 1,4 bonds.
4) amylopectin is branched / has 1,4 and 1,6 bonds.
92
New cards
Describe how a blood clot forms in large veins.
1) Idea of slow blood flow in (large) veins.
2) initiates clotting cascade.
3) prothrombin converted to thrombin.
4) leading to conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
5) fibrin is insoluble.
6) trapping red blood cells / platelets to form a clot.
2) initiates clotting cascade.
3) prothrombin converted to thrombin.
4) leading to conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
5) fibrin is insoluble.
6) trapping red blood cells / platelets to form a clot.
93
New cards
Explain how the properties of phospholipids contribute to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes.
1. (phospholipids) form a bilayer as they have a polar head and non-polar tails.
2. proteins are located between the phospholipids.
3. because of interactions between R groups of proteins and phospholipids.
4. phospholipids are free to move which makes the membrane fluid.
94
New cards
Explain how enzymes catalyse the break down of substrates.
1) active site that fits /eq. the substrate.
2) lowers the activation energy (for the reaction).
3) detail of how the activation energy is lowered (bonds are weakened)
2) lowers the activation energy (for the reaction).
3) detail of how the activation energy is lowered (bonds are weakened)
95
New cards
Explain why smokers with a high LDL:HDL ratio have a greater risk of death from CVD than non-smokers.
1. idea that smoking causes platelet damage.
2. increases the risk of formation of blood clots.
3. increases the risk of plaque formation/atheroma/ atherosclerosis.
4. increases blood pressure.
96
New cards
Describe the roles of prothrombin in the formation of blood clots.
1) idea that prothrombin is the inactive enzyme.
2) prothrombin is converted to thrombin /an active enzyme.
3) by thromboplastin.
4) thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
5) fibrin traps platelets/red blood cells to form clot.
2) prothrombin is converted to thrombin /an active enzyme.
3) by thromboplastin.
4) thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
5) fibrin traps platelets/red blood cells to form clot.
97
New cards
Suggest 2 differences between fibrinogen and fibrin.
1) idea that fibrinogen is globular and fibrin is fibrous.
2) fibrinogen is soluble and fibrin in insoluble.
3) idea that they are different sizes.
2) fibrinogen is soluble and fibrin in insoluble.
3) idea that they are different sizes.
98
New cards
Explain the nature of the genetic code.
1) triplet code/3 bases to each code/eq.
2) ref. to A,T,G,C.
3) idea that each triplet of bases codes for one amino acid.
4) idea that the code is not overlapping.
5) idea that the code is universal.
6) idea that the code is degenerate.
2) ref. to A,T,G,C.
3) idea that each triplet of bases codes for one amino acid.
4) idea that the code is not overlapping.
5) idea that the code is universal.
6) idea that the code is degenerate.
99
New cards
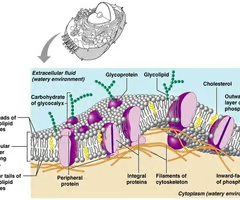
fluid mosaic model of cell membrane
100
New cards
Describe the correct location for the CFTR protein.
1) in the cell surface membrane.
2) of mucus producing cells.
2) of mucus producing cells.