FINAL EXAM ALL KEY TERMS ECON FUNDIES
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Measurement of economic activities *** review/ask re: specific definition
measurement of variables in the economy, i.e. GDP, distribution of income (income approach), economic output (exp. approach), production activities (supply side — product approach)
GDP
gross domestic product, the most common measure of economic activity. It is the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period.
Production Approach
focuses on production activities in economy, or the “supply side” (ex: how GDP is the market value of all final goods, services, and inventories newly produced within a country during a given period of time)
Expenditure Approach
focuses on use of economic output in economy — “demand side” ex: spending by households, firms and governments (and other countries)
Income Approach
focused on the distribution of income in economy
calculating growth rates *** REVIEW/ASK
market exchange rates*** REVIEW/ASK
the prices when one currency buys another
Aggregate production function
Total Factor Productivity
expresses improvements in technologies or economic conditions that allow capital and labor to be used more effectively
Marginal benefit of capital** REVIEW/ASK
the additional return or profit an economy earns from investing one more unit of capital.
rental rate of capital
GDP per capita
measurement tool used to assess the standard of living across different countries (in monetary terms, regarding the production of goods/services and income)
labor force
the sum of employed, unemployed, and those actively seeking a job individuals that are over the age of 16
cyclical unemployment
Unemployment may be caused by shocks and some rigidities in labor markets that cause employment and GDP to differ from full employment. Also known as the difference between actual employment and the natural rate of employment
frictional unemployment
This type of unemployment results from a matching process between workers and firms. An individual will be unemployed if the additional benefit from an extra day searching for “the” job is greater than the marginal cost. Similarly, a firm may wait before closing a job vacancy by comparing marginal benefits and costs. Search frictions relate to job turnovers and matching issues (time of job announcements, interviews, hiring, paperwork, etc.)
structural unemployment
The unemployment cause derives from the discrepancy between the skills demanded by firms and the skills that workers supply. Because the sectoral mix of economies changes over time, the contraction of some sectors releases workers who should flow to other expanding sectors. However, the innovative sectors may require skills that the recently laid-off workers do not have, which causes structural unemployment.
seasonal unemployment
Finally, seasonal unemployment relates to changes in economic activities because of seasonal changes (agriculture, construction, tourism, etc.)
natural rate of unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate that is consistent with “full” employment. The natural unemployment rate, u∗, derives from frictional, seasonal, and structural reasons
flexible wages —> triple check w/ ppl
wages that can quickly adjust up or down in response to changes in labor market conditions, like supply and demand, productivity, or economic shocks (e.g., recessions)
sticky wages
Sticky wages are the tendency for nominal wages to resist downward adjustments even when economic conditions, such as a recession, would otherwise cause them to fall. This stickiness is driven by factors like long-term labor contracts, minimum wage laws, and employee morale, which can lead to firms choosing layoffs over pay cuts to reduce costs during a downturn, thus prolonging unemployment
inflation rate —> NEED TO ADD
the percentage increase in the average price of a basket of goods and services over a specific time —> usually indicates a decrease in purchasing power, where money is worth less
price index / price indicies
a tool to measure the average price level of a group of goods and services relative to a base year
nominal wage
wage can be expressed in nominal terms or in real terms. The nominal wage is the workers’ compensation for time and effort in monetary terms – e.g., the wage might be $25/hour
real wage
expresses the worker’s compensation for
time and effort in terms of goods and services – e.g., an hour of work may be equivalent to a certain number of a specific good or comparable to a number of baskets of goods/services using the price level.
nominal interest
measure that allows us to compare different asset and liability alternatives. It provides a measure to evaluate the relative change in an asset/liability value over time.
real interest
illustrates how the purchasing power in goods and services grows. is the true cost of borrowing or return on saving, and reveals the actual change in purchasing power
aggregate consumption
the aggregation of households’ consumption choices that rely on households’ current income, their expected future income, their current wealth of assets and liabilities, fiscal policies, and their incentives to lend and borrow and their ability to consume.
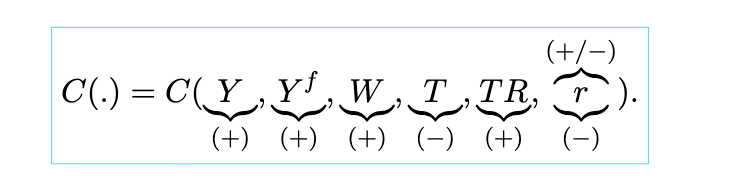
aggregate investment
a function of expected capital good returns, the current capital stock, the depreciation rate, and the real interest rate.
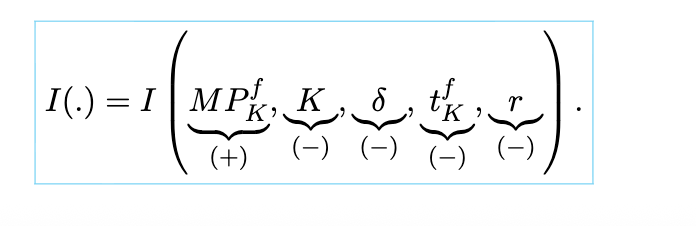
aggregate government spending —> **NEED TO REVIEW
given, the total spending by all levels of government (federal, state, local) on final goods and services, like infrastructure, defense, and public employee salaries.
exports
goods and services produced domestically and sold to foreign countries
imports
goods and services produced abroad and bought by domestic residents, representing an outflow of money from the economy
net exports
sum of exports and imports (usually exports - imports)
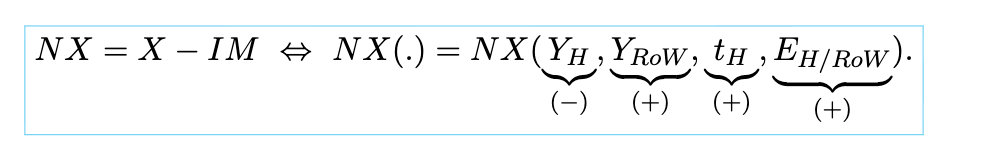
Keynesian cross
Also known as the aggregate expenditure-output model —> derives equilibrium GDP when the price level is constant.
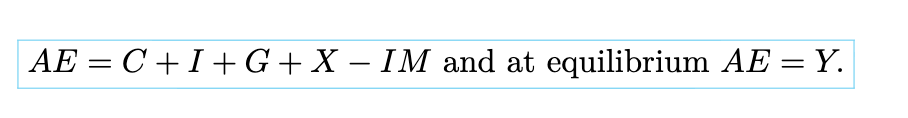
aggregate expenditure function **Check I don’t need to give a verbal definition of this
AE = C + I + G + NX
autonomous spending
Vertical intercept of the Keynesian Cross, where AS, which is spending independent of aggregate income, and m identifies the slope of the aggregate expenditure function related to changes in aggregate income
spending multiplier
illustrates how an additional dollar in expenditures can increase real GDP by more than one dollar —> calculated using marginal propensities and the tax rate
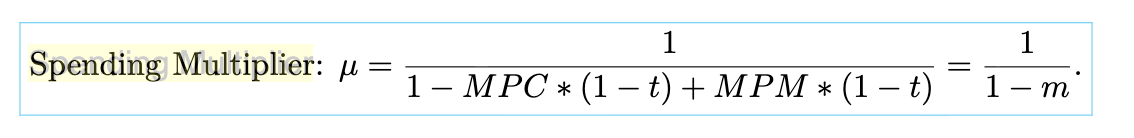
leakages
“leakages” of saving (reducing the marginal propensity of consumption), taxation (larger tax rates and less disposable income), and imports (affecting the negative effect of the marginal propensity of imports)
output gap
the difference between (short-run) GDP and full-employment GDP
recessionary gap
When actual GDP is below potential GDP, Y < Y* —> when actual unemployment exceeds the natural rate of unemployment
inflationary gap
When actual aggregate expenditures and GDP exceed the potential GDP, Y > Y*
Business cycle
short-term fluctuations in aggregate economic activity, employment/unemployment, and interest rates around their long-term trends. In order to understand them, an analysis of supply shocks or demand shocks is needed. They can be caused by either the economy’s demand side or supply side.
aggregate demand (AD)
illustrates the relationship between the economy's price level (index) and the economy's total expenditure for goods and service. It is a negative function of the price level because changes in the price level affect the real interest rate.
aggregate supply (AS)
illustrates the relationship between the economy's price level (index) and the economy's total production of goods and services. There are three types: short-run, medium-run and long-run.
SRAS
Also known as short-run aggregate supply, it follows from the aggregate demand at a constant price level.
MRAS
Known as the medium-run aggregate supply, it follows from price changes, expectations, and firms' actual labor costs.
LRAS
Known as long-run aggregate supply follows from a market-clearing in the labor market and is independent of the price level.
AD-AS model
a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level

money
an asset that serves as a medium of exchange and is used to make payments
monetary base
the sum of currency in the hands of the public and the amount of bank reserves
money supply
The sum of currency in the hands of the public and amount of bank deposits
reserve requirement
the minimum amount of reserves, as a percentage of a bank's deposits, that a central bank mandates a financial institution must hold and not lend out
money creation
the process where the total money supply of a country increases, primarily through commercial banks issuing new loans in a fractional reserve system, and by central banks creating reserves.
money multiplier
The money multiplier expresses the number of dollars of money supply that can be created from each dollar of the monetary base
policy rate —> **CHECK
the key short-term interest rate set by a country's central bank (like the Fed Funds Rate in the U.S.) to steer overall economic activity, influencing borrowing costs for banks, consumers, and businesses to manage inflation, employment, and growth
money neutrality in the long-run
when changes in money supply only affect nominal variables like prices and wages but have no lasting impact on real economic variables (interest rates, output, employment)
monetary stabilization
single vs. dual mandate
single mandate: when central banks are restricted to addressing price stability, dual-mandate when central banks can weigh option of addressing price stability OR economic stability
Philips Curve
a macroeconomic model showing an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation: low unemployment typically means higher inflation (as wages rise with high demand for labor), and high unemployment means lower inflation
bank runs
a self-fulfilling crisis event that happens when many depositors simultaneously withdraw funds due to fear the bank is insolvent, even if it's solvent.