bio 208 lecture exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/238
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:30 PM on 3/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
1
New cards
what is skeletal cartilage surrounded by?
perichondrium.
2
New cards
what is the epiphyseal plate and what cartilage is it made of?
growth hormone; hyaline
3
New cards
what is perichondrium
fibrous-like membrane
4
New cards
what are the three types of skeletal cartilage?
The three types of skeletal cartilage are hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage.
5
New cards
what is another name for the ends of long bones
articular cartilage
6
New cards
where is hyaline cartilage found
articulations (joints), nose, trachea, ribs, bronchi
7
New cards
where is elastic cartilage found
external ear, epiglottis
8
New cards
where is fibrocartilage found?
intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis, menisci
9
New cards
what are the two types of cartilage growth?
appositional and interstitial growth
10
New cards
what is appositional growth?
outward expansion from production of cartilage on the outer surface. (snowballing; adding more to external face)
growth in width
growth in width
11
New cards
what is interstitial growth
growth from within due to division of chondrocytes and secretion of matrix.
growth in length
growth in length
12
New cards
cartilage can be what?
calcified
13
New cards
cartilage hardens but it is not…
bone
14
New cards
functions of skeletal system
○ 1. Support
○ 2. Protection
○ 3. Anchorage
○ 4. Mineral storage
○ 5. Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
○ 6. Triglyceride storage
○ 7. Hormone production
○ 2. Protection
○ 3. Anchorage
○ 4. Mineral storage
○ 5. Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
○ 6. Triglyceride storage
○ 7. Hormone production
15
New cards
what are the 2 divisions of the skeletal system
\
\
axial and appendicular skeleton
16
New cards
what bones does the axial skeleton include
● Vertebrae
● Skull
● Rib cage
● Skull
● Rib cage
17
New cards
● Limbs
● Girdles
● Girdles
what bones does the appendicular skeleton include
18
New cards
bones are what?
organs
19
New cards
bones have what?
different types of tissue
20
New cards
different types of bones:
long, short, flat, irregular bones
21
New cards
what is long bone
■ - longer than wide Ex: Femur
22
New cards
what is short bone
■ somewhat cube-shaped Ex: carpals, patellas
23
New cards
what is flat bone
Thin, flattened Ex: Sternum
24
New cards
■ weird shapes Ex: hip bones, vertebrae
what is irregular bone
25
New cards
what is the structural unit of compact bone
osteon
26
New cards
what are the parts of an osteon and definitions of each part?
● Central canal/ haversian canal - Nerves and blood vessels
● Concentric Lamella - Fill spaces; rings
● Lacunae - House osteocytes
● Canaliculi - Canals that arms of osteocytes sit in; perforating/ volkman canals
● Concentric Lamella - Fill spaces; rings
● Lacunae - House osteocytes
● Canaliculi - Canals that arms of osteocytes sit in; perforating/ volkman canals
27
New cards
what do osteons do
\
\
● Connect blood and nerve supply to periosteum and medullary
28
New cards
what is Circumferential lamellae of compact bone
\
\
● Extend around entire circumference of bone
29
New cards
what is Interstitial lamellae of compact bone
\
\
● Fill in between osteons
30
New cards
whats the main part of spongy bone
■ Trabeculae
31
New cards
what is Trabeculae
● Interspersed with red bone marrow
32
New cards
two parts of flat bone structure
dipole, coverings
33
New cards
what is the dipole of flat bone
● Spongy bone sandwiched between compact bone
34
New cards
what is the PBJ of dipole
○ Bread: compact
○ Peanut butter: spongy
○ Jelly: red bone marrow
○ Peanut butter: spongy
○ Jelly: red bone marrow
35
New cards
what are the coverings of flat bones
periosteum, endosteum, articulations
36
New cards
what is the periosteum layers and what does each layer contain?
○ Outer fibrous layer - Contains sharpey’s fibers that connect to bone
○ Inner osteogenic layer - Contain osteogenic cells
○ Inner osteogenic layer - Contain osteogenic cells
37
New cards
what is the endosteum and what does it contain
○ Also contains osteogenic cells
38
New cards
what are the articulations of coverings of flat bones
● hyaline cartilage (found at sutures)
39
New cards
four structural parts of long bones and description of each? what does the medullary cavity contain
■ Epiphysis - Location: ends of the bone
■ Metaphysis - Location: between epiphysis and diaphysis
■ Diaphysis - Location: shaft of bone; cavity: medullary cavity; Covering: periosteum
■ Epiphyseal plate (growth plate) - Hyaline cartilage
medullary cavity - yellow bone marrow; Covering: endosteum
■ Metaphysis - Location: between epiphysis and diaphysis
■ Diaphysis - Location: shaft of bone; cavity: medullary cavity; Covering: periosteum
■ Epiphyseal plate (growth plate) - Hyaline cartilage
medullary cavity - yellow bone marrow; Covering: endosteum
40
New cards
the four cells of bones
○ Osteogenic/progenitor cells
○ Osteoblasts
○ Osteocytes
○ Osteoclasts
○ Osteoblasts
○ Osteocytes
○ Osteoclasts
41
New cards
what are Osteogenic/progenitor cells
■ Stem cells
42
New cards
description of osteoblasts
■ Bone builders
○ Secrete: Osteoid - *Collagen and calcium binding proteins, Strong but not hard*
○ Secrete: Osteoid - *Collagen and calcium binding proteins, Strong but not hard*
43
New cards
description of Osteocytes
■ Mature bone cells
■ Location: Lacunae
■ Location: Lacunae
44
New cards
description of Osteoclasts
■ Bone breakers/chewers
■ Function: bone resorption
■ Function: bone resorption
45
New cards
what are the organic components of bone
● Cells
● Osteoid
● Osteoid
46
New cards
description of inorganic bone
● Hydroxyapatites - Mineral salts, Calcium phosphate
● Hard and resists compression
● Hard and resists compression
47
New cards
what is ossification
● Bone remodeling; laying down new bones by osteoblasts
48
New cards
what is Endo__chon__dral Ossification
\
\
● Bone tissue replaces hyaline cartilage
● Affects which type of bones? Long bones
● Affects which type of bones? Long bones
49
New cards
steps of endochondral ossification
○ Bone collar forms around diaphysis (shaft) - Primary ossification center
○ Cartilage in diaphysis calcifies - Medullary cavity starts to form
○ Periosteal bud (blood supply); spongy bone forms
○ Secondary ossification center appears in the epiphyses - Medullary cavity is fully formed; Elongation of diaphysis
○ Epiphyses ossifies, leaving hyaline cartilage in the ends aka epiphyseal plate!
○ Cartilage in diaphysis calcifies - Medullary cavity starts to form
○ Periosteal bud (blood supply); spongy bone forms
○ Secondary ossification center appears in the epiphyses - Medullary cavity is fully formed; Elongation of diaphysis
○ Epiphyses ossifies, leaving hyaline cartilage in the ends aka epiphyseal plate!
50
New cards
what is Intramembranous ossification
\
\
● Bone replaces fibrous CT tissue
● Affects which types of bones? Cranial bones and clavicles
● Affects which types of bones? Cranial bones and clavicles
51
New cards
steps of Intramembranous ossification
\
\
○ Ossification center develops with osteoblasts in fibrous CT
○ Osteoblasts secrete osteoid calcifies and are trapped
○ Immature spongy bone; periosteum forms - Blood supply
○ Compact bone replaces immature bone; red marrow develops
○ Osteoblasts secrete osteoid calcifies and are trapped
○ Immature spongy bone; periosteum forms - Blood supply
○ Compact bone replaces immature bone; red marrow develops
52
New cards
what type of growth is Postnatal bone growth
\
\
Growth in length of long bones- Interstitial growth
53
New cards
what are the zones of interstitial growth and description of each?
■ 1. Proliferation zone: growth zone- mitosis, growing on the diaphysis side - Pushing the epiphysis away!
■ 2. Hypertrophic zone: older cells getting bigger; chondrocytes
■ 3. Calcification zone: chondrocytes die; blood vessels invade; matrix calcifies
■ 4. Ossification zone: osteoblasts create new bone
■ 2. Hypertrophic zone: older cells getting bigger; chondrocytes
■ 3. Calcification zone: chondrocytes die; blood vessels invade; matrix calcifies
■ 4. Ossification zone: osteoblasts create new bone
54
New cards
description of the Ossification zone
● Epiphyseal line- no more cartilage, just bone!
● Epiphyseal plate- hyaline cartilage
● Girls are done growing at 18
● Boys are done growing at 21
● Epiphyseal plate- hyaline cartilage
● Girls are done growing at 18
● Boys are done growing at 21
55
New cards
Appositional growth =
growth in width
56
New cards
what is hormonal control
■ Negative feedback loop releases PTH when blood calcium is low
57
New cards
what does hormonal control also contribute to
to the calcium homeostasis:
58
New cards
why is hormonal control important?
● Important because calcium is necessary for many body system including the Nervous System
59
New cards
what is wolf’s law of mechanical stress and an example?
● Bones grow or remodel in response to the demands placed on it
● Ex: Tennis player’s serving arm has thicker bone
● Ex: Tennis player’s serving arm has thicker bone
60
New cards
4 major stages of bone repair and description of each=
1. Inflammatory Stage (When blood vessels are torn, blood is released around the injured site and begins to lead to inflammation). Hematoma!! (a bruise that is formed by a buildup of *a lot* of blood under the skin).
2. Callus is made of fibrocartilage (blue). Blood vessels begin to reform as well.
3. Hard callus forms (yellow).
4. Remodeling of the bone (still has imperfections).

61
New cards

what is Osteomalacia
○ A portion of the bone that is softer than the surrounding bone. Occurs because of poor calcium absorption in the body.
62
New cards
what are rickets
○ Soft and weak bones that are found in children as a result of poor vitamin D intake.

63
New cards
what is Osteo*poro*sis
○ Body loses too much bone and it becomes weak; can fall in (looks porous).
64
New cards
risk factors of Osteo*poro*sis
\- Age (older)
\- Gender (females; older women)
\- Size of body and structure of skeletal system
\- Exercise and diet (lack of)
\- Smoking
\- Gender (females; older women)
\- Size of body and structure of skeletal system
\- Exercise and diet (lack of)
\- Smoking
65
New cards
the three structural classifications of joints:
■ Synovial
■ Fibrous
■ Cartilaginous
■ Fibrous
■ Cartilaginous
66
New cards
what are the joint structural classifications determined by
binding material and whether or not there is a joint cavity
67
New cards
the three Functional Classifications of joints
■ Synarthroses (immovable)
■ Amphiarthroses (slightly movable)
■ Diarthroses (freely movable)
■ Amphiarthroses (slightly movable)
■ Diarthroses (freely movable)
68
New cards
what are fibrous joints connected by
○ dense fibrous connective tissue
69
New cards
what are the three types of fibrous joints and description of each?
■ Sutures - Skull ; Functional classification: synarthroses
■ Syndesmosis - Functional classification: amphiarthrosis ; Connected by ligaments (like between fibula and tibia)
■ Gomphosis - Teeth; Functional classification: synarthroses
■ Syndesmosis - Functional classification: amphiarthrosis ; Connected by ligaments (like between fibula and tibia)
■ Gomphosis - Teeth; Functional classification: synarthroses
70
New cards
what is Cartilaginous connected by
○ cartilage
71
New cards
two types of Cartilaginous and description of each
■ Synchondroses (hyaline cartilage) - Functional classification: synarthrotic ; Epiphyseal plate ; Between manubrium and clavicle
■ Symphysis (fibrocartilage) - Functional classification: amphiarthrotic ; Pubic symphysis; Intervertebral discs
■ Symphysis (fibrocartilage) - Functional classification: amphiarthrotic ; Pubic symphysis; Intervertebral discs
72
New cards
synovial characteristics
■ 1. Joint cavity (articular)
■ 2. Synovial fluid
■ 3. Joint capsule (articular) - Outer fibrous layer; Inner synovial membrane- makes synovial fluid
■ 4. Articular cartilage (hyaline)
■ 5. Nerves and blood vessels
■ 6. Reinforcing ligaments
■ 2. Synovial fluid
■ 3. Joint capsule (articular) - Outer fibrous layer; Inner synovial membrane- makes synovial fluid
■ 4. Articular cartilage (hyaline)
■ 5. Nerves and blood vessels
■ 6. Reinforcing ligaments
73
New cards
what is bursae
● Flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane contains synovial fluid
● To reduce friction
● To reduce friction
74
New cards
what is tendon sheaths
● Cylindrical structures that surround muscle tissue
● Used to reduce friction and made up of synovial membrane to lubricate
● Used to reduce friction and made up of synovial membrane to lubricate
75
New cards
what factors increase stability of synovial joints
\
\
■ 1. Shapes of articular surfaces
■ 2. Number and positioning of ligaments
■ 3. Muscle tone
■ 2. Number and positioning of ligaments
■ 3. Muscle tone
76
New cards
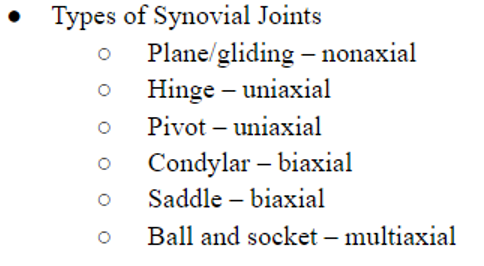
types of synovial joints and description of each
77
New cards
description of TMJ (Temporomandibular joint)
■ Joint type: Modified hinge joint
■ bones that make it up: Condyle of mandible; Mandibular fossa
■. Articular disc - Extension of fibrous layer of articular capsule (meniscus of the jaw)
■ bones that make it up: Condyle of mandible; Mandibular fossa
■. Articular disc - Extension of fibrous layer of articular capsule (meniscus of the jaw)
78
New cards
description of shoulder joint
■ Joint type: Ball and socket joint
■ bones that make it up: Humerus; scapula
■ Many stabilizing ligaments
■ Rotator cuff- group of tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint
■ bones that make it up: Humerus; scapula
■ Many stabilizing ligaments
■ Rotator cuff- group of tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint
79
New cards
description of elbow joint
■ Joint type:Hinge joint
■ bones that make it up: Humerus; Ulna (radius is connected)
■ Supporting tendons and ligaments - Ulnar collateral ligament; Attaches humerus and ulna; Most commonly torn ligament in elbow (tommy john’s)
■ bones that make it up: Humerus; Ulna (radius is connected)
■ Supporting tendons and ligaments - Ulnar collateral ligament; Attaches humerus and ulna; Most commonly torn ligament in elbow (tommy john’s)
80
New cards
description of hip joints
■ Joint type: Ball and socket Joint
■ bones that make it up: Femur; Acetabulum (coxal bone)
■ Acetabular labrum- rim of fibrocartilage surrounding socket
■ bones that make it up: Femur; Acetabulum (coxal bone)
■ Acetabular labrum- rim of fibrocartilage surrounding socket
81
New cards
knee joint description
■ Joint type: Hinge joint
■ bones that make it up: Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Patella
■ 3 different articulations: Femoropatellar joint, Lateral joint, Medial joint - Lateral and medial joint form tibiofemoral joint
■ Menisci (lateral and medial) - Fibrocartilage cushions space between bones; Absorb shock
■ collateral ligaments (extracapsular)
■ Cruciate ligaments - Determined by the attachment to the tibia
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) - Anteriorly attached to Tibia; Prevents tibia from moving too far forward
PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) - Posteriorly attached to tibia; Crosses anterior cruciate ligament; Prevents tibia from moving too far backward
■ Patellar ligaments - Attaches patella and tibia; Involved in the patellar reflex
\
■ bones that make it up: Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Patella
■ 3 different articulations: Femoropatellar joint, Lateral joint, Medial joint - Lateral and medial joint form tibiofemoral joint
■ Menisci (lateral and medial) - Fibrocartilage cushions space between bones; Absorb shock
■ collateral ligaments (extracapsular)
■ Cruciate ligaments - Determined by the attachment to the tibia
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) - Anteriorly attached to Tibia; Prevents tibia from moving too far forward
PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) - Posteriorly attached to tibia; Crosses anterior cruciate ligament; Prevents tibia from moving too far backward
■ Patellar ligaments - Attaches patella and tibia; Involved in the patellar reflex
\
82
New cards
common joint injuries
○ Torn ligament
○ Dislocation (luxation)
○ Sprain ligament
○ Dislocation (luxation)
○ Sprain ligament
83
New cards
what is Bursitis and tendonitis
\
\
■ -itis refers to inflammation
■ Inflammation of bursa
■ Inflammation of tendon or tendon sheath
■ Inflammation of bursa
■ Inflammation of tendon or tendon sheath
84
New cards
what is Osteoarthritis (OA)
\
\
● Arthritis between bones
● Bones directly contact one another (wear and tear)
● Bones directly contact one another (wear and tear)
85
New cards
what is Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
\
\
● autoimmune disorder
● Attacks the Synovial layer (can reduce synovial fluid in capsules- increases friction)
● Attacks the Synovial layer (can reduce synovial fluid in capsules- increases friction)
86
New cards
what is lime disease and an example
○ inflammatory disease
■ Ticks
■ Ticks
87
New cards
● Helpful prefixes that all refer to muscles
○ Sarco
○ Myo
○ mys
○ Myo
○ mys
88
New cards
description of skeletal muscle
■ Found: attached to bones
■ Voluntary
■ Striated
■ Voluntary
■ Striated
89
New cards
description of cardiac muscle
■ Found: only in heart
■ Involuntary
■ Intercalated discs
■ Striated
■ Involuntary
■ Intercalated discs
■ Striated
90
New cards
description of smooth muscle
■ Found: digestive and urinary tract
■ Involuntary
■ Non-striated
■ Involuntary
■ Non-striated
91
New cards

what is Excitability of muscle tissue
\
\
■ Respond to stimulus
92
New cards

what is Contractility of muscle tissue
\
\
■ Shorten forcibly when stimulated
93
New cards

what is Extensibility of muscle tissue
\
\
■ Ability to extend or stretch
94
New cards

what is Elasticity of muscle tissue
\
\
■ Cells are able to recoil
95
New cards
muscle functions
○ Produce movement
○ Maintain posture and body position
○ Stabilize joints
○ Generate heat
○ Support the body
○ Maintain posture and body position
○ Stabilize joints
○ Generate heat
○ Support the body
96
New cards
what are skeletal muscles?
■ Each muscle is vascularized and innervated
97
New cards
what is Epimysium
● - dense irregular CT that surrounds muscle (outermost)
98
New cards
what is Perimysium
● covers fascicle (group of fibers) by a layer of dense irregular CT
99
New cards
what is Endomysium
● wispy sheath CT that surrounds individual muscle fiber (innermost)
100
New cards
○ Microscopic anatomy of muscle
■ Epimysium
■ Surrounds the muscle
■ Perimysium
■ Fascicle
■ Endomysium
■ Individual muscle fibers (actual cells)
■ myofibril
■ Myofilament - Actin & myosin
■ Surrounds the muscle
■ Perimysium
■ Fascicle
■ Endomysium
■ Individual muscle fibers (actual cells)
■ myofibril
■ Myofilament - Actin & myosin