procedures 2 final
1/379
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
380 Terms
C7 vertebra is also known as:
vertebra prominens
Which structures are demonstrated on the lateral swimmer's technique?
lower cervical and upper thoracic
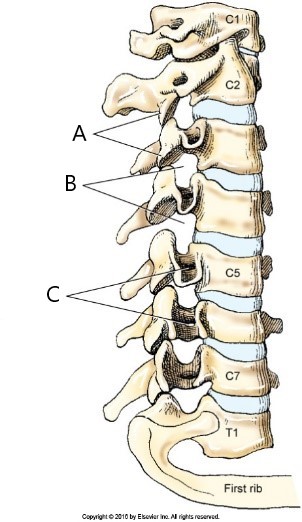
label B
intervertebral foramen
The Dens is located on which structure:
body of C2
The intervertebral foramina of the cervical spine open:
45 degrees anteriorly and 15 degrees inferiorly
Which of the following describes the Fuchs method?
AP, dens
Where is the central ray centered for a hyperflexion or hyperextension lateral cervical spine?
fourth cervical vertebra
Which vertebral process projects laterally and slightly posteriorly from the junction of the laminae and pedicles?
transverse process
The zygapophyseal joints of the thoracic spine form an angle of how many degrees with the midsagittal plane?
70-75 degrees
The part on the lumbar vertebra identified in this figure is the:
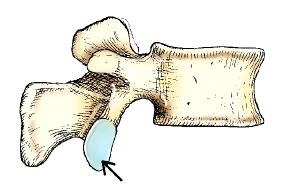
inferior articular process
The x-ray projection demonstrated in this figure is the:
AP, open mouth, atlas and axis
Where is the central ray directed of r a lateral thoracic spine?
level of T7
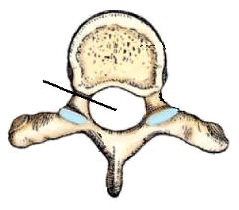
The part identified in this figure is the:
vertebral foramen
Where is the IR centered for a hyperflexion or hyperextension lateral projection of the cervical spine?
fourth cervical vertebra
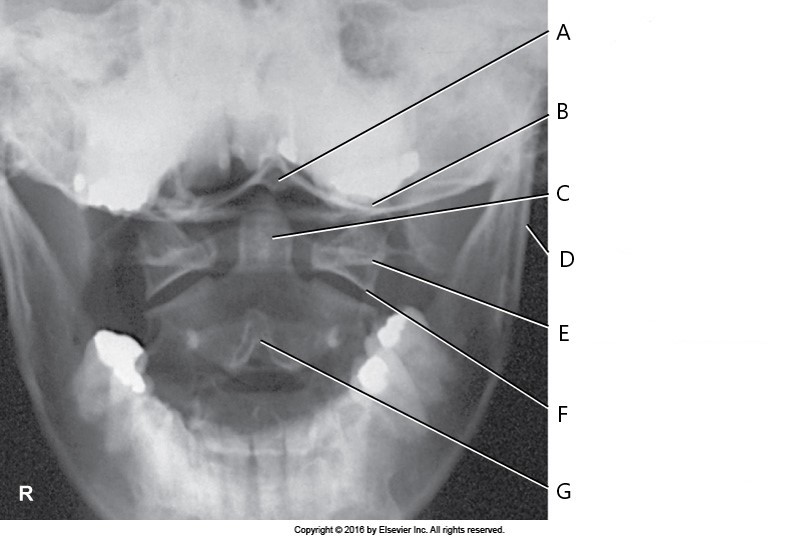
The structure labeled G is:
spinous process of C2
The bony part identified in this figure is the:
lamina
All are functions of the vertebral column, except:
produces cerebrospinal fluid.
Where is the central ray directed for a lateral cervical spine?
fourth cervical vertebra
What positioning maneuver should be used on a lateral projection of the cervical spine to achieve maximum shoulder depression?
suspended respiration after full expiration
What is the central-ray angulation for the AP projection of the dens, Fuchs method?
0 degrees
Which projection should be performed when C7 is not included on the lateral view?
Lateral swimmer's technique
What is the central-ray angle for the AP axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
15-20 degrees cephalad
An abnormal lateral curvature of the spine is termed:
scoliosis
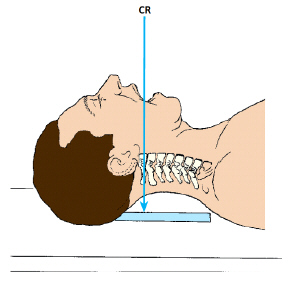
What projection and position are demonstrated in the image below?
left, lateral in hyperflexion
Which intervertebral foramina are demonstrated on an AP axial oblique projection of the cervical spine?
those farthest of the IR
Spinal nerves and blood vessels exit the spinal column through the:
intervertebral foramina
Which two vertebral areas have a kyphotic curve? (Select all that apply.)
thoracic and sacrococcygeal
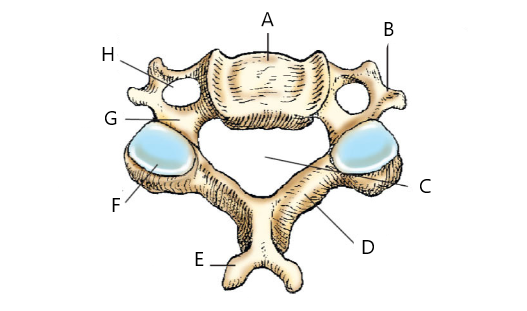
The structure labeled D above is:
lamina
An abnormal increase in the anterior concavity of the thoracic spine is termed:
kyphosis
Where is the IR centered for the lateral projection of the cervicothoracic region (swimmer's technique)?
C7-T1 interspace
Which intervertebral foramina are demonstrated on the PA axial oblique projection of the cervical spine?
those closest to the IR
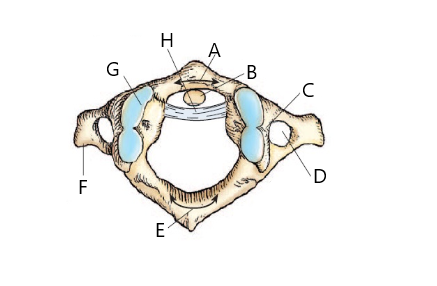
The structure labeled D in the image above is:
transverse foramen
How many vertebrae are there in the sacrum?
5
The respiration phase for the "open mouth" AP projection of the atlas and axis is:
softly phonate "ah" during the exposure
The short, thick processes that project posteriorly on each side of a vertebral body are called the:
pedicles
The intervertebral foramina of the thoracic spine are clearly demonstrated on which projection?
lateral
The second cervical vertebra is called the:
axis
The "swimmers" technique demonstrates the cervicothoracic region in which projection?
lateral
How many vertebrae make up the adult vertebral column?
26
The SID for a lateral cervical spine must be a minimum of how many inches?
72 inches
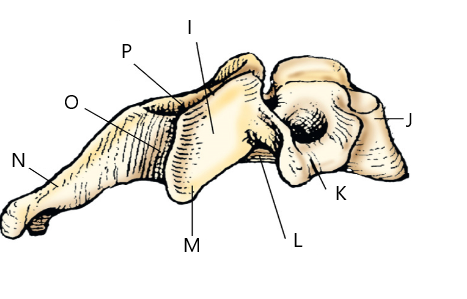
The structure labeled N is:
spinous process
Where is the central ray directed for the AP axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
fourth cervical vertebra
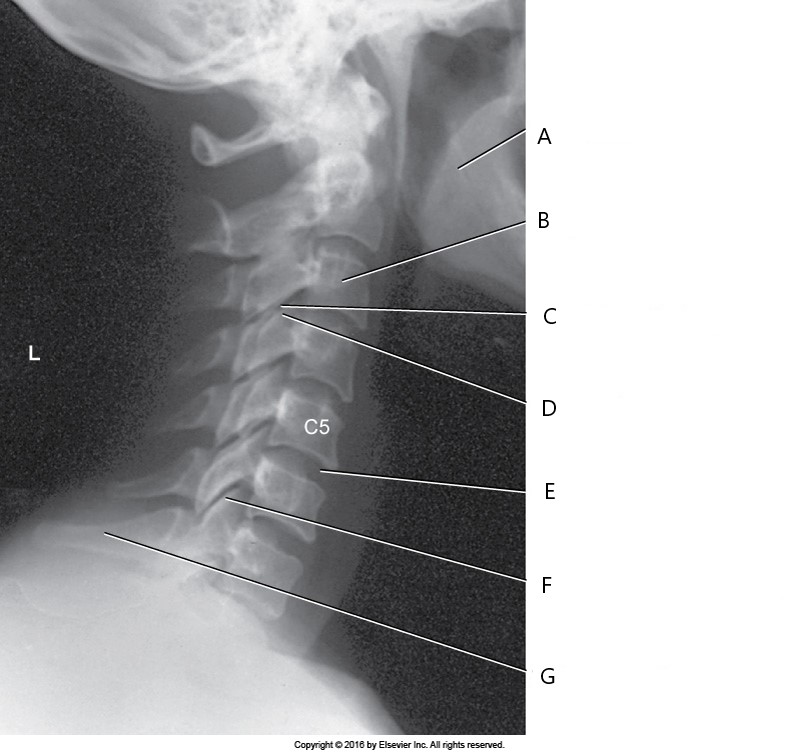
The structure labeled F is:
Zygapophyseal joint C6-C7
How much is the body rotated for a PA axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
45 degrees
When viewed from the side, the vertebral column should present how many curves?
4
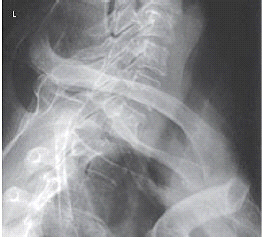
Which projection of the vertebral column is depicted in the figure below?
Lateral cervicothoracic spine
Which vertebral structures unite at the origin of both spinous processes of a typical cervical vertebra?
both lamina
The zygapophyseal joints of the cervical spine and are clearly demonstrated on which projection?
lateral

What dose letter C represent?
transverse process of T8
Which of the following breathing techniques can be used to help improve image quality for a lateral projection of the thoracic vertebrae?
shallow quiet breathing
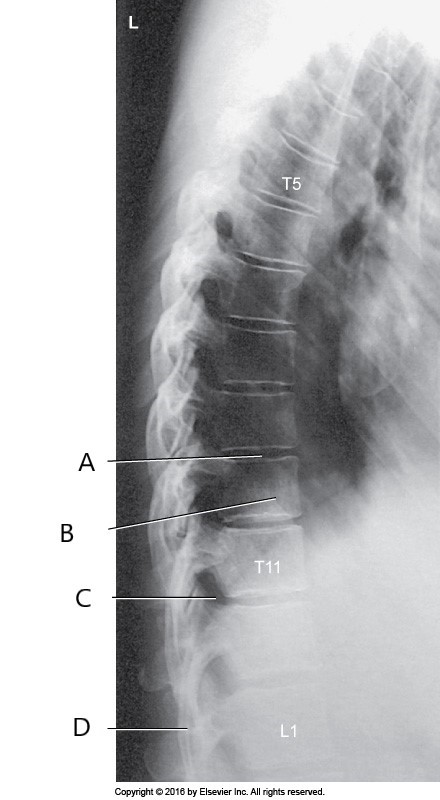
letter C represents?
Intervertebral foramen T11-T12
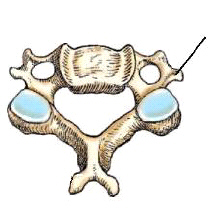
The bony part identified in this figure is the:
transverse process
How should the arms be placed for a lateral projection of the thoracic spine?
at right angles to the long axis of the body
Where is the IR centered for a lateral cervical spine?
fourth cervical vertebra
Which projection best demonstrates the intervertebral foramina of the thoracic region?
lateral projection
The zygapophyseal joints are best demonstrated in the thoracic vertebral column in which projection?
70 degree oblique
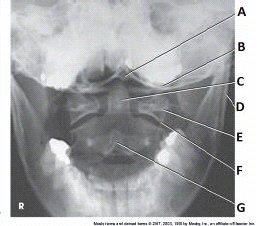
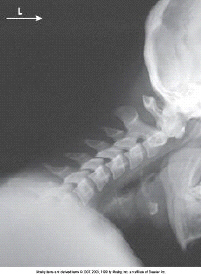
What anatomy is labeled with the letter E in the image below?
lateral mass of C1
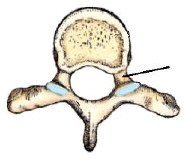
The part identified in this figure is the:
pedicle
The intervertebral foramina of the cervical spine are demonstrated on which of the following projections?
AP axial oblique and PA axial oblique
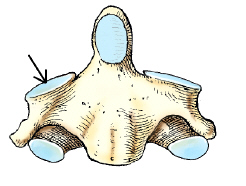
The part identified by the arrow on the vertebra in this figure is the:
superior articular process
The swimmer's technique lateral projection is performed to demonstrate what?
C7
The AP Dens (Fuchs) method is contraindicated if the patient:
has as suspected cervical fracture
Which two vertebral areas have a lordotic curve? (Select all that apply.)
cervical and lumbar
Which position of the Cervical spine best demonstrates the right intervertebral foramina when the CR is angled 15-20 degrees caudad?
RAO
Where is the central ray directed for an "open mouth" AP projection of the atlas and axis?
perpendicular through open mouth
An abnormal lateral curvature of the spine is termed:
scoliosis
What is the central-ray angle for the PA axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
15 to 20 degrees caudad
An abnormally increase in anterior convexity of the lumbar spine is termed:
lordosis
Which position of the cervical spine best demonstrates the left intervertebral foramina when the CR is angled 15-20 degrees cephalad?
RPO
What is the central ray angle for an AP thoracic spine?
0 degrees
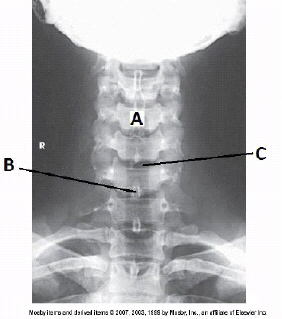
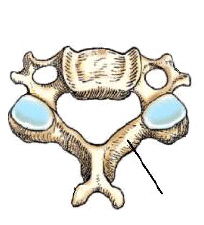
What is the projection and anatomy of interest in the figure below?
AP axial C-spine
Where is the central ray directed for a PA axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
fourth cervical vertebra
Where should the superior edge of the IR be placed for an AP projection of the thoracic vertebrae
1 ½ to 2 inches above the shoulders
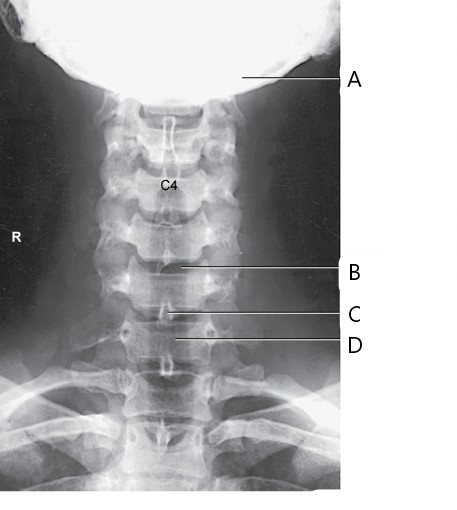
The structure labeled B in the image above is
intervertebral disk space of C5-C6
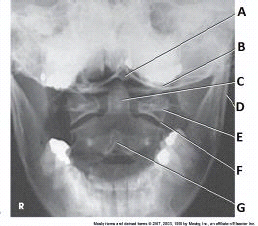
What anatomy is labeled with the letter C in the image below?
dens of C2
In which cervical vertebral structures are perforated with a foramen for the passage of the vertebral artery and vein?
transverse process
The articulations between the articular processes of the vertebral arches are called the _____ joints.
zygapophyseal
For which projection is the patient instructed to softly phonate "ah" during the exposure?
AP “open mouth” atlas and axis
How much is the body rotated for an AP axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
45 degrees
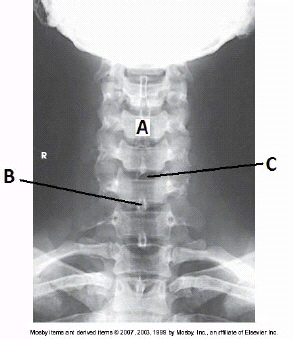
How is the central ray directed to obtain this image?
15 to 20 degrees cephalad
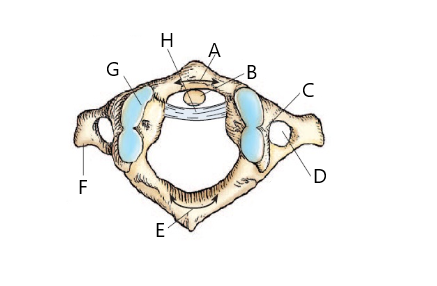
The structure labeled A is:
anterior arch of atlas
The First cervical vertebra is called the:
atlas
The respiration phase for a lateral cervical spine is:
suspended on full expiration
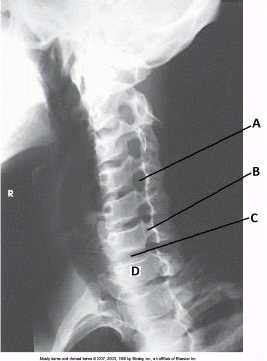
What anatomy is labeled with the letter A in the image below?
intervertebral foramen of C4-C5
The central-ray angle for an AP axial cervical vertebrae is:
15 to 20 degrees cephalad
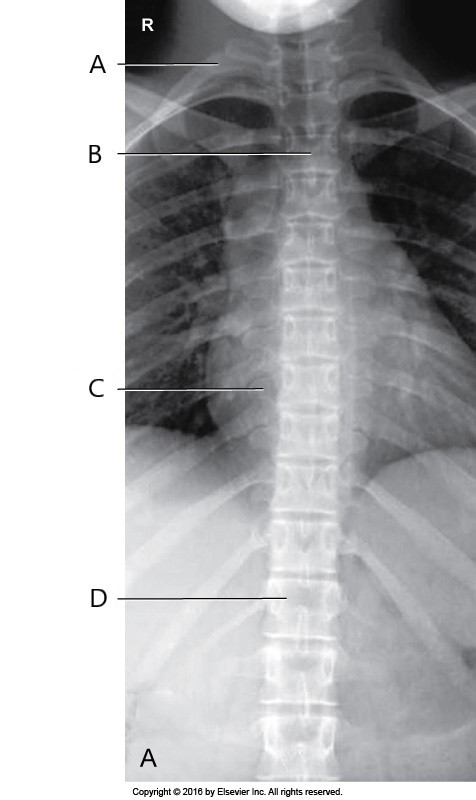
What does letter D represent?
T12
Where is the CR centered for an AP axial cervical spine?
fourth cervical vertebra
Which of the following should be performed to reduce the lordotic curvature of the lumbar spine for the AP projection?
flex the hips and flex the knees
Where is the central ray directed for an AP lumbar spine using a 11 x 14 Image Receptor when only the lumbar region is of interest?
L3
Where is the IR centered for an AP projection of the lumbosacral spine using a 14 x 17 Image Receptor?
iliac crests
The phase of respiration for an AP projection of the lumbar spine is:
suspend on expiration
Which of the following planes is placed perpendicular to the tabletop and centered to the midline of the grid for a lateral lumbar spine?
midcoronal plane
Which of the following devices can be used to perform a lateral projection of the lumbar spine?
radiolucent support sponge and sheet of leaded rubber
Where is the (14 x 17 inch IR) central ray directed for a lateral lumbosacral spine?
iliac crests
Which of the following describes the central ray centering point for the L5-S1 lateral projection?
2 inches posterior to the ASIS and 1 ½ inches below the iliac crest
When the spine cannot be placed in a true horizontal position for the L5-S1 lateral projection, the central ray must be angled:
5 degrees men, 8 degrees women – caudad
Which of the following is the preferred essential projection used to demonstrate the zygapophyseal joints of the lumbar spine?
AP oblique, RPO and LPO position
To demonstrate the zygapophyseal joints of the lumbar spine, the patient angle is:
45 degrees
Which zygapophyseal joints are demonstrated on the AP oblique projection of the lumbar spine?
joint closest to the IR
Where is the longitudinal plane of the lumbar spine positioned for the AP oblique projection?
2 inches medial to the elevated ASIS