Chapter 7: Inside the Cell (Final)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio 205 (146 – 161, skip 7.5 and 7.6)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
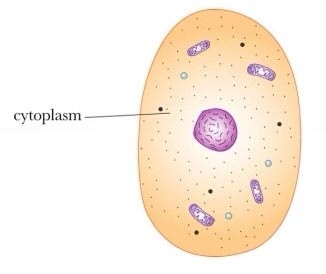
Cytoplasm
all contents inside of cell membrane, including organelles but no the nucleus
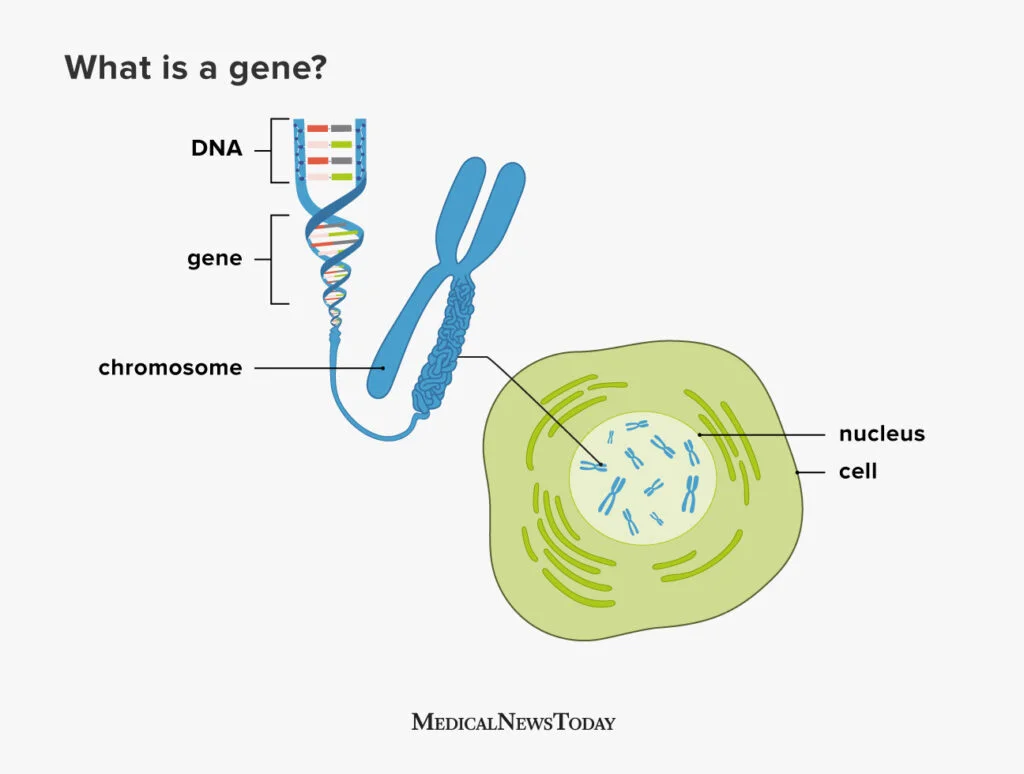
Genes
located on chromosomes, specific segments of DNA (or a sequence of nucleotides) that contain hereditary information for building functional RNA’s
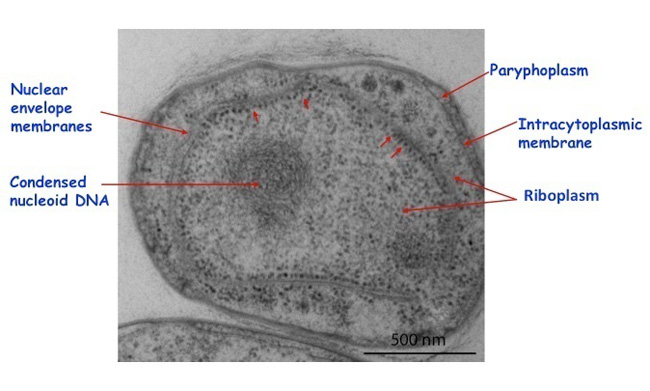
nucleoid
region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material
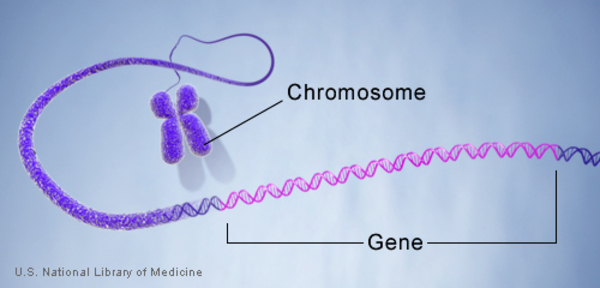
Chromosomes
threadlike structure of DNA and protein that carry genetic information
Plasmids
small, usually circular, supercoiled DNA molecules. Different than chromosomes, help to adapt under unusual circumstances
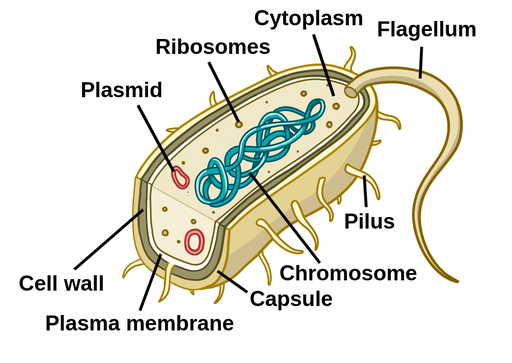
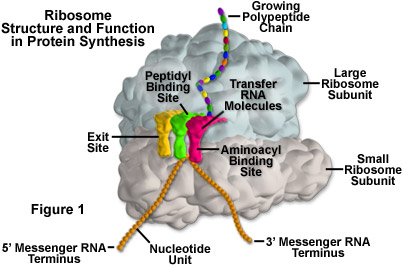
Ribosomes
molecular machines that are responsible for protein synthesis/translating RNA (2nd part of the central dogma)
Scattered in cytosol in the millions
composed of large and small subunits, each of which contains RNA (stores info to synthesis proteins) and protein molecules
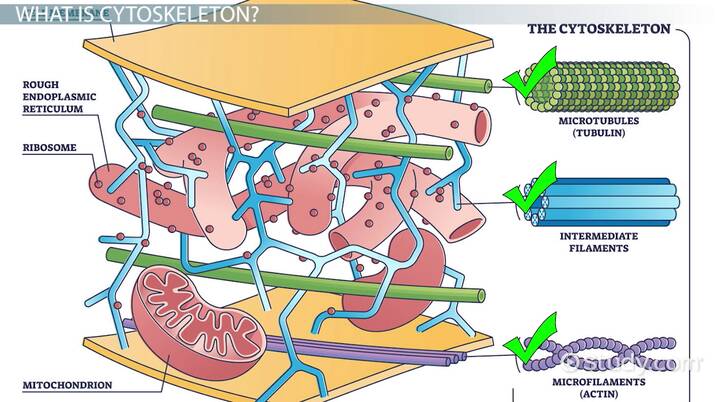
Cytoskeleton
web of protein filaments which provide structural support, helps with cell movement, and facilitates the transport of organelles
actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
Organelles
internal compartments in cells with enzymes or structures for specialized tasks, often bound by membrane
EX) nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus
Nucleus
membrane bound compartment where where eukaryotic chromosomes are enclosed
Enclosed in unique double-membrane structure called the nuclear envelope
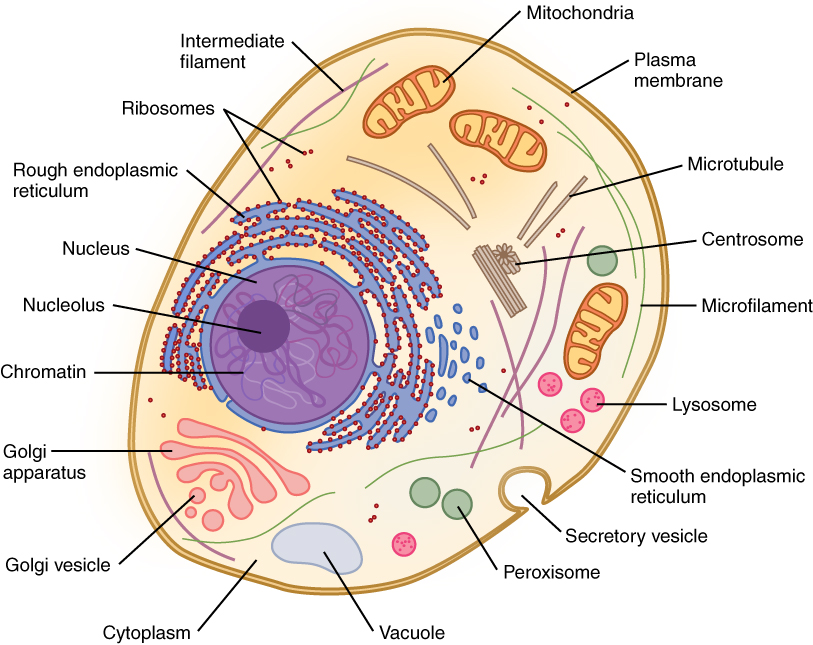
endoplasmic reticulum
A portion of the nuclear envelope extends to a cytoplasmic membrane-enclosed factory (organelle). involved in protein and lipid synthesis
has two parts
Rough ER (RER): Lined by knobby-looking ribosomes for protein production
Smooth ER (SER): Involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage
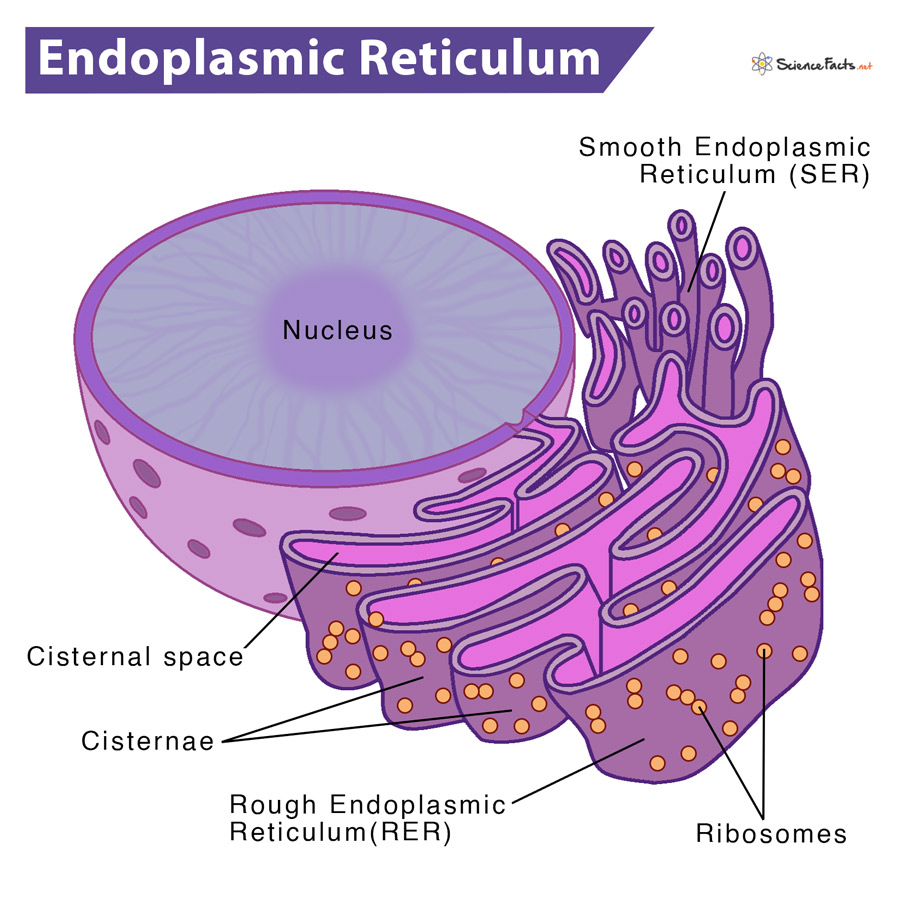
Lumen
interior if any sac-like structure in cell / body
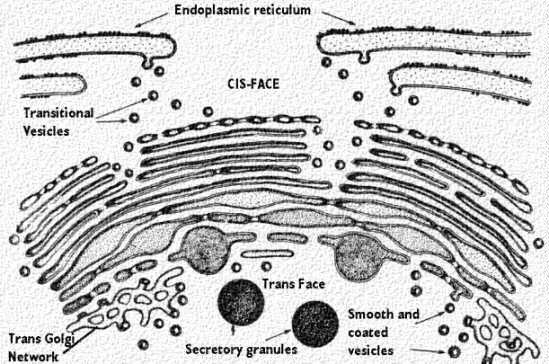
Golgi apparatus
stack of membranous sacks called cisternae that process, sort, and packag proteins and lipids into vesicles
Proteins that leave the RER go into the golgi apparatus
Cis: closest to nucleus
Trans: surface oriented toward plasma membrane
Lysosomes
contain digestive enzymes enclosed in a single membrane that help with breaking down worn-out cell parts and killing viruses/bacteria
digestion and recycling centers, part of the endomembrane system
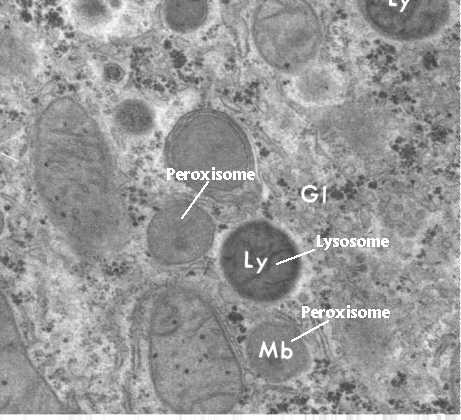
Peroxisomes
globular organelles, centers for reduction-oxidation reactions with fatty acids/ethonal/etc. which detoxify reactive molecules
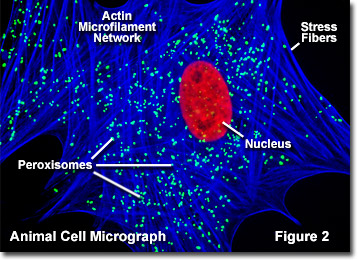
mitochondria
Makes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) with carbs and fats, which stores the chemical energy needed to maintain structure and function of cell
Has two membranes, inner (saclike series of cristae) and outer (cell surface)
solution enclosed within the inner membrane is called the mitochondrial matrix
chloroplast
double membrane plus membrane-bound sacs
production and sugars via photosynthesis
Surrounded by double membrane with a third membrane inside that forms flatten-sac-like structures called thylakoids
Arranged in connected stacks called grana
Stroma: fluid-filled space in between the grana, which contain enzymes that use chemical energy to produce sugars

cytoskeleton
actin filaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
structural support, movement of materials or cell
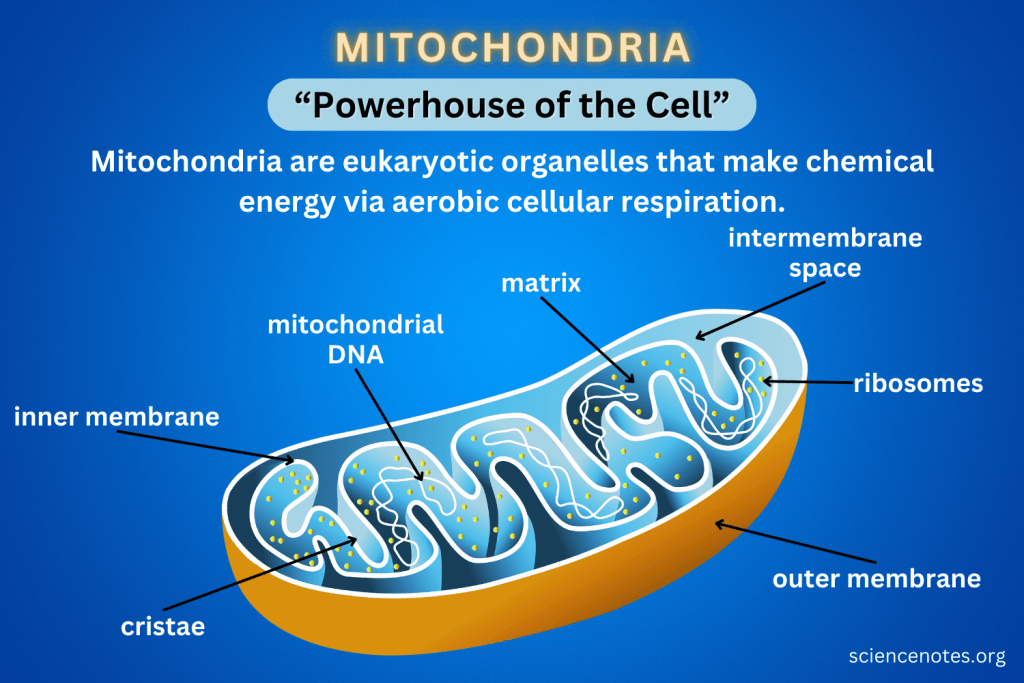
plasma membrane
protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment
phospholipid bilayer with transport and receptor proteins
has selective permeability
cell wall
outer layer outside the cell membrane
fibers running through carbs or protein matrix
protection, structural support
ONLY IN PLANT CELLS
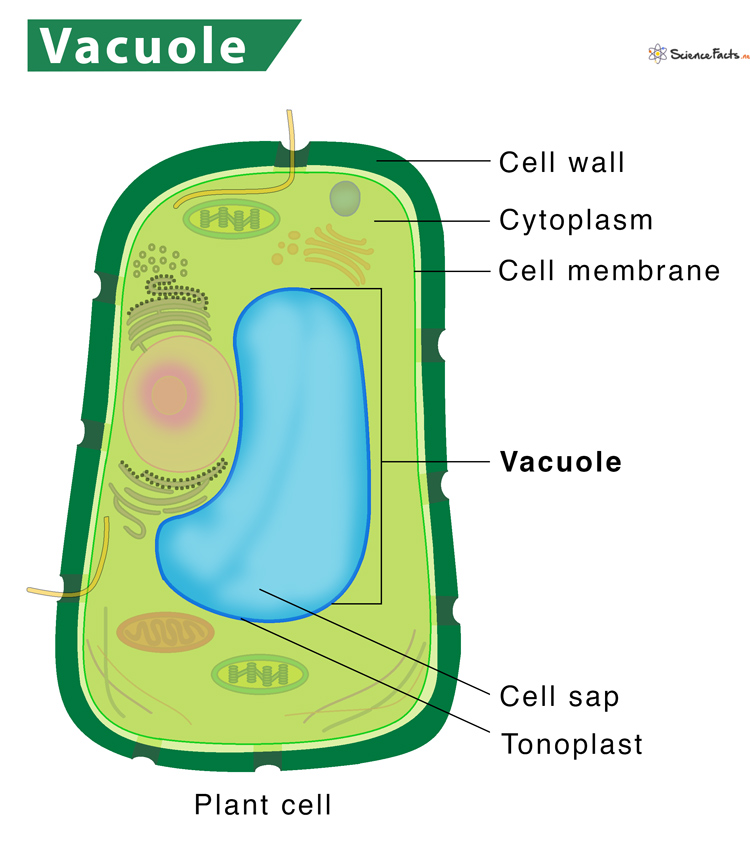
Vacuoles
membrane-bound comparements in cells that store carbs, water, pigments, oils, toxins, or hydrolases
storage, digestion, recycling
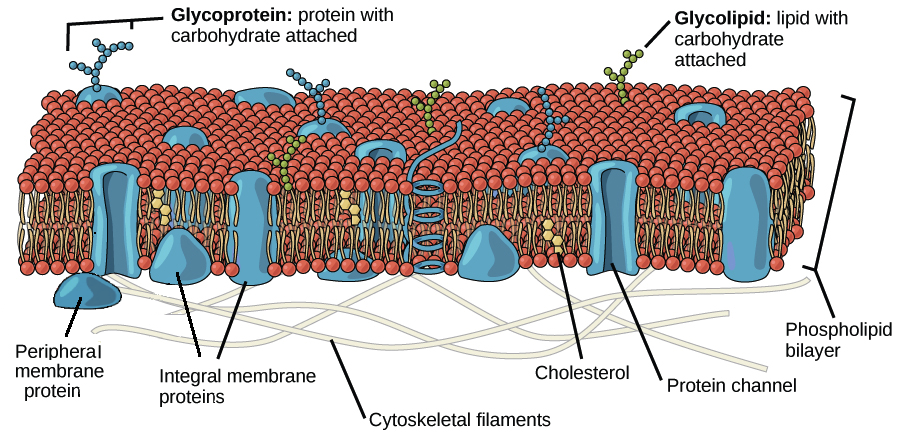
Phospholipid Bilayers
thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules
Phospholipids have hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic tail consisting of two fatty acid chains
All Cells have
a plasma membrane, which is the outer layer that separates the cell’s interior from its surrounding environment;
cytoplasm, which consists of the jelly-like cytosol inside the cell, plus the cellular structures suspended in it;
genetic material in the form of DNA; and
ribosomes, which are structures that build the cell’s proteins.
eukaryotic
membrane-bound organelles like a nucleus
are larger
Eukaryotes include both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Multicellular eukaryotes are made up of many eukaryotic cells

Prokaryotic
lack membrane-bound organelles.
have nucleoid, a region in the cell where the genetic material is located
genetic material typ. located in circular chromosomes
typically unicellular organisms but can live in groups
