biology biological molecules
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
covalent bonding?
atoms share a pair of electrons in their outer shells. as a result the outer shell of both atoms is filled and a more stable compound (molecule) is formed
ionic bonding?
ions with opposite charges attract one another. this electrostatic attraction is known as an ionic bond. these are weaker than covalent bonds
hydrogen bonding?
the electrons within a molecule arent evenly distributed but tend to spend more time at one position. this region is more negatively charged than the rest of the molecule. this molecule with uneven charge is said to be a polar molecule. the negative region and the positive region attract each other, forming a weak electrostatic bond - collectively form strong forces
polymerisation?
when lots of monomers join together to form long chains known as polymers
industrial polymers?
polythene and polyesters
natural polymers?
polysaccharides, polypeptides and polynucleotides
condensation reaction?
in the formation of polymers, each time a new subunit is attached a water molecule is formed
hydrolysis reaction?
polymers being broken down through the addition of water. the water molecules are used when breaking bonds that link the subunits of a polymer, thereby splitting the molecule into its constituent parts
metabolism?
all the chemical processes that take place in living organisms
what does 1 mole contain?
the same number of particles that there is in 12g of carbon12 atoms - 6.022×10²³
whats a molar solution?
a solution that contains one mole of solute in each litre of solution
what are organic molecules?
carbon containing molecules
monomer?
each individual molecule that makes up chains
what elements are polymers and monomers made of mainly?
C, H, N, O
whats the basic monomer in a carbohydrate?
sugar/ saccharide - single monomer = monosaccharide
monosaccharide x 2 =?
disaccharide
monosaccharide x n =?
polysaccharide
general formula of monosaccharides?
(CH2O)n
properties of monosaccharides?
-sweet tasting
-soluble
-3-7 carbons
examples of monosaccharides?
glucose, galactose, fructose
glucose info:
hexose (6 carbon)
sugar
C6H12O6
2 isomers - alpha glucose and beta glucose
what is a reducing sugar?
a sugar that can donate electrons to another chemical
test for reducing sugar?
benedicts test (CuSO4)
add 2cm³ benedicts reagent to food sample
heat above 70 degrees C
present result for reducing sugars?
green, yellow, orange, brick red (low to high conc)
glucose x 2 =?
maltose
glucose + fructose =?
sucrose
glucose + galactose =?
lactose
what is removed when 2 monosaccharides join?
water (condensation reaction)
what bond is formed when 2 monosaccharides join?
glycosidic bond
how do you hydrolyse a disaccharide?
add water. it will break the glycosidic bond and release the monosaccharides
how to test for NON reducing sugars?
liquidify the sample
add 2cm³ of benedicts reagent to 2cm³ sample
place in water bath >70 for 5 mins (no colour change = no reducing sugar present)
add 2cm³ HCl and place in water bath again for 5 mins (HCl will hydrolyse any disaccharides)
add NaHCO3 until solution is alkaline
retest with benedicts reagent (colour change now = non reducing sugar present)
polysaccharide properties:
insoluble
suitable for storage/ strength
break down into di/monosaccharides when hydrolysed
example of polysaccharide?
starch: many alpha glucose molecules joined together
test for starch?
2 drops of iodine solution to food sample and mix gently
presence of starch result?
blue-black
how is starch found in plants?
small grains in seeds and storage organs
whats starch made up of?
chains of alpha glucose monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds formed from condensation reactions
what are the chains like in starch
some branched, some unbranched. the unbranched chain is wound into a tight coil → makes compact
starch properties:
insoluble → doesnt affect water potential
doesnt diffuse out of cells as large and insoluble
compact
can hydrolyse to form alpha glucose (easy to transport and use in respiration)
the branched form has many ends which can be acted on by enzymes simultaneously meaning that glucose monomers are released rapidly
is starch found in animal cells?
no
wheres glycogen found?
animals and bacteria, NEVER plants
whats the difference in structure between starch and glycogen?
glycogen structure has shorter chains and is more highly branched
where is glycogen stored?
as small granules mainly in the muscles and the liver
glycogen properties and structure:
insoluble so doesnt tend to draw water into cells by osmosis
doesnt diffuse out of cells
compact
more highly branched than starch and so has more ends that can be acted on simultaneously by enzymes. It is therefore more rapidly broken down to form glucose monomers which are used in respiration - important to animals which have a higher metabolic rate
how does cellulose differ from starch and glycogen?
made of monomers of B- glucose
cellulose structure and properties:
straight, unbranched chains which run parallel to each other, allowing hydrogen bonds to form cross linkages between adjacent chains
the mass number of the bonds adds a considerable amount of strength to cellulose, making it a good valuable structure
structure of a cellulose molecule diagram
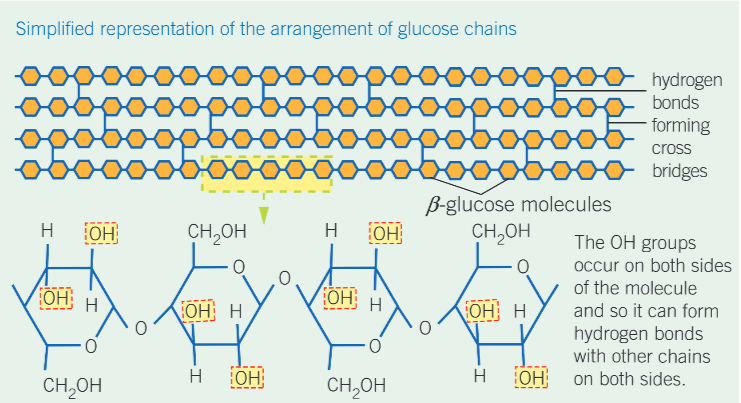
what do cellulose molecules form when grouped together?
microfibrils, which in turn are arranged in parallel groups called fibres
what does cellulose provide form cell walls?
rigidity. it also prevents the cell from bursting as water enters it by osmosis, by exerting an inward pressure that stops any further influx of water
what is celluloses functions important for?
maintaining stems and leaves in a turgid state so they can provide the max surface area for photosynthesis
what properties do all lipids share?
contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
insoluble in water
proportion of oxygen to carbon and hydrogen is smaller than in carbohydrates
soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone
what are the main groups of lipids?
triglycerides and phospholipids
what are the roles of lipids?
in cell membranes
source of energy
waterproofing
insulation
protection
role of lipids: cell membrances?
phospholipids contribute to the flexibility of membranes and the transfer of lipid-soluble substances across them
role of lipids: source of energy?
when oxidised, lipids provide more than twice the energy as the same mass of carbohydrate and release valuable water
role of lipids: waterproofing?
lipids are insoluble in water and therefore useful as a waterproofing. both plants and insects have waxy, lipid cuticles that conserve water, while mammals produce an oily secretion from the sebaceous glands in the skin
role of lipids: insulation?
fats are slow conductors of heat and when stored beneath the body surface help to retain body heat. they also act as electrical insulators in the myelin sheath around nerve cells
role of lipids: protection?
fat is often stored around delicate organs, like the kidney
fats vs oils storage?
fats: solid at room temp
oils: liquids
why are triglycerides called triglycerides?
3 (tri) fatty acids combined with glycerol (glyceride)
what does each fatty acid form with glycerol?
an ester bond in a condensation reaction
what does hydrolysis of a triglyceride therefore produce?
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what do differences in triglycerides come from?
the different properties of different fats and oils from the variations in fatty acids
how many fatty acids are there?
>70
what does each fatty acid have?
a carboxyl group with a hydrocarbon chain attached
saturated meaning?
no carbon=carbon double bonds - saturated with hydrogen atoms
mono-unsaturated meaning?
a single double bond
polyunsaturated meaning?
more than one double bond
why are triglycerides a good source of energy?
they have a high ratio of energy storing carbon-hydrogen bonds to carbon atoms
why are triglycerides good storage molecules?
they have a low mass to energy ratio, so lots of energy can be stored in a small volume. this is especially beneficial to animals as it reduces the mass they have to carry as they move
why are triglycerides insoluble in water?
they are large, non polar molecules, meaning their storage doesnt affect osmosis/ water potential as a result
why do triglycerides release water when oxidised?
they have a high ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, providing an important source of water
whats a phospholipid?
similar to a lipid except one of the fatty acid molecules is replaced with a phosphate molecule
what is a phospholipid made up of?
2 parts as fatty acids repel water, while phosphate molecules attract water
whats the head?
a hydrophilic head: interacts with water (is attracted to it) but not with fat
whats the tail?
a hydrophobic tail which orients itself away from water but mixes with fat
what does this mean a phospholipid is called?
polar
what does the polarity of a phospholipid mean?
when placed in water they position themselves so that the hydrophilic heads are close to the water and the hydrophobic heads are far away from the water
what does the phospholipids polarity mean related to its properties?
in an aqueous environment, phospholipid molecules form a bilayer within the cell surface membranes. As a result, a hydrophobic barrier is formed between the inside and outside of a cell
what does the hydrophilic phosphate head help do?
hold at the surface of the cell surface membrane
what does the phospholipid structure allow?
glycolipids to form by combining with carbohydrates within the cell surface membrane
what are glycolipids important in?
cell recognition
what is the lipid test? (steps)
take a completely dry and grease free test tube
to 2cm³ of sample being tested, add 5cm³ of ethanol
shake test tube to dissolve any lipid in sample
add 5cm³ of water shake gently
a milky white emulsion indicates the presence of a lipid
as a control, repeat the procedure using water, which should remain clear
whats the lipid test also known as?
the emulsion test
why does lipids turn cloudy in the test?
the lipid is finely dispersed in the water to form an emulsion. light passing through this emulsion is refracted as it passes from oil droplets to water droplets, appearing cloudy
what are amino acids?
the basic monomer units which combine to make a polymer called a polypeptide
what can polypeptides be combined to form?
proteins
how many of the 100 amino acids identified occur naturally in proteins?
20
what does the fact that the same 20 amino acids occur in all living organisms provide evidence for?
evolution
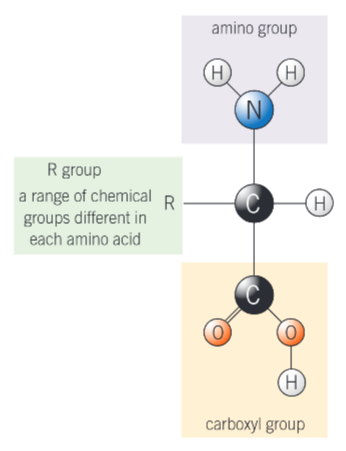
what does every amino acid have?
a central carbon atom to which are attached 4 different chemical groups
what are these 4 chemical groups?
amino group (NH2)
carboxyl group (COOH)
hydrogen atom (H)
R (side) group) - variety of different chemical groups
whats the general structure of an amino acid?
what is the type of reaction that occurs when amino acids monomers combine to form a dipeptide?
condensation reaction ( water is lost )
how is the water made?
combining an -OH from the carboxyl group of one amino acid with an -H from the amino group of another amino acid
what do the 2 amino acids then become linked by?
a new peptide bond between the carbon atom of one amino acids and the nitrogen atom of the other
how can the peptide bond be broken down to give back its 2 constituent amino acids?
hydrolysis
what is the process by which many amino acid monomers join?
polymerisation- giving a long chain of amino acids called a polypeptide
what does the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain form?
the primary structure of a protein
what is this sequence of amino acids determined by?
DNA
why are there limitless types of primary protein structure?
due to to mass number of possible sequences of the 20 naturally occuring amino acids