Organic/Structure and bonding Reagents, Distinguishing & Reactions
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
H2 (with Pt, Ni catalyst or heat)
ADDITION - double bond breaks and adds 2 H
Br2
ADDITION - Alkanes to Haloalkanes (add two Br)
SUBSITION - Alkane to Haloalkane (two H is replaced by two Br)
Cl2
ADDITION - Alkenes to Haloalkanes (add two Cl)
HBr
ADDITION - Alkene to Haloalkane (Adds H and Br)
H+/H20
ADDITION -Alkene to Alcohol (adds H and OH)
H+/MnO4-
ADDITION - Alkene to diol (two OH is added) this can also be considered as oxidation
OXIDATION - Alcohol to carboxylic acid (OH turns into COOH) purple to colourless
KOH(aq)
SUBSITION - haloalkane to alcohol (atom/group is swapped to OH)
PCl3, PCl5, SOCl2
SUBSITION - replaces OH with Cl
NH3
SUBSTITUTION - alkane to amine (replaces H with NH2
Conc. H2SO4
ELIMINATION - Alcohol to alkene (one H and OH is removed and double bond is formed)
KOH(alc)
ELIMINATION - Haloalkane into alkene (group like Cl is removed and H and double bond is formed)
H+/Cr2O7^2
OXIDATION - Alcohol to Carboxylic Acid (OH to COOH) orange to green
Ca2Co3
Acid Base - Calcium Carbonate. turns COOH to COO- + Co2 + H2O
Na2CO3
Acid Base - Sodium Carbonate. COOH to COO- + CO2 + H2O
What needs to be present in a monomer
C=C double bond must be present in a ________
Polymer definition
monomers joint together without the double bond with ~ on both ends
Acidified Dichromate + Heat
Alcohol present (turns green) or stays orange if nothing
Damp Red Litmus
Amine present (turns blue) or stays red if nothing
Damp Blue Litmus
Carboxylic Acid present (turns red) stays blue if nothing
Acidified Permanganate + Heat
Alkene (to form diol) or Alcohol present (turns colourless) stay purple if nothing.
Bromine Water
Alkene present (colourless rapidly) or Alkane (colourless slowly in UV light) or stays orange if nothing
Sodium Carbonate Solution
Carboxylic Acid (fizz) or no fizz if nothing
Water Layers?
1 or 2 layer
Alcohol, Amine & Carboxylic Acid
1 layer
Alkene, Alkane, Alkyne & Haloalkane
2 Layers
Geometric Isomer
Each carbon must have different atoms attachede to it and a C=C double bond is present to prevent rotation for it to exist as a geometric isomer
Order of prefixes (meth, eth, etc)
Meth, Eth, Prop, But, Pent, Hex, Hept, Oct
Chloro
Chlorine, Cl
Bromine
Bromo, Br
Fluorine
Fluoro, f
Iodine
Iodo, I
HOW to get acid base reaction?
Mix any acid and base together. Common for carboxylic acid to react with an amine
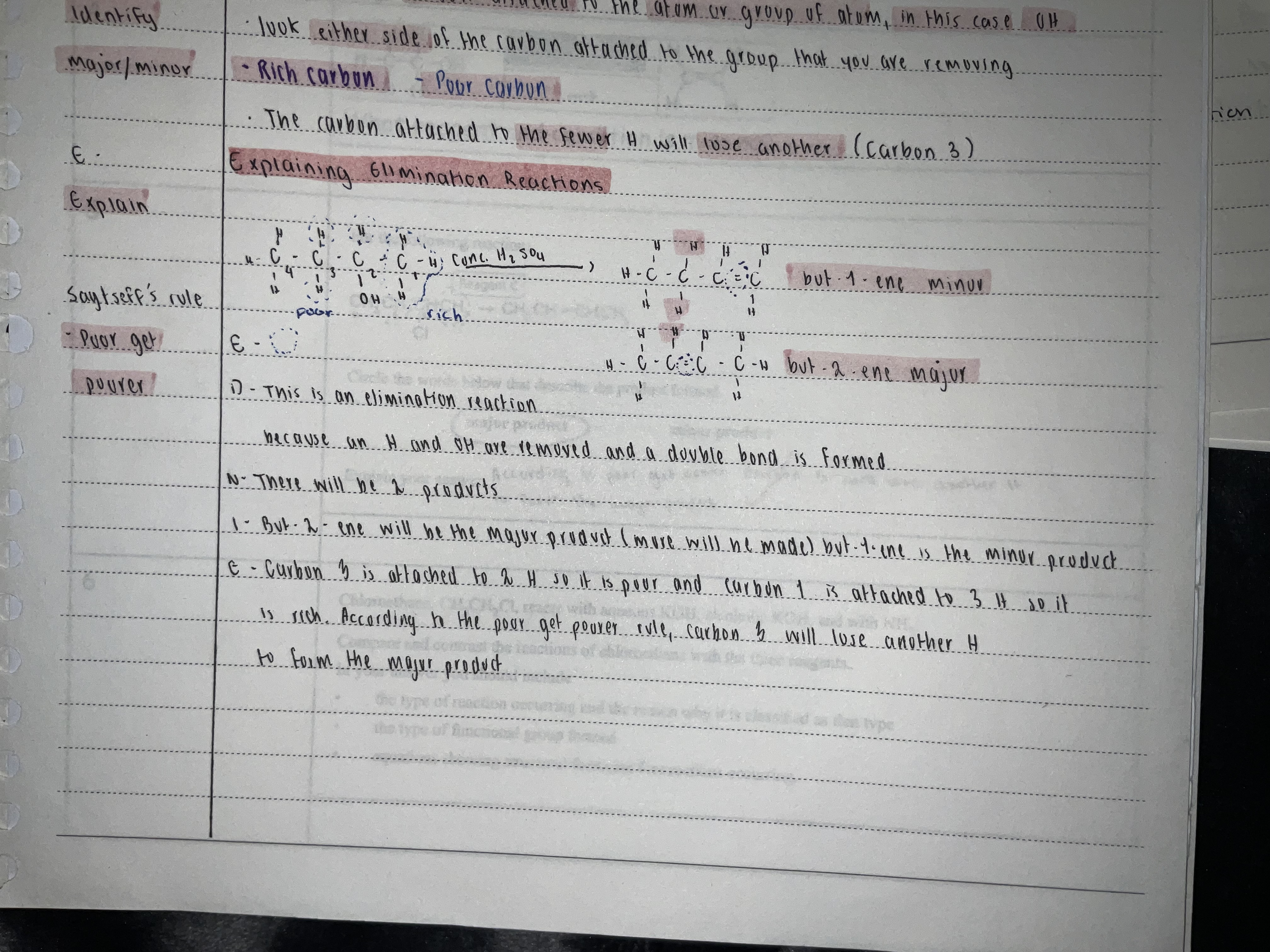
Acronym for Elimination reaction
EDNIE
E - equation
D - define (elimination)
N - number of products (if symmetrical one products if asymmetrical two product if one of each then one product)
I - identify major and minor products
E - Explain
Classification
Primary Alcohol - Alcohol is connected to a carbon that is connected to ONE CARBON
Secondary Alcohol - Alcohol is connected to a carbon that is connected to TWO CARBON
Tertiary Alcohol - Alcohol is connected to a carbon that is connected to THREE CARBON
Acronym for ADDITION
ESNIDE
E - Equation
S - Symmetry (If symmetrical one products if asymmetrical two product if one of each then one product)
N - number of products
I - Identify major and minor
D - Define (Addition)
E - Explain

Oxidation reaction
Addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen
Addition reaction
A C=C double bond breaks and 2 atoms or group of atoms are then attached to the carbons
Substitution reaction
One atom or group of atoms is swapped for another
WHAT is Acid Base reaction
reaction that occurs between an acid and a base (acid gives H to the base)
Elimination reaction
When 2 atoms or group of atoms are removed and a C=C double bond is formed
acronym for polarity
R - regions of electron density (negative charge)
S - shape of molecule
B - bond dipoles
B - bonding regions
D - dipoles cancel
VSEPR
R - regions of electron density
R - repulsion
S- shape
Acronym for types of solids
S - state the solid
S - structure
P - properties
Molar Mass
g mol^-1
Mass
g
Energy
KJmol-1
moles
n, n=m/M
Acidified dichromate
orange to green, Cr2O7²-
Acidified Permanganate
purple to colourless, MnO4^-
Metallic Solid
ONLY metal
metallic atoms held by strong metallic forces and metallic atoms are surrounded by delocalised electrons that are free to move around the structure
molecular solid
ONLY non metals and not in the covalent list
made up of molecules held by weak intermolecular forces
Ionic
Metallic WITH non metal
made up ions which are permanent charge either + or - held by strong ionic forces
Covalent network
SiC, SiO2, C (Diamond), C (Graphite), Si
Carbon atoms. Held by strong covalent forces