Genetics: Meiosis, Karyotypes, and Mendelian Genetics
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Meiosis
Two-step cell division producing gametes.
Mitosis
Cell division creating two identical daughter cells.
Sister Chromatids
Identical halves of a duplicated chromosome.
Homologous Chromosomes
Similar, non-identical chromosome pairs from parents.
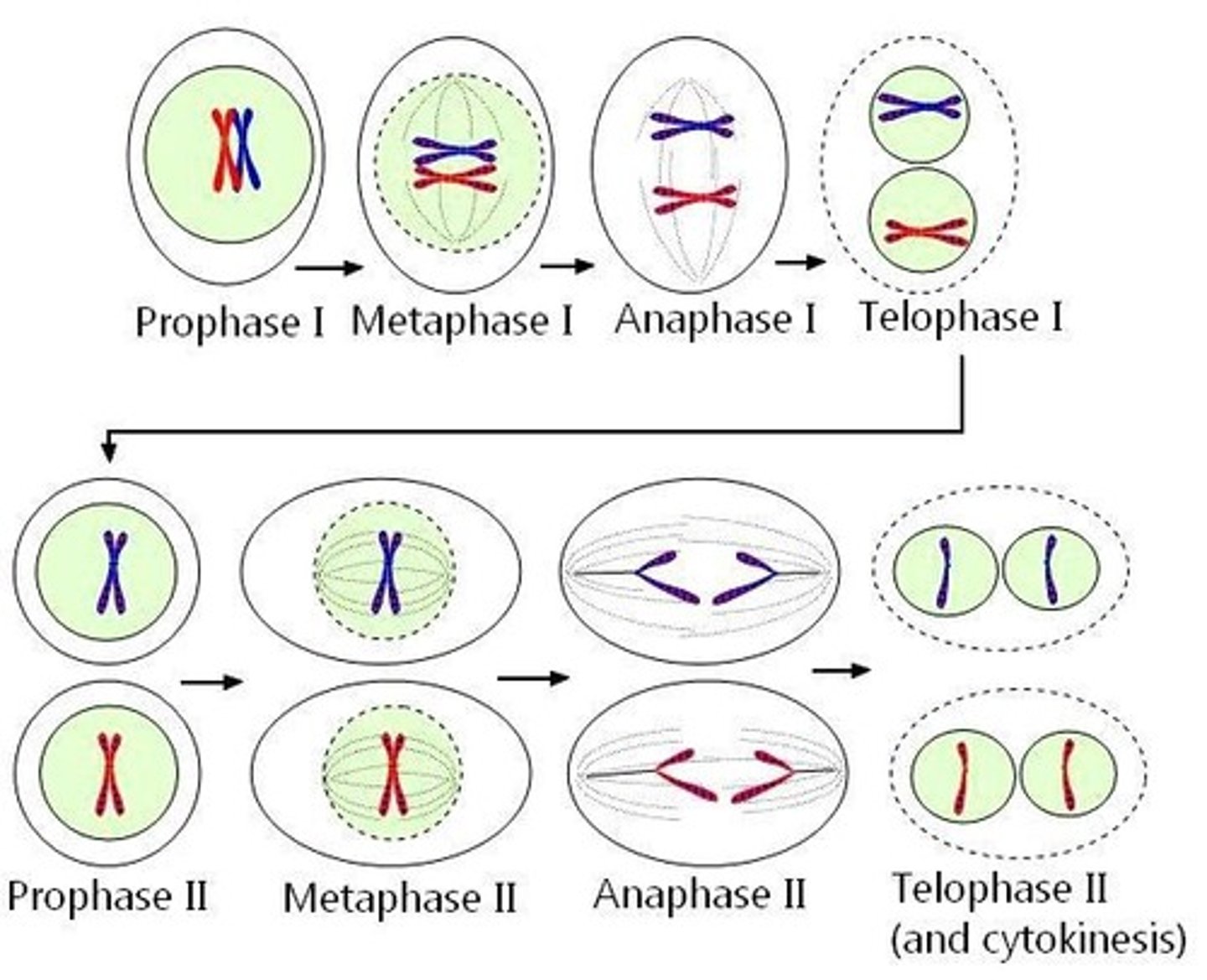
Meiosis I
First division separating homologous chromosome pairs.
Meiosis II
Second division separating sister chromatids.
Prophase I
Chromosomes condense and homologues pair up.
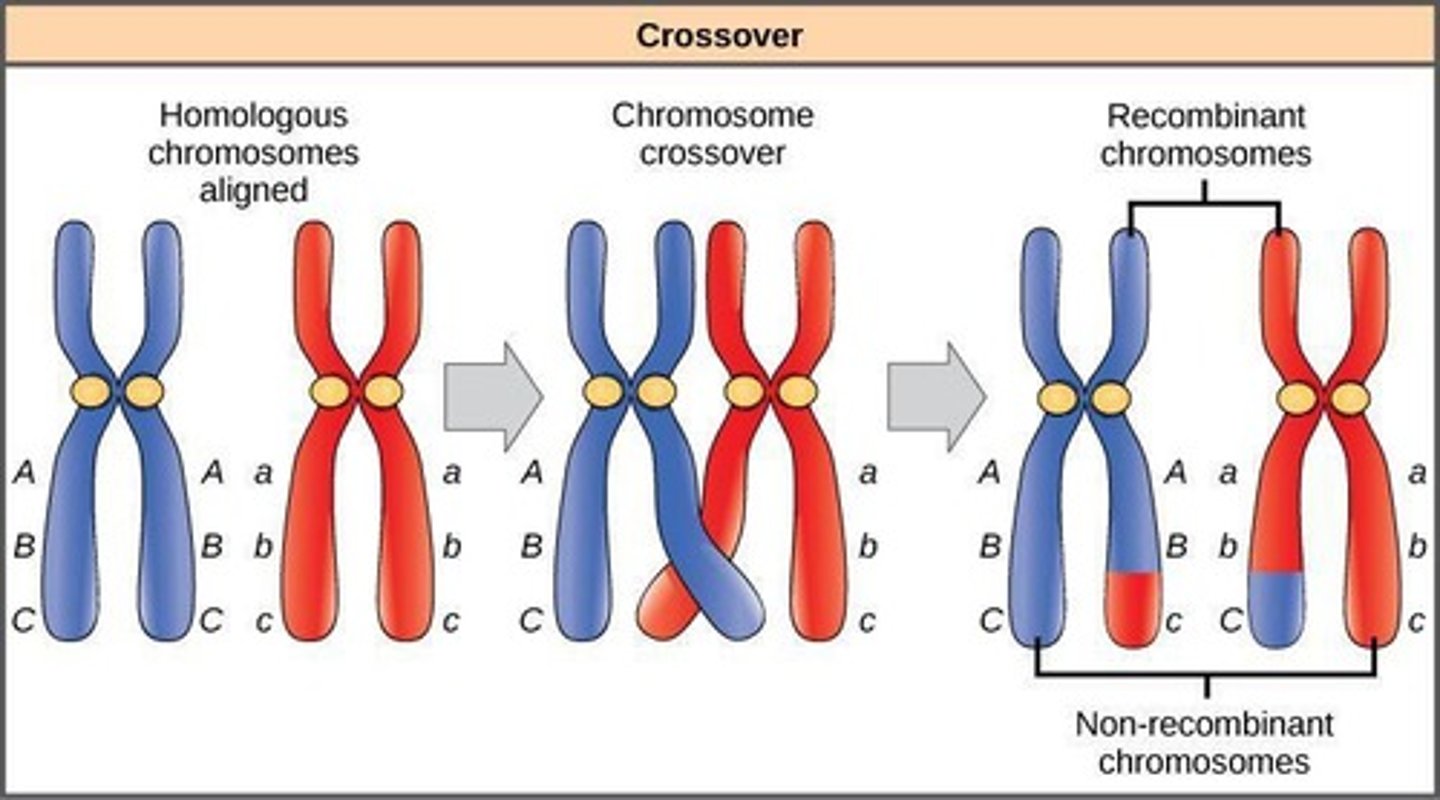
Crossing Over
Homologous chromosomes exchange DNA segments.
Metaphase I
Homologous pairs line up at cell equator.
Anaphase I
Homologues pulled apart to opposite cell ends.
Telophase I
Chromosomes reach poles; cytokinesis forms haploid cells.
Interphase
Cell growth and DNA replication before meiosis.
Prophase II
Haploid cells' chromosomes condense for division.
Metaphase II
Chromosomes align at metaphase plate.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate to opposite cell ends.
Telophase II
Gametes form; each chromosome has one chromatid.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm forming new cells.
Haploid Cells
Cells with one chromosome from each pair.
Gametes
Reproductive cells: sperm or egg.
Genetic Variety
Diversity in genetic makeup of gametes.
DNA
Molecule carrying genetic information.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene.
Equator
Imaginary line where chromosomes align during metaphase.
Nuclear Membrane
Barrier enclosing the nucleus.
Chromatid
Single strand of a duplicated chromosome.
Genetic Mixing
Process creating diverse genetic combinations in gametes.
Crossover Frequency
Up to 25 crossovers per homologous pair.
Metaphase Plate
Plane where chromosomes align during metaphase.
Crossover
Exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes.
Random orientation
Arrangement of homologues during metaphase I.
Gametes
Sex cells produced through meiosis.
Diploid
Cell with two sets of chromosomes (2n).
Karyotype
Photographic representation of an individual's chromosomes.
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell.
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate properly.
Trisomy
Presence of three copies of a chromosome.
Monosomy
Presence of one copy of a chromosome.
Down Syndrome
Trisomy 21; causes mental limitations and physical traits.
Meta-Female
Trisomy X; 47 chromosomes with XXX configuration.
Turner's Syndrome
Monosomy X; 45 chromosomes with one X.
Klinefelter's Syndrome
XXY males; 47 chromosomes with reduced fertility.
Super Male Syndrome
XYY males; 47 chromosomes with aggressive behaviors.
Chromosomal aberrations
Deviations from normal chromosome structure or number.
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosome pairs, one from each parent.
Metaphase I
Stage where homologues align before separation.
Anaphase I
Stage where homologous chromosomes separate.
Anaphase II
Stage where sister chromatids separate.
Growth medium
Nutrient solution for cell culture.
Staining
Process to visualize chromosomes under a microscope.
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
Chromosomal defects
Abnormalities in chromosome number or structure.
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg to form a zygote.
Embryos
Early developmental stage post-fertilization.
Sterility
Inability to reproduce.
Mental impairment
Cognitive deficits associated with chromosomal disorders.
Physical traits
Observable characteristics resulting from genetic makeup.
Karyotype
Visual representation of an individual's chromosomes.
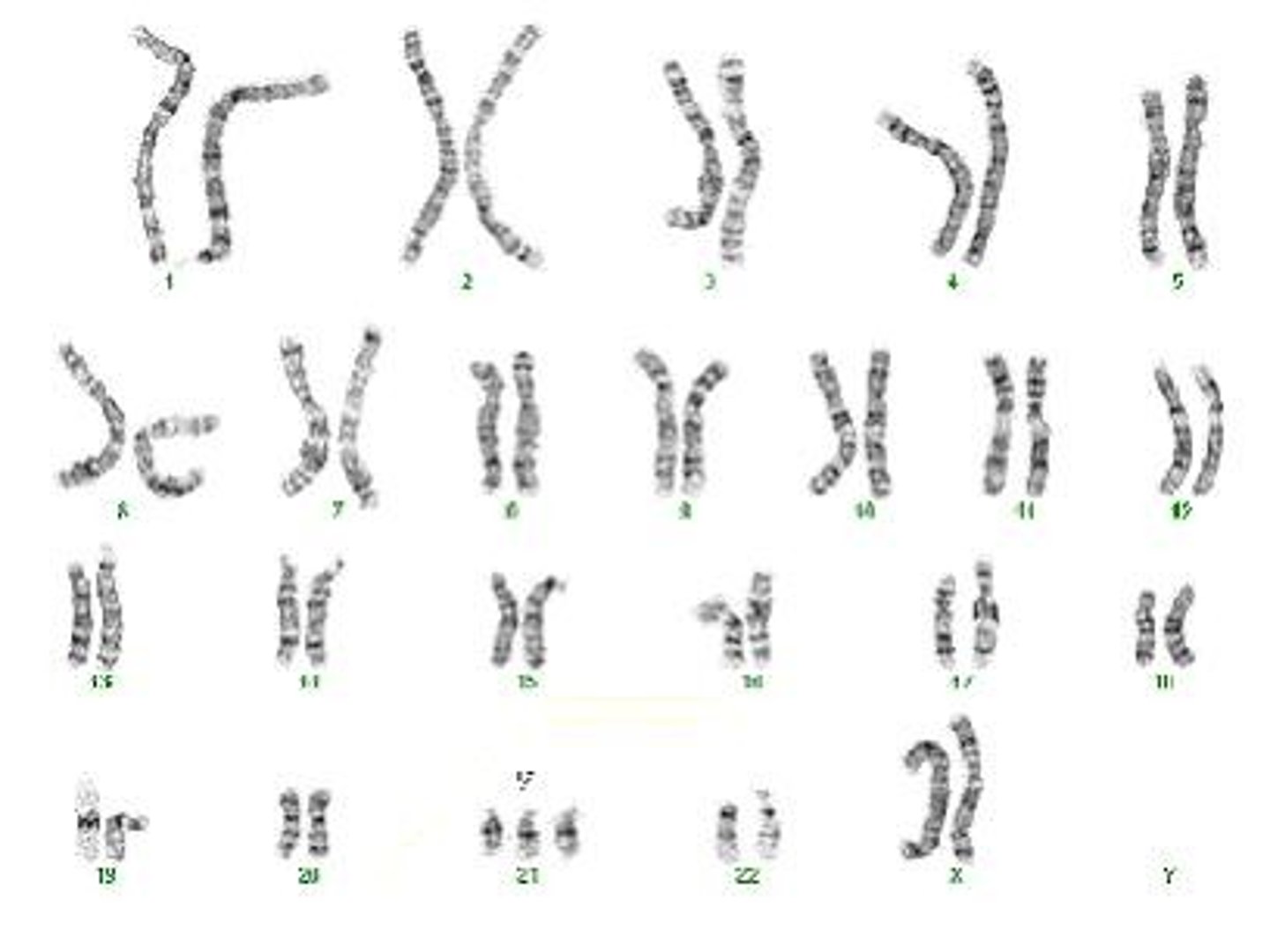
Autosomes
Non-sex chromosomes; humans have 22 pairs.
Sex Chromosomes
Chromosomes determining an individual's gender; 2 total.
Down's Syndrome
Genetic disorder caused by an extra chromosome 21.
Turner's Syndrome
Condition in females with a missing X chromosome.
Kleinfelter's Syndrome
Condition in males with an extra X chromosome.
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk known as the father of genetics.
P Generation
Pure-breeding parent generation in Mendel's experiments.
F1 Generation
First filial generation from P generation crosses.
F2 Generation
Second filial generation from F1 generation crosses.
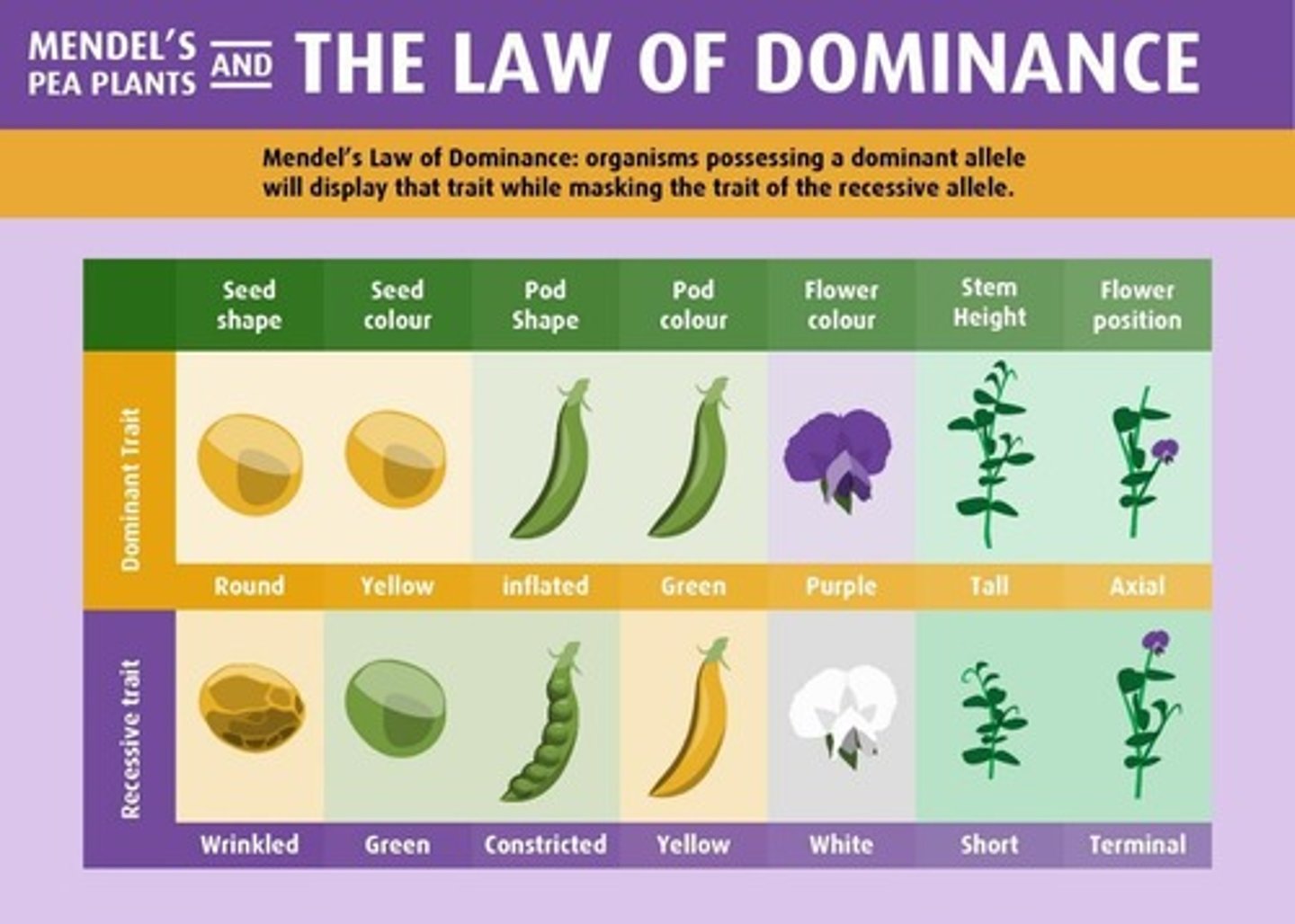
Law of Dominance
One trait is dominant over another in hybrids.
Dominant Trait
Trait expressed in the phenotype of hybrids.
Recessive Trait
Trait not expressed in the presence of dominant.
Alleles
Different forms of the same gene.
Law of Segregation
Alleles segregate during gamete formation.
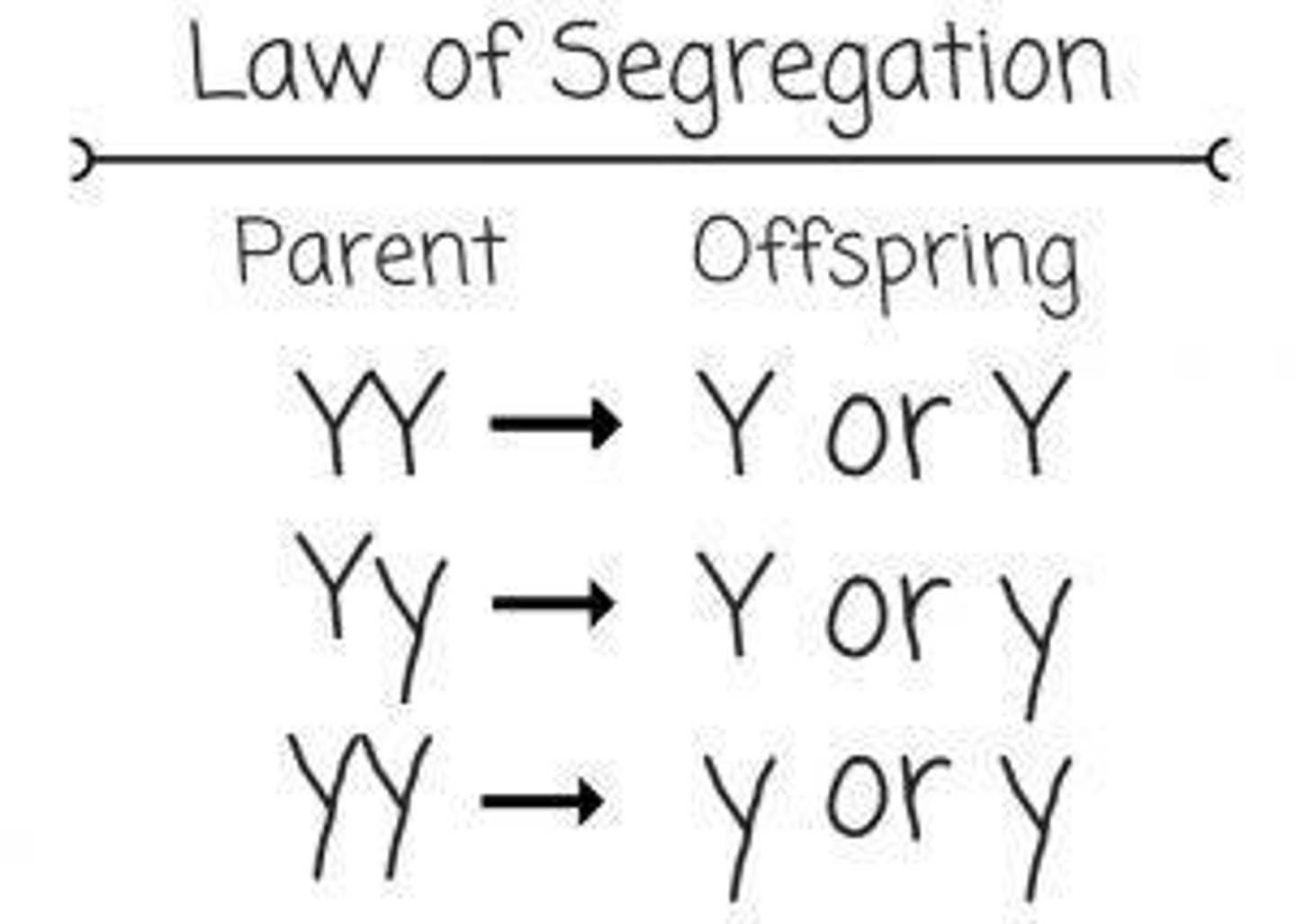
Homozygous
Individual with two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
Individual with two different alleles for a trait.
Purebred
Organism homozygous for a specific trait.
Hybrid
Organism heterozygous for a specific trait.
Gametes
Reproductive cells carrying one allele per trait.
Phenotype
Physical expression of a genetic trait.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism.
Self-fertilization
Process where an organism fertilizes itself.
Contrasting Traits
Traits that differ from one another, like tall vs. short.
Mendelian Genetics
Study of inheritance patterns established by Mendel.
Plant Inheritance
Genetic traits passed through generations in plants.
Chromosomes
Structures containing genetic material in cells.
Factors
Historical term for genes used by Mendel.
Hybrid
Offspring of unlike parents; heterozygous.
Homozygous Dominant
Genotype with two dominant alleles (GG).
Heterozygous
Genotype with one dominant and one recessive allele (Gg).
Homozygous Recessive
Genotype with two recessive alleles (gg).
Punnett Square
Tool for visualizing genetic crosses and zygote outcomes.
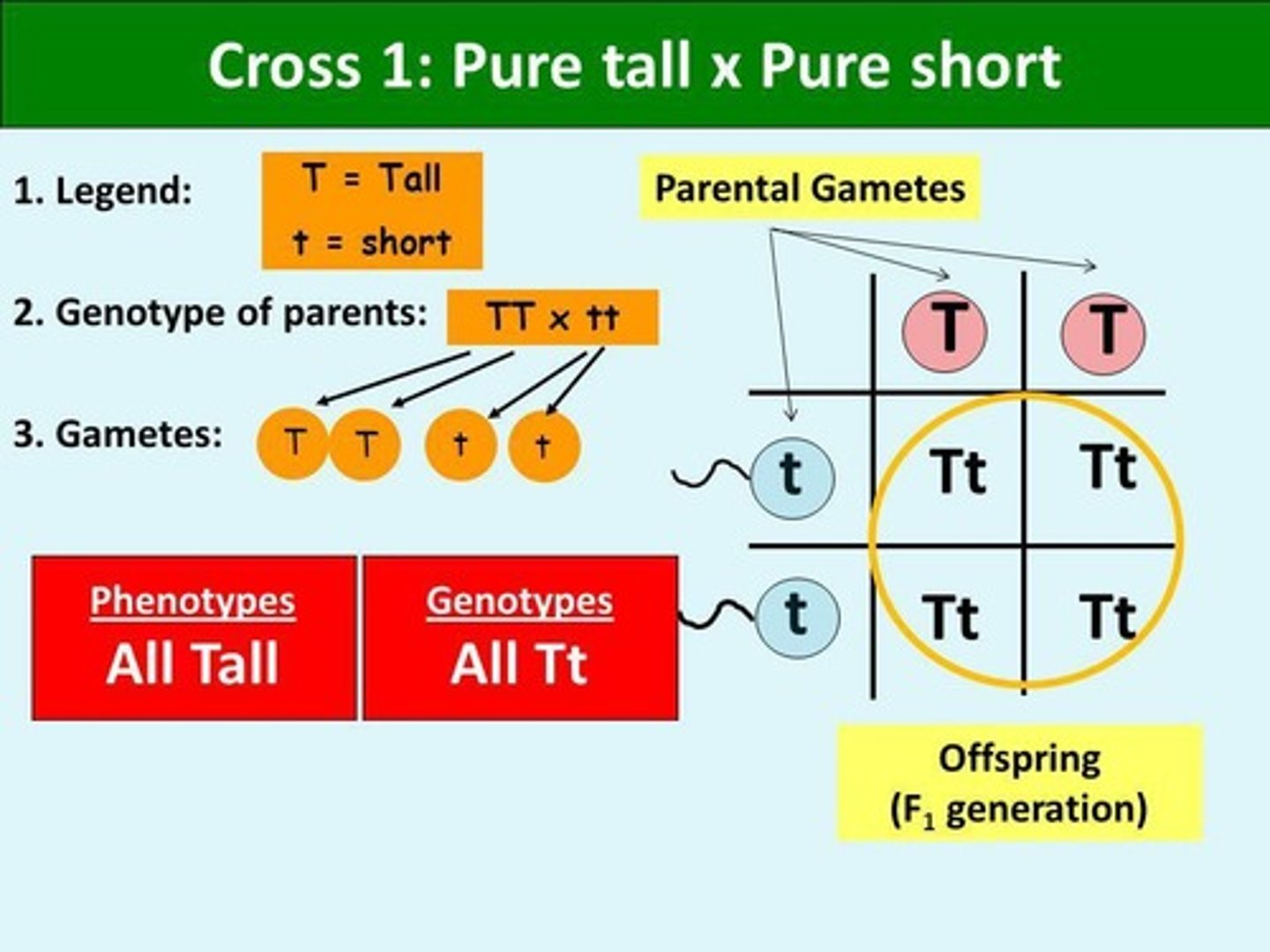
Gametes
Reproductive cells carrying alleles for traits.
Phenotype
Physical appearance resulting from genotype.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an individual.
F1 Generation
First filial generation, all heterozygous.
P Generation
Parental generation in genetic crosses.
Dihybrid Cross
Cross involving two pairs of contrasting traits.
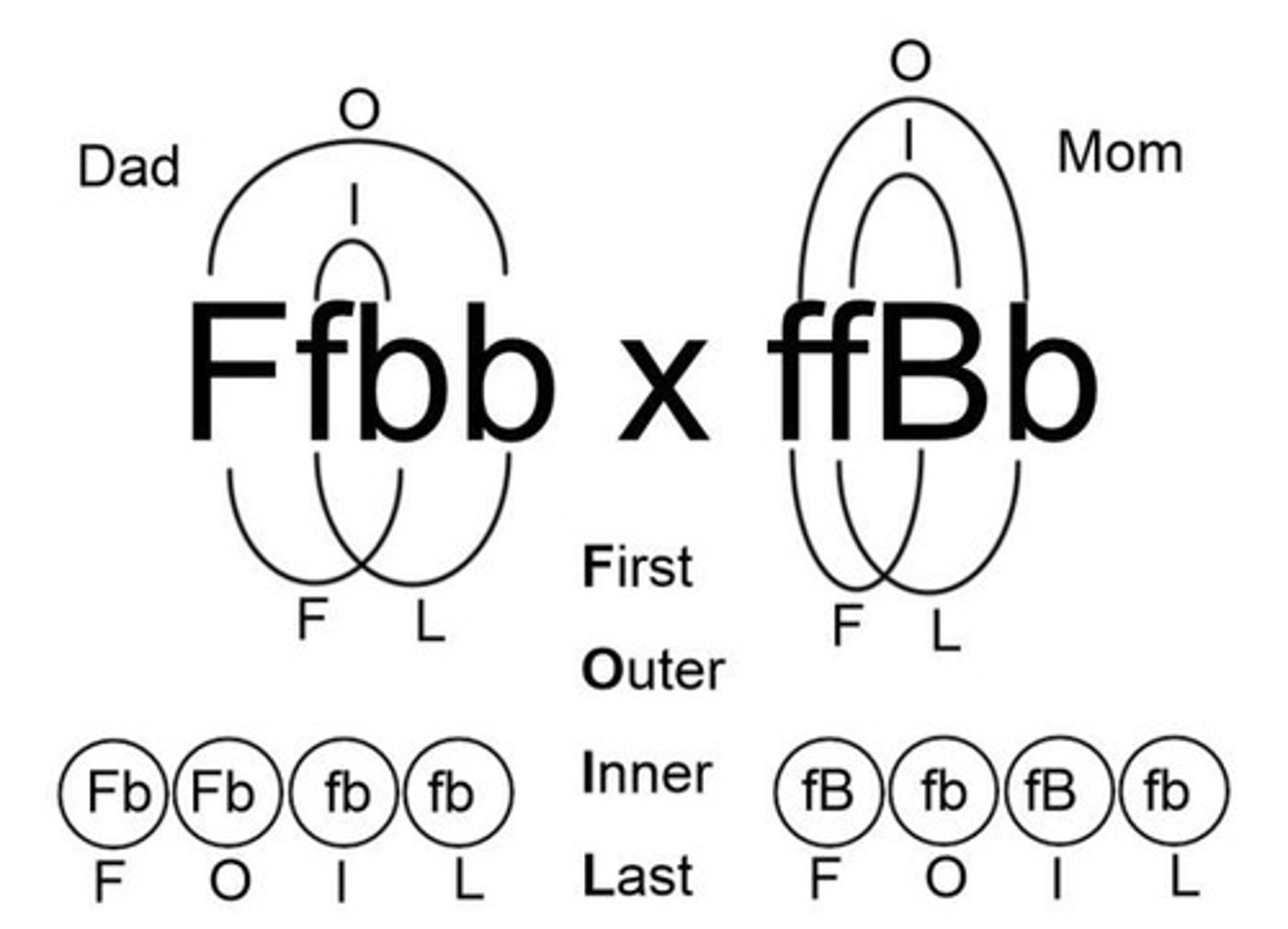
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes segregate independently during gamete formation.
FOIL Method
Technique for determining gamete combinations.
Phenotype Ratio
Ratio of different phenotypes in offspring.
Genotype Ratio
Ratio of different genotypes in offspring.
Dominant Trait
Trait expressed in the phenotype if present.