Exam 4
1/319
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
320 Terms
Fentanyl brand
Abstral, Duragesic, Fentora
Fentanyl class
Opioid analgesic
Fentanyl use
Pain
Fentanyl MOA
Opioid agonist at the mu receptor
Fentanyl dose
IV: 50-100 mcg loading dose with 25-50 mcg/hr titrated to patient need, transdermal patch: 25-100 mcg/hr
Fentanyl contraindications
Do not use in opioid naive patients
Fentanyl BBW
Life threatening respiratory depression, addiction, misuse, abuse, risk of concomitant use with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants
Dexmedetomidine brand
Precedex
Dexmedetomidine class
Sedative
Dexmedetomidine use
Sedation
Dexmedetomidine MOA
Selective alpha 2 adrenergic agonist, inhibits norepinephrine release, peripheral alpha 2b-adrenoceptors
Dexmedetomidine dose
ICU sedation: 1 mcg/kg IV over 10 minutes followed by 0.2-0.7 mcg/kg/hr maintenance, procedural sedation: 1 mcg/kg IV over 10 minutes with 0.6 mcg/kg/hr maintenance
Dexmedetomidine contraindications
None
Dexmedetomidine BBW
None
Ketamine brand
Ketalar
Ketamine class
General anesthetic
Ketamine use
Anesthesia
Ketamine MOA
Noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist that blocks glutamate
Ketamine dose
IM: 4-10 mg/kg, IV: 0.5-2 mg/kg
Ketamine contraindications
None
Ketamine BBW
None
Lidocaine brand
Lidoderm, Xylocaine
Lidocaine class
Analgesic anesthetic
Lidocaine use
Anesthesia
Lidocaine MOA
Local antiarrhythmic class IB
Lidocaine dose
Topical 4.5 mg/kg/day divided in 4 doses or apply 5% patch to painful area for 12 hours every day
Lidocaine contraindications
Use with caution in patients with known drug sensitivities
Lidocaine BBW
Fatal events have occured with high blood levels from topical exposure and is more likely in young children
Midazolam brand
Nayzilam, Versed
Midazolam class
Benzodiazepine
Midazolam use
Sedation, agitation, end of life, seizures
Midazolam MOA
Binds to stereospecific benzodiazepine receptors on the postsynaptic GABA neuron, essentially enhances the inhibitory effects of GABA on neuronal excitability. Impact on GABA-A and not GABA-B receptors
Midazolam dose
Preop sedation: 0.1-0.35 mg/kg over 20-30 seconds, seizures: 5 mg nasal spray as a single dose in one nostril; may repeat dose in 10 minutes in alternate nostril based on response and tolerability
Midazolam contraindications
None
Midazolam BBW
Has been associated with respiratory depression and respiratory arrest, especially when used for sedation in noncritical settings
Naloxone brand
Evzio, Narcan
Naloxone class
Opioid antagonist
Naloxone use
Opioid overdose
Naloxone MOA
Pure opioid antagonist that competes and displaces opioid at receptor sites
Naloxone dose
IV/IM/SQ: initial 0.4-2 mg repeated q2-3 min up to 10 mg total, intranasal: 1 spray (4 mg) as a single dose in one nostril, may repeat in 3-5 min if respiratory depression persists
Naloxone contraindications
None
Naloxone BBW
None
Propofol brand
Diprivan
Propofol class
General anesthetic
Propofol use
Anesthesia, RSI
Propofol MOA
Short acting lipophilic IV general anesthetic, results in CNS depression through GABA-A agonism and glutamatergic activity through NMDA receptor blockade
Propofol dose
Initial IV: 5 mcg/kg/min (or 0.3 mg/kg/hr) increase by 5-10 mcg/kg/min (or 0.3-0.6 mg/kg/hr) every 5-10 min until desired sedation level is achieved, maintenance: 5-50 mcg/kg/min (0.3-3 mg/kg/hr)
Propofol Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to eggs, soybeans, soy production, caution with hypertriglyceridemia
Propofol BBW
None
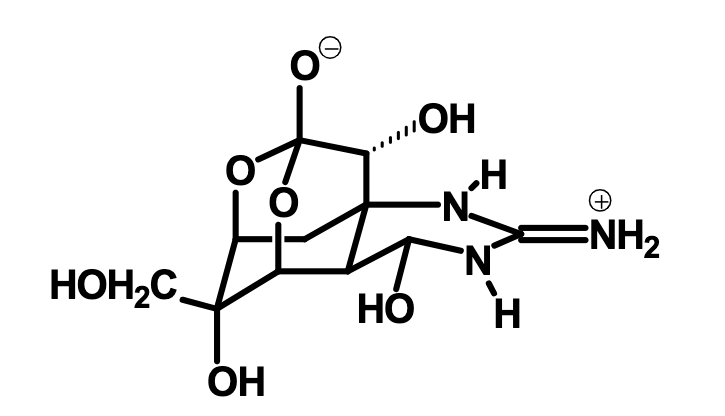
What is this?
Tetrodotoxin, a sodium channel neurotoxin that comes from pufferfish and greater blue ring octopus
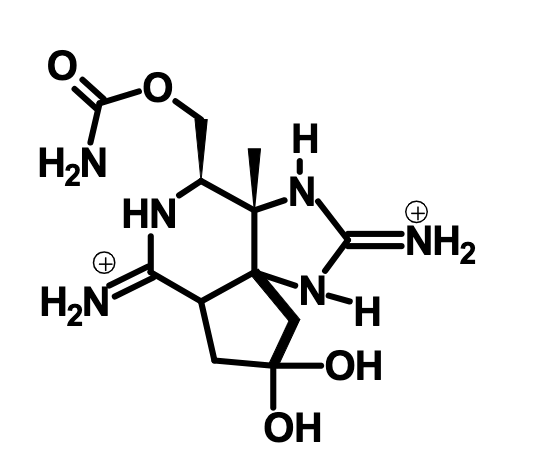
What is this?
Saxitoxin, a sodium channel neurotoxin that comes from dinoflagellates
What is the primary MOA for neurotoxins?
Block the sodium channel from the outside in its ionized form
What is the primary MOA for alcohols, phenols, and benzocaine?
Block sodium channel from within the membrane in its unionized form
What is the primary MOA for local anesthetics?
Block sodium channel from the inside, most efficient MOA
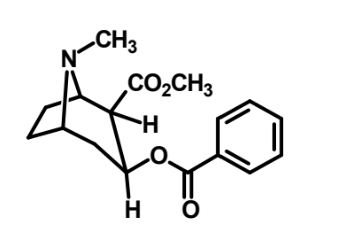
What is this?
Cocaine
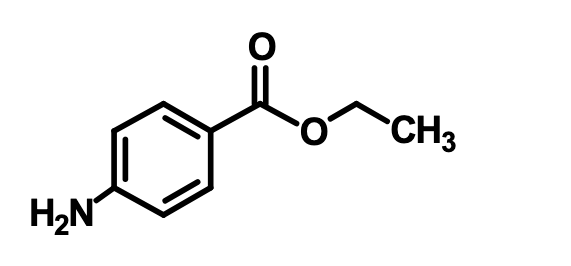
What is this?
Benzocaine
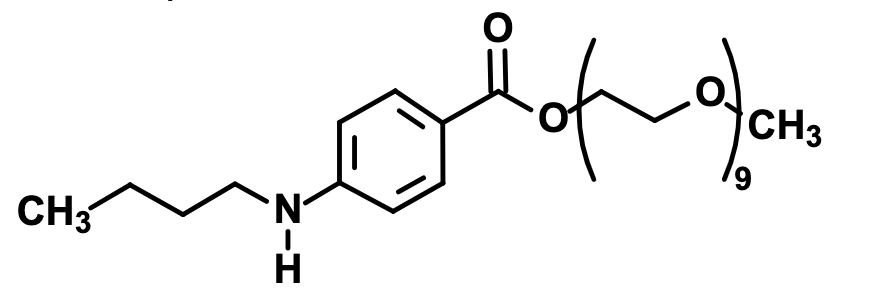
What is this?
Benzonatate
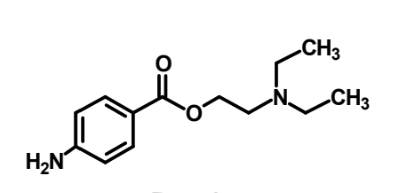
What is this?
Procaine
What are some SAR features of benzoic acid esters?
Aromatic ring, para EDG, ester better than amid, 2-4 carbon chain, usually tertiary basic amine
What does coadministration of a benzoic acid ester with a vasoconstrictor prevent?
Degradation by esterases, diffusion away from injection site
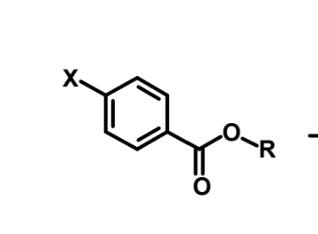
How is this metabolized?
Rapid ester hydrolysis
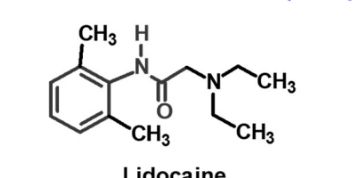
What is this?
Lidocaine
What is the general MOA of inhalation general anesthetics?
Membrane fluidization
How is the action of barbiturates terminated?
Drugs redistributing to fat
What is rapid sequence intubation?
Airway management technique for quickly securing an airway
What are indications for intubation?
Respiratory failure, apnea, GCS < 8, rapid change of mental status, airway injury, high risk for aspiration, trauma to larynx
What is the pharmacist’s role in intubation?
Assist with medication and dose selection, obtaining meds, drawing up meds at appropriate dose, recommend treatments for medication side effects
When might we use premedications for RSI?
Patient appears anxious, hypotensive, hypertensive
What does the induction agent do?
Sedate patient prior to procedure
What does the paralytic agent do?
Paralyzes the muscles to reduce risk of injury with intubation
What are possible complications of RSI?
Bradycardia, hypotension
Why do we give premedications in RSI?
Help with anxiety and blunt any negative physiological response that occurs during intubation such as a spike in BP or pain
When would we use midazolam in RSI?
Premedication for anxiety
Midazolam MOA
GABA agonist, fast acting BZP with short duration of action
What is the usual dose of midazolam?
1-2 mg IV push
Fentanyl MOA (RSI)
Central opioid agonist that blunts the sympathetic surge associated with pain receptor stimulation
Why is fentanyl a preferred opioid for RSI?
High degree of lipophilicity with fast onset and short duration of action
Fentanyl dose
1-3 mcg/kg IV 3 minutes prior to intubation
Which patients would benefit from the addition of fentanyl as a premedication?
Cardiac issues such as ischemic heart disease and aortic dissection
When do we use atropine in RSI?
Premedication more common in pediatric patients for bradycardia
Atropine MOA
Muscarinic antagonist
Why might a patient become bradycardic during intubation?
Vagus nerve activation
Lidocaine MOA
Suppresses reflexes, induces peripheral GABA receptors, brain stem depression, slows cerebral metabolism
When do we use lidocaine for RSI?
Premedication to blunt sympathetic response to intubation in patients with elevated ICP or have asthma with bronchospasm
What are adverse effects of lidocaine?
Hypotension, arrythmias
Why do we sedate the patient prior to administering the paralytic agent?
Don’t want tehm to remember the experience, overall better patient care
Propofol MOA
Highly soluble GABA agonist
What about propofol makes its kinetics optimal for induction?
Fast onset, short duration of action, highly lipophilic, no renal/hepatic considerations
What effects does propofol have minus sedation?
Reduces ICP, bronchodilation, hypotension, bradycardia
Can propofol be used in patients with an egg allergy since it’s a lipid emulsion?
Yes
Etomidate MOA
Stimulates GABA to block neuroexcitation and induce sedation and unconsciousness
What cardiovascular effects does etomidate have?
Very minimal, won’t negatively impact one way or the other
What is the dose of etomidate?
0.2-0.6 mg/kg, generally eyeballed though
Ketamine MOA
Inhibits glutamate at NMDA receptor, highly lipophilic so crossed BBB easily, provides analgesia and amnesia
What cardiovascular effects does ketamine have?
Hypertension, tachycardia, increased CO, induces bronchodilation
When is midazolam a good option as an induction agent?
No IV access
Which induction agent is generally our first option and why?
Etomidate, neutral cardiac profile
How do depolarizing NMBAs work?
Bind to Ach receptors leading to membrane depolarization and keeps it open so muscles cannot contract and relax
How do non depolarizing NMBAs work?
Competitively block Ach receptors but do not activate them
Why is paralysis with a NMBA indicated prior to intubation?
Keep the patient from moving around for their safety