Science Review 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:43 PM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
Epididymis
Once sperm are produced by the testes they move into and mature in the _____
2
New cards
Carry both semen and urine but not at the same time
The purpose of the urethra is to ____.
3
New cards
Hormones
The menstrual cycle is triggered each month by ___
4
New cards
Fallopian tube
Fertilization usually takes place in the ____
5
New cards
Testicles
The male hormone testosterone is produced by ______
6
New cards
Zygote
Fertilized egg is called ___
7
New cards
Scrotum
Keeps testes outside the body and below body temperature
* One of the external male reproductive organs (external meaning outside)
* One of the external male reproductive organs (external meaning outside)
8
New cards
Ejaculation occurs
Semen leaves the male boy when the penis erect and _____
9
New cards
Sperm
Name given to the male gamete?
10
New cards
Seminiferous tubules
Sperm production begins in the ______
11
New cards
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Production of testosterone in the interstitial cells is stimulated by ____
12
New cards
Endometrium
The layer of the uterine wall that is shed during menstruation is the ___.
13
New cards
Semen
Substance produced by the seminal vesicles and prostate gland is known as ___
14
New cards
Gamete
Another name for sex cell is ___
15
New cards
Endocrine glands
Produce and secrete hormones into the bloodstream
16
New cards
Hormones
Chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands, and transported by the bloodstream are
17
New cards
Only a neighboring cell
When a hormone is released it will have its effect at
18
New cards
Endocrine system
All the cells, tissues, and glands that secrete hormones are called
19
New cards
Gigantism
This disorder is caused by the hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH) from the anterior pituitary
20
New cards
Hypothyroidism
The disorder that is an enlargement of the thyroid gland due to dietary iodine deficiency is called ______
21
New cards
Calcitonin
Controls the calcium levels in the bloodstream
22
New cards
Insulin
Controls the level of sugar in the blood
23
New cards
Thyroid
This gland secretes thyroxine which controls iodine in the blood
24
New cards
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
It stimulates thyroid gland to release specific hormones
25
New cards
Adrenaline
Controls the “fight or flight” response of the body.
26
New cards
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
It stimulates the adrenal gland to release specific hormones.
27
New cards
Oxytocin
Released by hypothalamus to control muscle contraction of uterus
28
New cards
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
Regulates body temperature, blood pressure and water supply
29
New cards
Glucogen
Stimulates the liver to convert glycogen to glucose.
30
New cards
The order of its Nitrogen bases (A - T / C - G)
The genetic information in a DNA molecule is determined by ___
31
New cards
A phosphate group
DNA is made of a 5-carbon sugar, a nitrogen base, and ____
32
New cards
* Adenine
* Guanine
* Cytosine
* Thymine
* Guanine
* Cytosine
* Thymine
The 4 Nitrogen bases of DNA are
33
New cards
DNA to RNA to protein
By the processes of transcription and translation, the genetic information of a cell passes from:
34
New cards
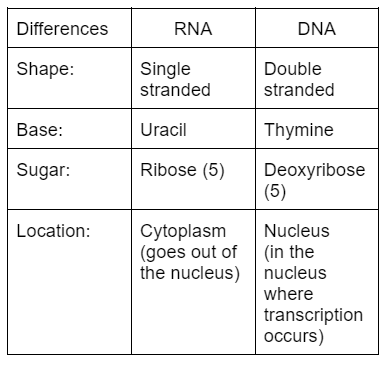
Differences between DNA and RNA
35
New cards
Genes
Codons are grouped together to form ___ which are translated into one protein.
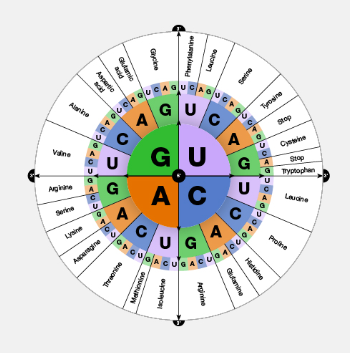
36
New cards
\
DNA is copied to a strand of mRNA (messenger RNA) during the process of ___
37
New cards
T-T-G-A-A-C
A strand of DNA with the sequence A-A-C-T-T-G will produce a complementary strand during **DNA replication**
\n
***** DNA:
**A**pple in the **T**ree, **C**ar in the **G**arage
\n
***** DNA:
**A**pple in the **T**ree, **C**ar in the **G**arage
38
New cards
C-U-A-A-C
A DNA chain has the following sequence of bases: G-A-T-T-G. The matching **m-RNA strand** should have which sequence?
\n
\* m-RNA:
**A**pples are **U**nder, **C**ar in the **G**arage
\n
\* m-RNA:
**A**pples are **U**nder, **C**ar in the **G**arage
39
New cards
Codons
Three bases are group together to form a ____
40
New cards
Pentose sugar, phosphate group and a base
DNA and m-RNA contain _____
41
New cards
Anticodon for UAG
CAU
42
New cards
Point mutation
Single base substitution
\
\n
\
\n
43
New cards
64
How many different ways can 4 bases combine?
44
New cards
Different number of carbon
Deoxyribose (5) differs glucose (6) because
45
New cards
Estrogen and progesterone
2 Hormones in the ovary
46
New cards
Stimulates secondary sex characteristics
Function of testosterone
47
New cards
Stage of menstrual cycle that breaks the wall
Stage of menstrual cycle that breaks the wall
48
New cards
Implantation, egg implanted in the uterus
What would happen if fertilization occurs
49
New cards
Nucleotide structure
Formed by the condensation of the sugar, phosphate and one of the 4 bases
50
New cards
CAU UAG AUA UAU
GUA AUC UAU AUA
51
New cards
Make sequence coding strand
ATC GCA UAG CGU
52
New cards
During Translation
m RNA passes nucleus from the cell
53
New cards
ATC AGT CCT
TTC AGT CCT
54
New cards
The fertilized egg will get implanted in the uterus
What would happen inside the uterus
55
New cards
Glucogen will convert glycogen to glucose
Auntie she keep her lunch for a day pancreas help her body cope with low blood sugar
56
New cards
Hot humid day
Hot humid day
57
New cards
Pineal Gland
This hormone ‘melatonin’ is secreted by the gland
58
New cards
Testis through the vas deferens and out the urethra
Sperm travels from the _____
59
New cards
Spermatogenesis requires a temperature lower than the body
The testicles are located at the external part of the male body because
60
New cards
Seminiferous tubules - epididymis - vas deferens - urethra
Correct pathway of the sperm
61
New cards
14 days before menstruation
Ovulation usually occurs _____
62
New cards
Thymine - DNA; Uracil - RNA
Nucleotide base of DNA and RNA
63
New cards
Contains 5 carbons
How does Deoxyribose differ from glucose?
64
New cards
64 ways
How many different ways can 3 of the 4 bases be combined
65
New cards
Luteinizing hormone
The production of testosterone in the interstitial cells is stimulated by the _____
66
New cards
Progesterone
Hormones works with estrogen to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg
67
New cards
mRNA
Used as template to make proteins
68
New cards
rRNA
Makes up ribosomes
69
New cards
tRNA
Matches amino acids to help make proteins
70
New cards
Parathyroid Hormone
It regulates the minerals in the body-calcium and phosphorus in the bloodstream.
71
New cards
To regulate daily activities of the body and controls its overall development
Endocrine System are consists of many glands which secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream to _____ and ______
72
New cards
Gland - Hormone
A ____ is the smallest living unit in the body that produces and releases chemical substance called _____
73
New cards
Negative feedback
Control system to reduce or minimize any changes or conditions of the body, which keeps the whole body system stable.
74
New cards
Thermostat
The Endocrine System is similar to a _____ because it may turn on when the temperature is below normal and may turn off when the temperature is above normal.
75
New cards
Recessive Disorders
To have an autosomal recessive disorder, **you inherit two changed genes, sometimes called mutations**. You get one from each parent. Their health is rarely affected because they have only one changed gene. Two carriers have a 25% chance of having an unaffected child with two unaffected genes (left).
76
New cards
Sickle cell anemia
Is a genetic blood disorder.
77
New cards
Tay-Sachs disease
Is characterized by the lack of an important chemical in the brain.
78
New cards
Phenylketonuria or PKU
Is a rare genetic disorder that can cause serious mental retardation in infants.
79
New cards
Cystic fibrosis
Is a disease in which some glands produce too much mucus that it clogs and damages the lungs.
80
New cards
Sex-linked disorders
And in humans this is the X or the Y chromosomes. And so some of the more familiar sex-linked traits are **hemophilia, red-green color blindness, congenital night blindness, some high blood pressure genes, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and also Fragile X syndrome**.
81
New cards
Human genetic syndrome
Genetic Disorders. Sickle Cell Disease. Cystic fibrosis. Cystic Fibrosis Liver Disease. Brain, Nerves and Spine.
82
New cards
Cri du chat
Is caused by the deletion of part of the short arm of chromosomes 5.
83
New cards
Is the result from the loss of a segment in chromosomes 7.
Is the result from the loss of a segment in chromosomes 7.
84
New cards
Down syndrome
(trisomy 21) is known as mongolism.
85
New cards
Edward syndrome
(trisomy 18) happens when there is an extra number 18 chromosome.
86
New cards
Patau’s syndrome
(trisomy13) is caused by extra copy of number 13 chromosome
87
New cards
Klinefelter’s syndrome
(XXY) is another genetic disorder
88
New cards
Turner's syndrome
Has 45 chromosomes about 96-98% with this condition do not survive at birth.
89
New cards
10,000
The human body contains at least ____ different kinds of proteins.
90
New cards
20
There are __ different amino acids (building blocks of protein)
91
New cards
Mutation
It is the change in genetic material
92
New cards
Mutagens
The different types of agents, whether they are in the form of physical or chemical that can cause the alteration of the structure or sequence of DNA
93
New cards
Genes
Basic unit of heredity
94
New cards
Insertion
Genetic material added from another chromosome
95
New cards
Translocation
Happens when a part of a chromosome breaks off and combined
96
New cards
Deletion
Happens when there is a loss of part of a chromosome
97
New cards
Duplication
Happens if there are extra copies of a part of a chromosome
98
New cards
Inversion
Happens when the direction of a part of a chromosome is reversed
99
New cards
Nucleobases
100
New cards
Base Pair