Anatomical Terminology Bio 211
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:03 AM on 2/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy
the study of structure, examine relationships among parts of the body as well as the structure of individual organs
2
New cards
Physiology
the scientific discipline that studies the function of body structures
3
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
examines structures that cannot be viewed by unaided eye
4
New cards
Cytology
study of single body cells and their internal structures
5
New cards
Histology
the study of tissues
6
New cards
Gross Anatomy/Macroscopic Anatomy
investigates the structure and relationships of large body parts that are visible to the unaided eye
7
New cards
Comparative Anatomy
examines the similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species
8
New cards
Developmental Anatomy
investigates the changes in structure within an individual from conception through maturity
9
New cards
Embryology
is concerned specifically with developmental changes occurring prior to birth
10
New cards
Regional Anatomy
examines all the structures in a particular region of the body as one complete unit (ex: bones, muscles, connective tissues, etc.)
11
New cards
Surface Anatomy
examines both superficial anatomic markings and internal body structures as they relate to the skin covering them
12
New cards
Systemic Anatomy
studies the gross anatomy of each system in the body
13
New cards
Pathologic Anatomy
examines all anatomic changes resulting from disease
14
New cards
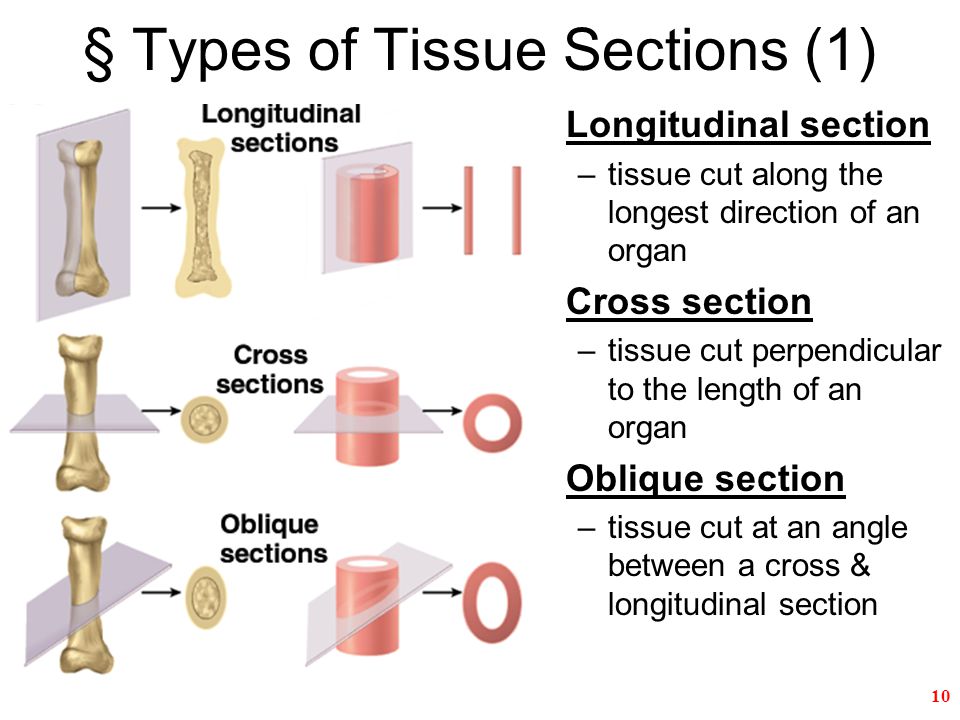
Radiographic Anatomy
studies the relationships among internal structures that may be visualized by specific medical imaging procedures (ex: ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or x-ray)
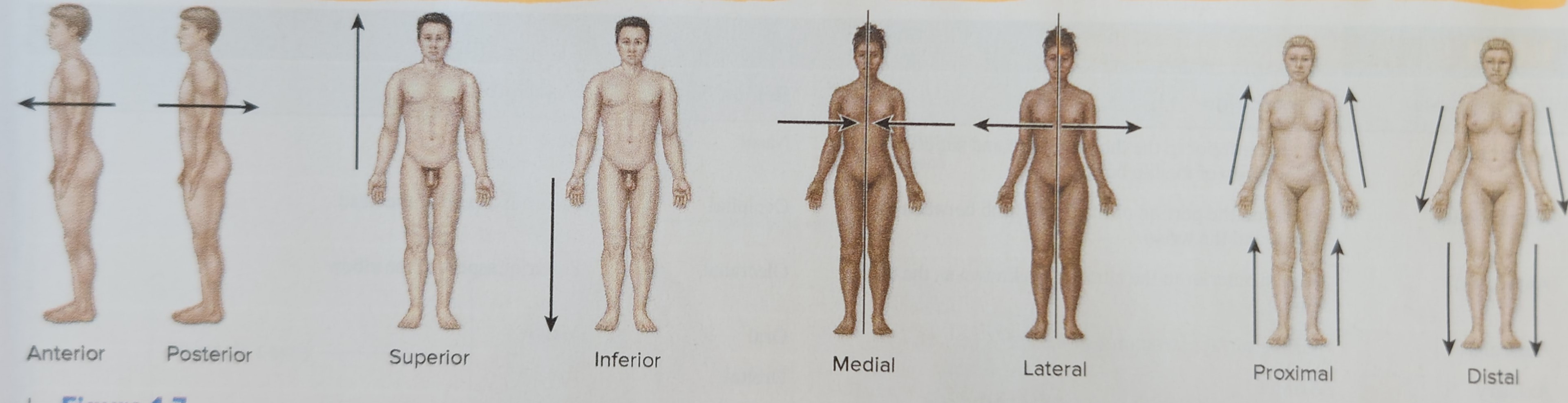
15
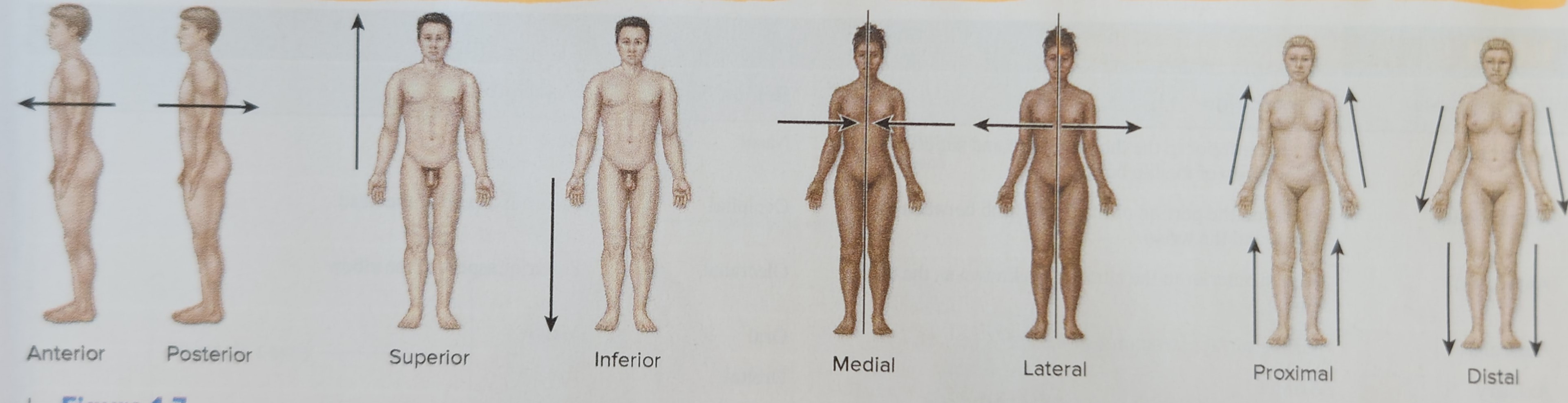
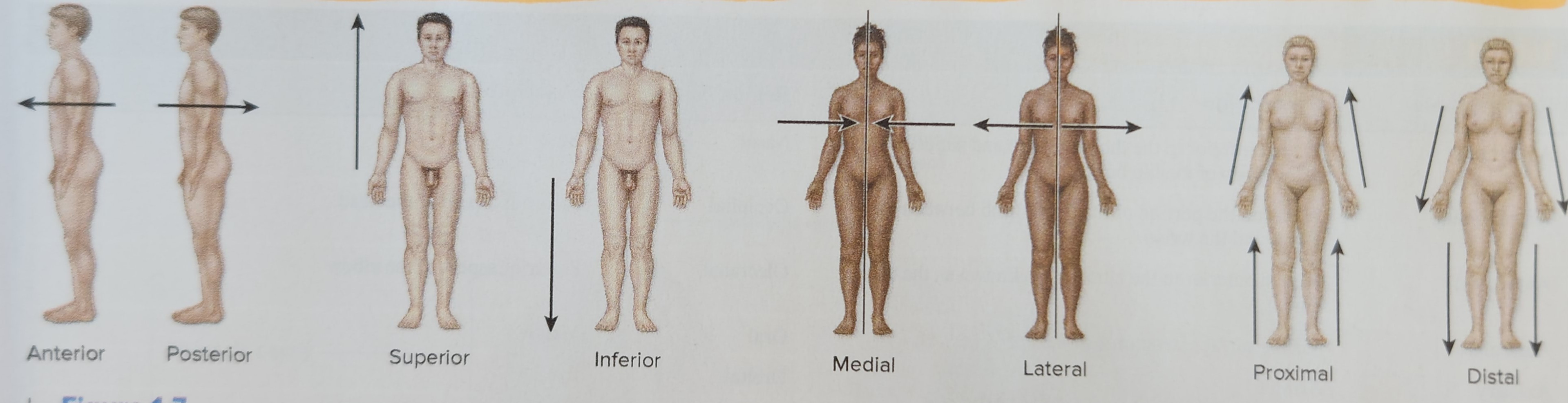
New cards
Surgical Anatomy
investigates the anatomic landmarks used before and after surgery
16
New cards
1. Chemical Level, 2. Cellular Level, 3. Tissue Level, 4. Organ Level, 5. Organ System Level, 6. Organism Level
Rank the levels of organization in the human body from smallest to largest.
17
New cards
Chemical Level
simplest level of the hierarchy, and it involves atoms and molecules
18
New cards
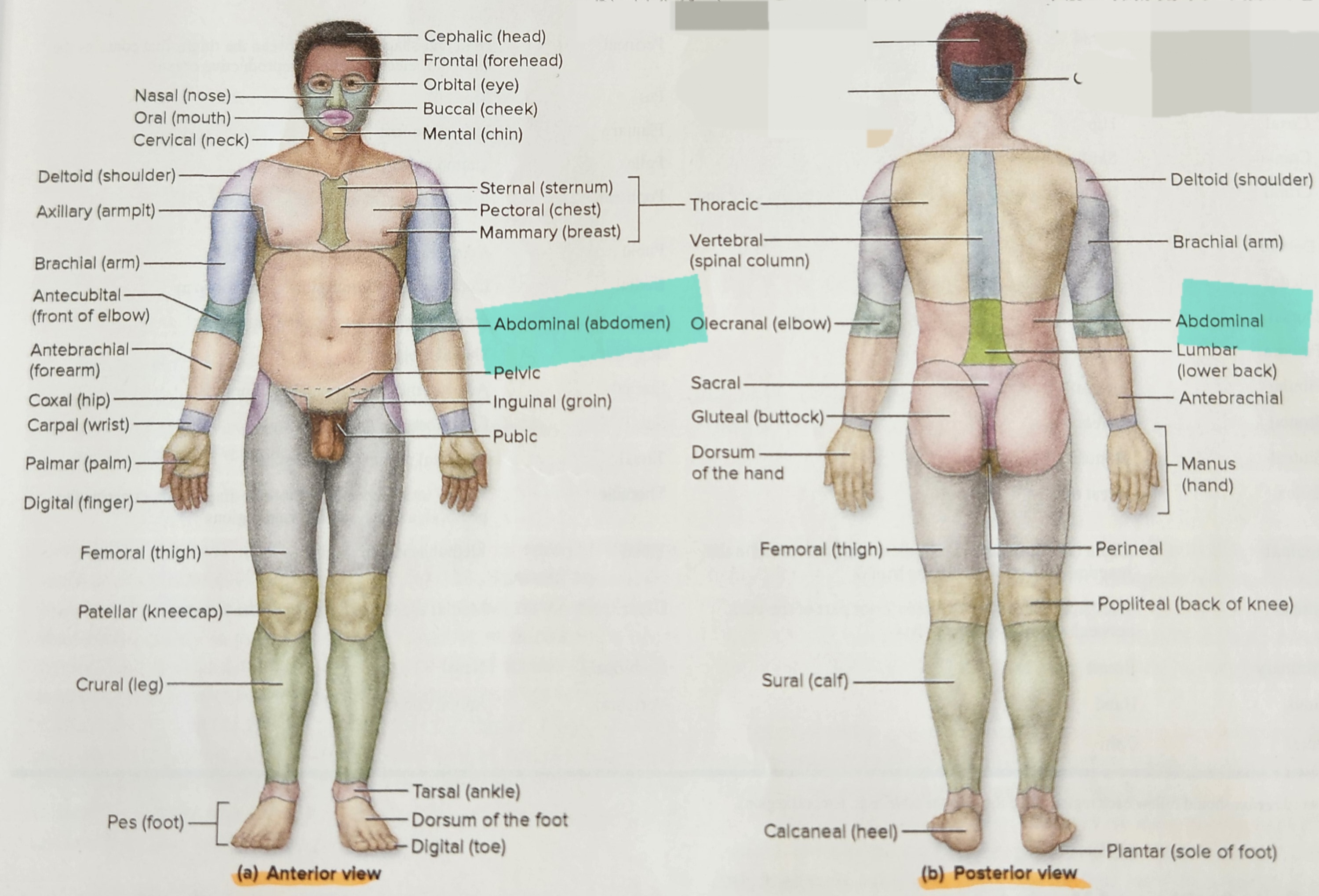
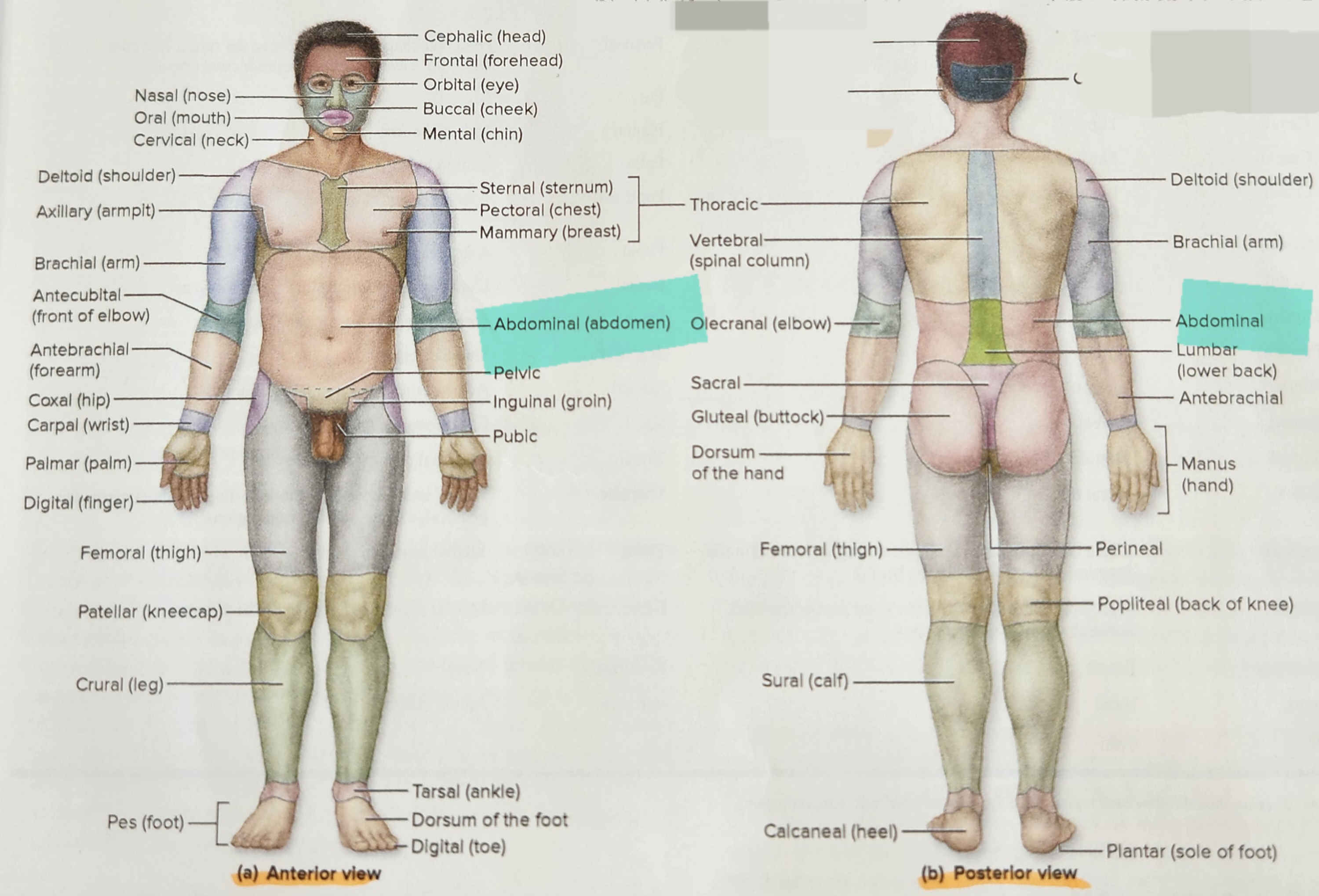
Atom
smallest units of matter
19
New cards
Molecule
two or more atoms combine they form a….
20
New cards
Macromolecules
more complex molecules which include some proteins and DNA and form organelles
21
New cards
Cellular Level
consists of cells, 2nd level of the hierarchy, formed from the atoms and molecules from the chemical level
22
New cards
Cells
smallest living structures and serve as the basic units of structure and function in organisms,
23
New cards
Tissue Level
groups of similar cells with a common function form the 3rd stage of the hierarchy
24
New cards
Tissues
precise organizations of similar cells that perform specialized functions
25
New cards
epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue
Four types of tissues
26
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that covers exposed surfaces and lines body cavities
27
New cards
Connective Tissue
Tissue that protects, supports, and interconnects body parts and organs
28
New cards
Muscle Tissue
Tissue that produces movement
29
New cards
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that conducts impulses for internal communication
30
New cards
Organ Level
different tissue types combine to form this level, 4th level
31
New cards
Organs
contain two or more tissue types that work together to perform specific, complex functions
32
New cards
Organ System Level
consists of related organs that work together to coordinate activities and achieve a common function (5th level)
33
New cards
Organismal Level
highest level of structural organization in the body, all body systems function inter dependently in this
34
New cards
11 Organ Systems
How many organ systems are in the human body
35
New cards
Integumentary System
Organ system that provides protection, regulates body temperature, site of cutaneous receptors, synthesizes vitamin D, prevents water loss
36
New cards
Hair, skin, and associated glands
Organs in the Integumentary System
37
New cards
Skeletal System
Organ system that provides support and protection, site of hemopoiesis (blood cell production), stores calcium and phosphorus, provides sites for muscle attachments
38
New cards
Skull, sternum, rib, cartilage, upper limb bones, vertebrae, sacrum, lower limb bones, knee joint
Organs in the Skeletal System
39
New cards
Muscular System
Organ system that produces body movement, generates heat when muscles contract
40
New cards
Sartorius muscle, orbicularis oculi muscle, pectoralis major muscle, aponeurosis, tendons
Organs in the Muscular System
41
New cards
Nervous System
Organ system which is a regulatory system that controls body movement, responds to sensory stimuli and helps control all other systems of the body. Also responsible for consciousness, intelligence, and memory
42
New cards
Sense organ (eye), brain, spinal cord, nerves
Organs in the Nervous System
43
New cards
Endocrine System
Organ system that consists of glands and cell clusters that secrete hormones, some of which regulate body and cellular growth, chemical levels in the body, and reproductive functions
44
New cards
Testes (male), kidney, pancreas, adrenal glands, thymus, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, pineal gland, hypothalamus
Organs in the Endocrine System
45
New cards
Cardiovascular System
Organ system that consists of the heart (a pump), blood, and blood vessels; the heart moves blood through blood vessels to distribute hormones, nutrients, and gases, and pick up waste products
46
New cards
Blood vessels, heart
Organs in the cardiovascular system
47
New cards
Lymphatic System
Organ system that transports and filters lymph (interstitial fluid transported through lymph vessels) and initiates an immune response when necessary
48
New cards
Tonsils, cervical lymph nodes, thymus, axillary lymph nodes. thoracic duct, spleen, inguinal lymph nodes, popliteal lymph node, lymph vessel
Organs in the lymphatic system
49
New cards
Respiratory System
Organ system that is responsible for exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between blood and the air in the lungs
50
New cards
Nasal cavity, nose, pharynx (throat), larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, thoracic diaphragm
Organs in the respiratory system
51
New cards
Digestive System
Organ system that mechanically and chemically digests food materials, absorbs nutrients, and expels waste products
52
New cards
Oral cavity (mouth), salivary glands, pharynx (throat), esophagus, liver, stomach, large intestine, small intestine
Organs in the digestive system
53
New cards
Urinary System
Organ system which filters the blood and removes waste products from the blood, concentrates waste products in the form of urine, and expels urine from the body
54
New cards
Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra
Organs in the urinary system
55
New cards
Male Reproductive System
Organ system that produces male sex cells (sperm) and male hormones (ex: testosterone); transfers sperm to the female
56
New cards
Ductus deferens, prostate gland, urethra, testis, seminal vesicle, epididymis, penis, scrotum
Organs in the male reproductive system
57
New cards
Female Reproductive System
Organ system that produces female sex cells (oocytes) and female hormones (ex: estrogen and progesterone), receives sperm from male, site of fertilization of oocyte, site of growth and development of embryo and fetus, and produces and secretes breast milk for nourishment of newborn
58
New cards
Mammary glands, ovary, uterus, vagina, external genitalia (clitoris, labia), uterine tube
Organs in the female reproductive system
59
New cards
Anatomic Position
position where an individual stands upright with the feet parallel and flat on the floor. The head is level, and the eyes look forward toward the observer, The arms are at either side of the body with the palms facing forward and the thumbs pointing away from the body
60
New cards
Supine Position
position where an individual is lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up (basically laying on their back)
61
New cards
Prone Position
position where an individual is lying horizontally with their face down (lying on their face and stomach)
62
New cards
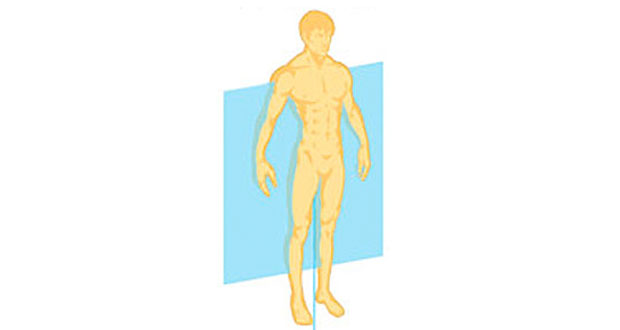
Coronal Plane (Frontal Plane)
a vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts. Anterior portion contains the chest and the posterior portion contains the back
63
New cards
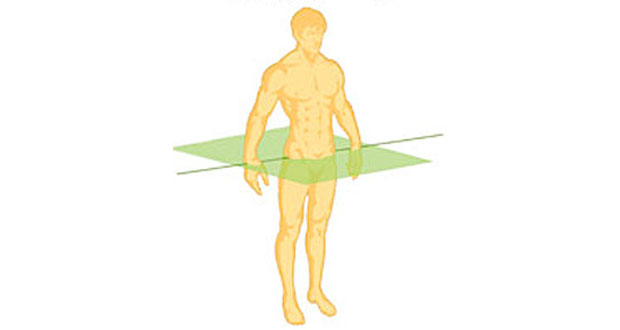
Transverse Plane (Cross-Sectional Plane or Horizontal Plane)
plane that cuts perpendicularly along the long axis of the body or organ. The body or organ is separated into both superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts, and the relationship of neighboring organs at a particular level is revealed
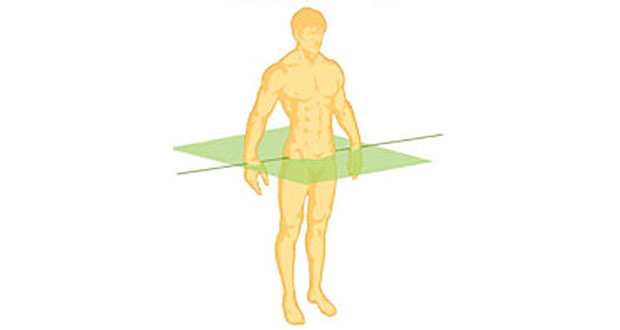
64
New cards
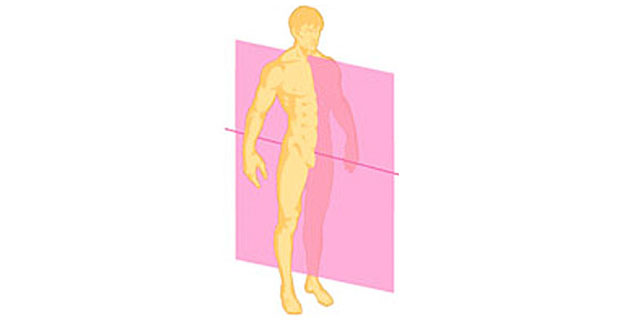
Midsagittal Plane (Median Plane)
a plane that extends through the body or organ vertically and divides the structure into right and left halves
65
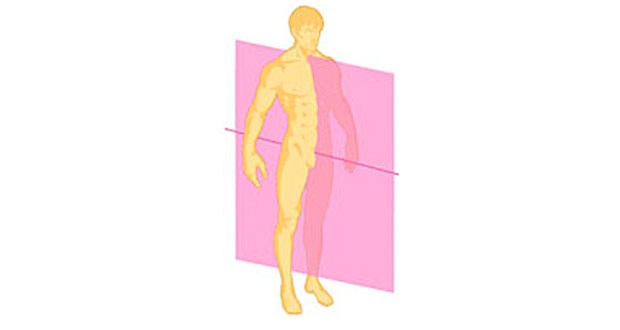
New cards
Sagittal Plane (Parasagittal Plane)
a plane that is parallel to the midsagittal plane, but either to the left or right of it. Divides the structure into right and left portions that may or may not be equal
66
New cards
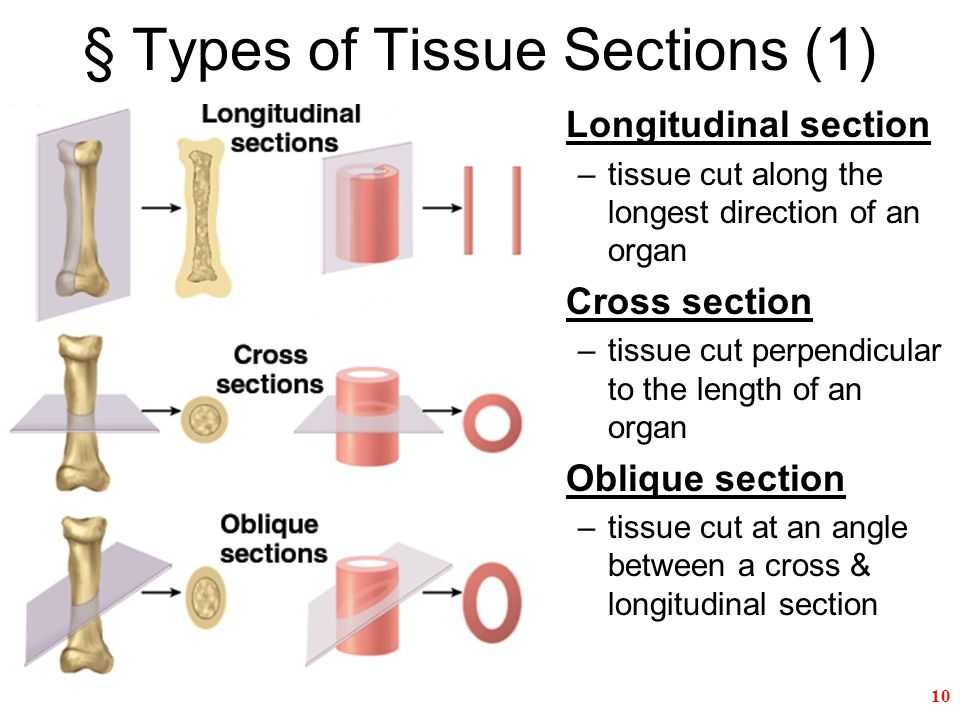
Longitudinal Section
(a section) tissue cut along the longest direction of an organ
67
New cards
Oblique Section
plane that passes through a specimen at an angle
68
New cards
Anterior (ex: the stomach is anterior to the spinal cord)
In front of; toward the front surface
69
New cards
Posterior (ex: The heart is posterior to the sternum)
In back of; toward the back surface
70
New cards
Dorsal (ex: the spinal cord is on the dorsal side of the body)
Toward the back side of the human body
71
New cards
Ventral (ex: The umbilicus (navel, belly button) is on the ventral side of the body)
Toward the belly side of the human body
72
New cards
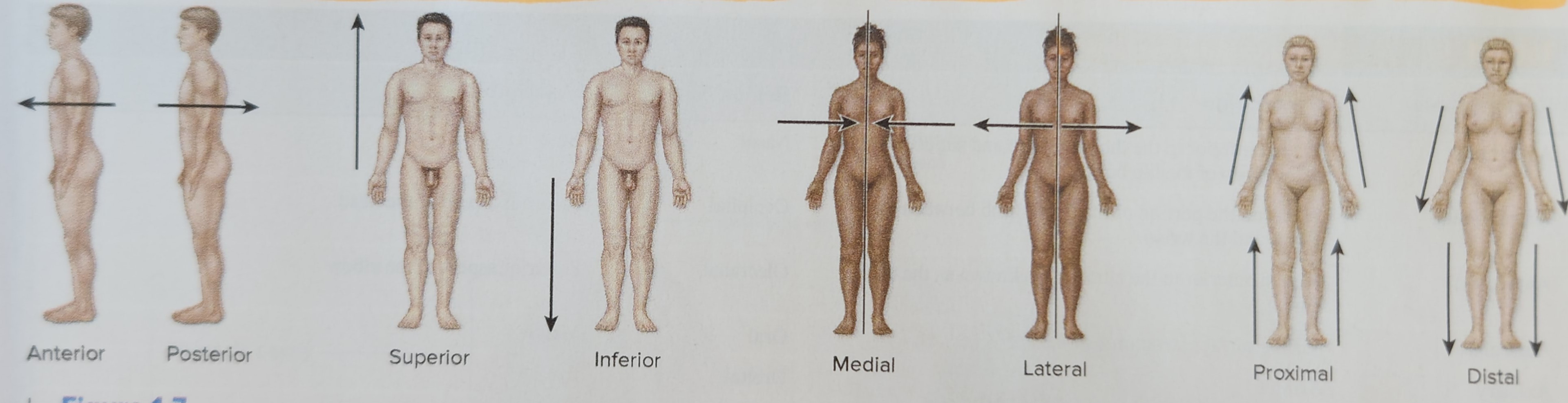
Superior (cranial) (ex: The chest is superior to the pelvis)
Closer to the head
73
New cards
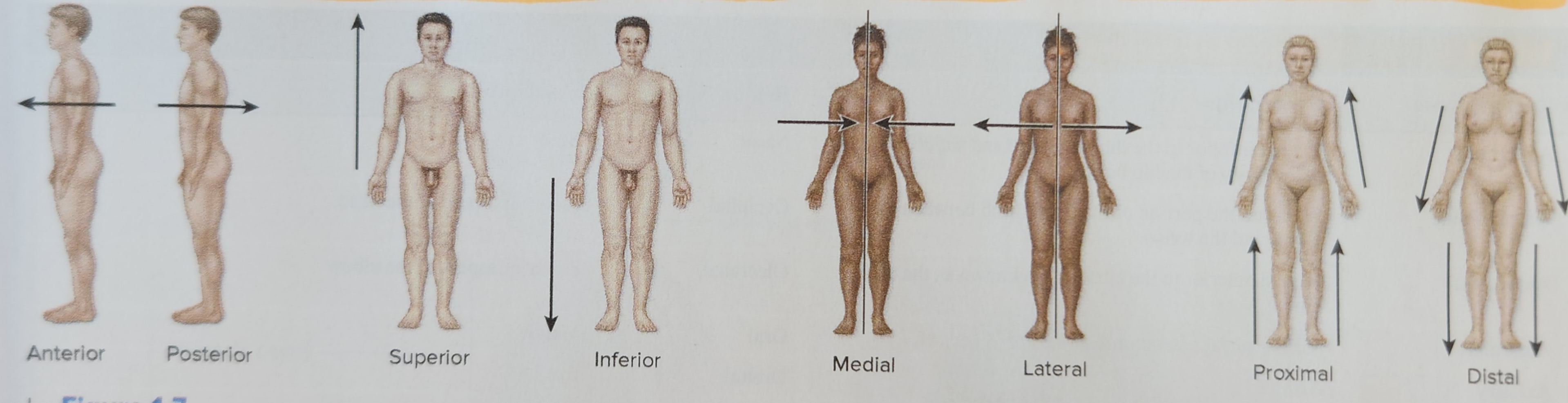
Inferior (Caudal) (The stomach is inferior to the heart)
Closer to the feet
74
New cards
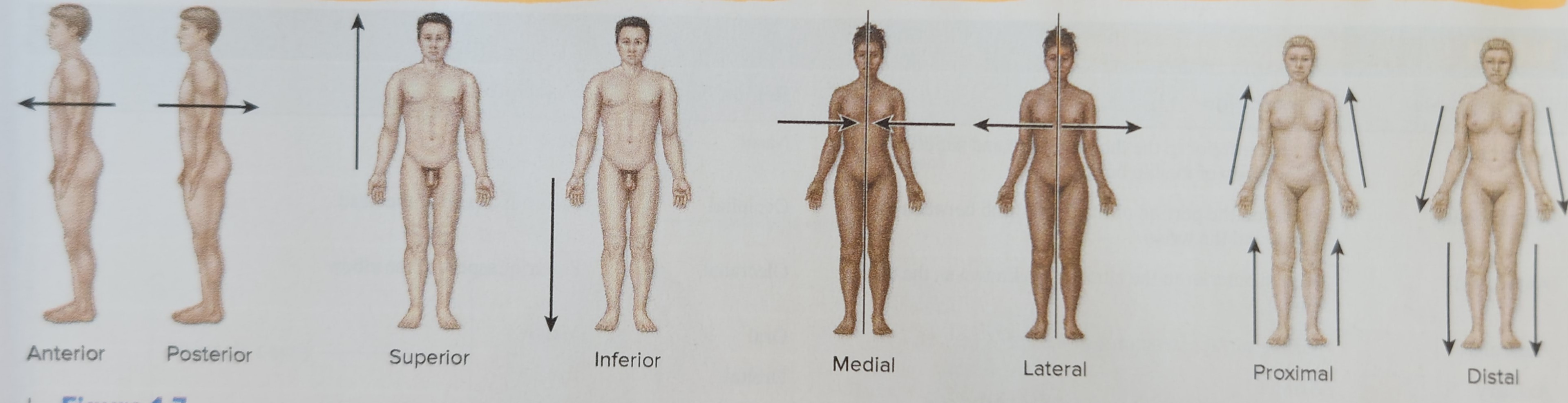
Medial (ex: The lungs are medial to the shoulders)
Toward the midline of the body
75
New cards
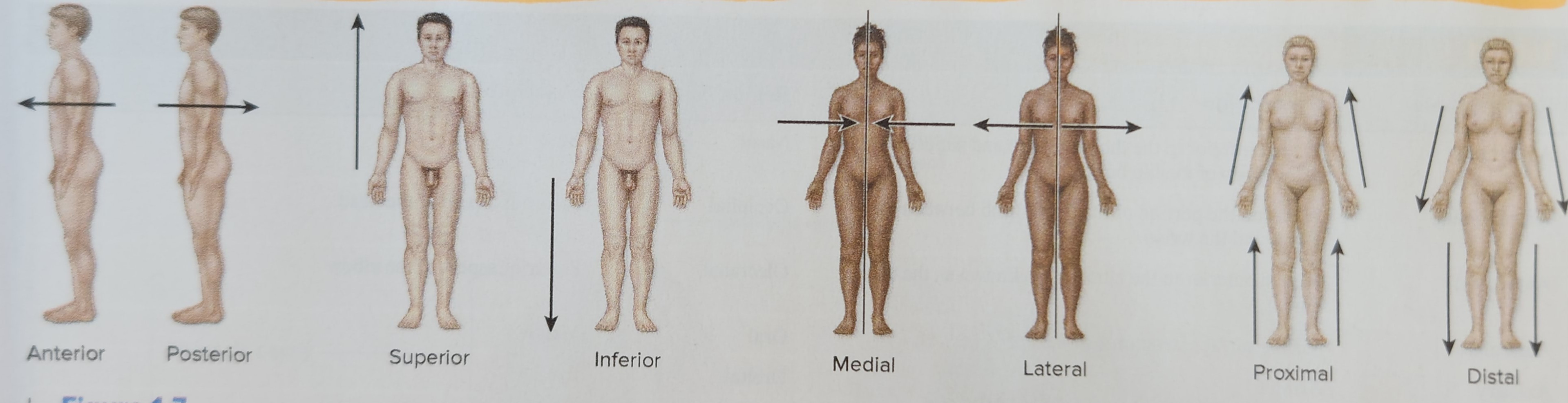
Lateral (ex: The arms are lateral to the heart)
Away from the midline of the body
76
New cards
Deep (ex: The heart is deep to the rib cage)
On the inside, internal to another surface
77
New cards
Superficial (ex: The skin is superficial to the biceps brachii muscle)
On the outside, external to another structure
78
New cards
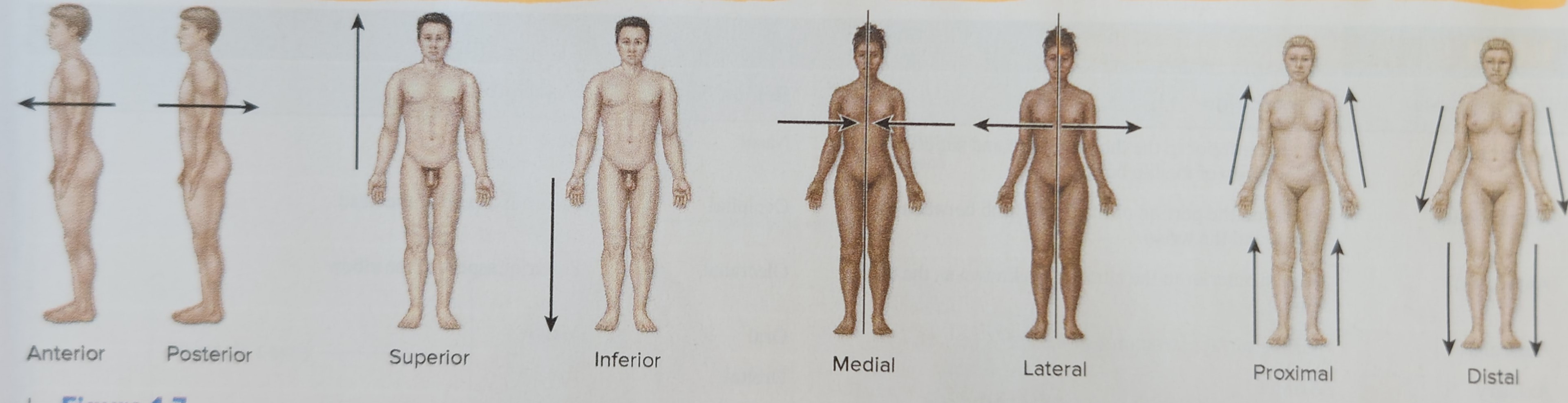
Proximal (ex: The elbow is proximal on the hand.)
Closest to point of attachment to trunk
79
New cards
Distal (ex: The wrist is distal to the elbow.)
Furthest from point of attachment to trunk
80
New cards
2 regions (Axial and Appendicular region)
How many main regions is the human body partitioned into and what are their names
81
New cards
Axial Region
region of the body that includes the head, neck, and trunk; forms the main vertical axis of the body
82
New cards
Appendicular Region
region of the body that includes the limbs/appendages which attach to the body’s axis
83
New cards
Abdominal Region
Abdomen
84
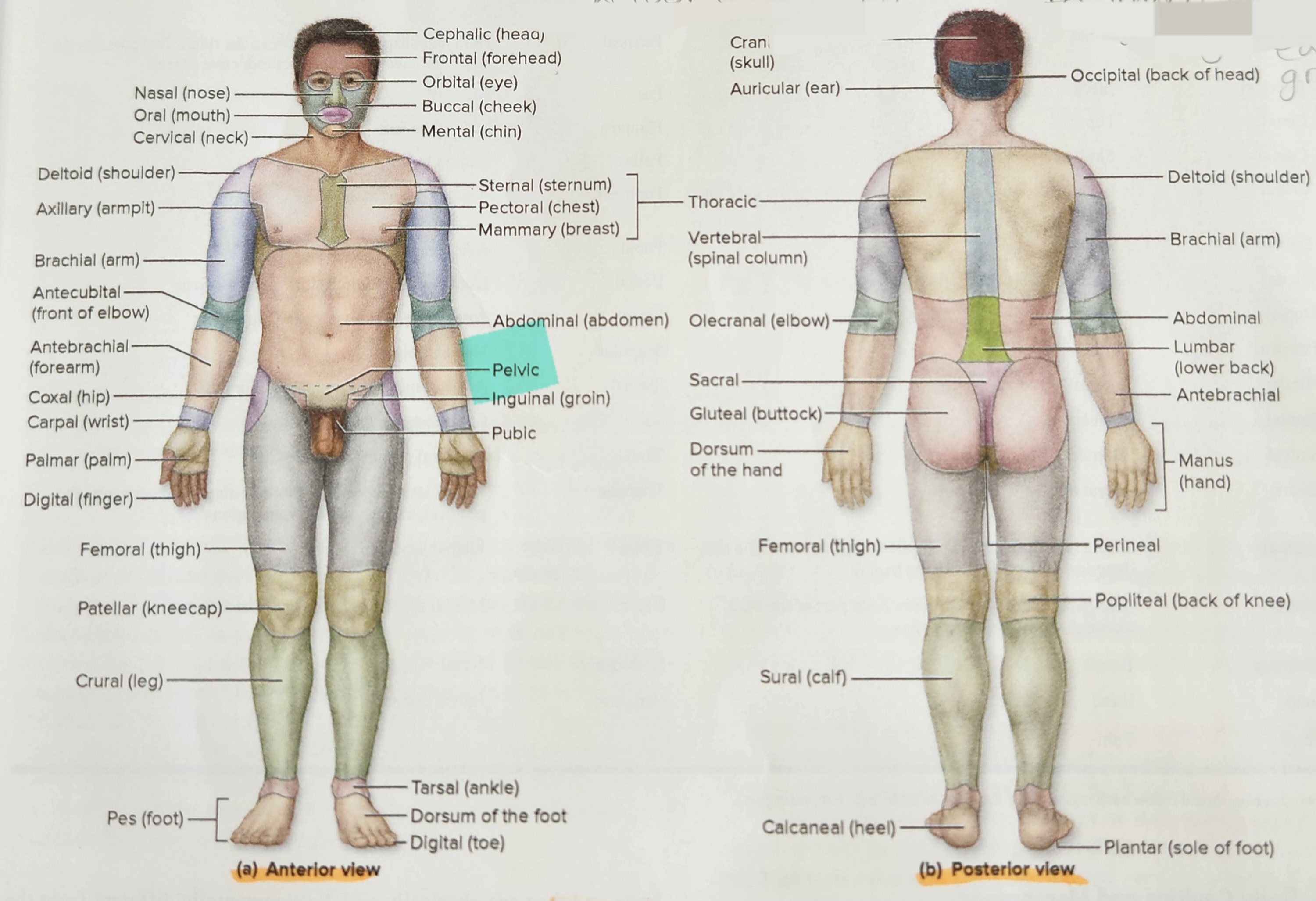
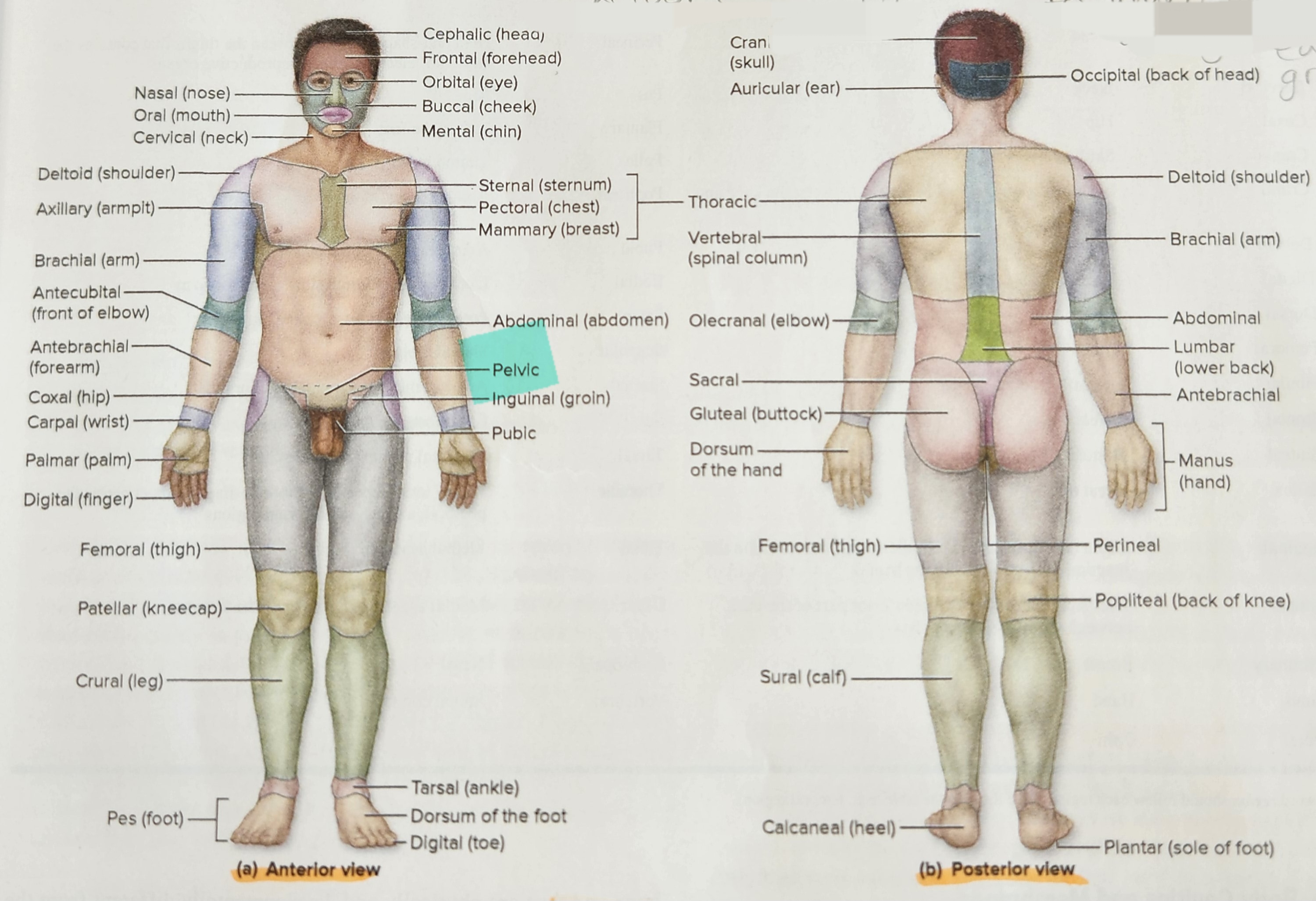
New cards
Antebrachial Region
Forearm (the portion of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist)
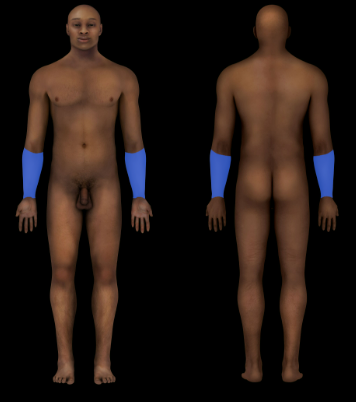
85
New cards
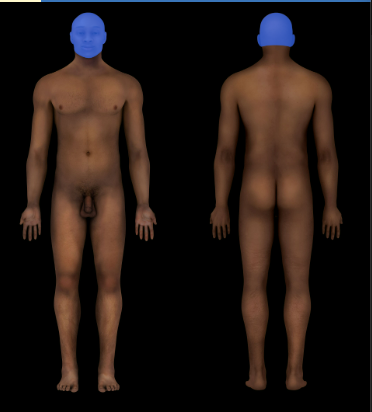
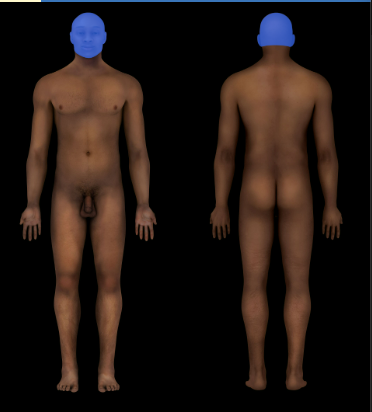
Cephalic Region
Head
86
New cards
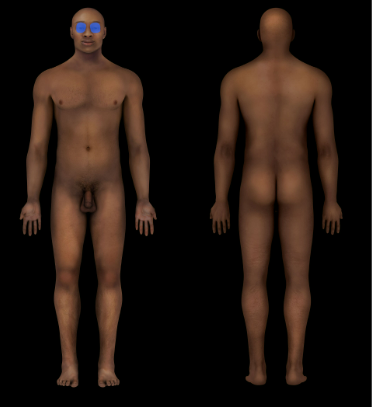
Orbital Region
Eye
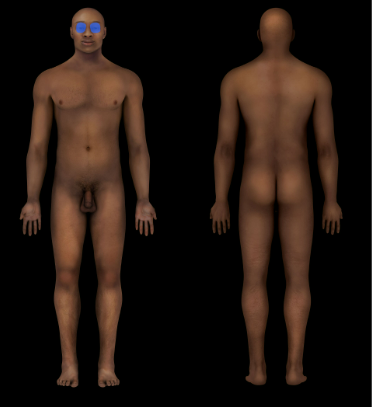
87
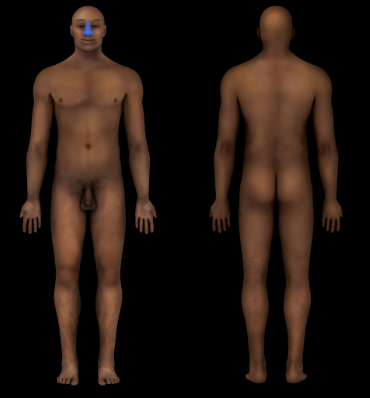
New cards
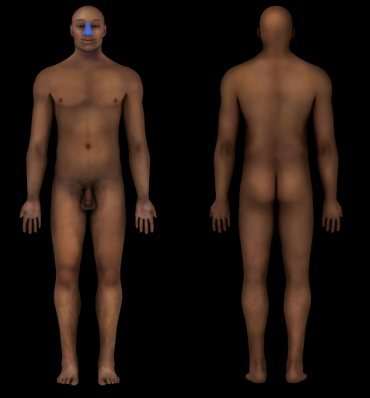
Nasal Region
Nose
88
New cards
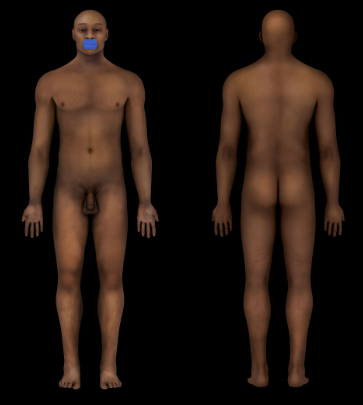
Oral Region
Mouth
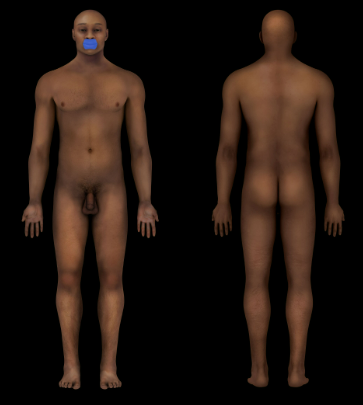
89
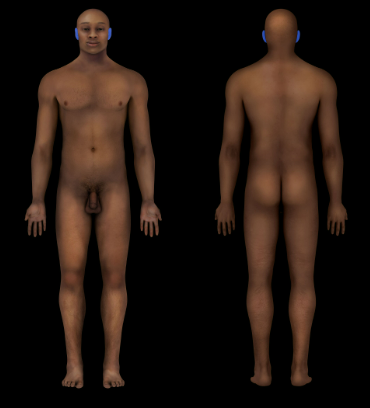
New cards
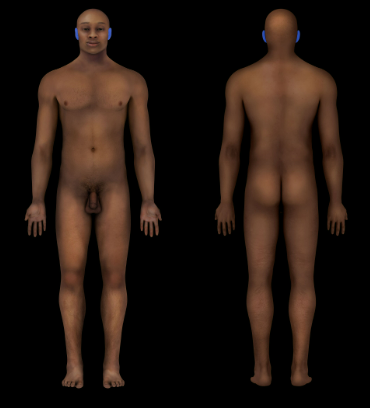
Auricular Region
Ear (visible surface structure)
90
New cards
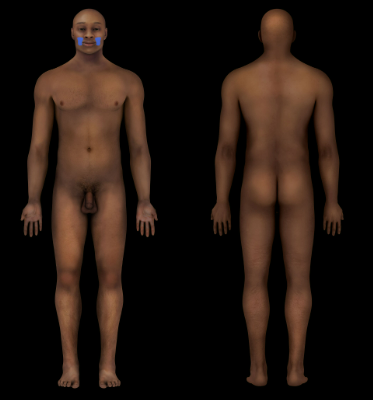
Buccal Region
Cheek
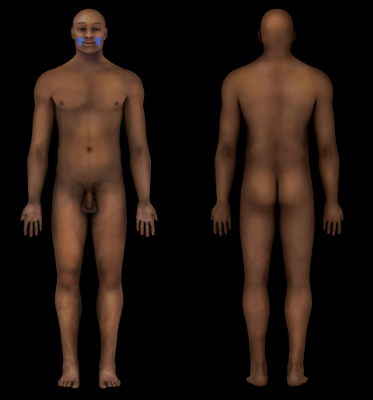
91
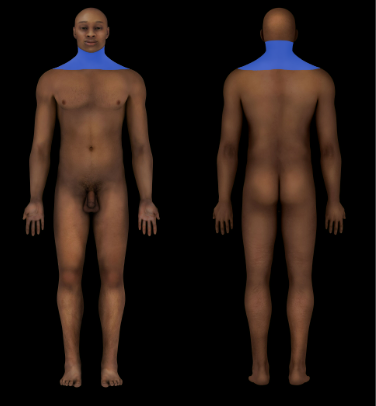
New cards
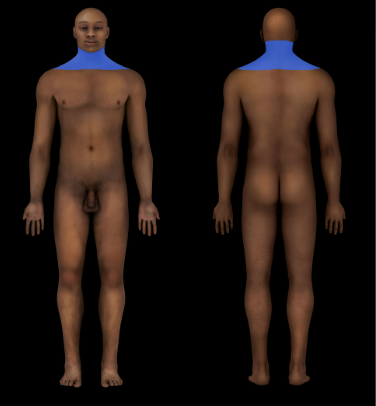
Cervical Region
Neck
92
New cards
Trunk Region
The main part of the body that contains the chest, abdomen, pelvis, and back.
93
New cards
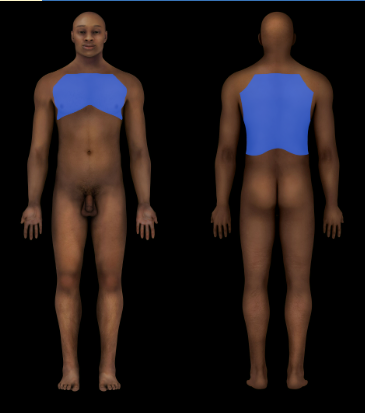
Thoracic Region
Thorax
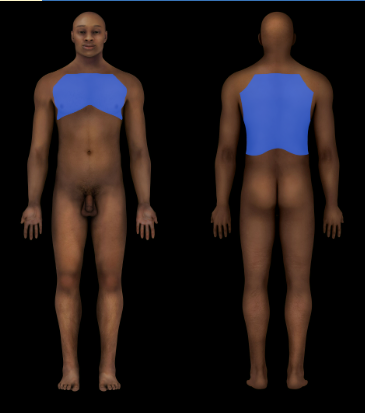
94
New cards
Pelvic Region
Pelvis
95
New cards
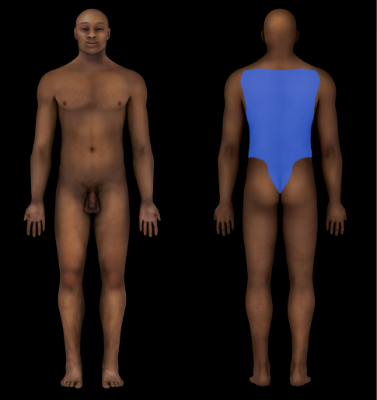
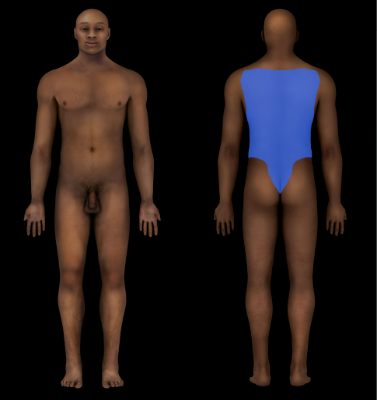
Dorsal Region
Back
96
New cards
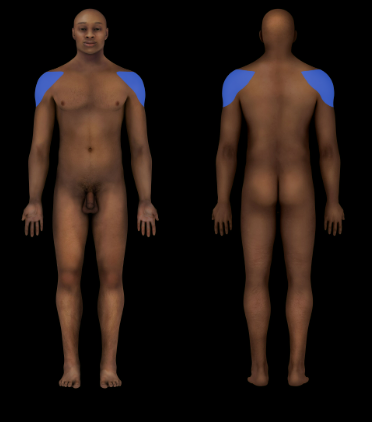
Deltoid Region
Shoulder
97
New cards
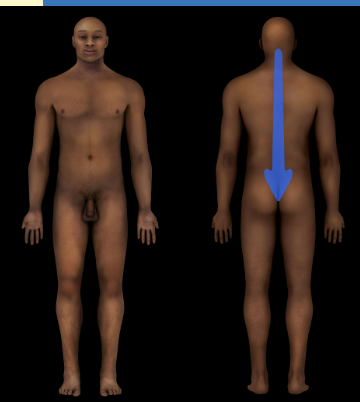
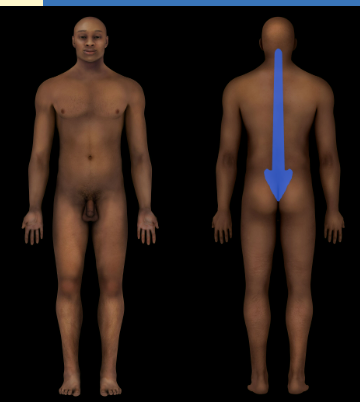
Vertebral Region
Spinal Column
98
New cards
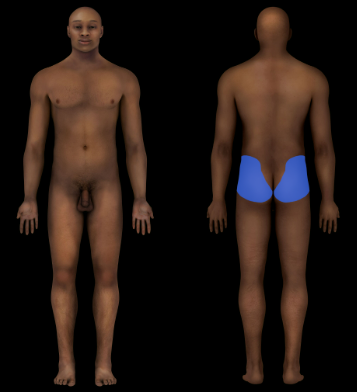
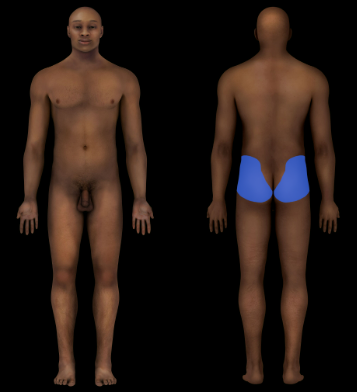
Gluteal Region
Buttock
99
New cards
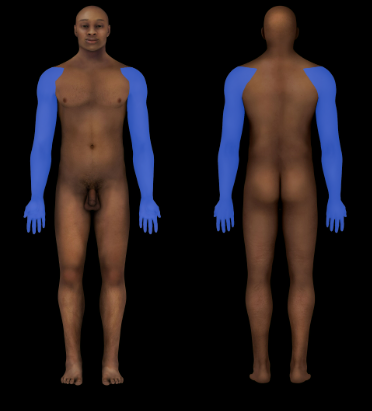
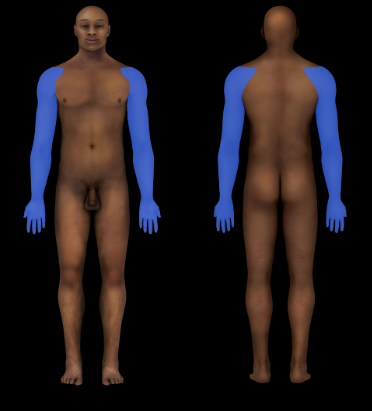
Upper Limb Region
Arm
100
New cards
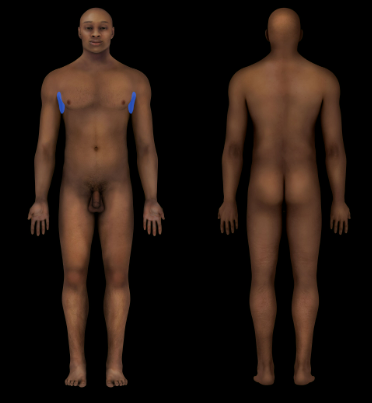
Axillary Region
Armpit