Introduction to Geology, Cosmology, and Plate Tectonics for Earth Science Students
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What do geologists study?
Geologists study the materials that comprise Earth, its history, and the processes at work on Earth.
Who are considered the Fathers of Geology?
James Hutton (1726-1797) and Charles Lyell (1797-1875).
What is the Principle of Uniformitarianism?
The principle that processes observed on Earth today have worked in much the same way throughout the geologic past.
What are the characteristics of an energetically open system in geology?
An energetically open system absorbs energy from the Sun.
What defines a chemically closed system in geology?
A chemically closed system allows for the exchange of all atoms on the planet.
What are the criteria for a good hypothesis in scientific research?
A good hypothesis must be testable, verifiable, and possess predictive power.
What does the Theory of Plate Tectonics encompass?
It unifies observations from various fields, including continental drift, sea-floor spreading, fossil distributions, seismology, and volcanology.
What is cosmology?
Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe.
What model did Ptolemy propose regarding the structure of the Universe?
Ptolemy proposed the Geocentric model, which places Earth at the center of the Universe.
What significant model did Nicolaus Copernicus introduce?
Nicolaus Copernicus introduced the Heliocentric model, which places the Sun at the center of the Universe.
What evidence did Jean-Bernard-Leon Foucault provide regarding Earth?
Foucault provided evidence that the Earth spins on its axis.
What is the significance of the Doppler effect in astronomy?
The Doppler effect explains the change in frequency of waves, including light, when the source moves relative to the observer.
What does red shift indicate in the context of the Universe?
Red shift indicates that an object is moving away from the observer, suggesting the expansion of the Universe.
What is the Big Bang theory?
The Big Bang theory posits that the Universe began from a hot and dense singularity that expanded rapidly.
How old is the Universe according to current estimates?
The Universe is approximately 13.7 billion years old.
What is a nebula?
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust and gases, often associated with stellar birth and death.
What is the Nebular Hypothesis?
The Nebular Hypothesis states that the solar system condensed from a rotating nebula.
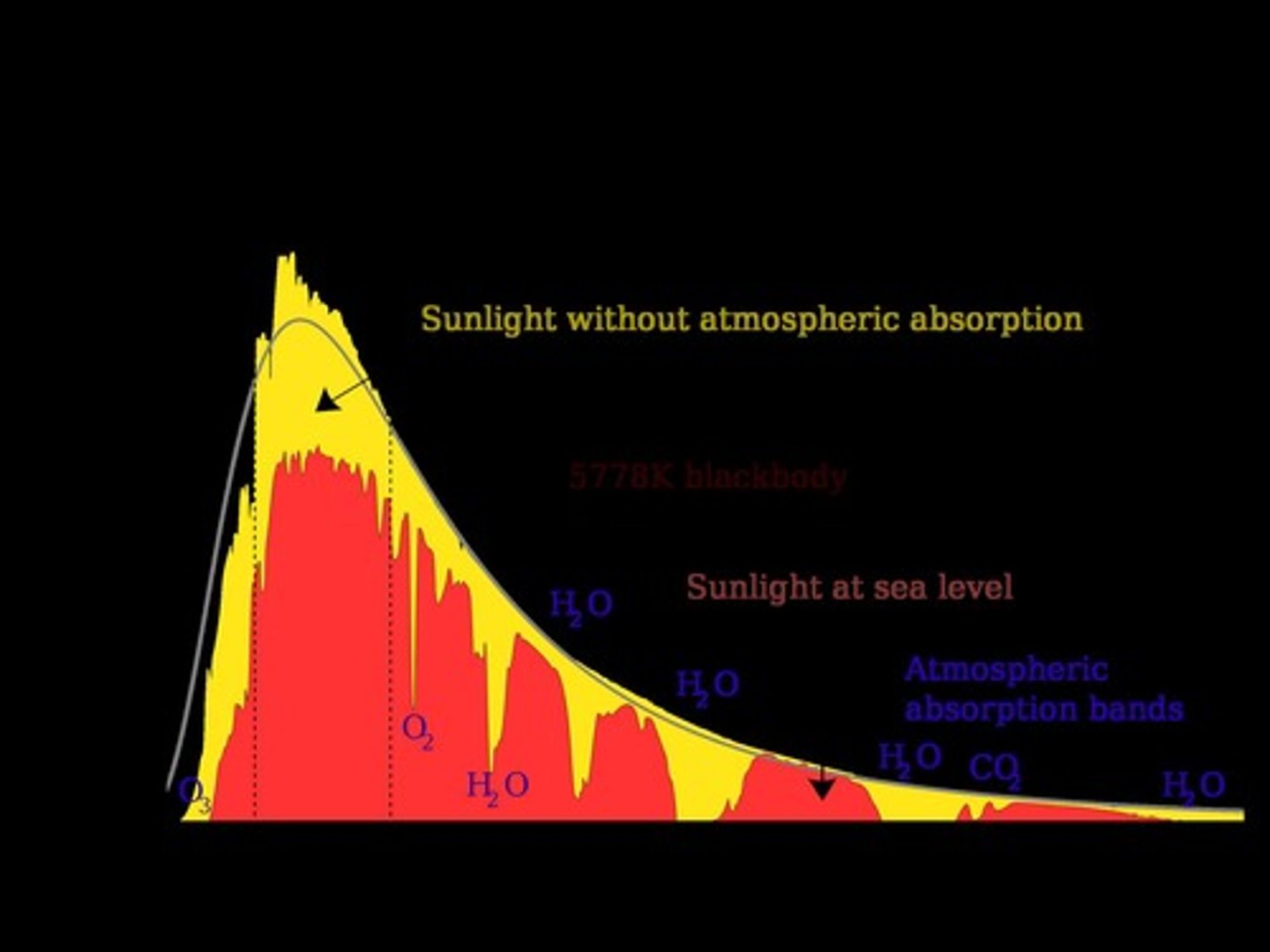
What is the composition of the Earth's atmosphere?
The atmosphere is composed of approximately 78.08% nitrogen and 20.95% oxygen.
What is the lithosphere?
The lithosphere is all of Earth's rock and sediments.
What is the hydrosphere?
The hydrosphere includes all water on Earth, both surface and groundwater.
What is the cryosphere?
The cryosphere is the portion of Earth where water is in solid form, including snow, ice, and glaciers.
What is the biosphere?
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on the planet and their interactions with abiotic parts.
What is the Van Allen Belts' function?
The Van Allen Belts trap particles that protect life on Earth from harmful radiation.
What is the significance of coronal mass ejections (CME)?
CMEs spread solar material throughout the Universe, influencing space weather.
What is the Milky Way Galaxy?
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy containing 200-300 billion stars.
What is the approximate size of the Milky Way Galaxy?
The Milky Way is over 100,000 light years across.
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
Core, mantle, and crust.
Why does Earth have a core, mantle, and crust?
Because Earth was melted, leading to differentiation based on density.
What characterized the surface of early Earth?
It was inhospitable with constant volcanism, extreme temperatures, and no stable crust.
What gases made up the first atmosphere of Earth?
Mostly hydrogen (H) and helium (He).
What was the second atmosphere of Earth composed of?
Similar to modern volcanic gases, including water, nitrogen, CO2, CO, methane, hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia, but missing oxygen.
What evidence indicates the absence of oxygen in early Earth rocks?
The presence of pyrite and uraninite sediments, which only form in non-oxidizing environments.
What are the main components of Earth by percentage?
Iron (34.6%), Oxygen (29.5%), Silicon (15.2%), Magnesium (12.7%), Other (8%).
What is the silica tetrahedron?
A key component in most common rocks/minerals, represented by SiO4.
How does pressure and temperature change within the Earth?
Pressure and temperature increase as you go deeper into the Earth.
What is the average density of Earth?
Approximately 5.5 g/cm³.
What are the two types of crust on Earth?
Oceanic crust and continental crust.
How thick is the continental crust?
25 to 70 km thick, typically granitic in composition.
How thick is the oceanic crust?
7 to 10 km thick, thinnest at mid-ocean ridges and thickest at the continental shelf, basaltic in composition.
What is the composition of the mantle?
Rich in iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg), making up 84% of Earth's volume.
What is the core primarily composed of?
Enriched in iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni), with densities up to about 13 g/cm³.
What is the significance of plate tectonics?
It explains the movement of Earth's rigid plates over a ductile mantle.
Who developed the Continental Drift hypothesis?
Alfred Wegener in 1915.
What is a subduction zone?
A region where dense oceanic lithosphere slides under lighter continental lithosphere, forming trenches and volcanic chains.
What is the difference between compressive and tensional stress?
Compressive stress squeezes materials together, while tensional stress pulls them apart.
What are the two physical layers of Earth?
Lithosphere (rigid crust and upper mantle) and asthenosphere (plastic, ductile layer below the lithosphere).
What is the process of seafloor spreading?
New crust forms at mid-ocean ridges and moves laterally away from them.
What is a hotspot in geology?
A stationary area in the mantle that creates a linear series of volcanoes as tectonic plates move over it.
What is the average rate of tectonic plate movement?
Typically 1-10 cm/year.
What is the significance of paleomagnetism in geology?
It helps to understand the historical orientation and movement of tectonic plates based on magnetic minerals in rocks.
What is the role of temperature in rock deformation?
Higher temperatures make rocks behave more plastically.
What is the difference between elastic and plastic deformation?
Elastic deformation is temporary and recovers shape after stress, while plastic deformation is permanent.
What are the major types of plate boundaries?
Divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries.
What distinguishes a scientific theory from a hypothesis?
A theory is a well-substantiated system of ideas that explains a broad range of phenomena.
What is the approximate age of the Earth according to cosmological studies?
4.5 billion years
Which of the following is a limitation that geological studies often face?
Time constraints due to long-term processes
What does a 'light year' measure?
the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.5 trillion kilometers.
What are chondrites?
meteorites that provide clues about the early solar system's composition and age.
Which layer of the Earth makes up the largest percentage of its volume?
mantle
What process generates Earth's magnetic field?
The dynamo effect, caused by the movement of molten metal in the outer core, generates Earth's magnetic field.
What geological feature provides evidence for continental drift and plate tectonics?
Matching rock types across continents
What term describes the fracturing or breaking of rocks when stress limits are exceeded?
Rupture
Which factor promotes plastic flow in rock deformation?
Higher temperature
What is the geologic record?
preserved evidence of Earth's history, including past climates, life forms, and tectonic activity.
What distinguishes the inner planets from the outer planets in our solar system?
Inner planets are smaller, rocky, and dense, while outer planets are larger, gaseous, and less dense.
What geological feature provides evidence for seafloor spreading and plate tectonics?
Mid-ocean ridges
What does 'carrying capacity' refer to in the context of human population?
Earth's ability to sustain human life at a comfortable level.
What gradients influence whether rocks deform elastically, plastically, or rupture?
Geobaric (pressure) and geothermal (temperature)
Which of the following observations provided evidence against the geocentric model of the universe?
Galileo's telescopic observations
What is the primary composition of the Earth's core?
iron and nickel, which contributes to the planet's magnetic field.
What protects the Earth from harmful solar wind particles?
The magnetosphere, generated by Earth's magnetic field, deflects solar wind particles.
What is the distance to the Moon?
about 381,555 km (average).
What is the distance from the Earth to the Sun?
roughly 149.6 million km (about 93 million miles).
What is the distance to Alpha Centauri?
approximately 4.3 light years
How many galaxies does the Universe contain?
over 100 billion galaxies
How many stars does the Milky Way produce per year?
about 7 stars per year
What evidence did Galileo provide that supported the heliocentric model?
observation of moons orbiting Jupiter and the phases of Venus supported the heliocentric model.
What is the significance of Foucault's pendulum experiment?
provided tangible evidence for Earth's rotation.
What type of galaxy is the Milky Way?
spiral-shaped
Approximately how many stars does the Milky Way galaxy contain?
over 300 billion stars
How is Earth's age primarily determined?
determined using radiometric dating of long-lived radioactive isotopes
What process led to the formation of planets from dust and gas in the early solar system?
Planetesimals formed from dust, colliding and sticking together to form planets.
During the 20th century alone the population grew from what to what?
1.65 billion to 6 billion
What was the population at the dawn of agriculture, about 8000 B.C?
approximately 5 million
Topography
physical features of the land surface represented by changes in elevation
population has experiences exponential growth why?
life expectancy has increased (78.6 yrs)
birth rates increased
people are more mobile