Chronic adaptations to aerobic training - respiratory
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Increased pulmonary ventilation during maximal exercise
Ventilation increases due to higher tidal volume (TV) and respiratory frequency (RF), supplying more oxygen to working muscles
At rest and submaximal exercise, ventilation may be reduced due to improved oxygen extraction
Increased tidal volume
Aerobic training strengthens respiratory muscles, increasing the amount of air inspired and expired per breath
This improves oxygen diffusion into alveoli capillaries and delivery to working muscles.
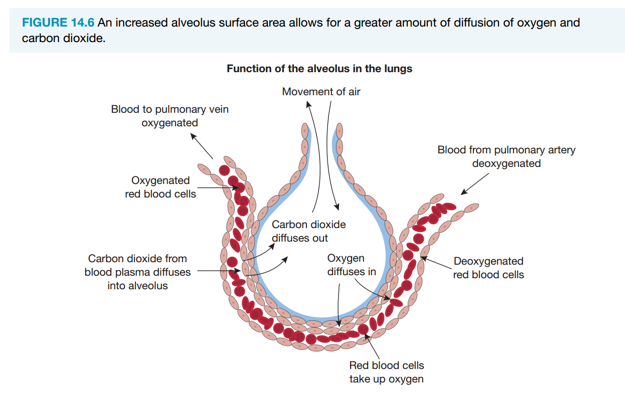
Increased pulmonary diffusion
Aerobic training increases alveoli surface area, improving oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange between alveoli and capillaries. Combined with increased ventilation, more oxygen is inhaled, extracted, and delivered to working muscles.
Decreased resting and submaximal respiratory frequency
Athletes breathe fewer times per minute at rest and submaximal exercise due to improved pulmonary function and increased oxygen extraction from alveoli to capillaries.
Total lung capacity adaptation
Increase
Pulmonary ventilation adaptation
Rest: Decrease
Submaximal exercise: Decrease
Maximal exercise: Increase
Tidal volume adaptation
Rest: No change
Submaximal exercise: Increase
Maximal exercise: Increase
Respiratory frequency adaptation
Rest: Decrease
Submaximal exercise: Decrease
Maximal exercise: Increase
Pulmonary diffusion adaptation
Increase
Increased alveolar surface area (pulmonary diffusion)
Aerobic training increases alveoli surface area, improving oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange. More oxygen is extracted and transported to working muscles.
Increased tidal volume
Aerobic training strengthens respiratory muscles, increasing the amount of air inspired and expired per breath, enhancing oxygen delivery to working muscles.
Decreased resting and submaximal respiratory frequency
Improved pulmonary function allows fewer breaths per minute at rest and submaximal exercise, increasing oxygen extraction efficiency from alveoli to capillaries.
Increased ventilation during maximal exercise
At maximal workloads, tidal volume and respiratory frequency increase, allowing greater oxygen delivery to working muscles.