CSD 460: Exam 1 - Middle Ear
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
what are the bony parts of the middle ear called
ossicles
what are 3 ossicles in the middle ear
malleus, incus, stapes
which is the biggest ossicle
malleus
which is the smallest ossicle
stapes
what is the main function of the middle ear
impedence matching
which ossicle is in contact with the eardrum
malleus
which ossicle is in contact with the oval window of the cochlea
stapes
ossicles are suspended by ___
ligaments
ossicles route sound vibrations striking the eardrum directly to the ___
oval window
what are the 2 middle ear muscles
stapedius muscle and tensor tympani muscle
what is the main function for the middle ear muscles
protect the ear from noise damage
what is the stapedius muscle attached to
stapes
what is the tensor tympani attached to
malleus
what does the stapedius muscle contract to
loud sound
what does the tensor tympani contract to
touch to lateral air and air pressure changes in the EAC
what is the stapedius innervated by
facial nerve (CNVII)
what is the tensor tympani innervated by
trigeminal nerve (CNV)
tensor tympani originates from ___ wall of the cavity
anterior
stapedius originates from ___ wall of the cavity
posterior
what are the purposes of the eustachian tube
equalize air pressure and drain fluids into nasopharynx
eustachian tube connects the ME to the ___
upper part of the throat (nasopharynx)
how much of the eustachian tube is encased in bone
1/3
how much of the eustachian tube is encased in cartilage
2/3
the eustachian tube is normally __
closed
the eustachian tube normally sits at a ___ degree angle for an adult
45
why are children more susceptible to middle ear infections
children’s eustachian tube sits horizontally making it harder for fluids to drain
what imbalances air pressure
colds, allergies, and changes in elevation
what two muscles help open/close the eustachian tube
tensor veli palatini and levator veli palatini
which eustachian tube muscle allows it to open/close
tensor veli palatini
which eustachian tube muscle allows it to elongate/shorten
levator veli palatini
with a eustachian tube, it allows for ____ to occur
air exchange
An eustachian tube that’s always open is called ___
patulous eustachian tube
what is the the most common disorder of the middle ear, which causes conductive hearing loss and is seen in 70% of children in the USA before they reach age 2
otitis media
If fluid pressure builds in the middle ear, the tympanic membrane faces the threat of perforation. Which procedure is done to avoid this?
insertion of P.E. tubes
if the eustachian tube is swelled shut, in order for air pressure to leave, it goes through _____
pars flaccida of the TM
what 2 mechanisms does sound go through in the ME to compensate for loss of energy
areal ratio and complex lever system
what parts of the ME is the areal ratio applied to
eardum/tympani membrane and footplate of stapes
how much sound is recovered because of areal ratio
25 dB
what ossicles are the complex lever system applied to
malleus and incus (long process)
how much sound is recovered because of the complex lever system
2 dB
because our ears have air-cochlear fluid mismatch, our ears have developed a ____
middle ear (ME) transfer function
the ossicles overcome loss of sound by increasing what
pressure
what is the reflex that allows for the stapedius muscle to contract in both ears even if only one ear was stimulated
consensual reflex
what reflex allows for muscles that are meant to block sound to activate
acoustic reflex
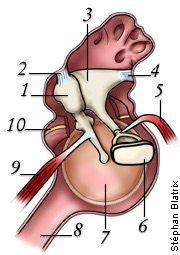
what is 1
malleus
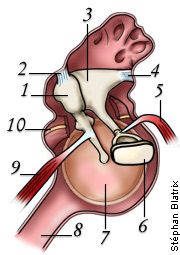
what is 3
incus
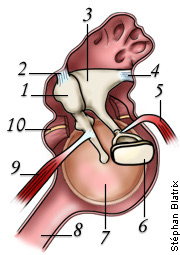
what is 6
stapes
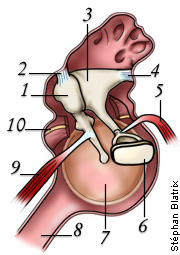
what is 8
eustachian tube
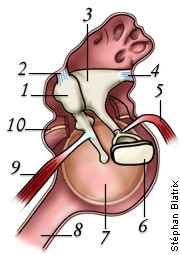
what is 5
stapedius muscle
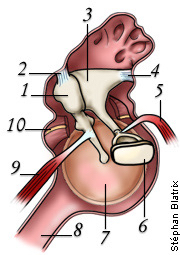
what is 9
tensor tympani musclehw
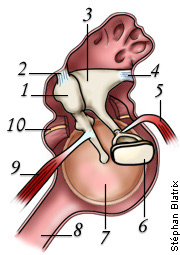
what is 7
tympanic cavity