SEHS UNIT 1.2 - The Muscular System
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
General characteristics common to muscle tissue
contractility
extensibility
elasticity
atrophy
hypertrophy
controlled by nerve stimuli
fed by capillaries
Contractibility
Ability of a muscle to contract when stimulated by a neuron
Extensibility
Ability of muscle to be stretched beyond its resting length
Elasticity
Ability of muscle to return to its normal resting length after being stretched (Similar to a rubber band or spring)
Atrophy
Muscle mass loss due to inactivity
Hypertrophy
Muscle mass gain due to increased activity
Nerve control
Movement occurs based upon stimulation for the central nervous system
Fed by capillaries
Network of blood vessels delivering blood carrying nutrients, O2 and glucose to the muscles, and remove CO2.
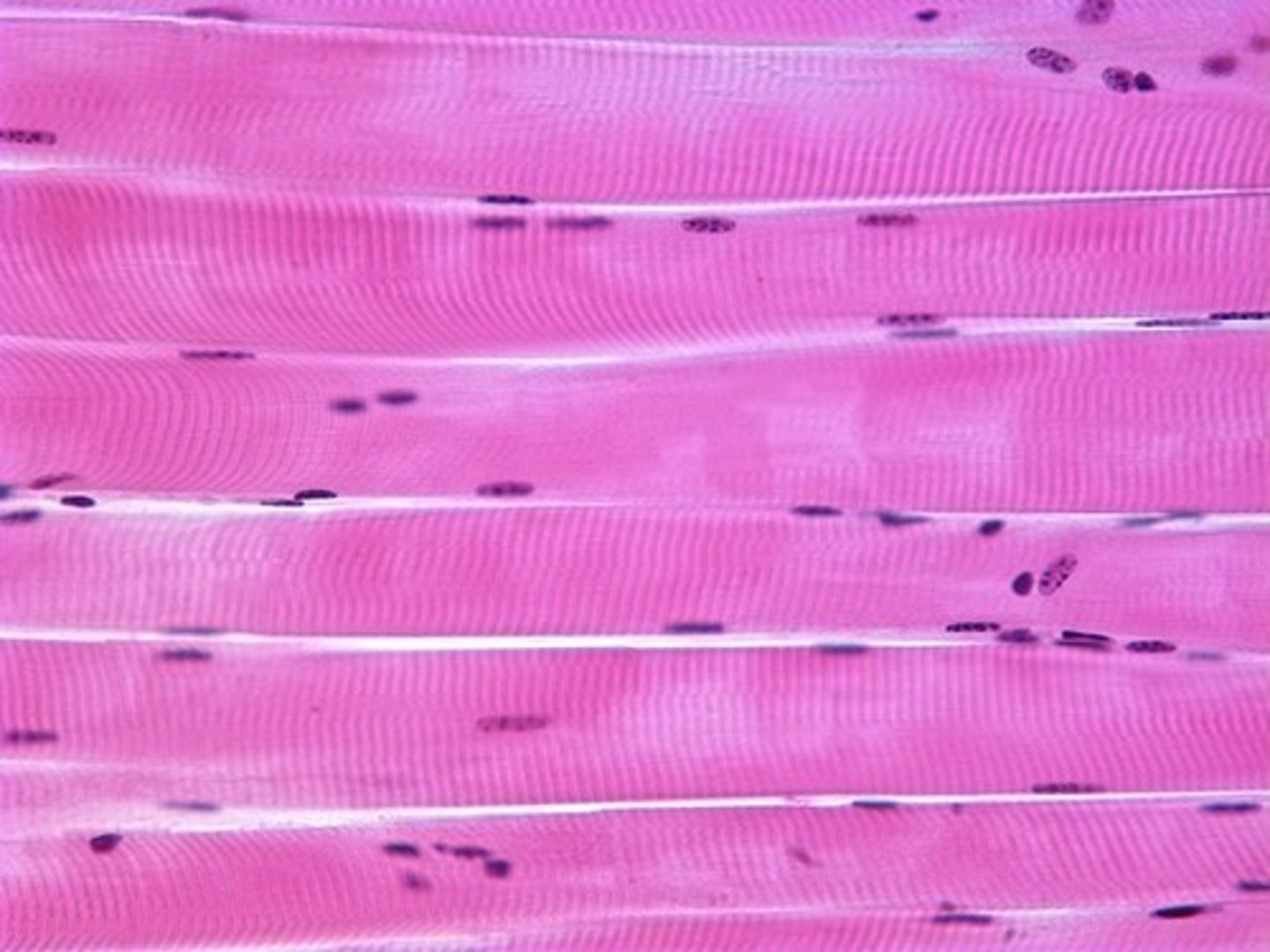
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary
Striated and
Multinucleated (Bicep brachii)
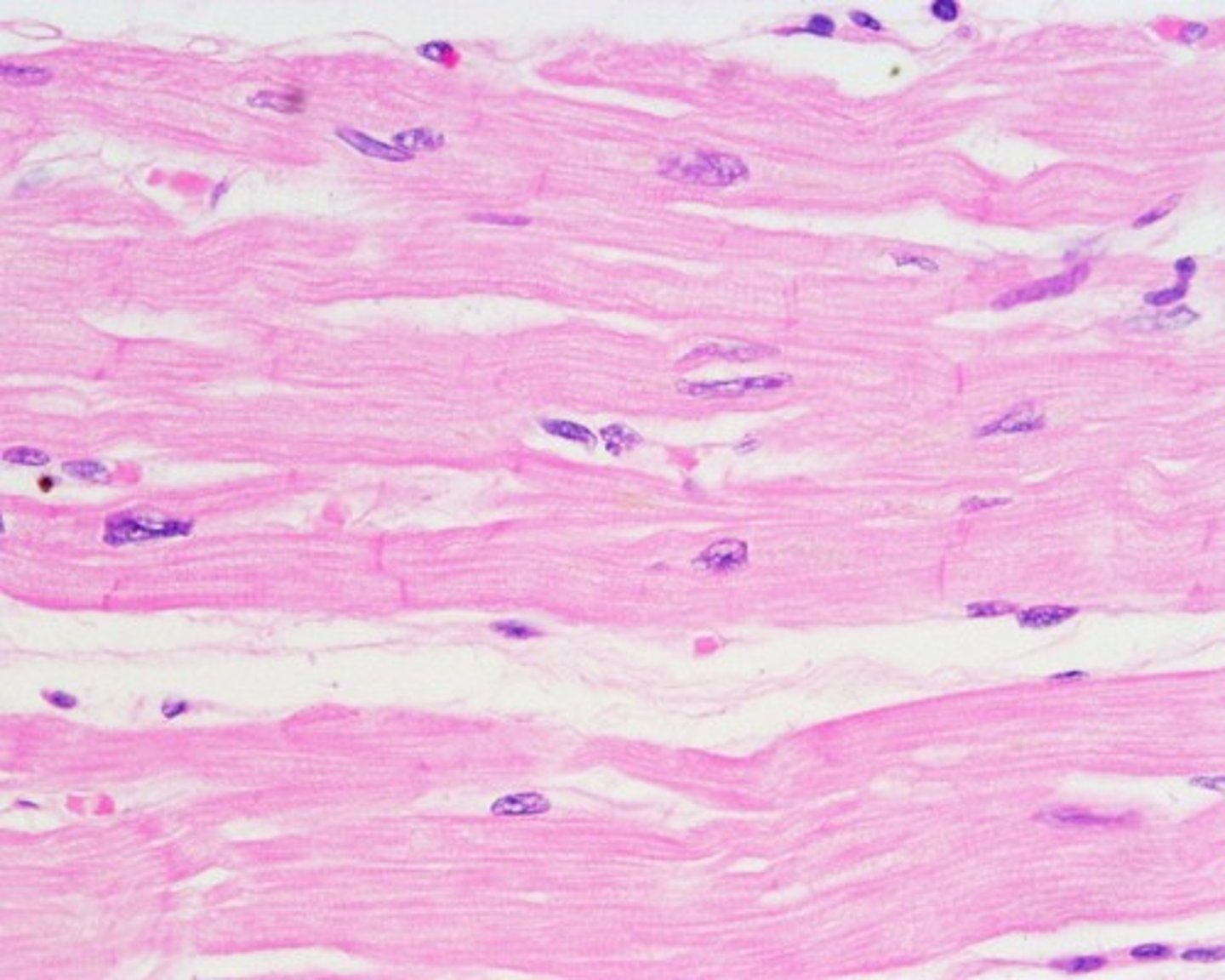
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary,
Striated,
Branched, and
Uninucleated (Heart)
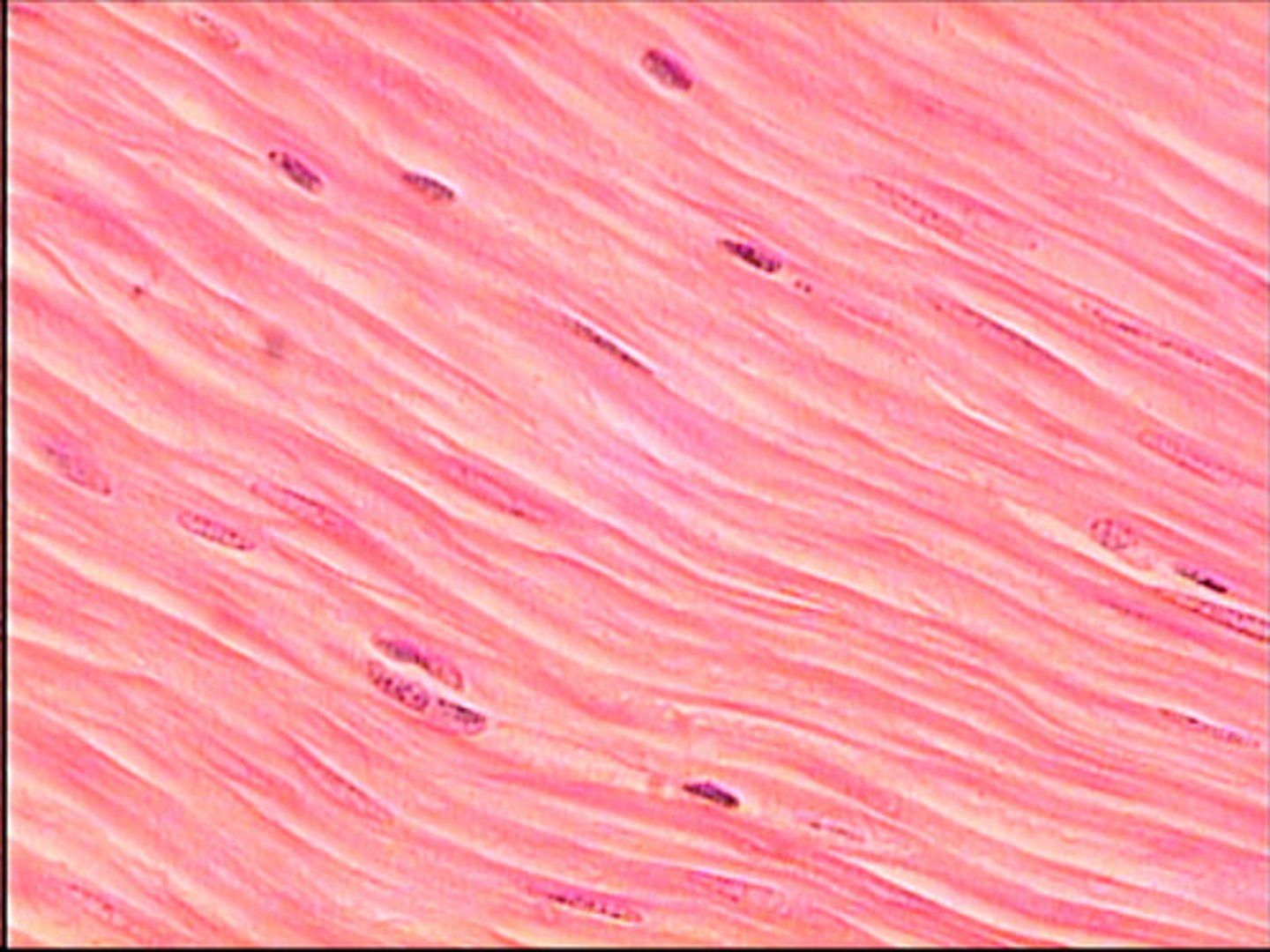
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary
nonstriated
tapered and
Uninucleated (Blood vessels)
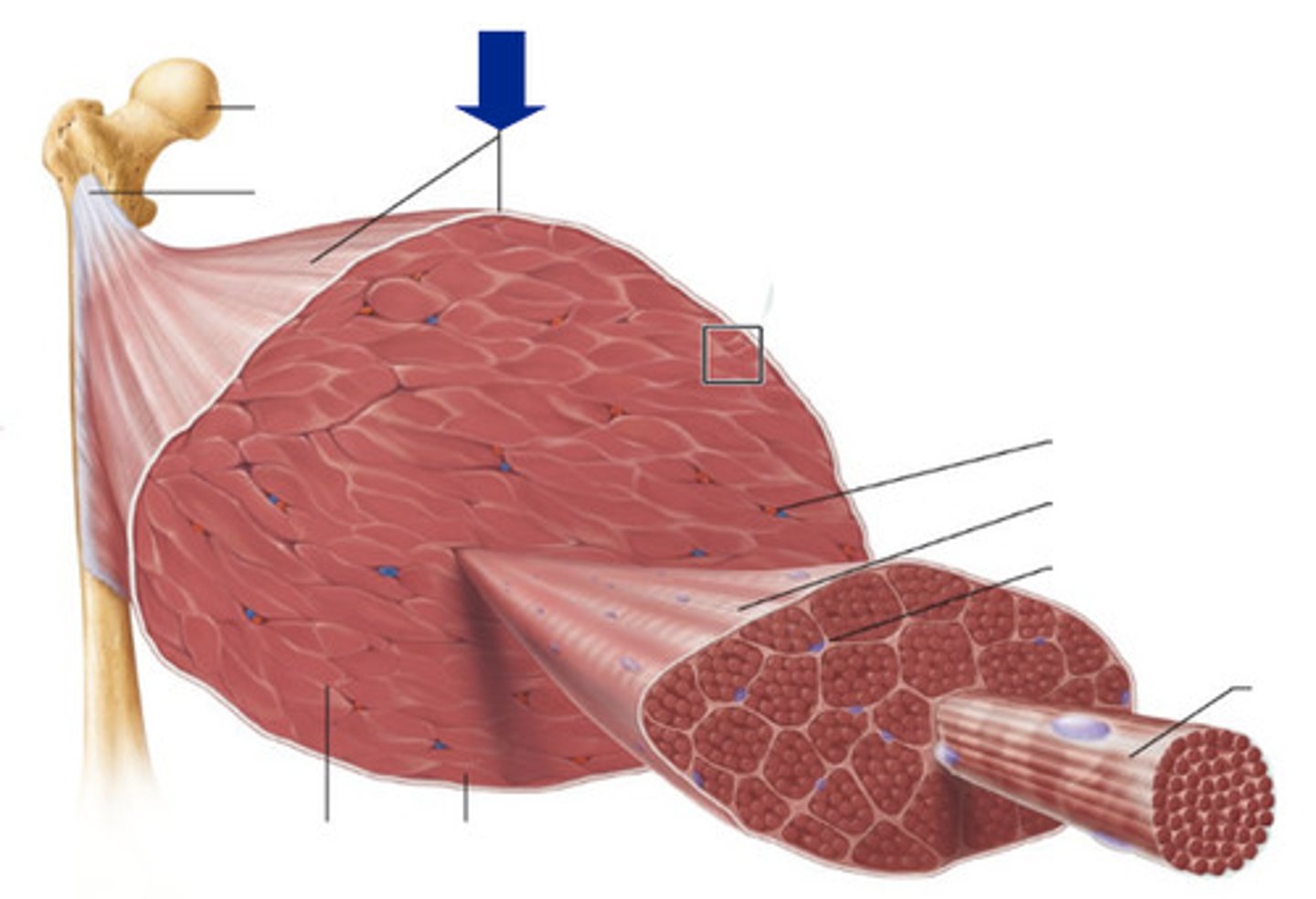
Muscle Fiber
A single strand of muscle cell
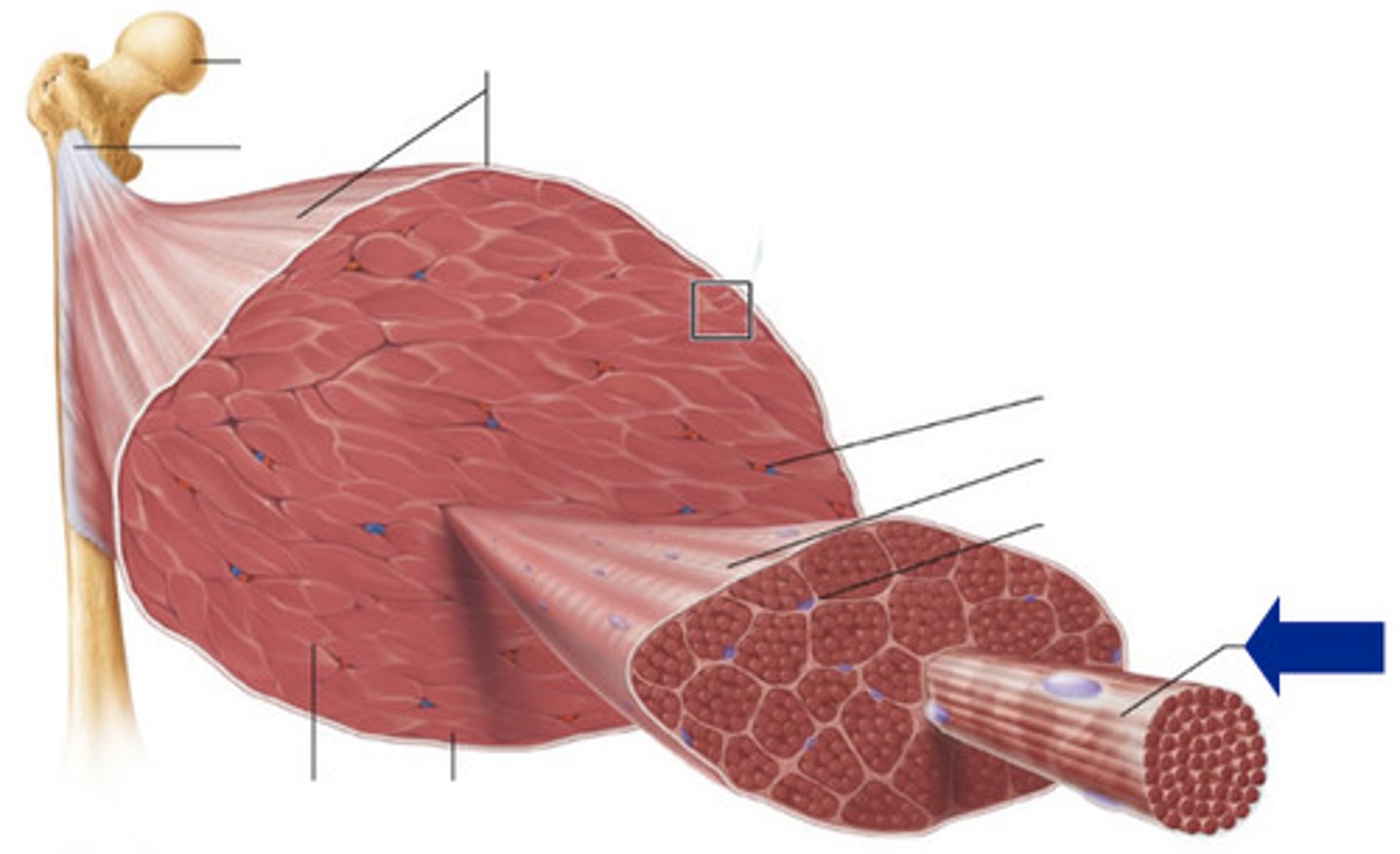
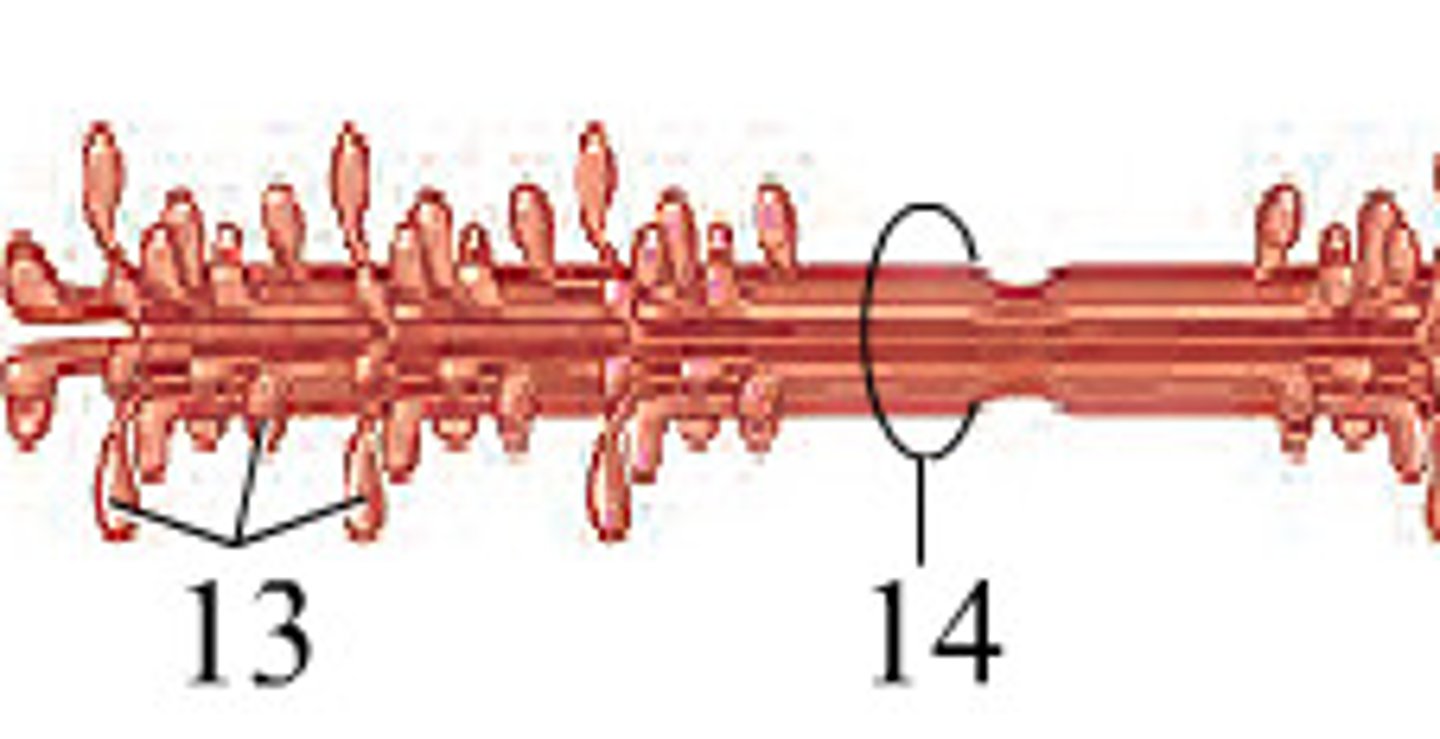
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers
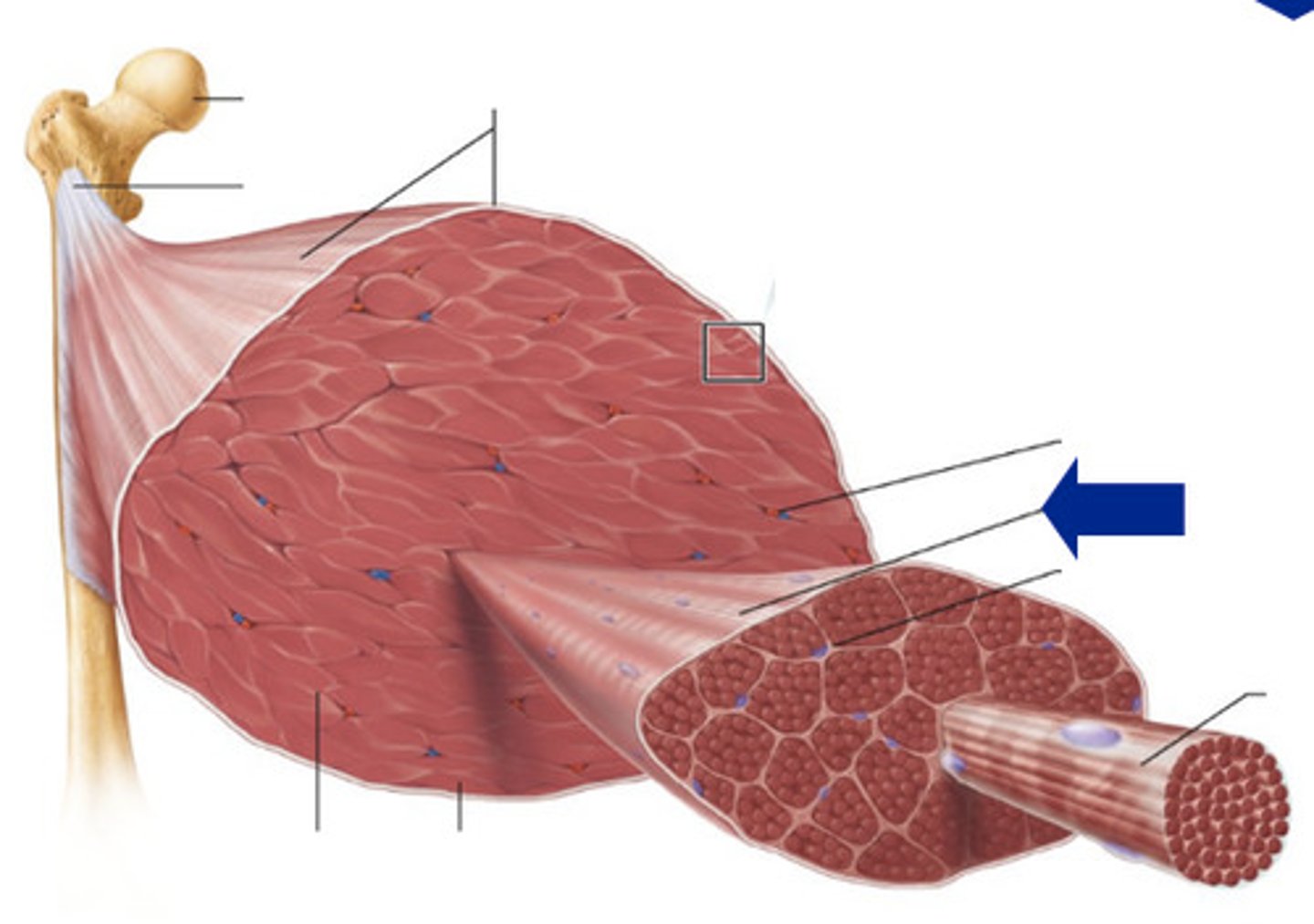
Myofibril
Made of many sarcomere sub-units and is a strand which runs the length of a muscle fiber
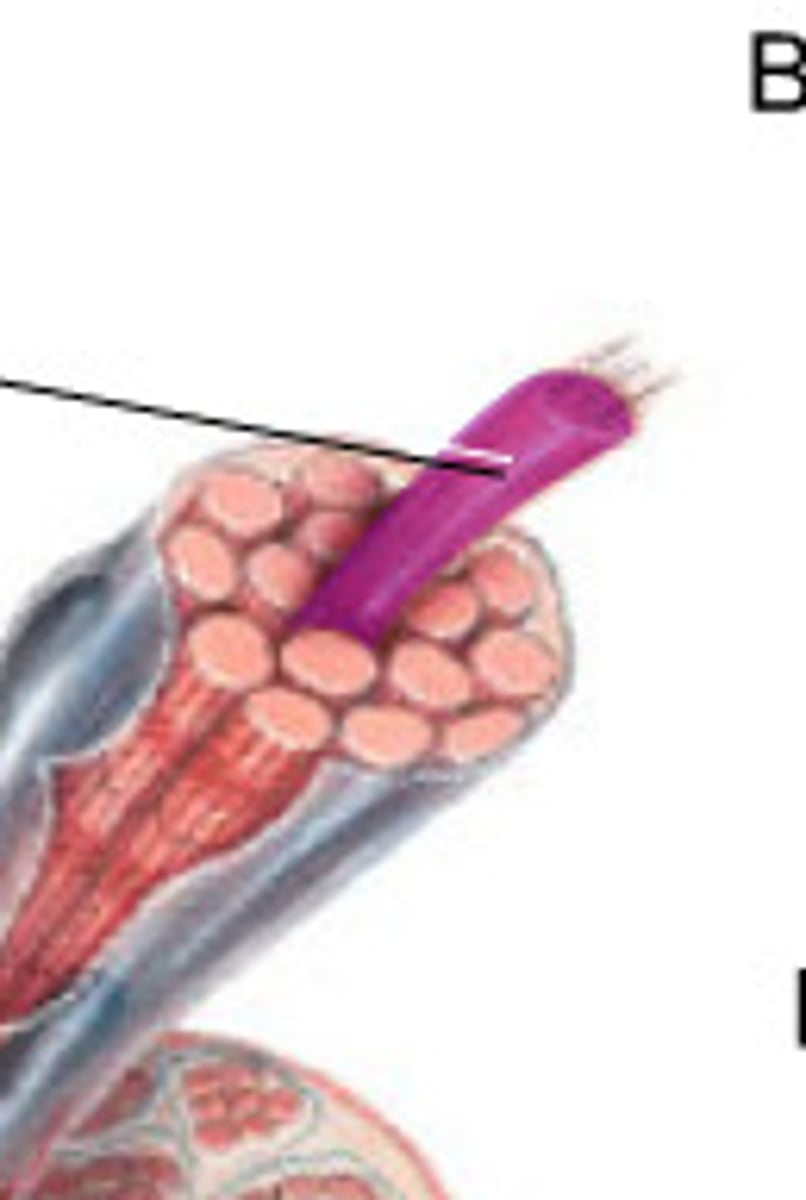
Sarcomere
The smallest part of the muscle. Is the contractile unit which is made primarily of actin and myosin filaments
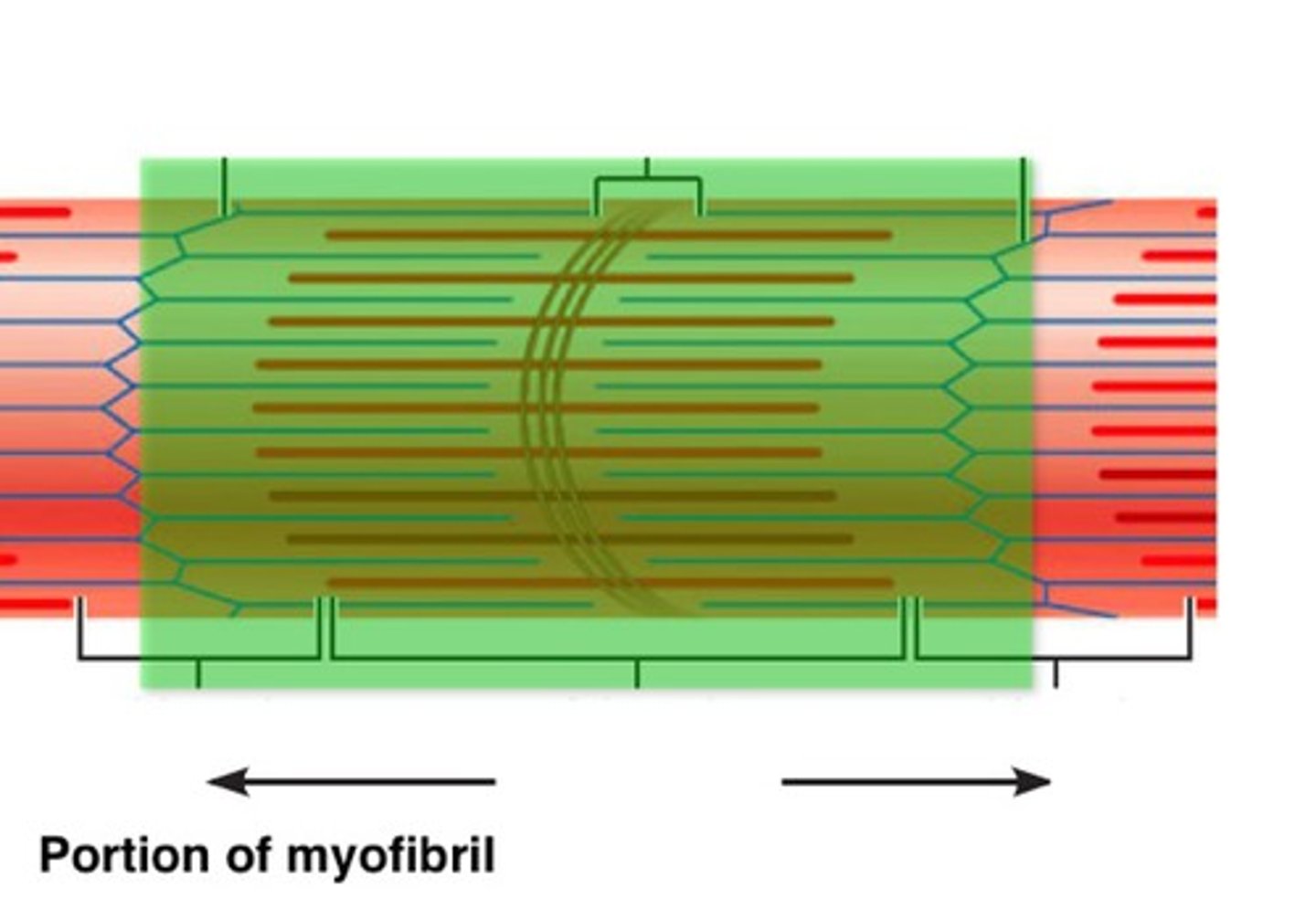
Actin
Thin Filaments that get pulled to the M line during contractions
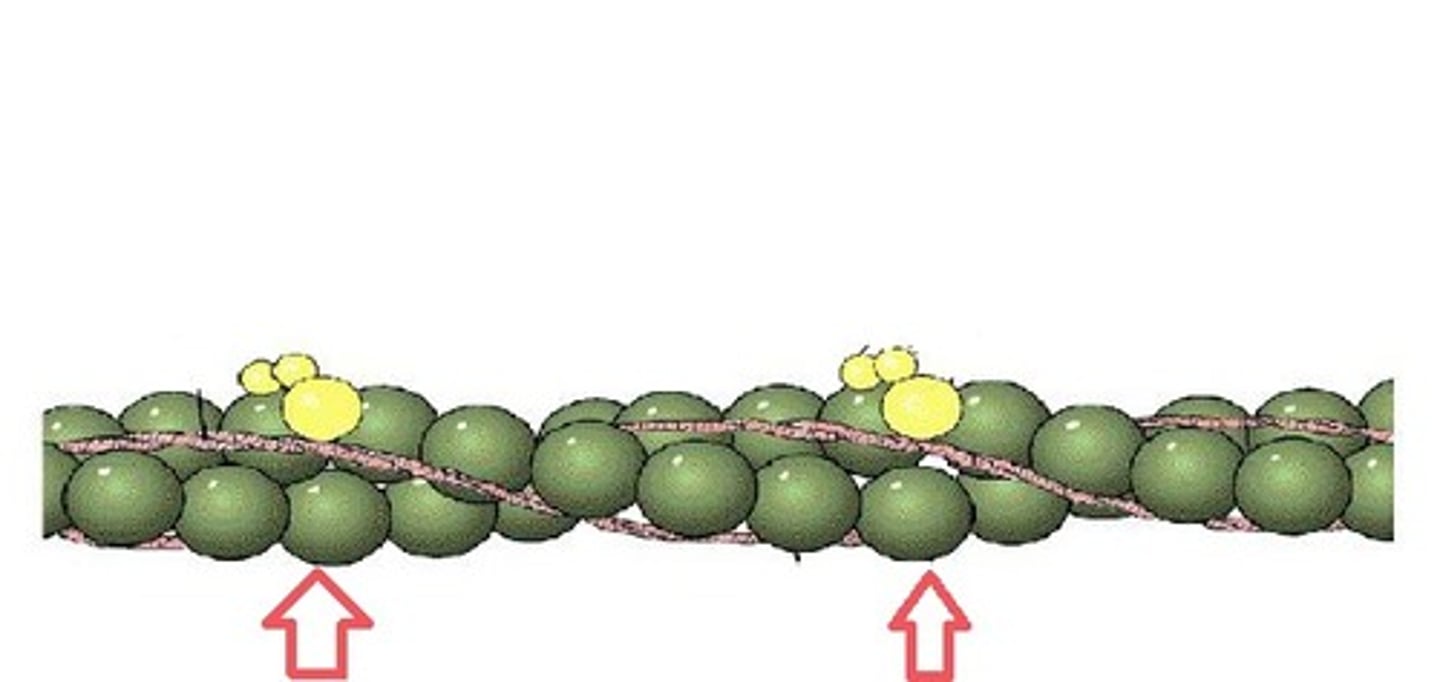
Myosin
Thick filaments that are stationary during sarcomere contractions
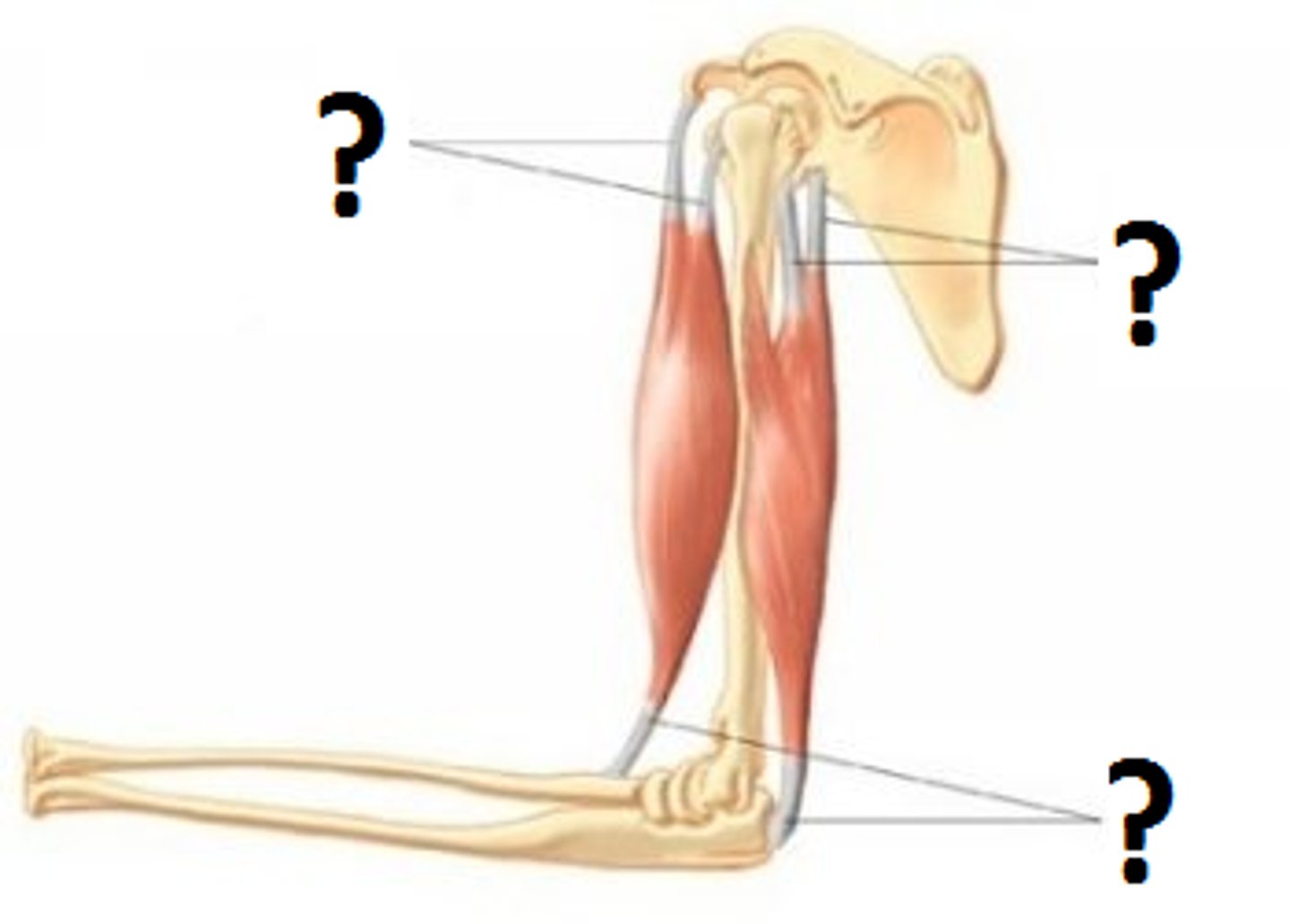
Tendons
Connective tissue that connects muscles to bones
Endomysium
Inside the muscle. The layer surrounding a muscle fiber.
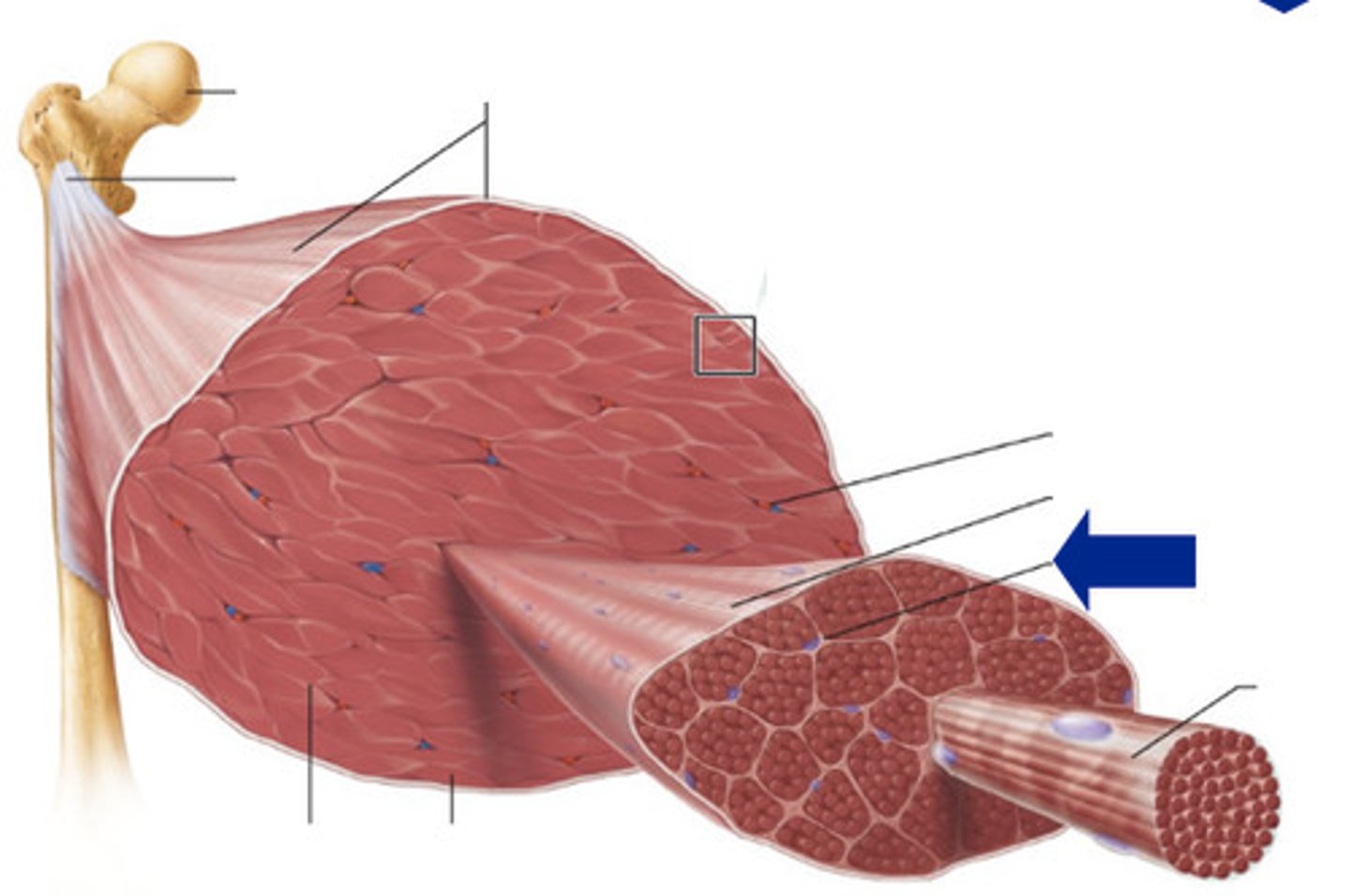
Perimysium
The layer surrounding a muscle fascicle
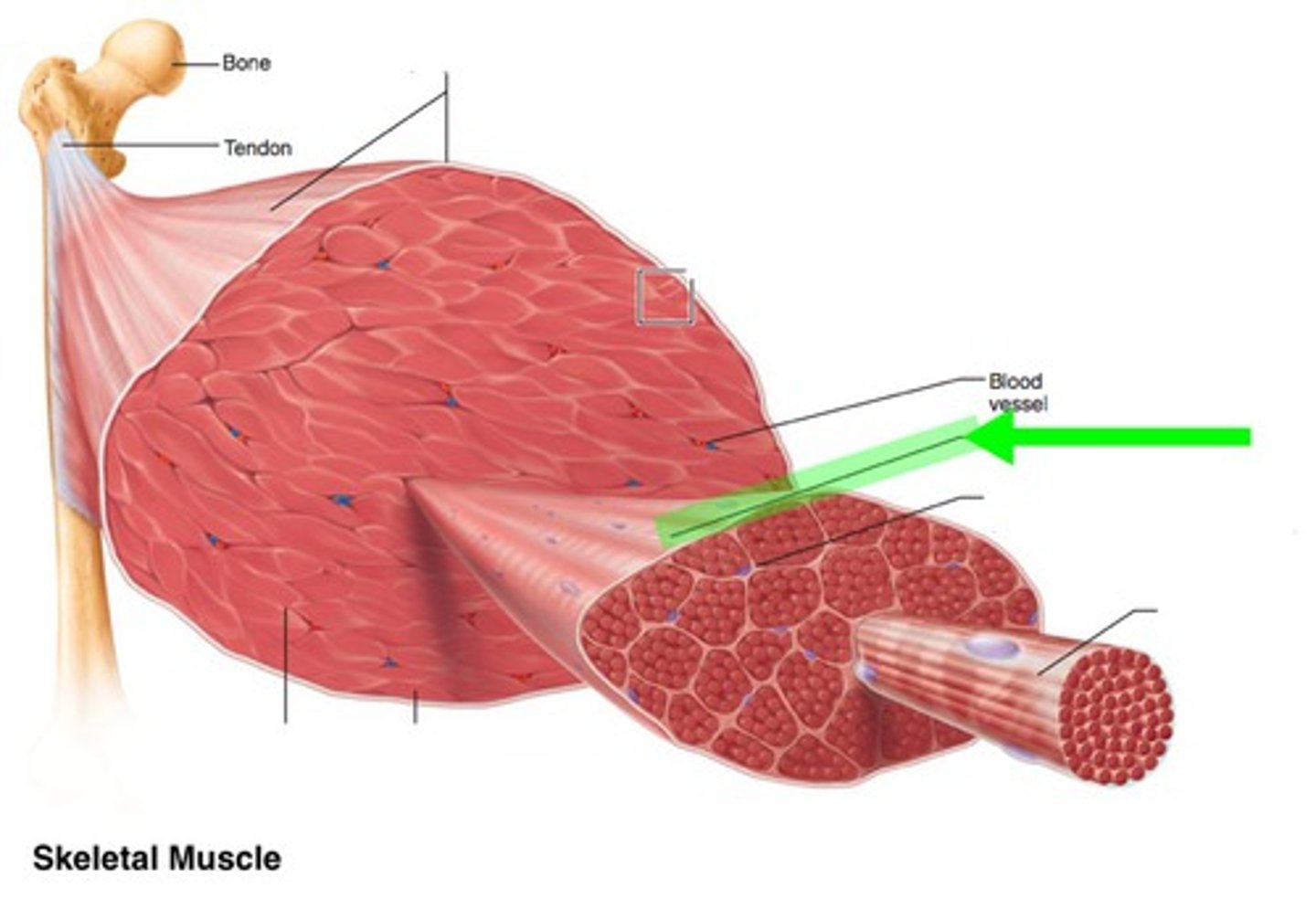
Epimysium
The outside layer on top of a muscle body
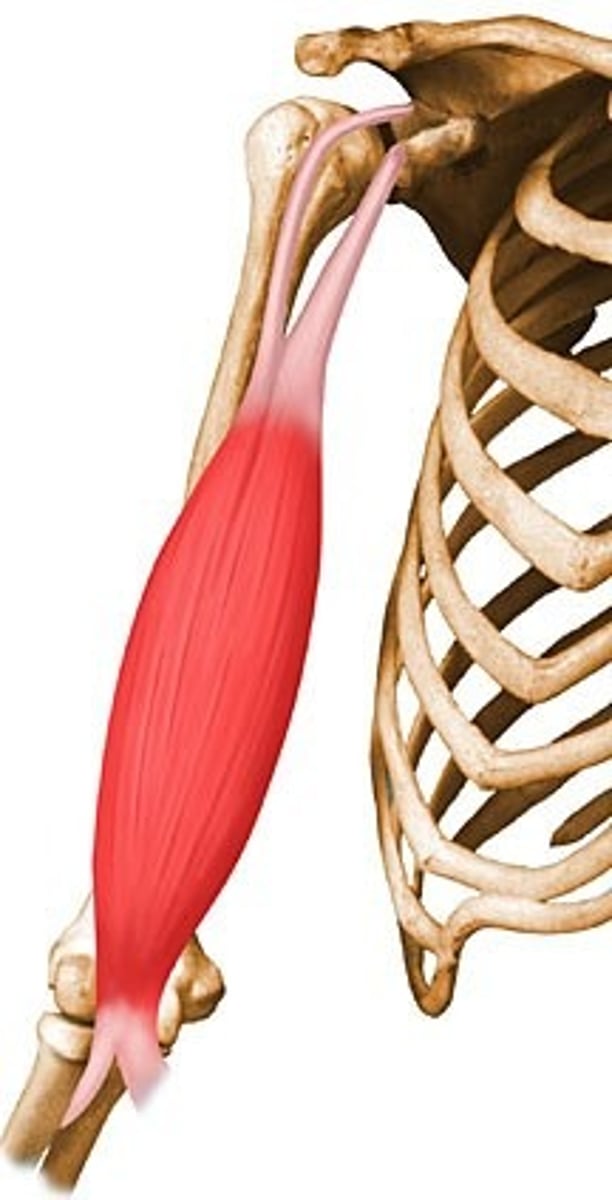
Origin
Where muscle attaches to a stationary bone, which does not move during contractions
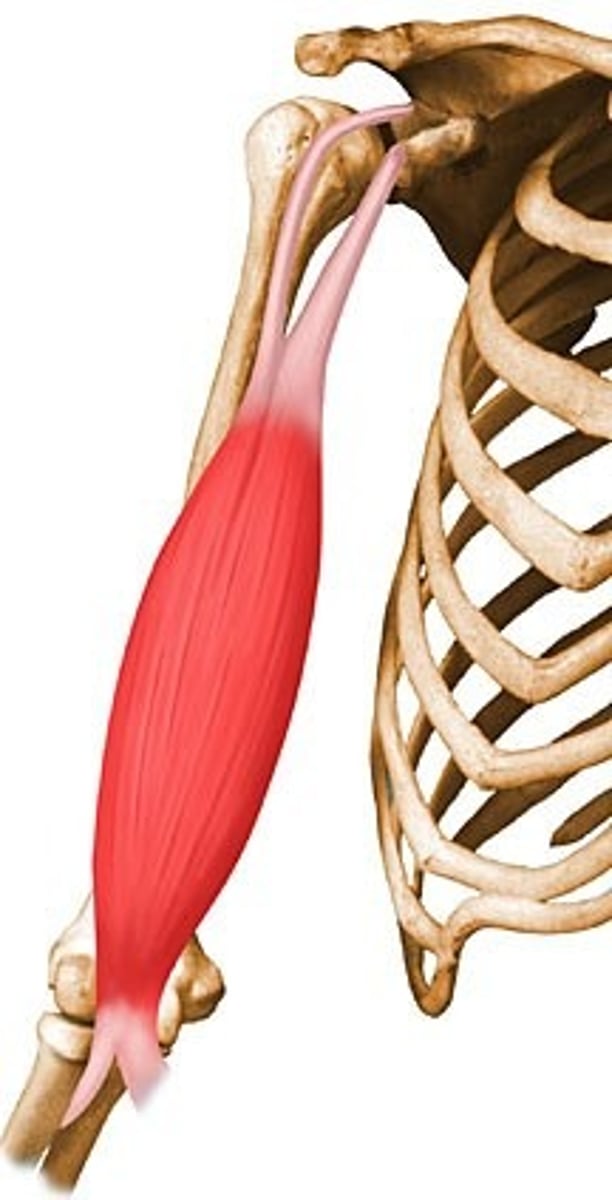
Insertion
Where muscle attaches to a moving bone during contraction
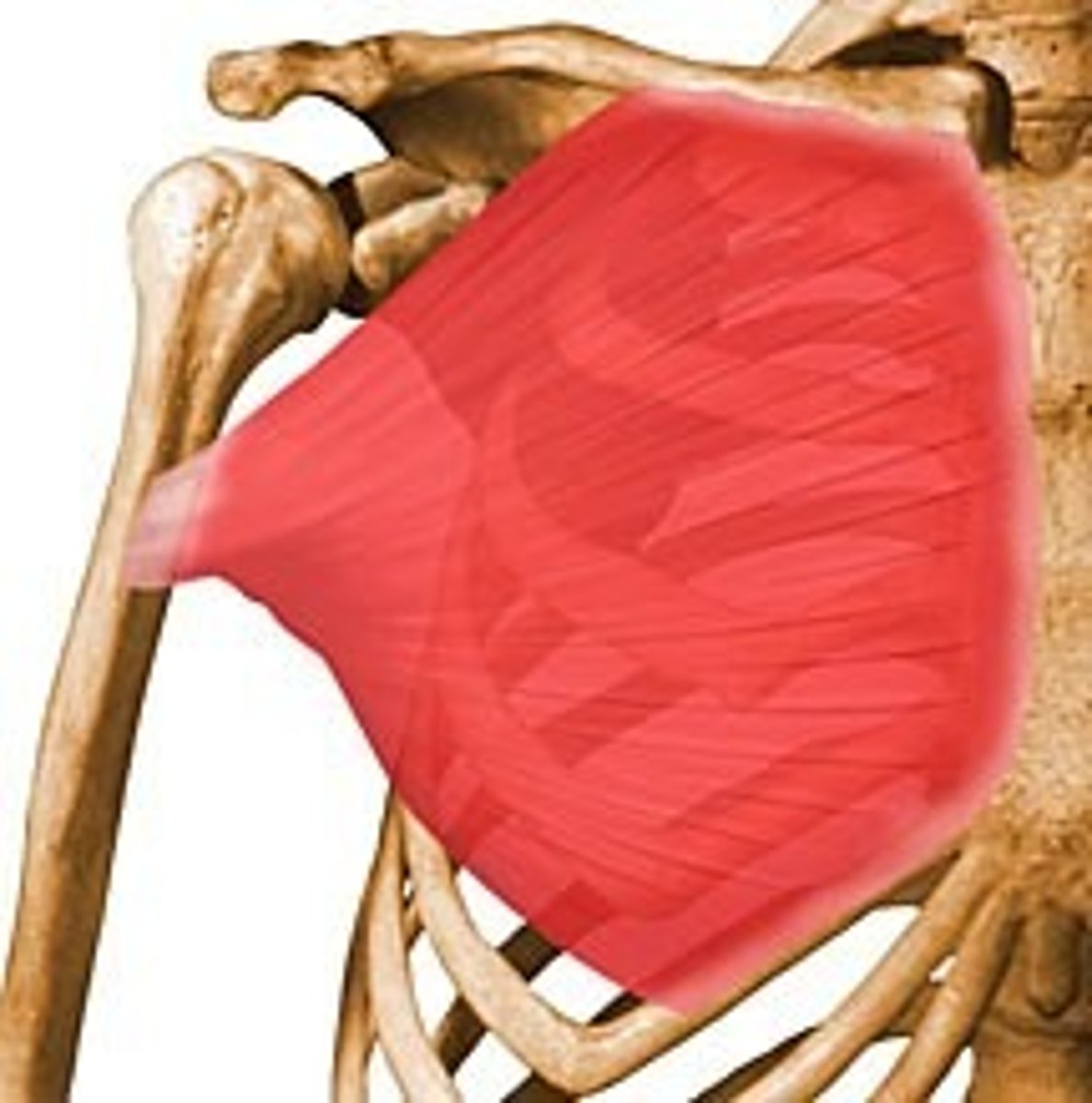
Pectoralis Major
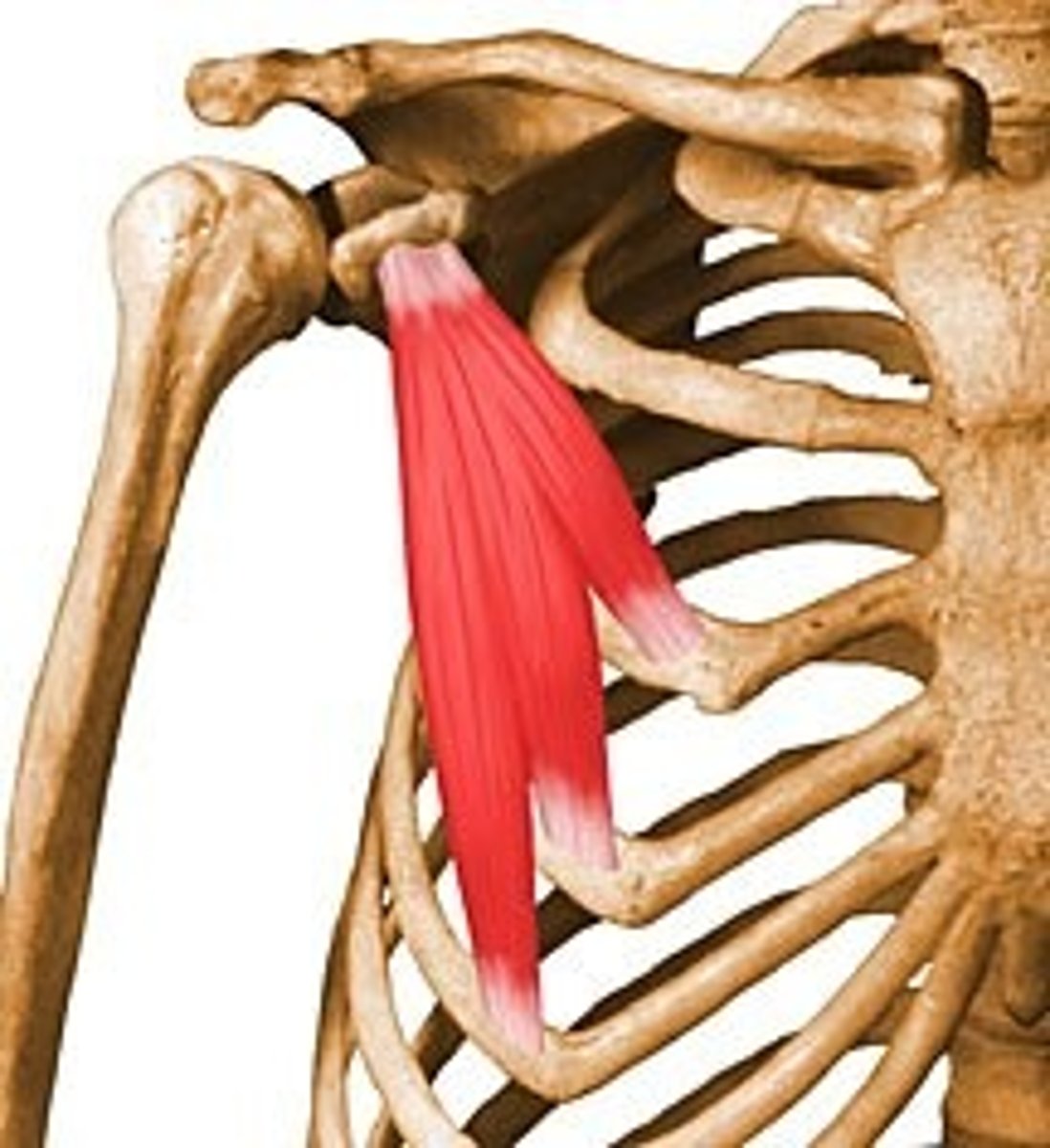
Pectoralis Minor
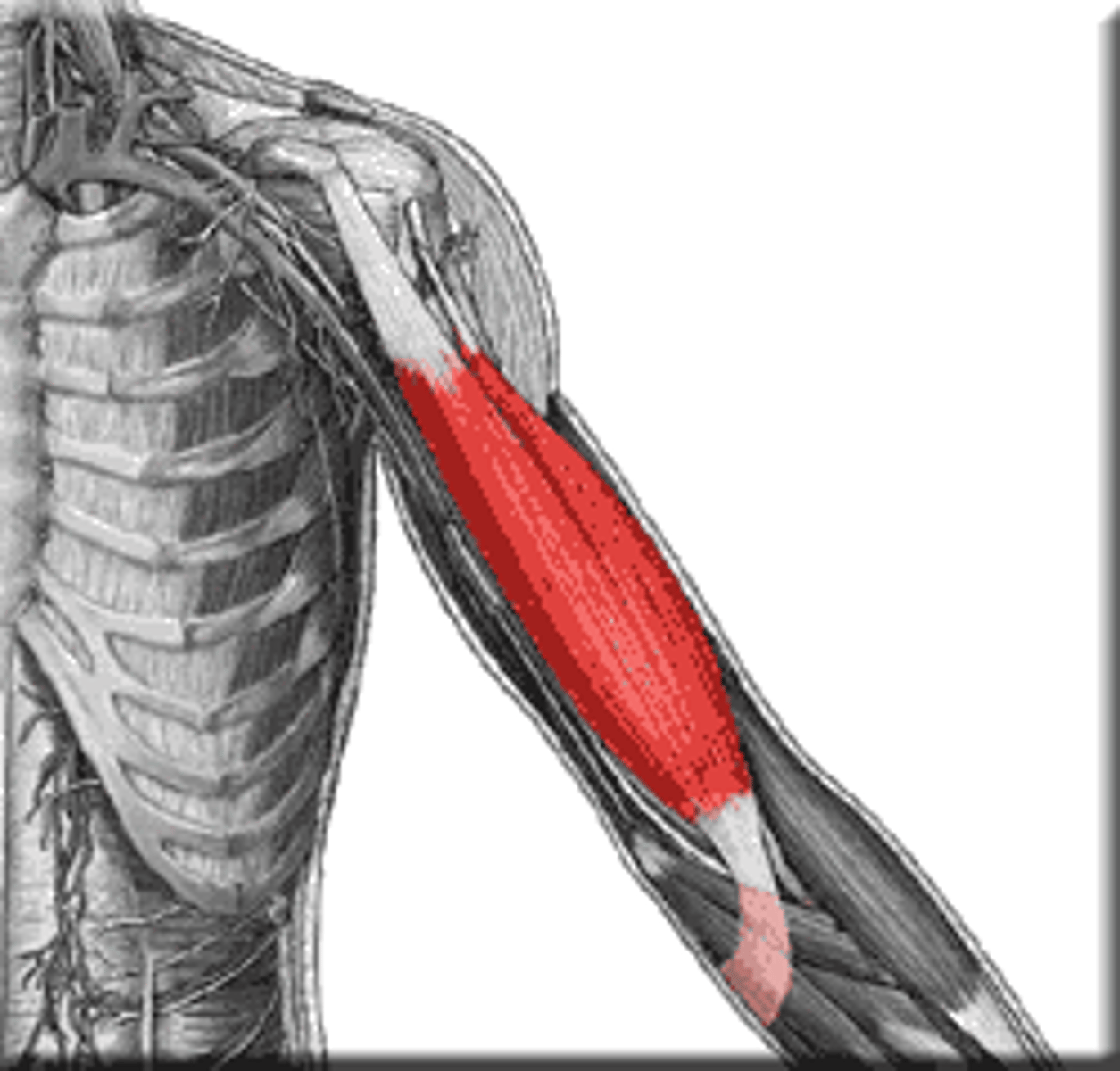
Biceps Brachii
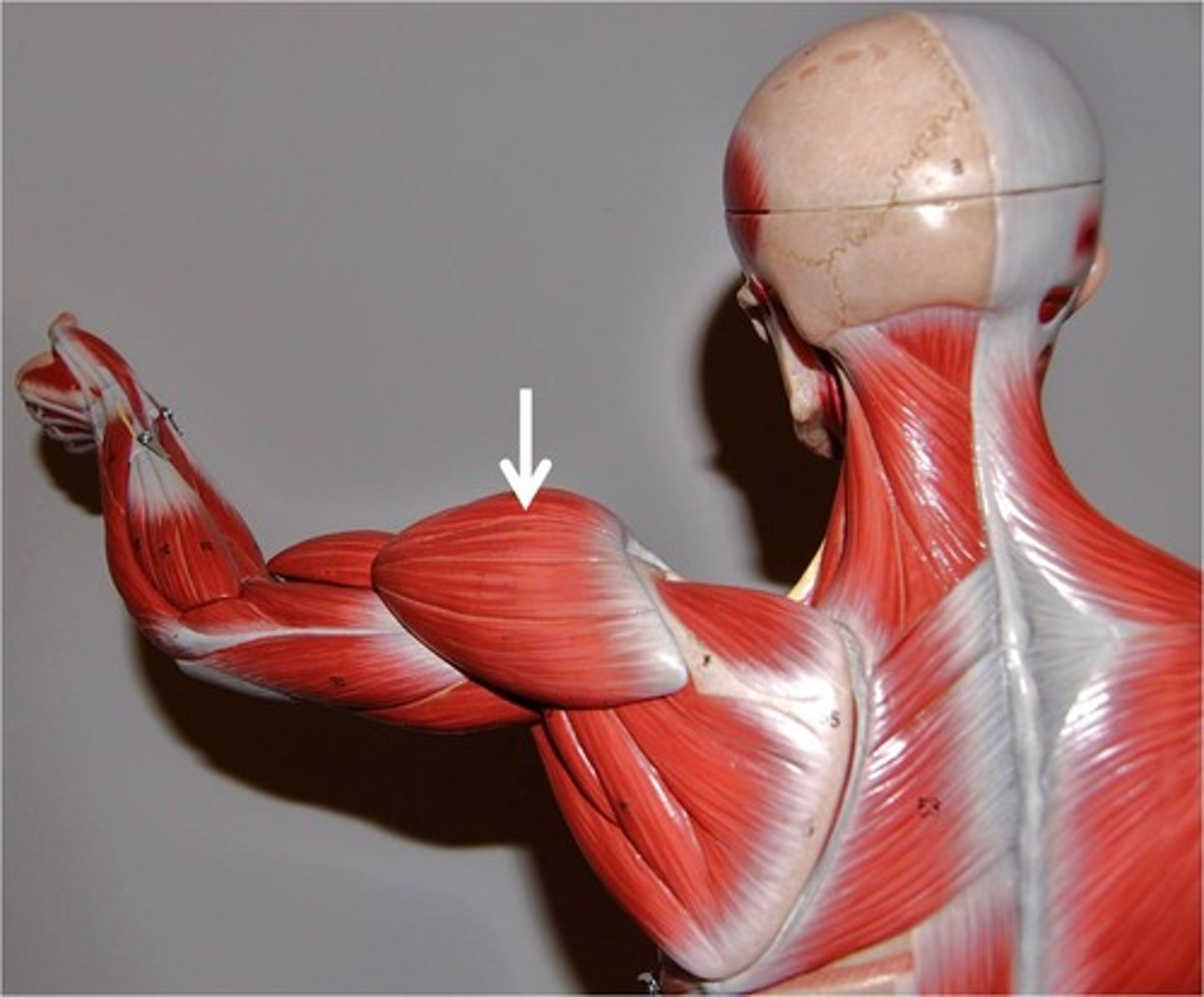
Deltoid
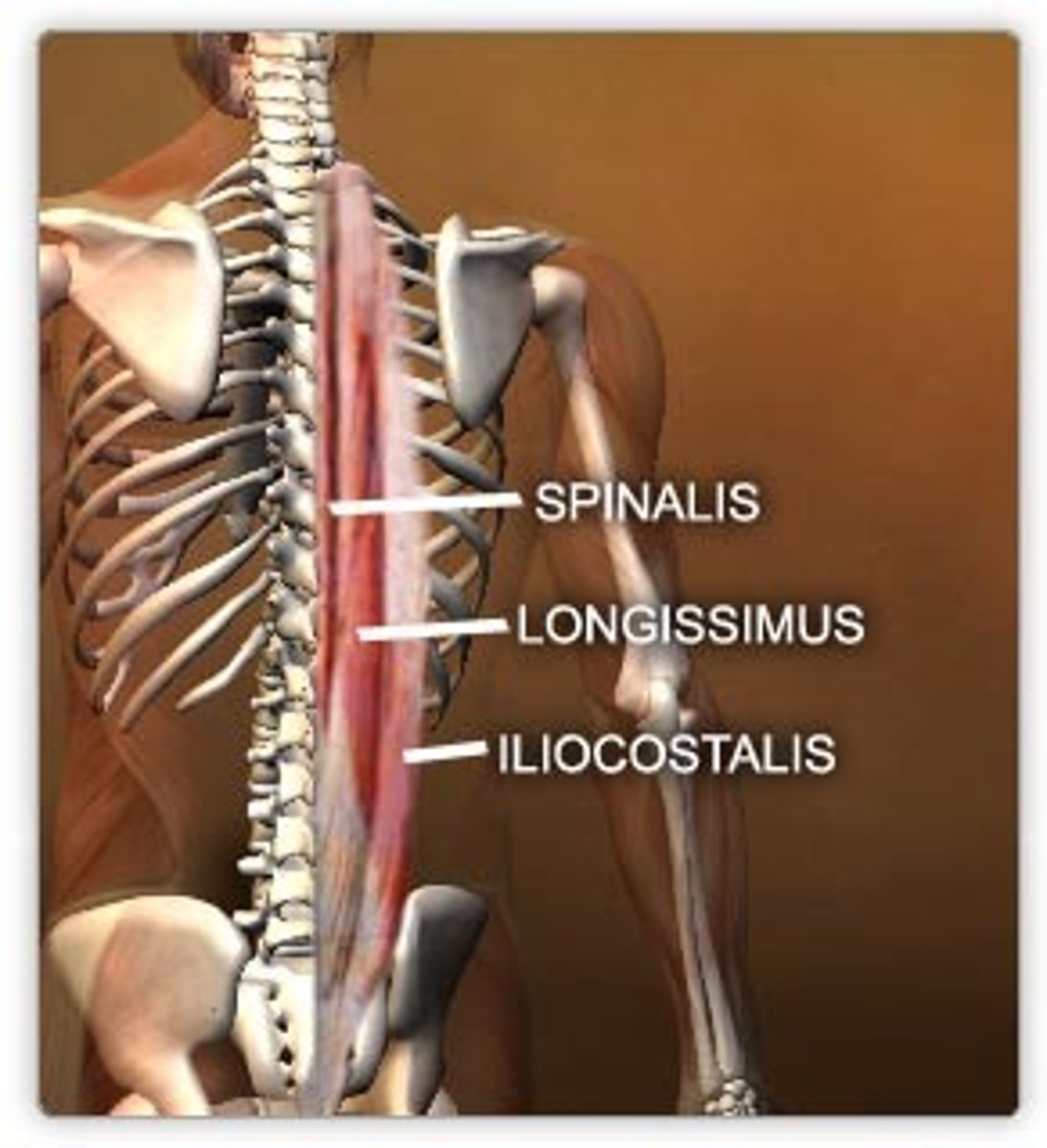
Erector Spinae
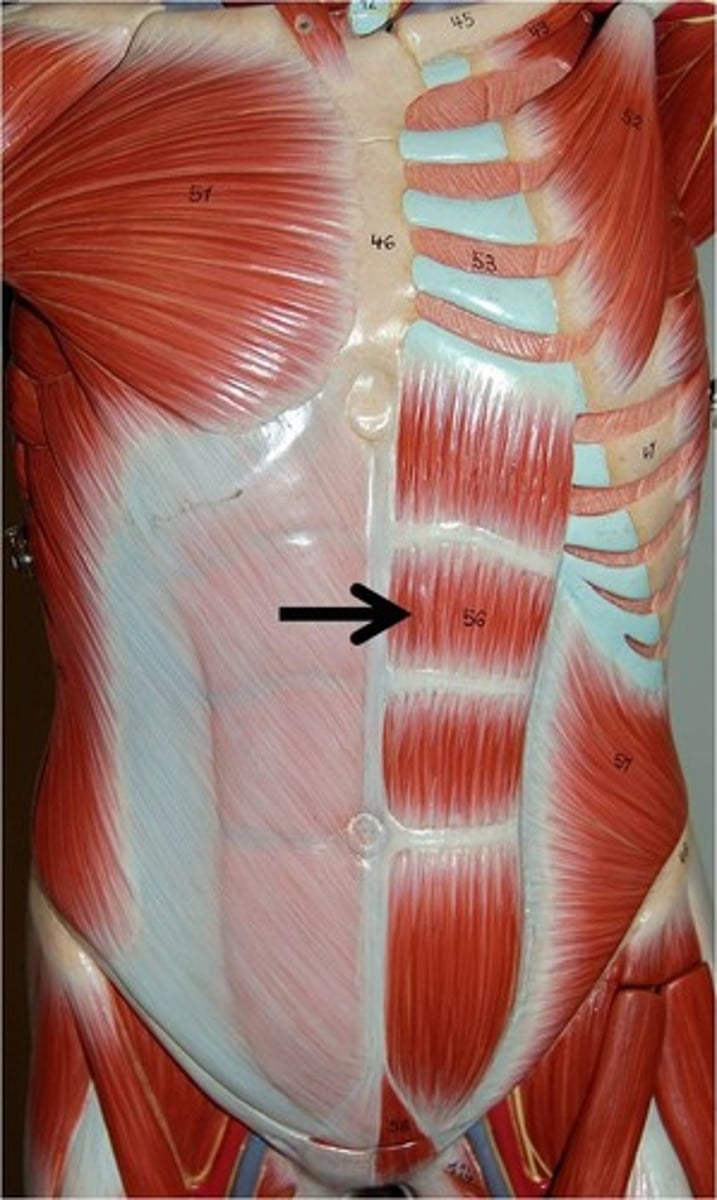
Rectus Abdominis
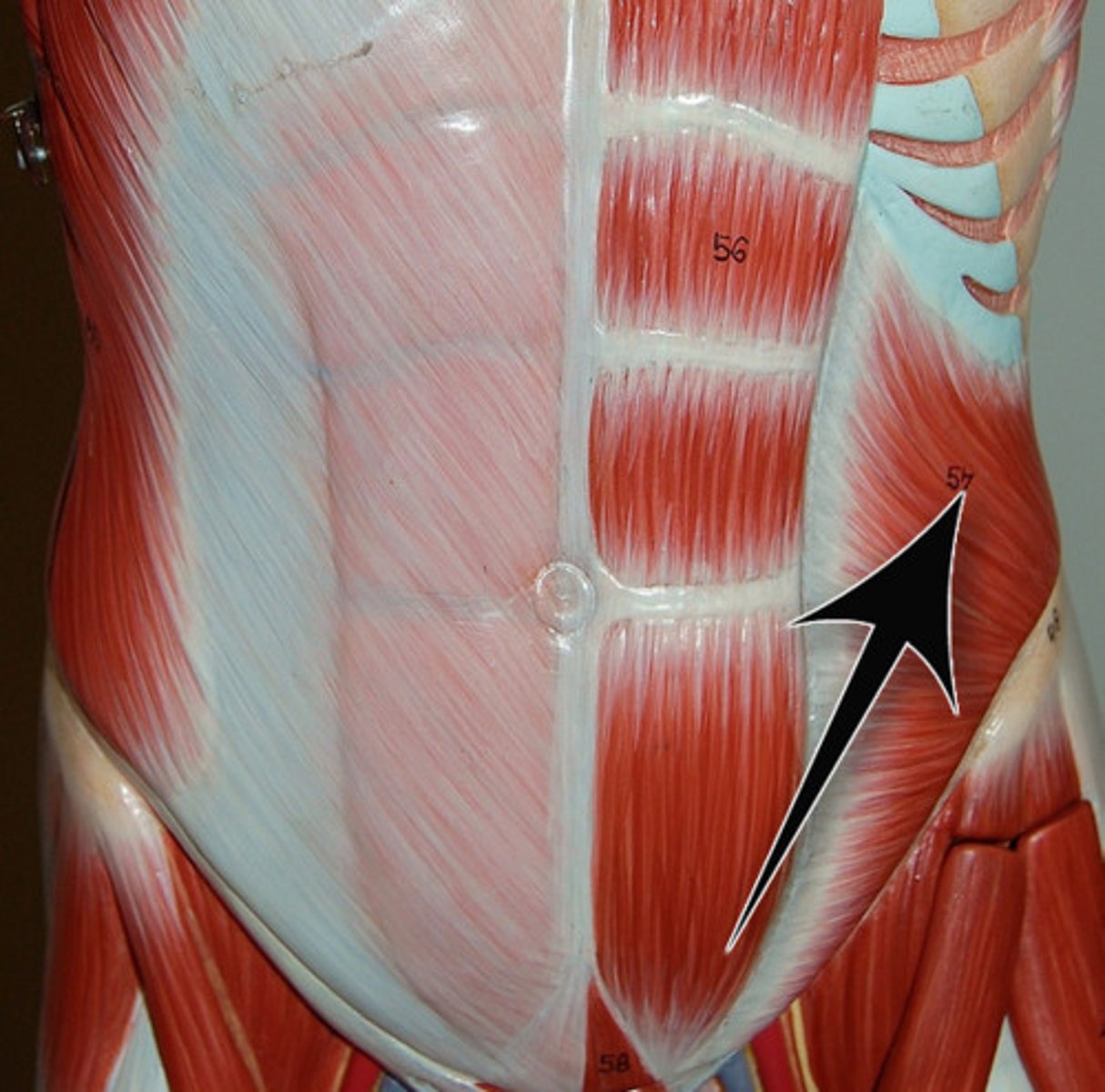
External Obliques
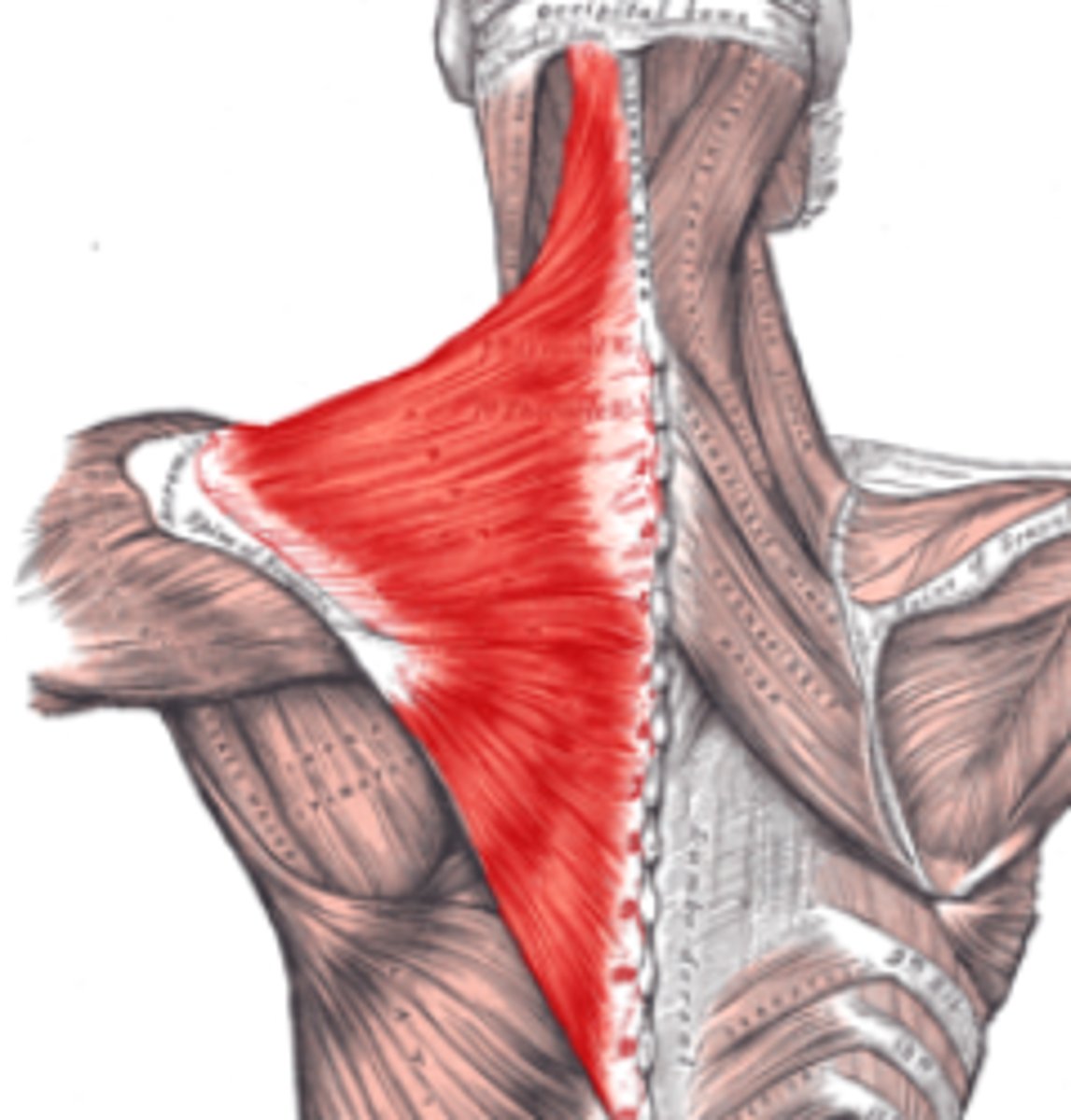
Trapezius
Latissimus Dorsi
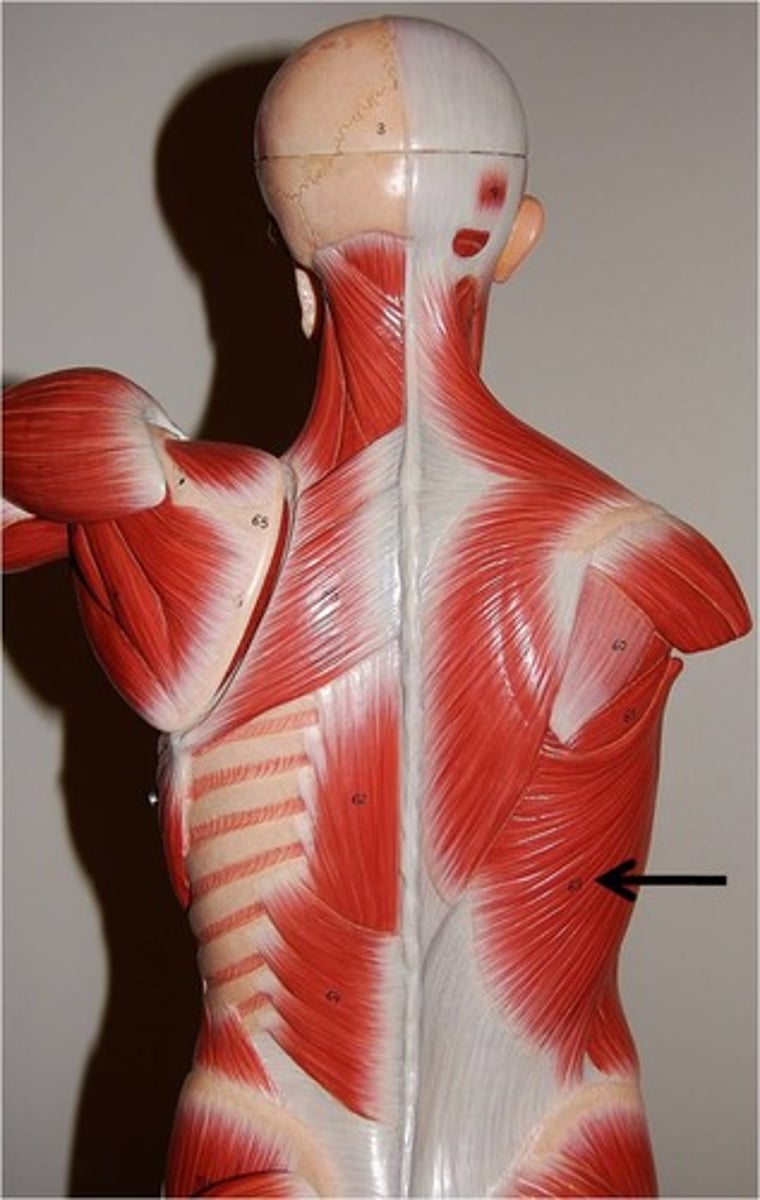
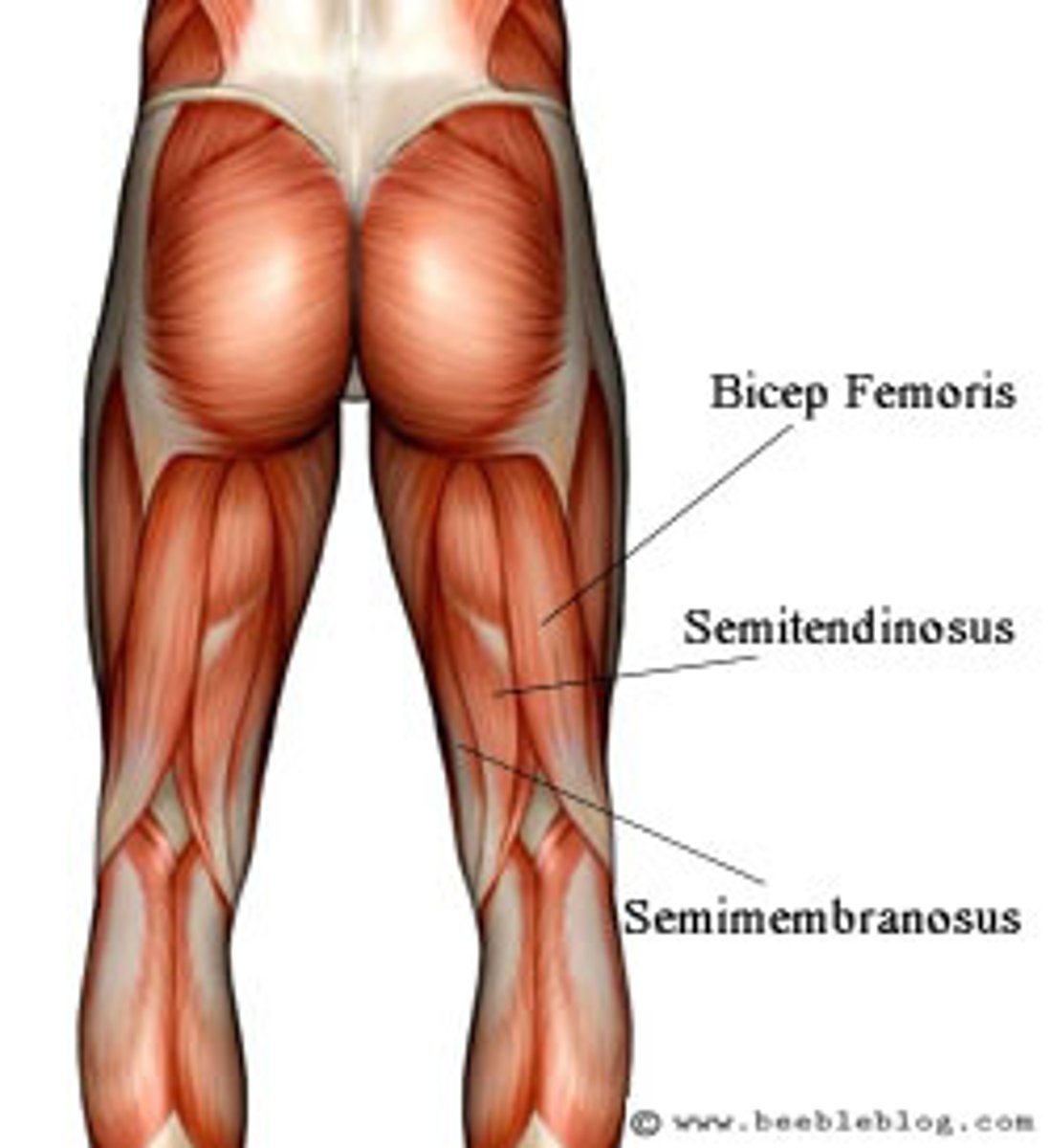
Hamstrings
Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
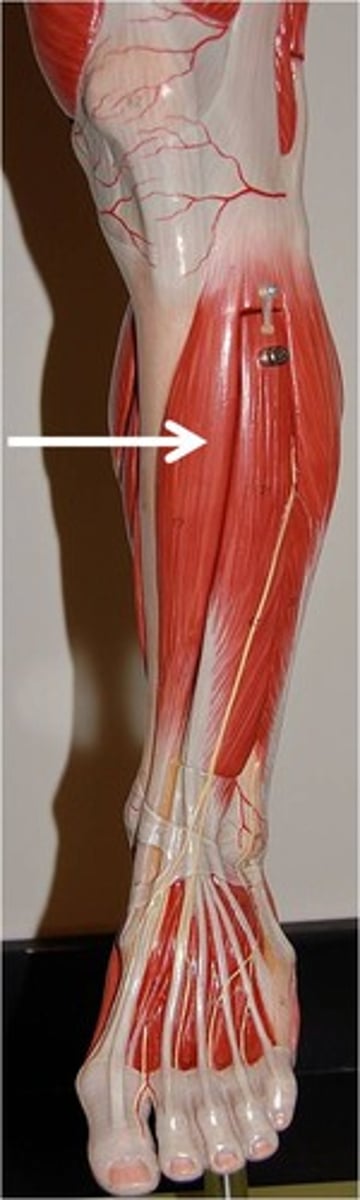
Tibialis Anterior
Gastrocnemius
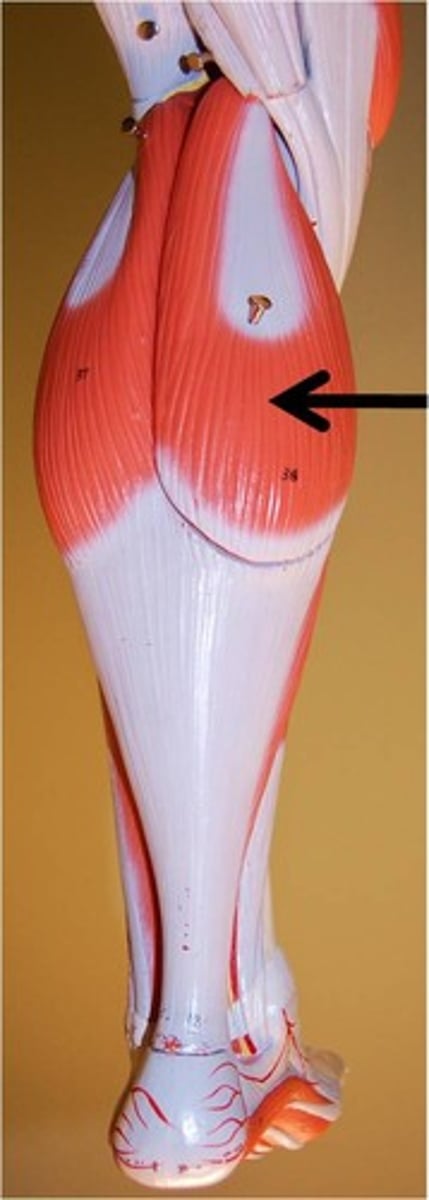
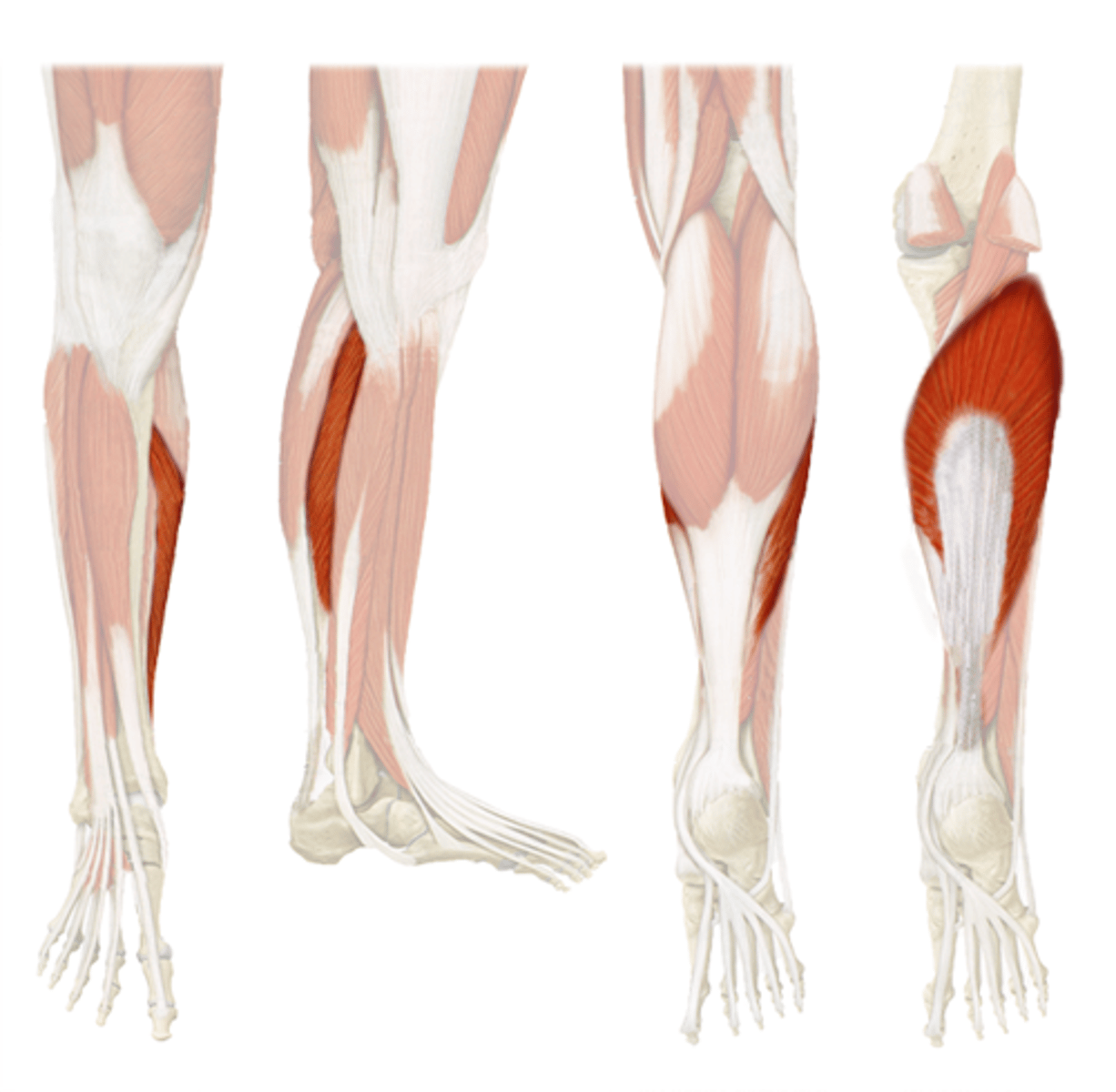
Soleus
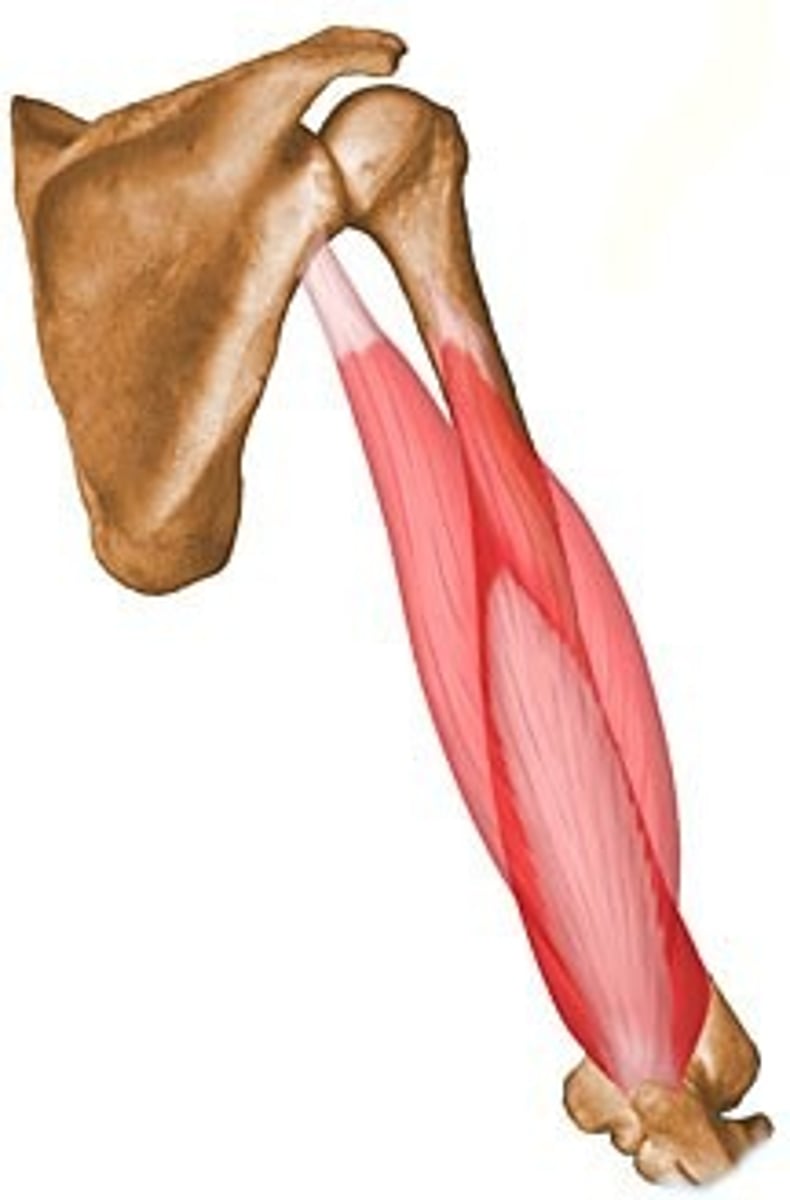
Triceps Brachii
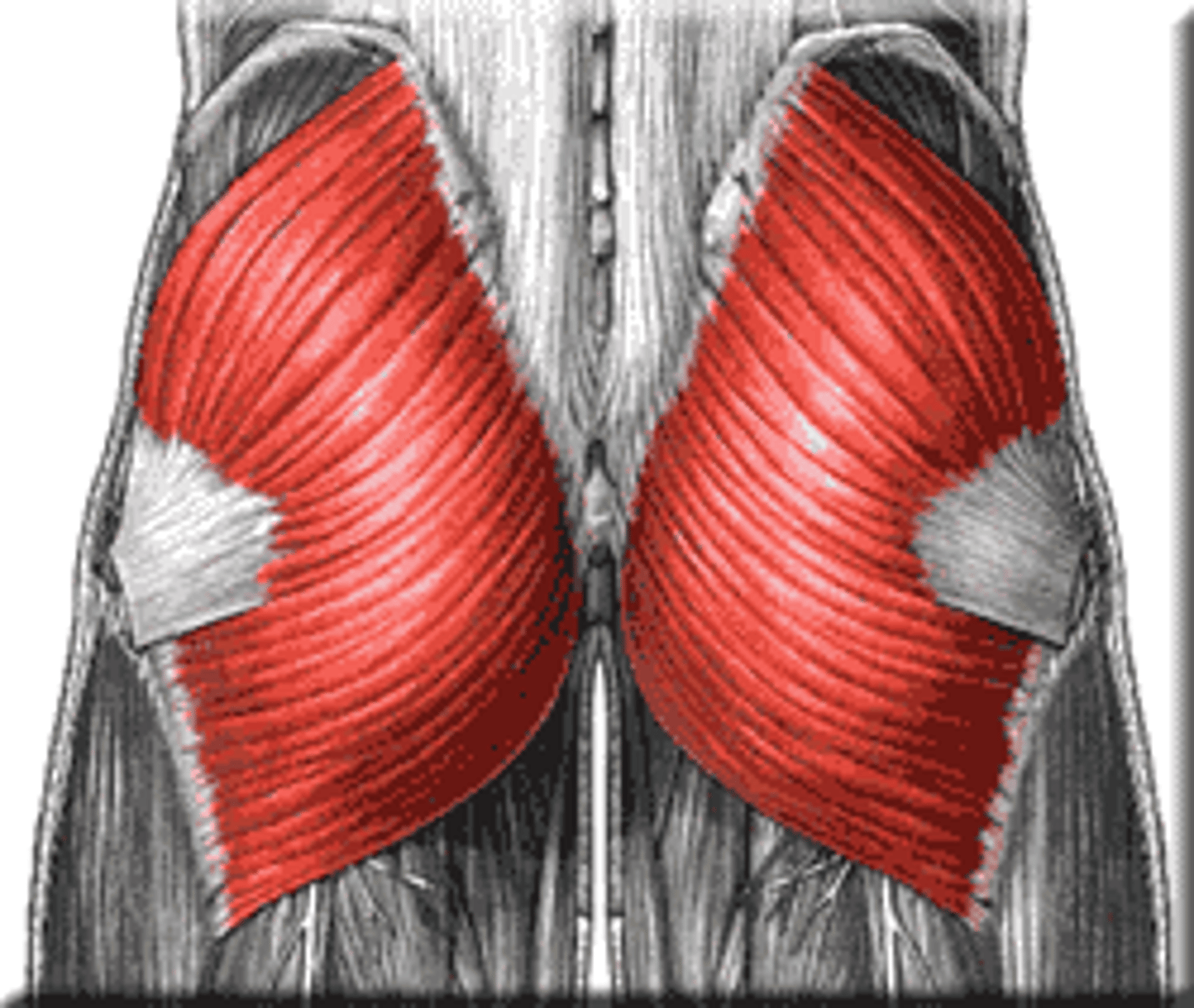
Gluteus Maximus
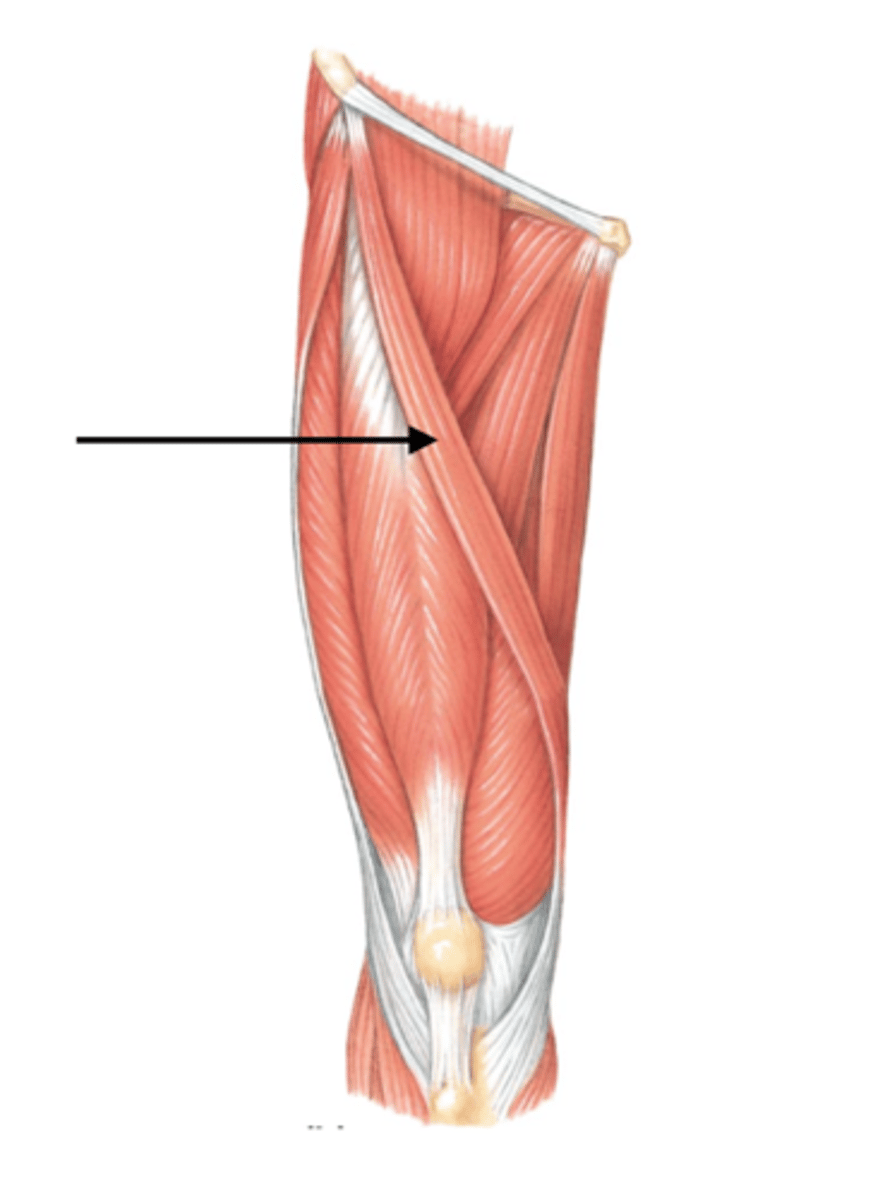
Sartious
Longest muscle in the body
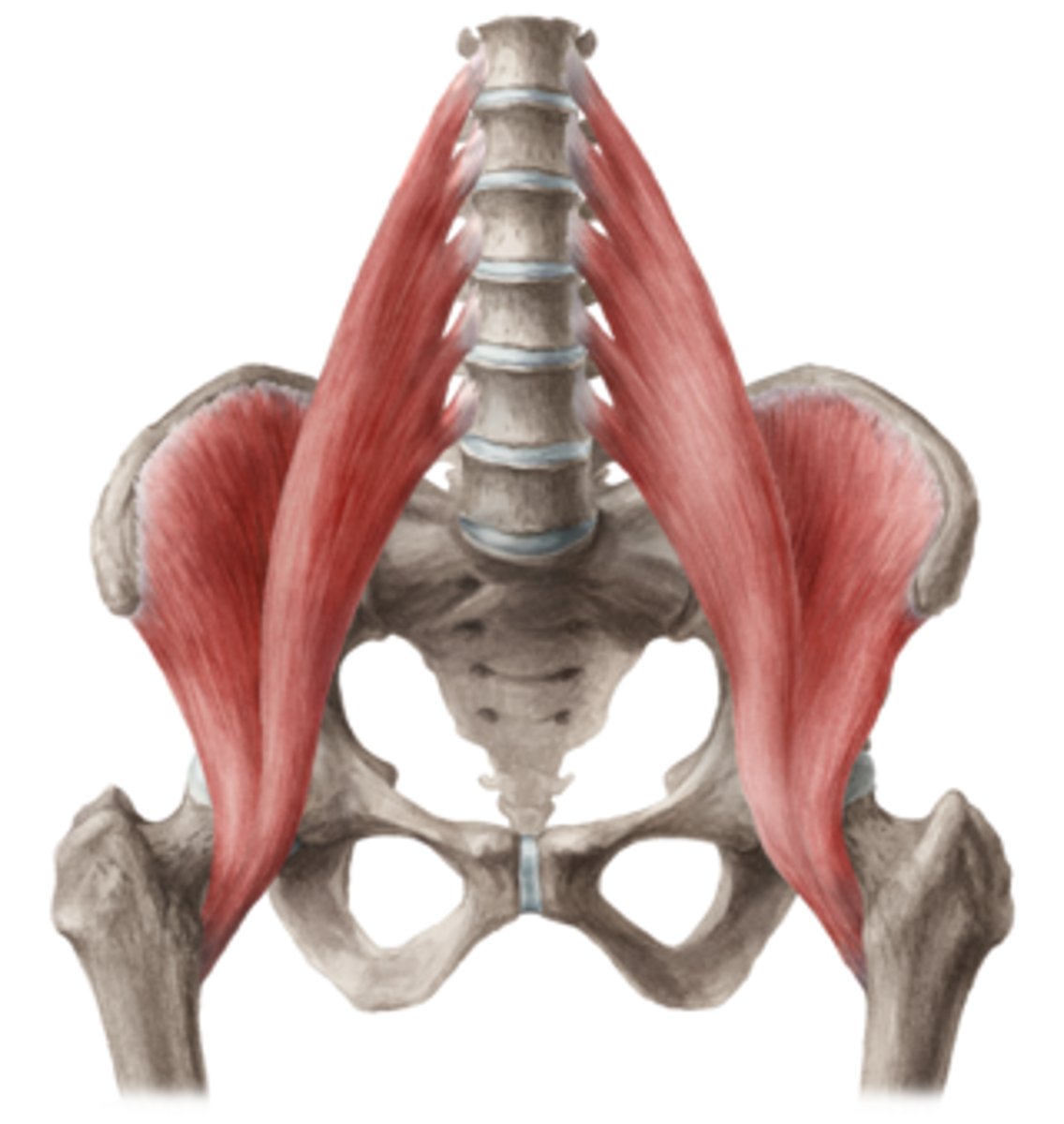
Iliopsoas
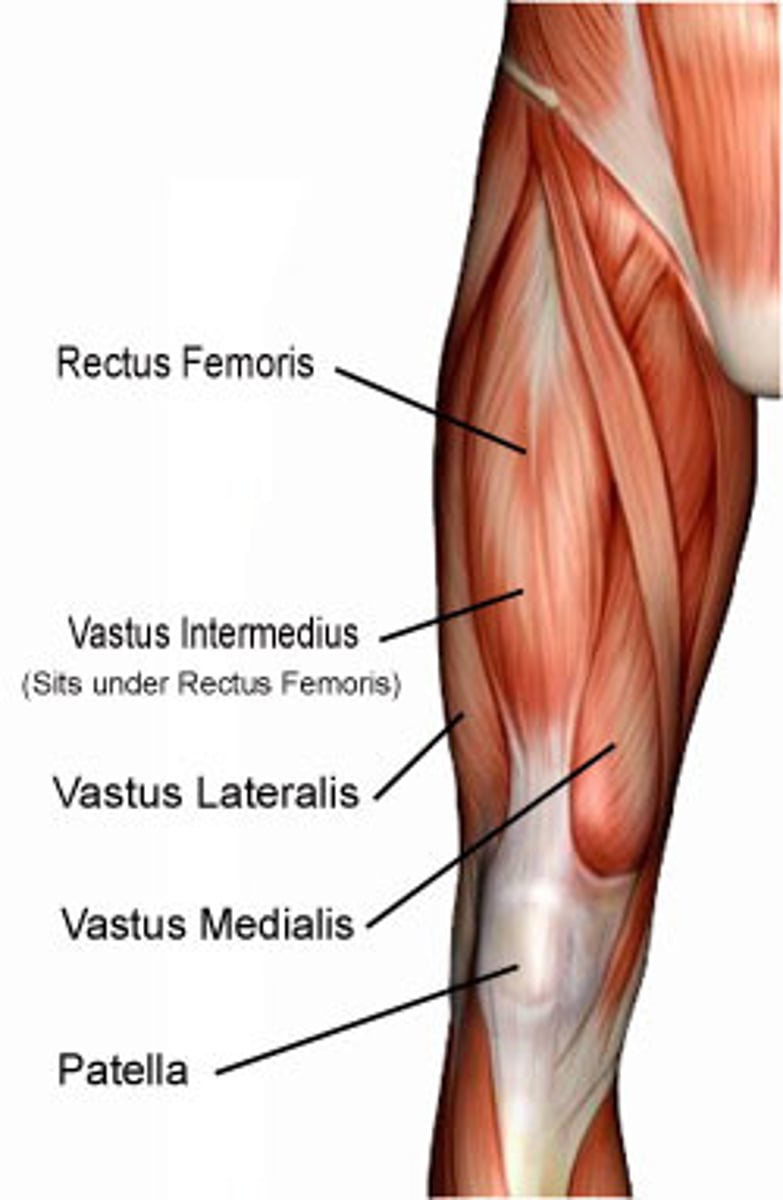
Quadriceps
rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius