Separate Chemistry 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What can we use to identify some metal ions?
Flame tests
Flame test results for metal ions: lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium and copper
Lithium- Red
Sodium- Yellow
Potassium- lilac
Calcium- orange-red
Copper blue-green
How do we test for metal ions with hydroxide precipitates?
Some metal ions form metal hydroxide precipitates
The sample solution is placed in a test tube and a few drops of dilute sodium hydroxide are added
What colour precipitate will copper, iron (+2) and iron (+3) form when dilute sodium hydroxide was added?
Copper- blue
Iron (+2)- green
Iron (+3) brown
What kind of compounds do transition metals form?
Coloured compounds
What kind of compounds do non-transition metals form?
White or colourless compounds
What is the test for sulfate ions?
Add dilute hydrochloric acid and then barium chloride solution
Sulfate ions form a white precipitate of barium sulfate
What is the test for carbonate ions?
Add acid
Carbonate ions form bubbles of carbon dioxide
What is the test for halide ions?
Add dilute nitric acid then silver nitrate solution
Chloride ions form white precipitate
Bromine ions form a cream precipitate
Iodine ions form a yellow precipitate
What are the halides?
Chlorine, bromine, iodine
What is the test for ammonium ions?
Add sodium hydroxide solution
When adding heat to the substance in the test tube ammonia gas is produced
You can test for the ammonia with damp red litmus paper that will turn blue if ammonia is present
What is the test for ammonia?
Damp red litmus paper turns blue (This one is more important)
Hydrogen chloride gas reacts with ammonia to form a white smoke of ammonium chloride
What are instrumental methods of analysis?
Analysis using machines to detect and analyse substances
What are the improvements of instrumental methods of analysis compared to chemical tests and analysis?
Sensitivity- they can detect very small amounts of different substances
Accuracy- They measure amounts of different substances very accurately
Speed of tests- they carry out each analysis quickly and the machines can run all the time
What is a flame photometer?
An instrumental method of analysis based on flame tests which can measure the brightness of a spectrum of light emitted by the metal ions (You do not need to recall how a flame photometer works)
What can the data from a flame photometer be used for?
Identifying the metal ions present in a sample by comparing the spectrum of light they produce with a different spectrum from a known substance
Determining the concentration of ions in a solution using a calibration curve
What are the names of the first 4 alkanes?
Methane, ethane, propane, butane
What are alkenes?
A homologous series of unsaturated hydrocarbons
What does a hydrocarbon being saturated mean?
It only contains single bonds
What does a hydrocarbon being unsaturated mean?
It has double bonds
What is the molecular formula for alkenes?
CnH2n
How should you draw hydrocarbons?
Hydrogen can only make 1 bond so you only draw one line
Carbon can make 4 bonds so you have to draw 4 lines
If there is a double bond for a carbon, the 2 lines count as 2 bonds
What is a functional group?
A characteristic of a molecule that tells you what homologous series it belongs to
What happens in the complete combustion of alkenes?
Carbon is oxidised to make carbon dioxide
Hydrogen is oxidised to make water vapour
What colour compounds do alkenes form when added to bromine water?
They produce colourless compounds
Why can bromine react with alkenes?
Because they are unsaturated (Have double carbon bonds)
Double bonds can open up to the bromine and become single bonds (Remember bromine goes around in pairs)
What is the test to tell the difference between alkanes and alkenes?
Add a few drops of bromine water
The solution stays orange in an alkane
The solution is decolourised in an alkene
What is an addition reaction?
When two reactants join together so make a single, large product
What are addition polymers?
Relatively large molecules made by combining smaller molecules
What is a polymer?
A substance of high average molecular mass
Made up of repeating units
Contains many monomers
What is a monomer?
A molecule that can bind to identical molecules to form a polymer
Equation model for polymerisation
The two lines sticking out are the new bonds formed when the double bond is broken
n is the number of units linked together
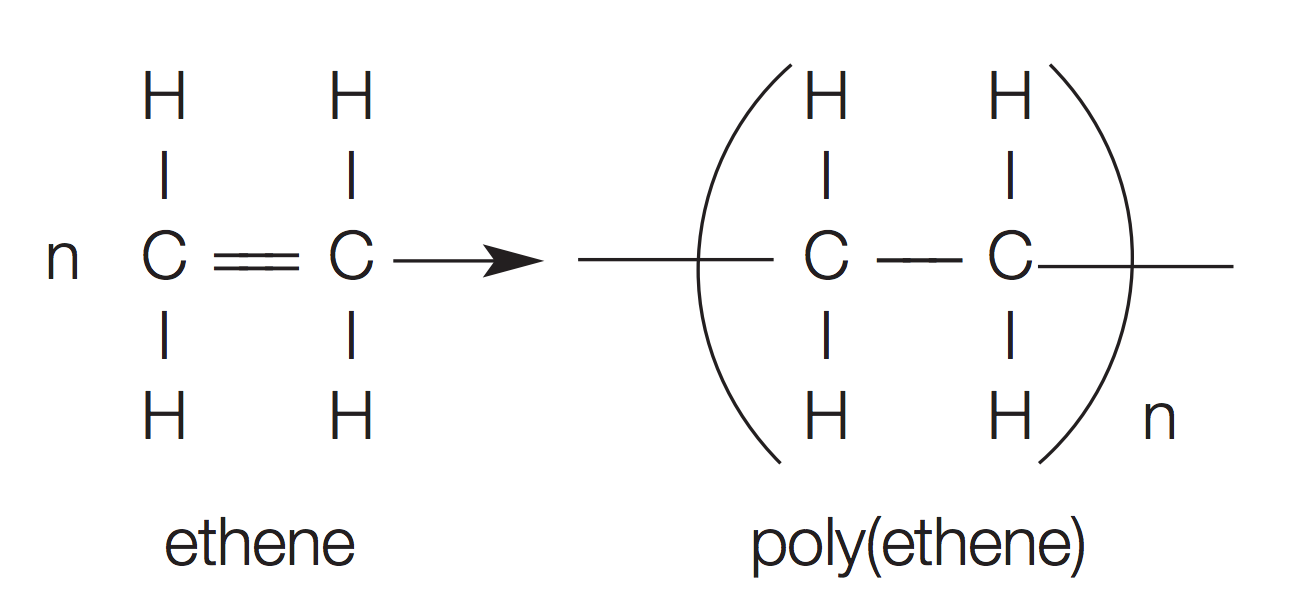
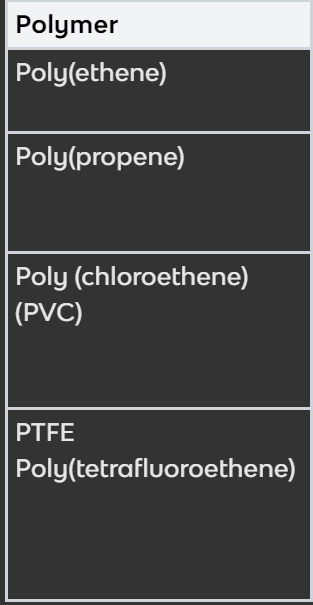
What are the properties and uses of these different polymers?
See image
Polymer | Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|
Poly(ethene) | Flexible, cheap, good electrical insulator | Plastic bags, bottles, clingfilm |
Poly(propene) | Flexible, shatterproof, has a high softening point | Buckets and bowls |
Poly (chloroethene) (PVC) | Tough, cheap, long-lasting, good electrical insulator | Window frames, gutters, pipes, insulation for electrical wires |
PTFE Poly(tetrafluoroethene) | Tough, slippery, resistant to corrosion, good electrical insulator | Non-stick coating for frying pans, containers for corrosive substances, insulation for electrical wires |
What is a condensation reaction?
This reaction is when two small molecules (monomers) react with each other and release a small molecule like water or alcohol
What kind of polymer is polyester?
A condensation polymer
What monomers does polyester have to have?
A molecule containing two carboxylic acid groups (a dicarboxylic acid group)
A molecule containing two alcohol groups (a diol group)
What does a carboxylic acid group look like?
See image
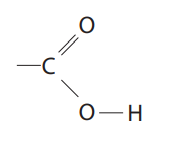
What does an alcohol functional group look like?
See image
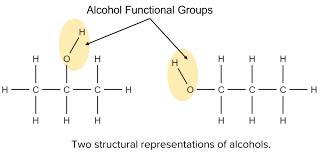
What kind of link is formed when a molecule containing two carboxylic acid groups and a molecule containing two alcohol groups react?
They form and ester link each time they react with each other
One molecule of water forms each time an ester link forms
How are long polyester molecules made from carboxylic acid groups and alcohol groups?
Polymers need two different monomers- a molecules containing two carboxylic acid groups and another molecule containing two alcohol groups
When these two molecules react, the carboxylic acid group gives up an OH molecule and the alcohol gives up a H atom- this produces a water molecule
The two molecules have a free bond at the end and can then join together by forming an ester link
Another molecule with the similar groups to this one can react with it
This process continues producing a very long polyester molecule
What are biological polymers?
Naturally occurring polymers
Examples of naturally occurring polymers?
DNA- Found in the nucleus of cells, has a double helix structure
Made of monomers called nucleotide which contain a base (which can differ), a sugar and a phosphate
Proteins- polymers made from monomers called amino acids
Each amino acid has two reactive functional groups which allow many amino acids to bond together to form a protein
What is is the polymer starch, made of?
Many sugar monomers joined together
What is the main raw material needed to make addition polymers and condensation polymers?
Crude oil
What does biodegradable mean?
Materials that will eventually rot away:
Microbes feed on them
This breaks them down
What are the advantages and disadvantages of most artificial polymers not being biodegradeable?
Advantage- objects made from polymers last a long time
Disadvantage- It will not break down easily when disposed of
How effective are landfill sites at disposing of polymers?
Polymers are not biodegradable so they last for many years
We are running out of landfill sites to contain them
How effective is burning polymers at disposing of them?
Many polymers release toxic gasses when they are burnt
How effective is recycling polymers?
Polymers can be melted and formed into new objects
We can break them down into new raw materials
How effective are biodegradable polymers at solving polymer problems of disposal?
These are being developed and they will rot away in landfill sites which solves the problems of polymers not being disposed of effectively
Advantages of landfill sites?
Waste is disposed of quickly
Waste is out of sight once covered over
Disadvantages of landfill sites?
Space for landfill sites is running out
Most polymers are not biodegradable and will last for many years
Landfill sites are unsightly and attract pests
What is the functional group of alcohols?
-OH
What is the homologous series of alcohols like?
They have the functional group -OH
Have similar chemical properties
Has the general formula CnH2n+1OH
Show a gradual variation in physical properties, such as boiling point
What do all alcohols end with in their name?
-ol
What is the functional group -OH of alcohols called?
A hydroxyl group
What are the reactions of alcohols with water and sodium and what do they do when ignited?
Methanol, ethanol and propanol all:
Dissolve in water to form a neutral solution
React in sodium to produce hydrogen
Burn in air
How can ethanol be oxidised into ethanoic acid?
Combustion
Can be oxidised by chemicals called oxidising agents
The action of microbes
How is ethanol produced?
Produced from carbohydrates in an aqueous solution by a process called fermentation
Carbon dioxide is also produced from this reaction
The carbohydrates can be sugars from fruit like grapes or the breakdown of starch from wheat or barley
Yeast is a single-celled fungus that provides enzymes for the fermentation to happen
Why is fractional distillation used to obtain a concentrated solution of ethanol?
Ethanol has a lower boiling point than water
Note that it is not possible to obtain pure ethanol by this method alone, The rest of the water must be absorbed chemically.
How is fractional distillation used to obtain a concentrated solution of ethanol?
A filtered mixture from fermentation is heated up in a flask
Pure ethanol boils at 78oC and when boiled, a vapour with a high proportion of ethanol in it will rise up the fractionating column
The column has a heat gradient so it is coolest at the top- this causes any water that may have evaporated to condense because of the difference in temperature
The ethanol vapour is condensed in the condenser and then is collected in a beaker
This gives us our concentrated ethanol solution
What are the characteristics of carboxylic acids?
Have the same functional group -COOH
Have similar chemical properties
Has the general formula CnH2n+1COOH
Shows a gradual variation in physical properties such as boiling points
What is the naming convention of carboxylic acids?
Names end in -anoic acid
What is the name of the functional group of carboxylic acids, -COOH?
A carboxyl group
How does carboxylic acid react with carbonates, reactive metals and water?
Reacts with carbonates to produce a salt, water and carbon dioxide
Reacts with magnesium and other reactive metals to produce a salt and hydrogen
Dissolves in water to produce acidic solutions
Why are carboxylic acids weak acids?
They can only partially dissociate into ions when they are dissolved in water
What are nanoparticles?
Structures consisting of only a few hundred atoms
Why are nanoparticulate materials useful compared to bulk materials?
They are materials that have different properties from the same substance as a bulk material. This makes them useful for:
Sunscreens- they still absorb harmful UV light but cannot be seen
Lightweight strong materials such as carbon nanotubes in tennis rackets
Future drug delivery systems- buckyballs consist of hollow balls of carbon atoms
Catalysts- because they are made up of small particles unlike bulk materials, they have a larger surface area, increasing the rate of reaction
What is the surface area to volume ratio like for nanoparticles and how is this useful?
Nanoparticles have a very small size meaning they have a very large volume to surface area ratio. This makes them useful as catalysts because they will have a larger surface area, for example coatings for self-cleaning surfaces and clothes
What are the hazards and risks of nanoparticles?
They can be inhaled, absorbed through the skin or transported into cells
Take a long time to break down
Attract toxic substances to their surfaces
General properties and examples of glass ceramics?
Transparent
Hard but brittle
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Examples: Window glass, bottles
General properties and examples of clay ceramics?
Opaque
Hard but brittle
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Examples: bricks, china, porcelain
General properties and examples of polymers?
Vary from transparent, translucent and opaque
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Often tough and ductile
Example: Bottle, crates, carrier bags
General properties and examples of objects made of metals?
Can be polished to a shine
Good conductors of heat and electricity
Hard, tough and ductile
Example: Cars, bridges, electrical cables
What is the general formula of a carboxylic acid group?
CnH2n+1COOH
What is the nature of the product in addition polymerisation?
Only a single product- the polymer
Non biodegradable
Resistant to acids
What is the nature of the product in condensation polymerisation?
Two products- the polymer and water (or another small molecule)
Biodegradable
Hydrolyzed by acid (broken down by acids)
What are the melting and boiling points of polymers and why are they solid at room temperature
They have relatively high boiling points
There are weak intermolecular forces holding a polymer together, but there are so many that to break all of these would require quite a lot of energy
This means that there would be enough intermolecular forces holding the structure of a polymer together to be solid at room temperature
What is the test for aluminium and calcium ions?
Add sodium hydroxide
They both turn white
How can we distinguish between aluminium and calcium ions?
Add excess sodium hydroxide
Calcium stays white
Aluminium turns colourless