Chem SAC1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Fuel
A substance that can easily release stored energy
Fossil fuel
non-renewable fuels such as coal, petrol and natural gas formed in the geological past from remains of living organisms
Bio-fuel
renewable fuels derived from plants or animals biogas, biodiesel and bioethanol
non renewable
resources that are used faster than they can be replaced
renewable
replenished in short period of time
Fossil fuel advantages
relatively high energy content, natural gas and petrol easy to transport
Fossil fuel disadvantages
Non renewable, high level emissions
Biofuel disadvantages
Lower energy content, limited supply of raw materials from which to produce it, bioethanol require use of farmland otherwise used for food production
biofuel advantages
renewable, can be made from waste material, CO2 absorbed during photosynthesis
Bio gas
Biogas is the gas released in the breakdown of organic waste by anaerobic (absence of oxygen) bacteria. Biogas mainly consists of methane and carbon dioxide it generates electricity via combustion however energy released per gram is lower than natural gas because methane content in biogas is much lower.
Biodiesel
Biodiesel is an ester produced from the reaction of a triglyceride and an alcohol. Triglyceride can be vegetable or animal oil alcohol is typically methanol
Bioethanol
Produced via fermentation which is carbohydrates converted into an alcohol with enzymes to catalyse reaction. Ethanol must be separated from water to make it useful as a fuel, distillation utilises different boiling points of the liquids to separate them
Fermentation reaction
C6H12O6 (aq) → 2CH3CH2OH (aq) + 2CO2 (g)
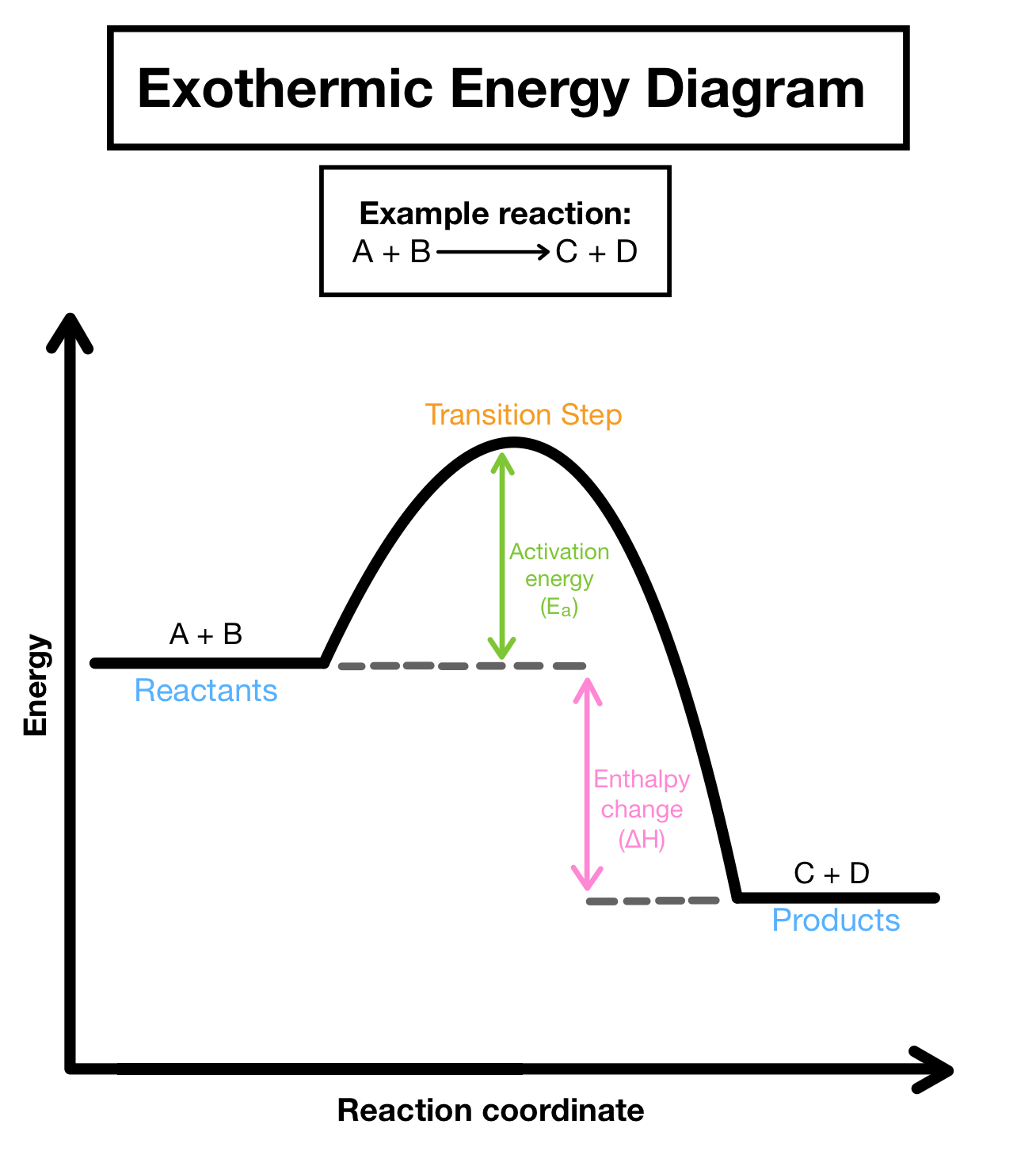
Exothermic reaction
Energy released in the form of heat into the atmosphere
enthalpy is negative
products have lower enthalpy than the reactants
forming bonds
The energy required to break bonds in the reactants is less than the energy released when new bonds are formed in the products.
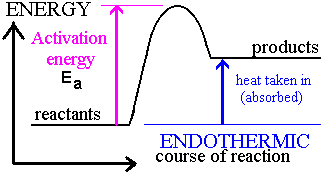
Endothermic reaction
Heat energy absorbed from atmosphere
enthalpy is positive
products have greater enthalpy than reactants
breaking bonds
The energy required to break bonds in reactants is greater than the energy released when the new bonds are formed in the products.
Molar enthalpy change
the change in enthalpy per mol of a substance undergoing reaction kj mol-1
products minus reactants
Exothermic
Endothermic
Specific heat capacity
energy required in joules to increase 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius without changing its state
Oxidising agent
is reduced and causes oxidation
Reducing agent
is oxidised causes reduction
Oxidation number increases
substance is oxidised therefore reducing agent
Oxidation number decreases
substance is reduced and therefor is the oxidising agent
cathode
reduction, electrons are reactants higher half equation in electrochemical series
anode
oxidation, electrons are products lower half equation in electrochemical series flipped
Accuracy
how close the experimental value is to the true value
precision
how close experimental values are to each other
random error
follow no regular pattern affect the precision
e.g error estimating second decimal place
temp variation solution not mixed consistently
variation in gas flow rate