Neurological system
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
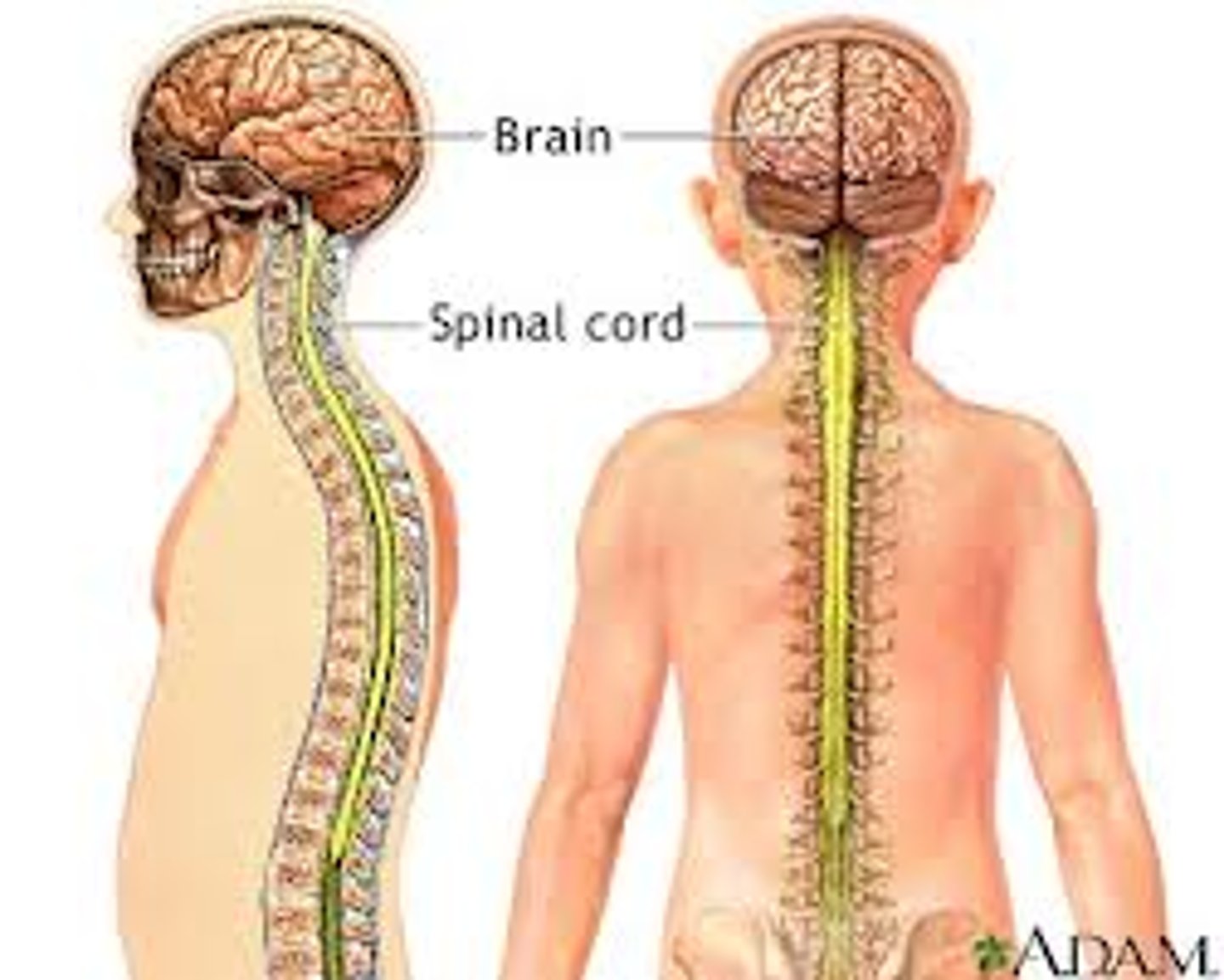
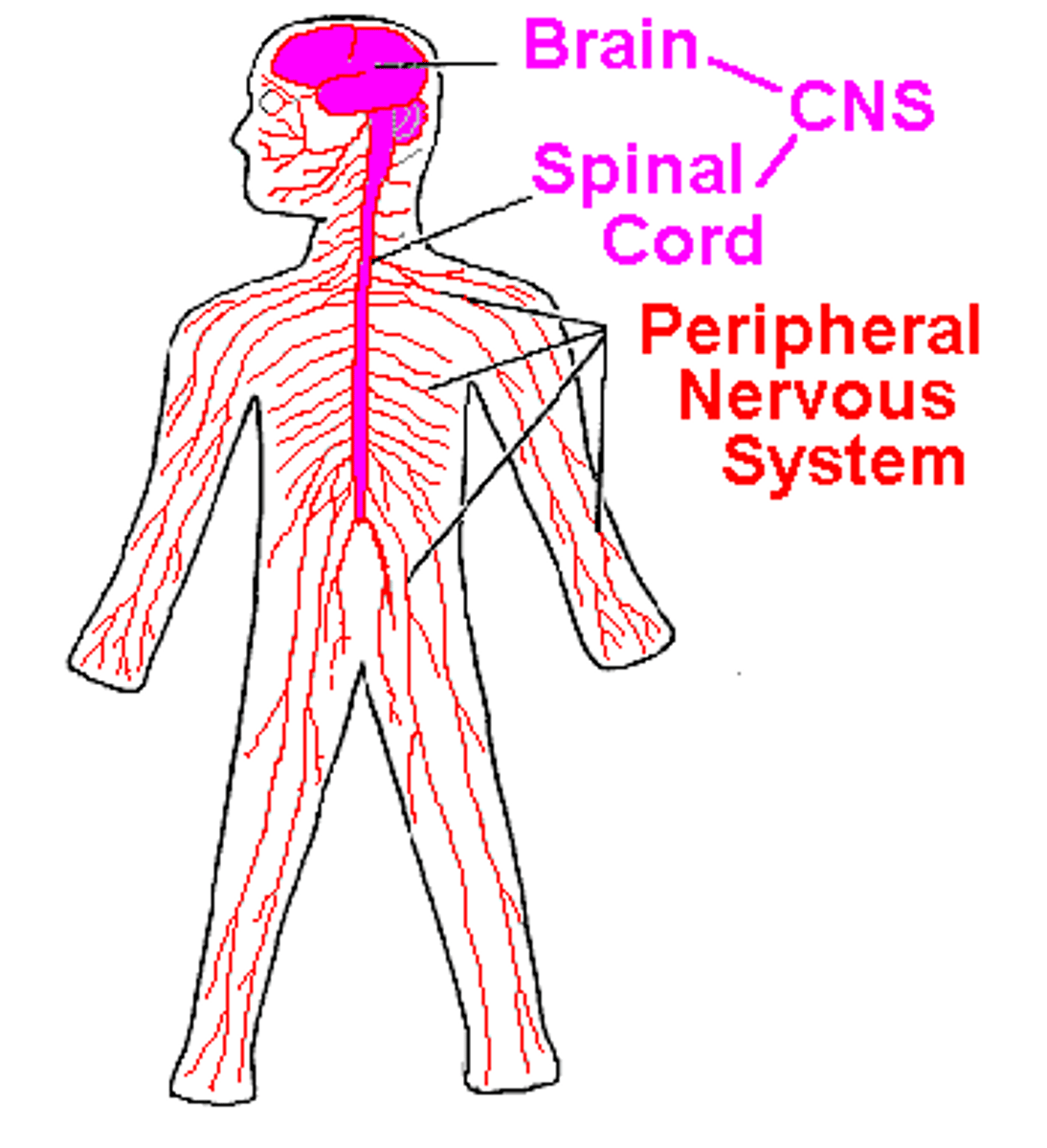
Components of the CNS
> brain
> spinal cord
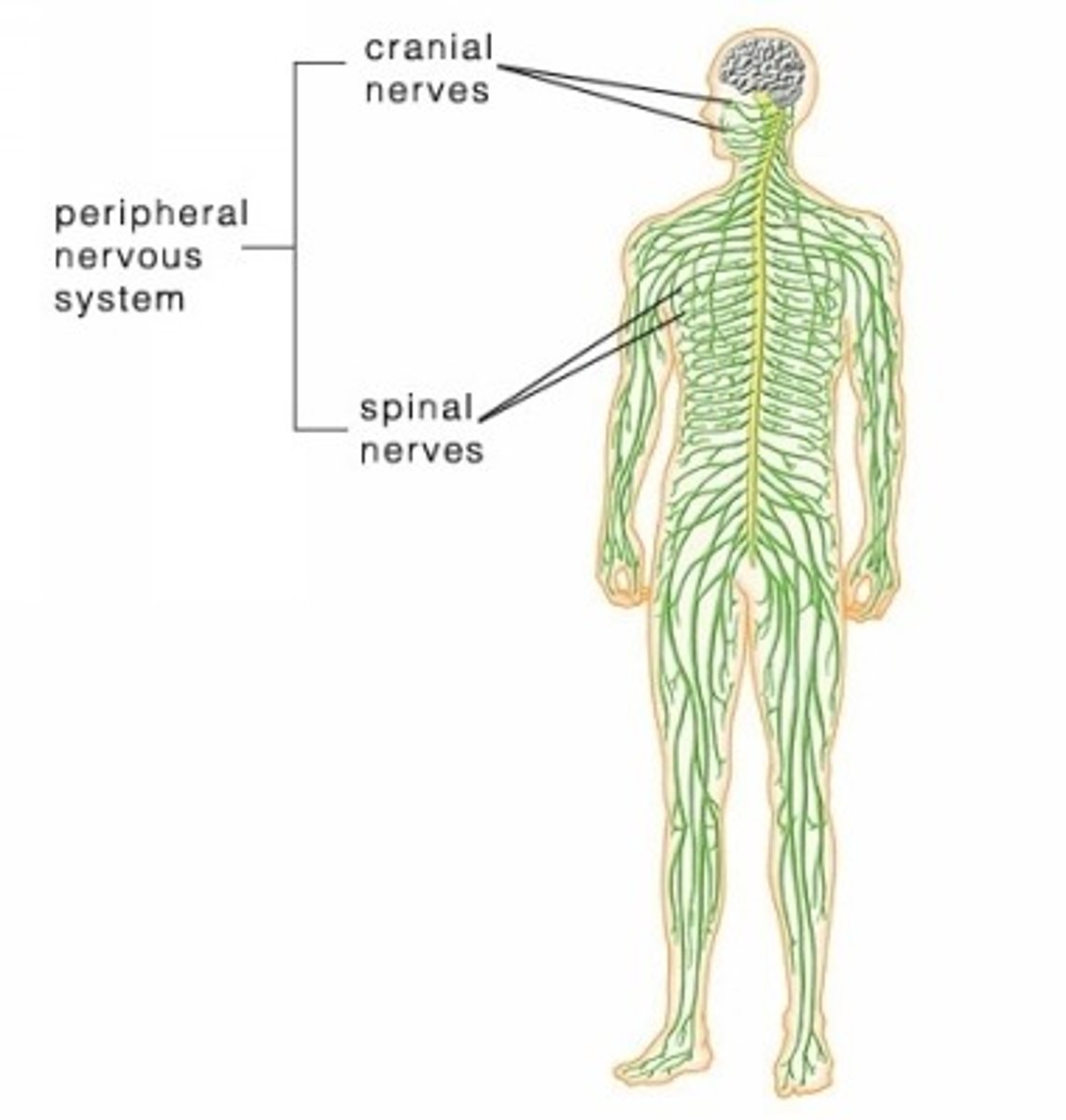
Components of the PNS
> somatic NS
> autonomic NS (enteric NS)
3 main functions of NS
1. sensory function
2. integrative function
3. motor function
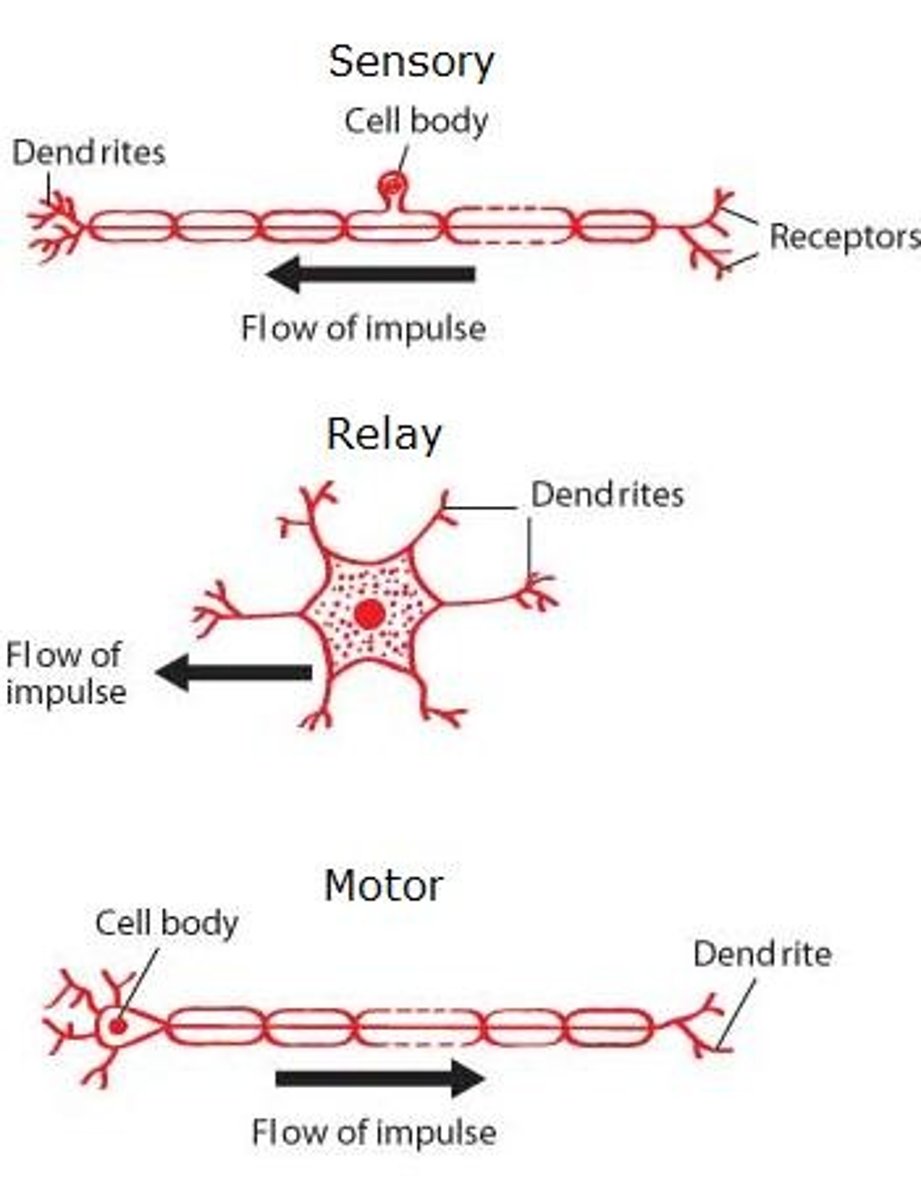
3 types of neurone
Components of nerve tissue
> cluster of neuronal cell bodies - ganglion in PNS, nucleus in CNS
> bundles of axons - nerve in PNS, tract in CNS
> white matter - primarily myelinated axons
> grey matter - neuronal cell bodies, unmyelinated axons and neuroglia
Glial cells (neuroglia)
> make up half vol. of CNS
> glial - glue - holds everything together
> don't generate or propagate action potentials
> can multiply and divide
> have different functions
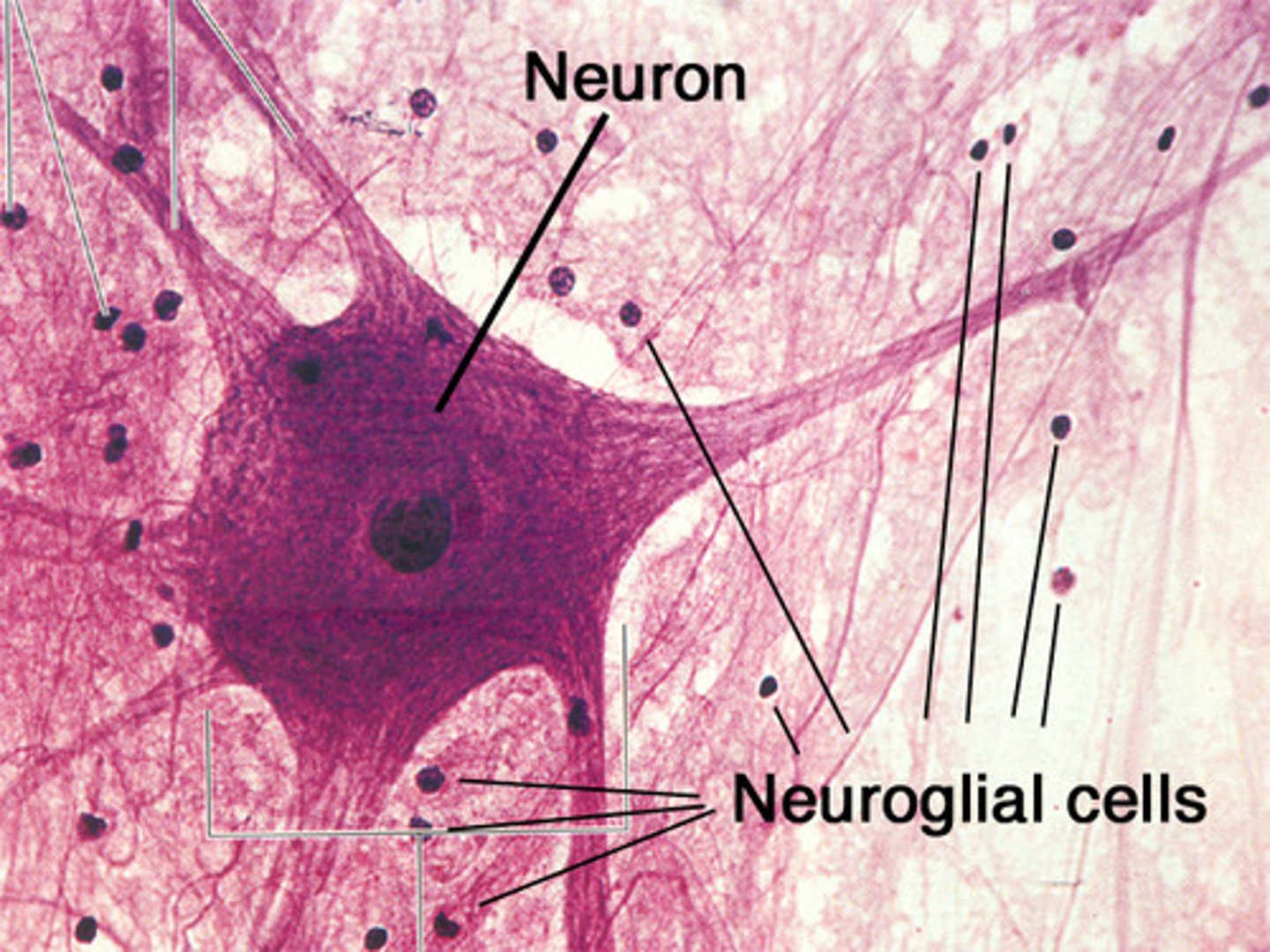
3 components of the neuroglia of the CNS
1. astrocytes
2. oligodendrocytes
3. microglia
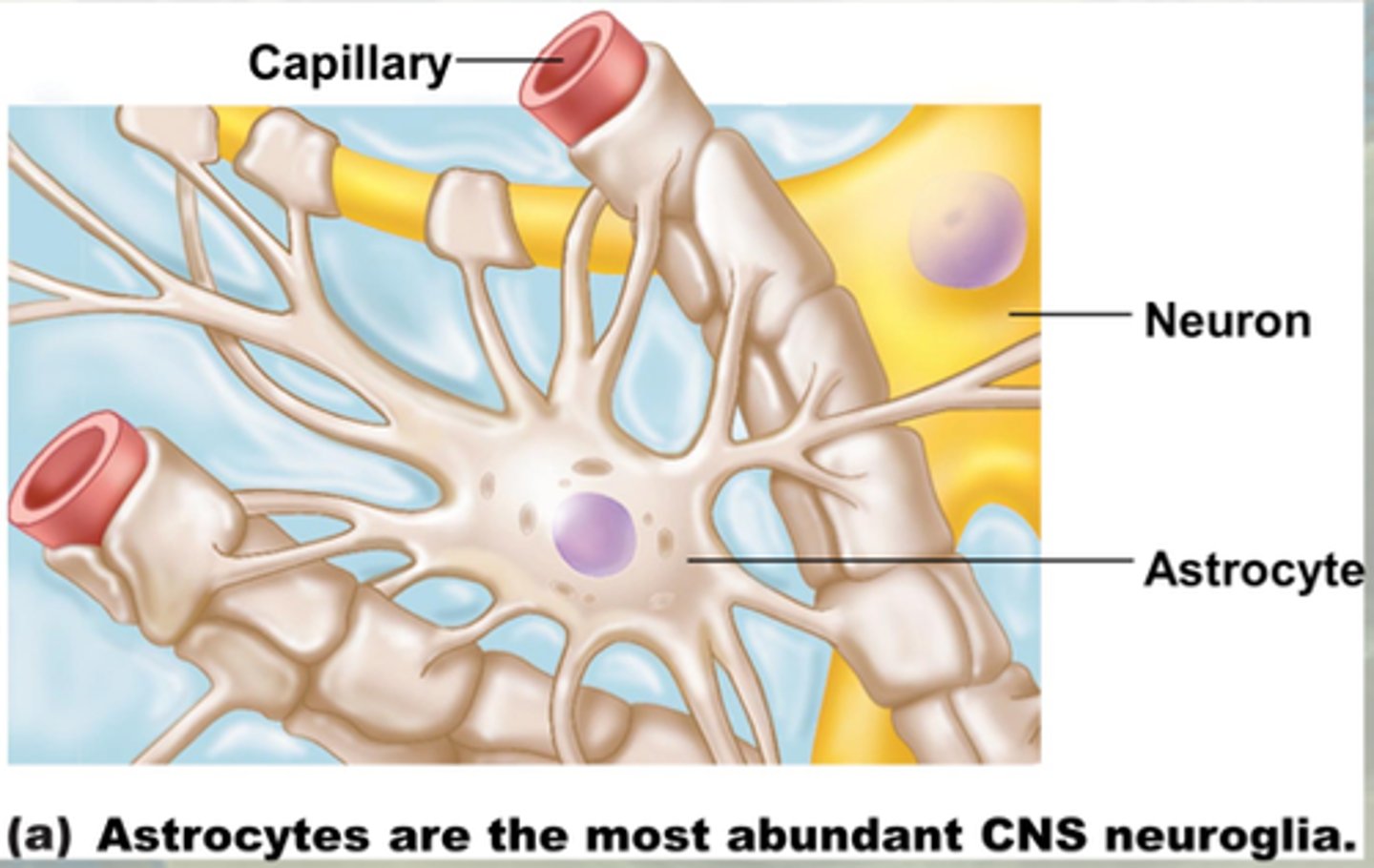
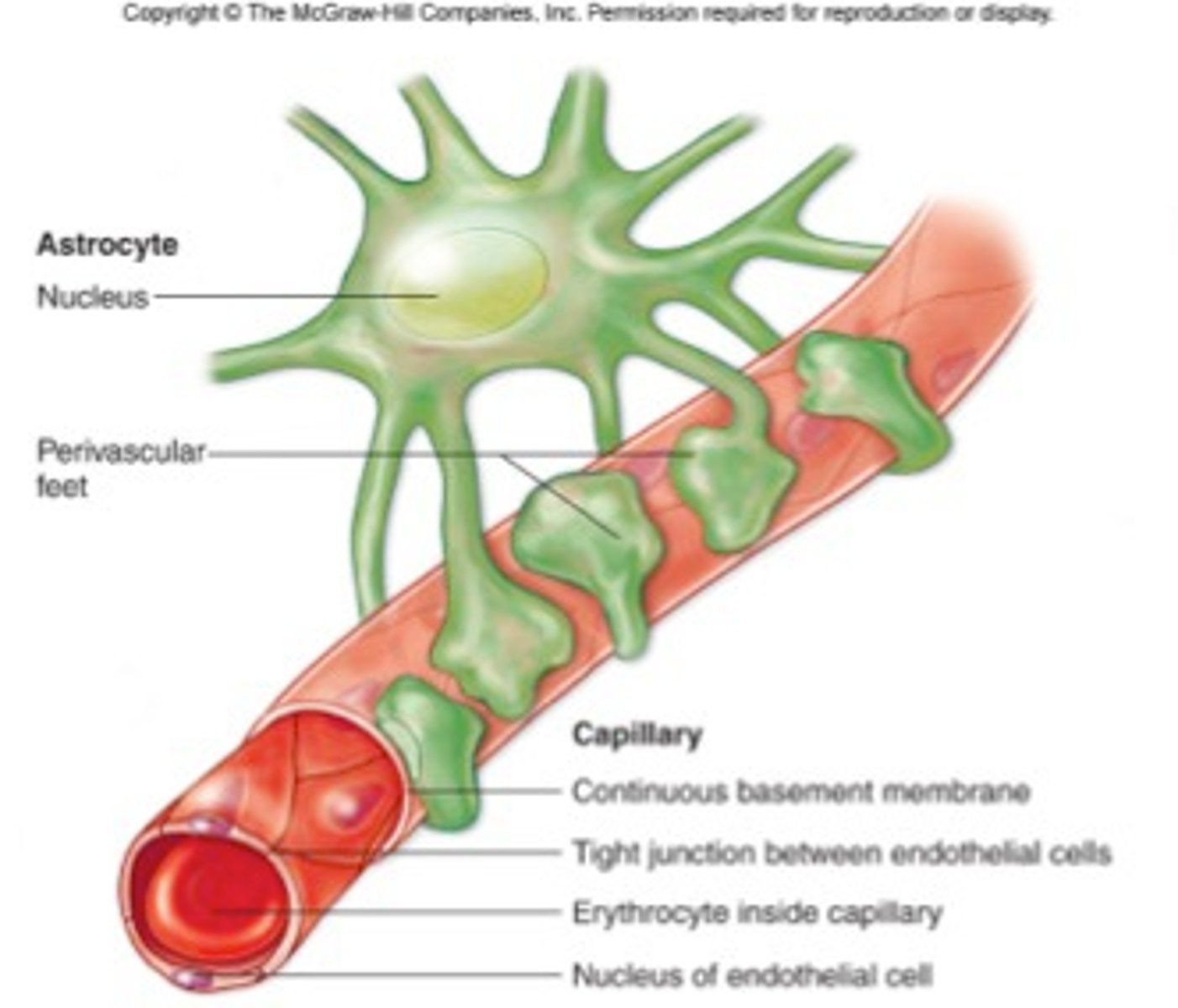
Astrocytes
> strength
> support
> protection
> wrap around capillaries to protect CNS
> creates blood brain barrier
> help maintain appropriate
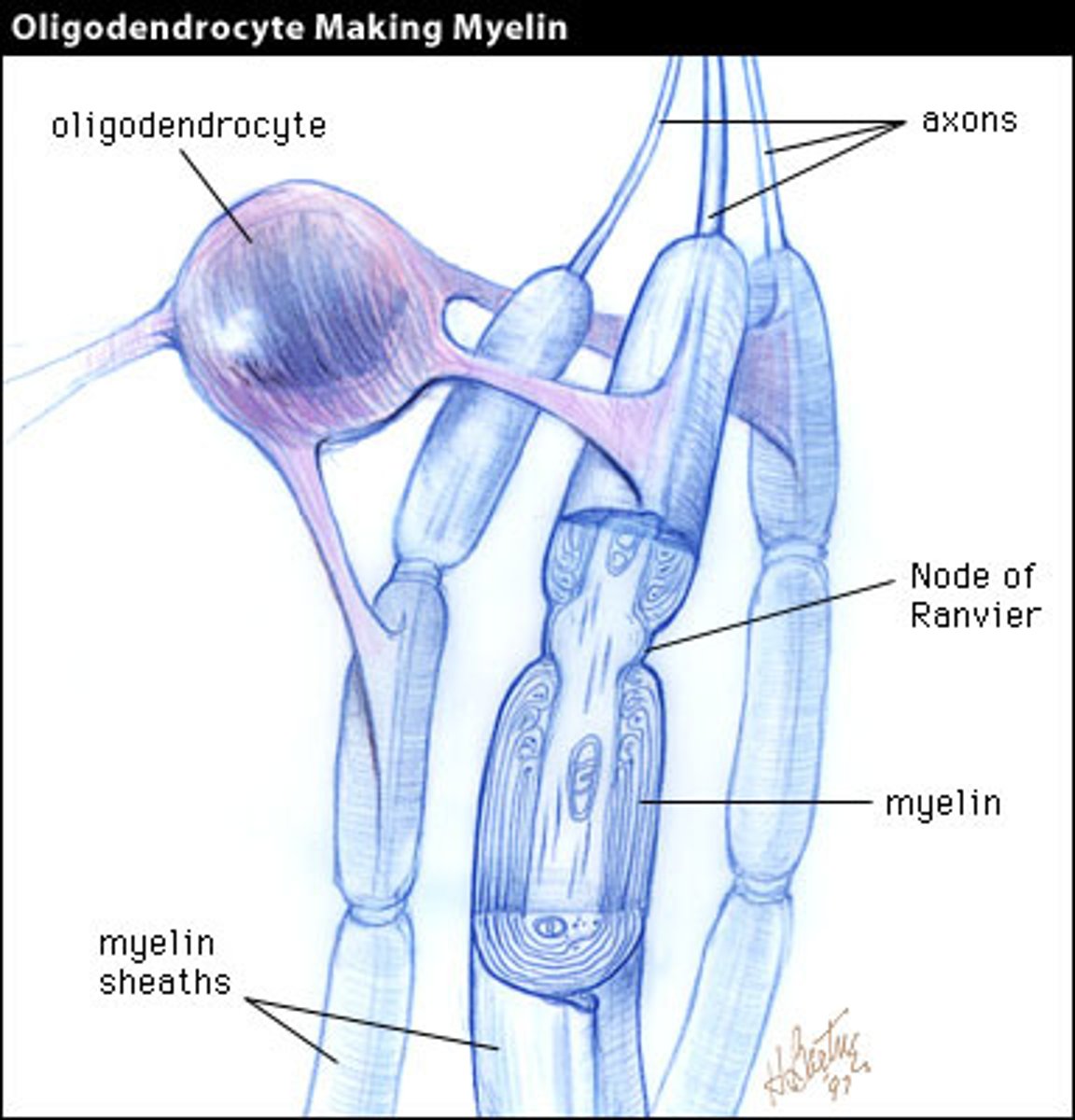
Oligodendrocytes
> responsible for myelination
> formation and maintenance
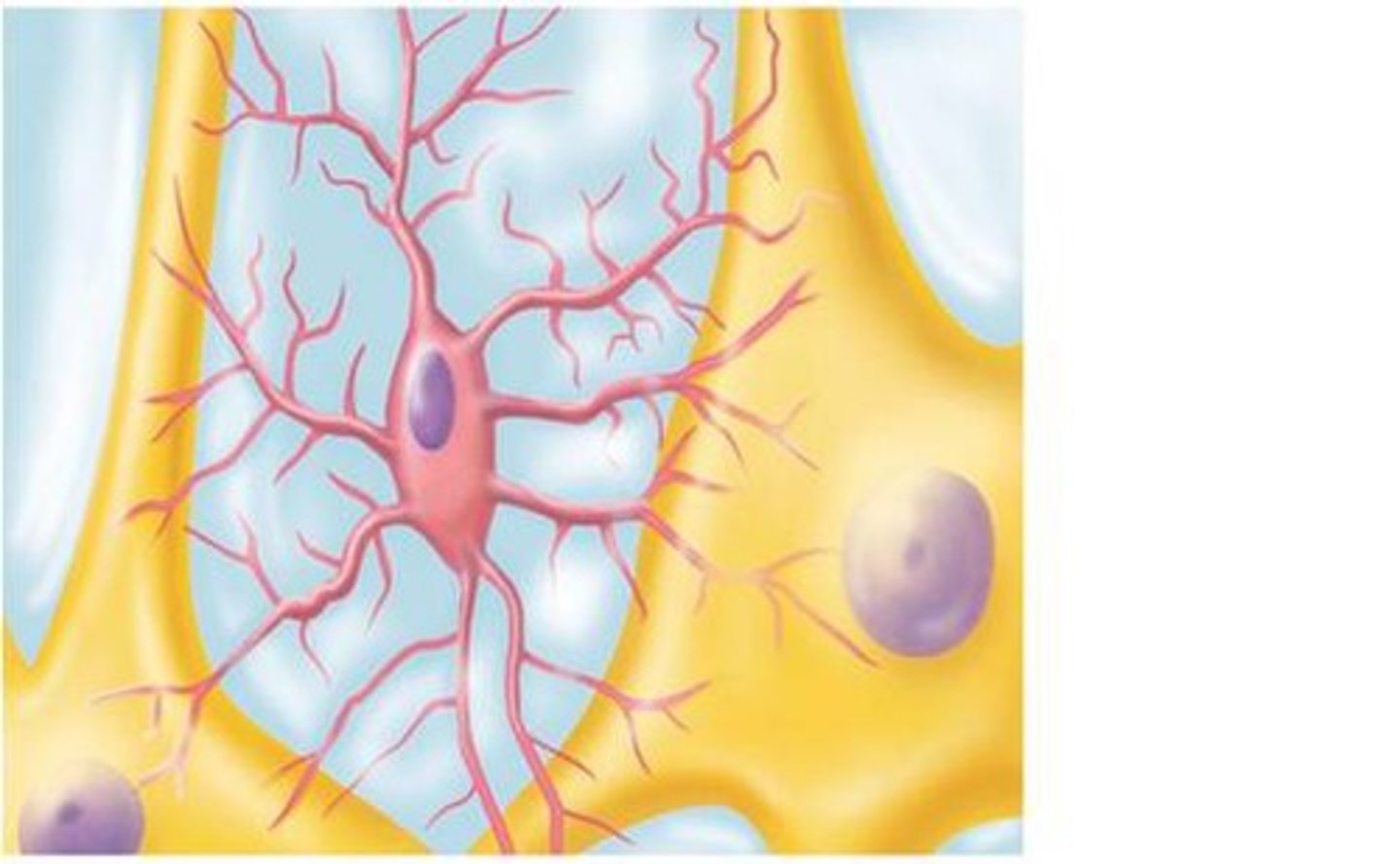
Microglia
> remove cellular debris
> phagocytise microbes and damaged nerve tissue
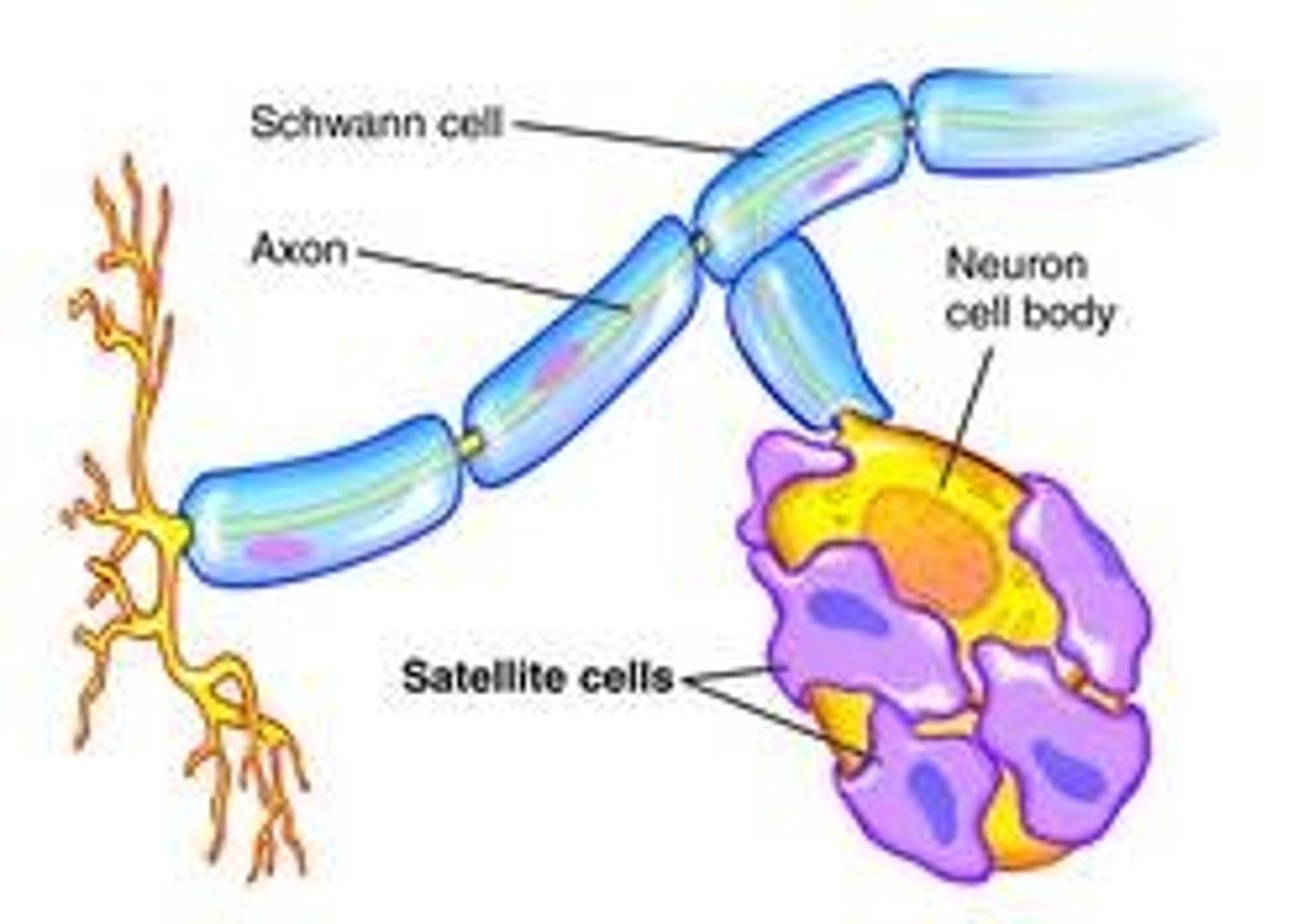
2 components of the neuroglia of the PNS
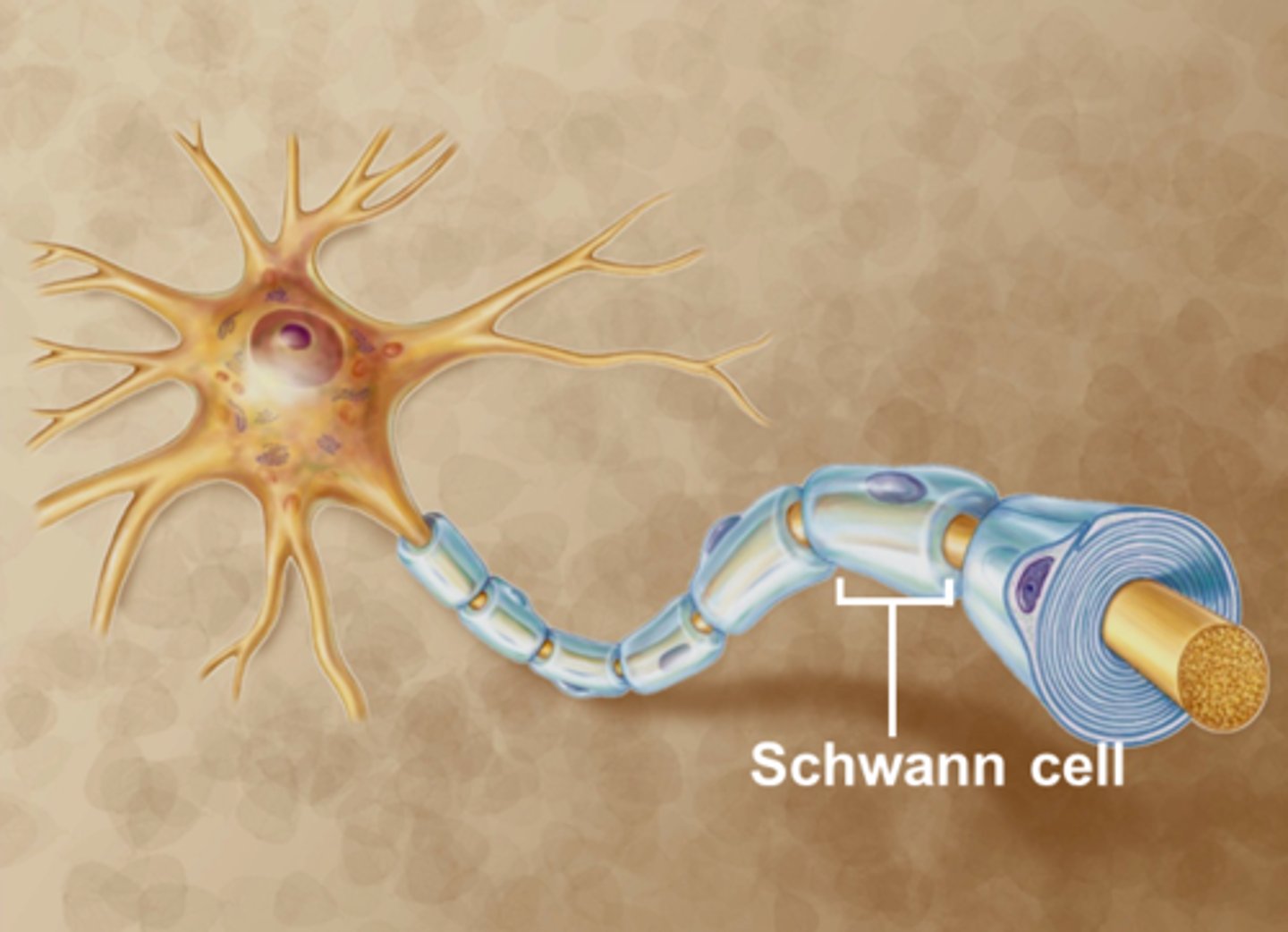
1. Schwann cells
2. satellite cells
Schwann cells
> encircle PNS
myelinates axons
> participates in axon regeneration
> easier in the PNS
Satellite cells
> provides structural support and material exchange between cells bodies and interstitial fluid
Regeneration and repair
> plasticity: the NS has a capability to change based on experience however there's limited regeneration capacity
> CNS neurogenesis is almost non-existent: inhibitory influences of oligodendrocytes and absence of growth stimulating cues
> PNS neurogenesis is possible if the cell body remains intact and the Schwann cells remain active
Blood brain barrier (BBB)
> layer of tight junctions which seal the endothelial cells of BBB capillaries
> astrocytes surround capillaries
> only certain compounds allowed through
> trauma, toxins and inflammation can cause disruption of BBB
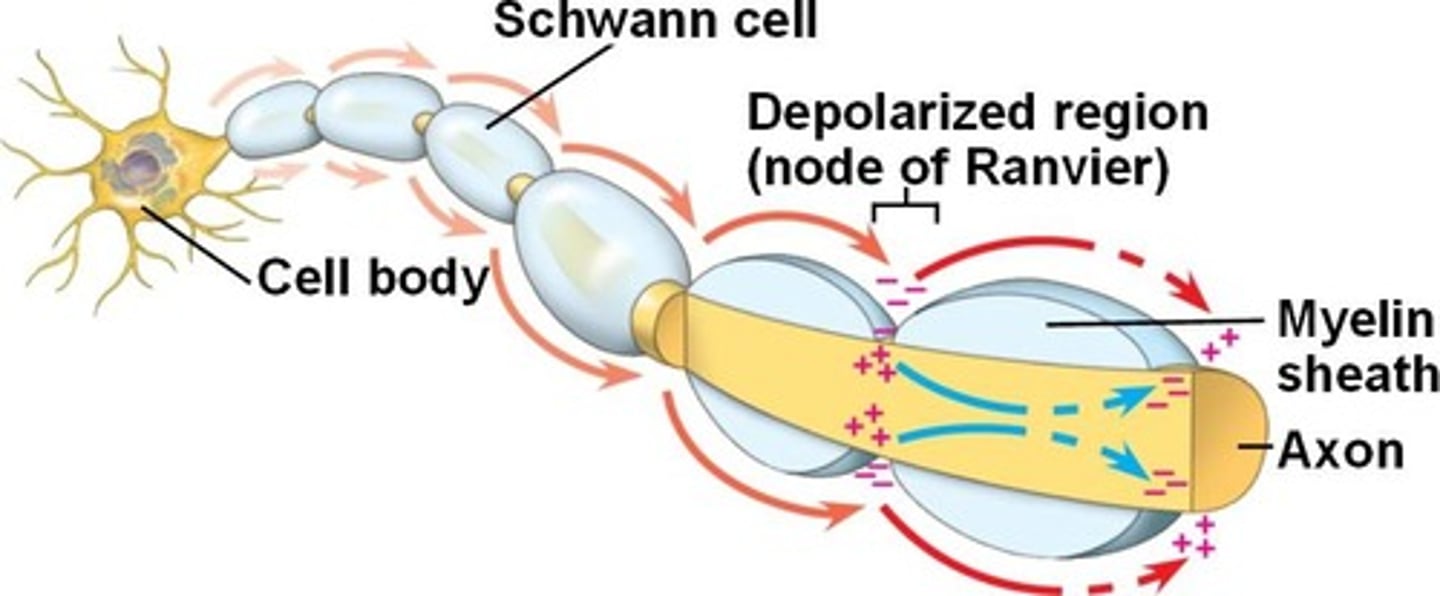
Saltatory conduction
action potentials travel down axon and jump from node to node via nodes of ranvier
What happens at the synapse?
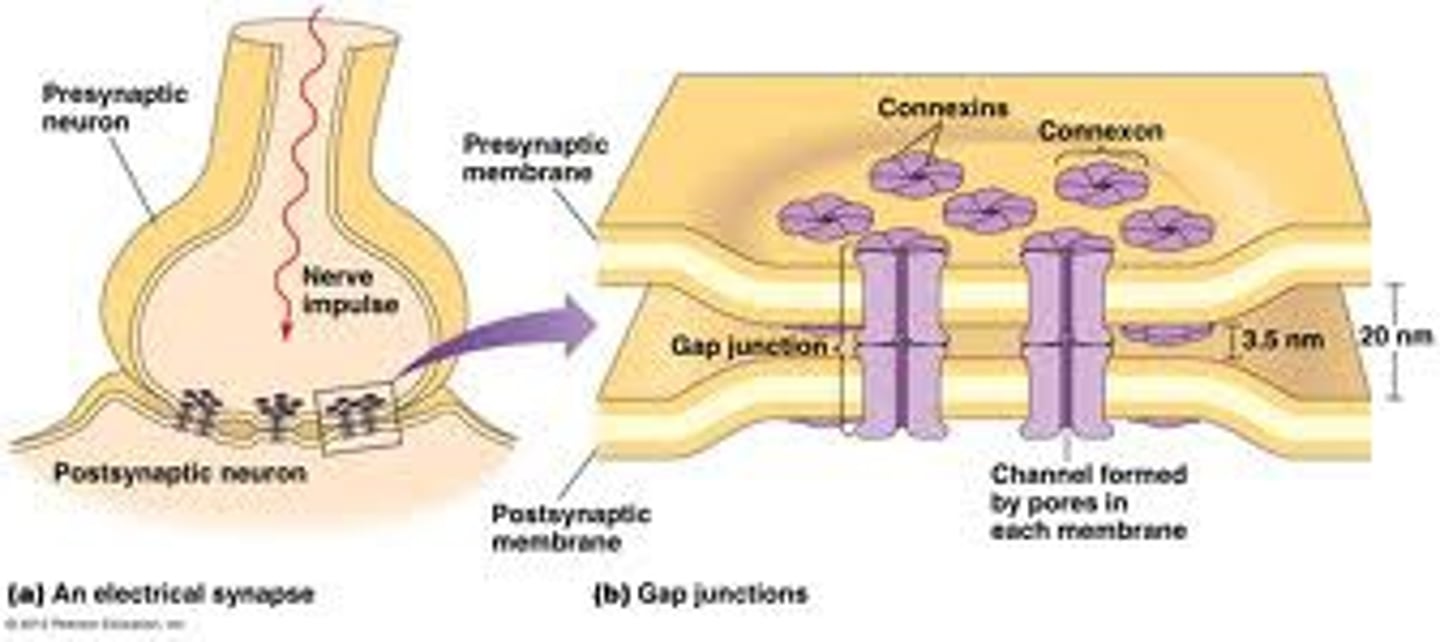
Electrical synapse
> conduct directly between neurons
> use gap junctions
> happen in visceral smooth muscle and cardiac muscle
> good for fast communication and synchronisation
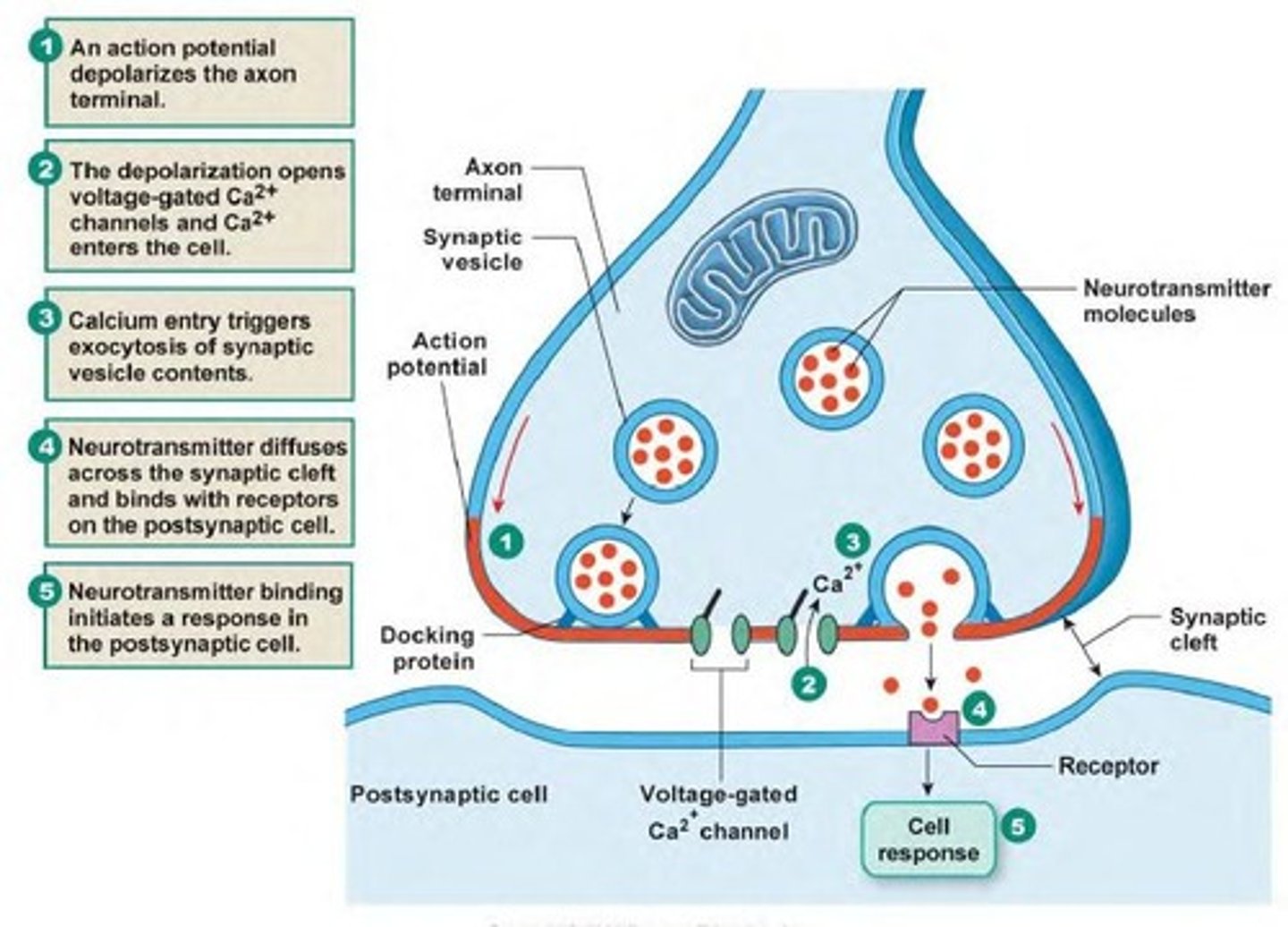
Chemical synapse
> most common
> use a neurotransmitter to transmit impulses
> slower than electrical
> more diverse
> neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory
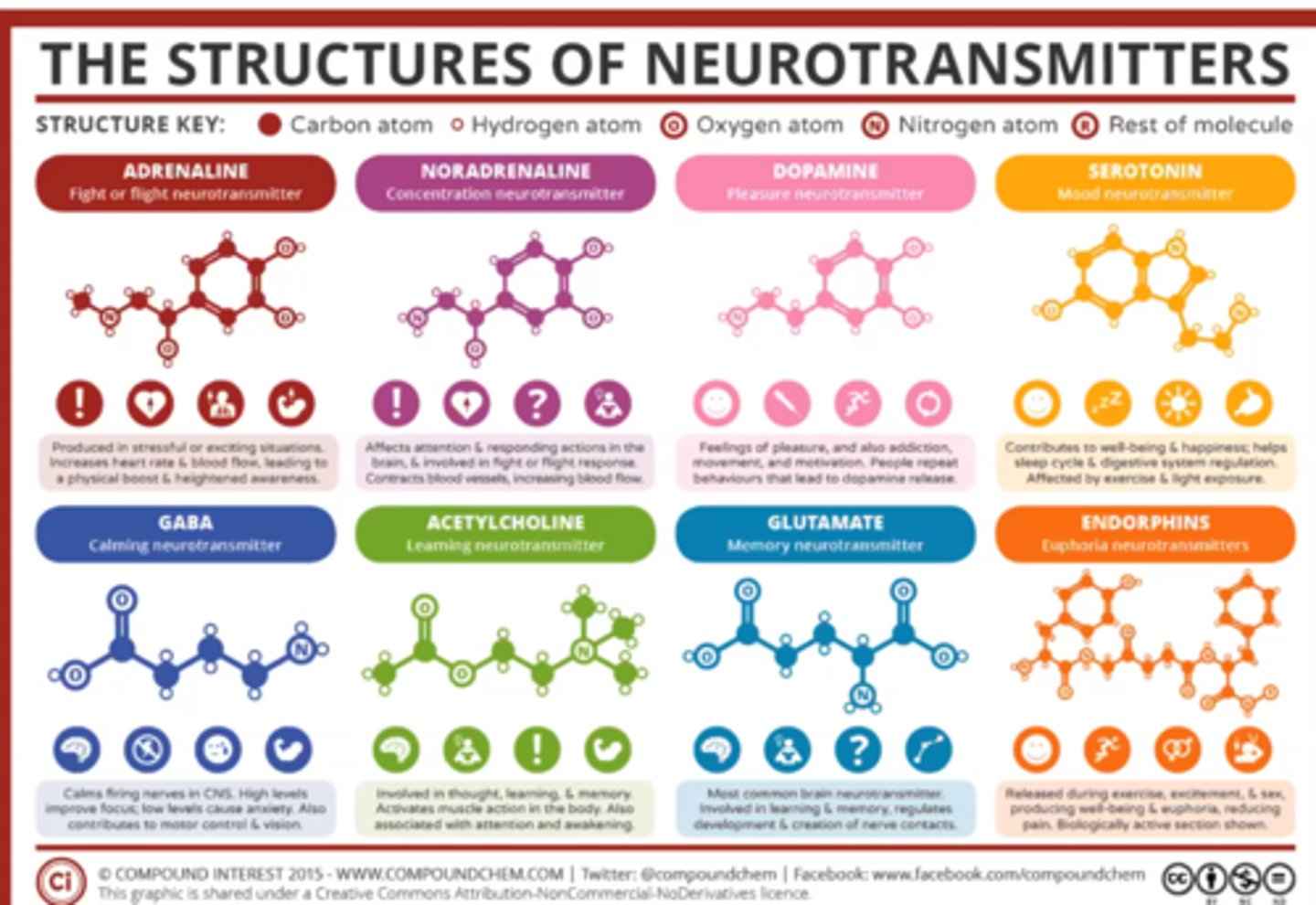
Types of neurotransmitters
Parts of the brain
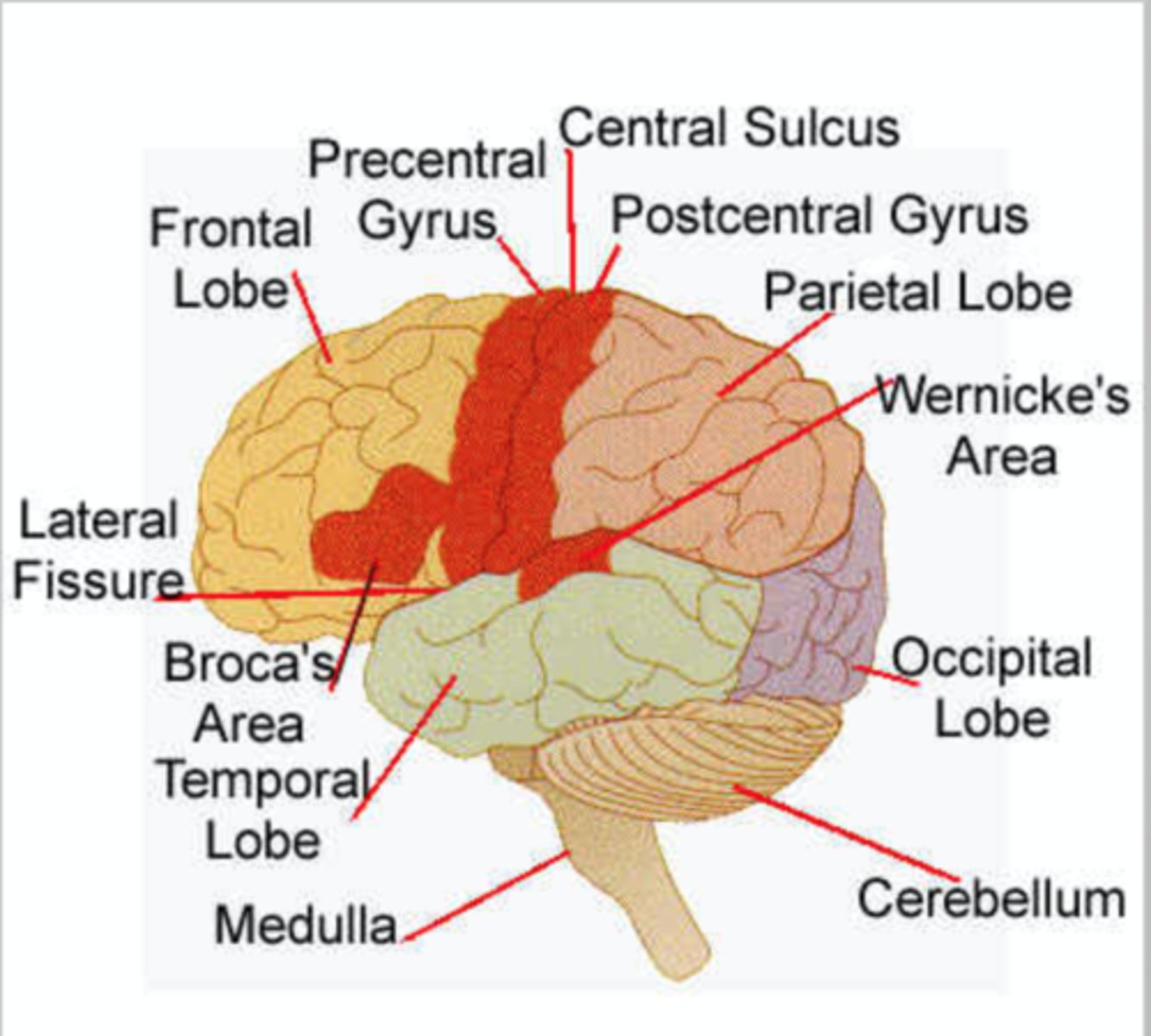
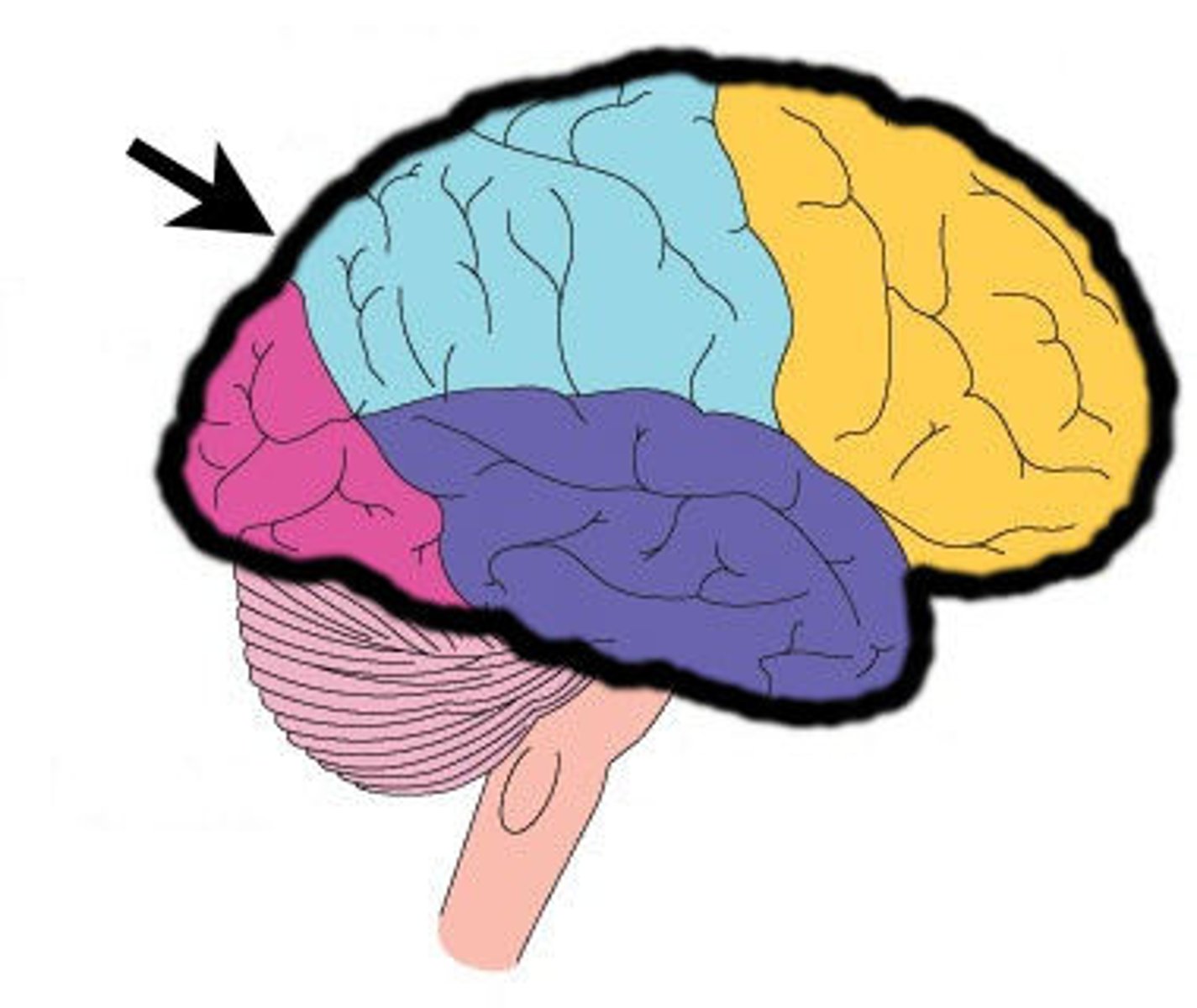
Cerebrum
> conscious thought processes, intellectual functions
> memory storage and processing
> conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions
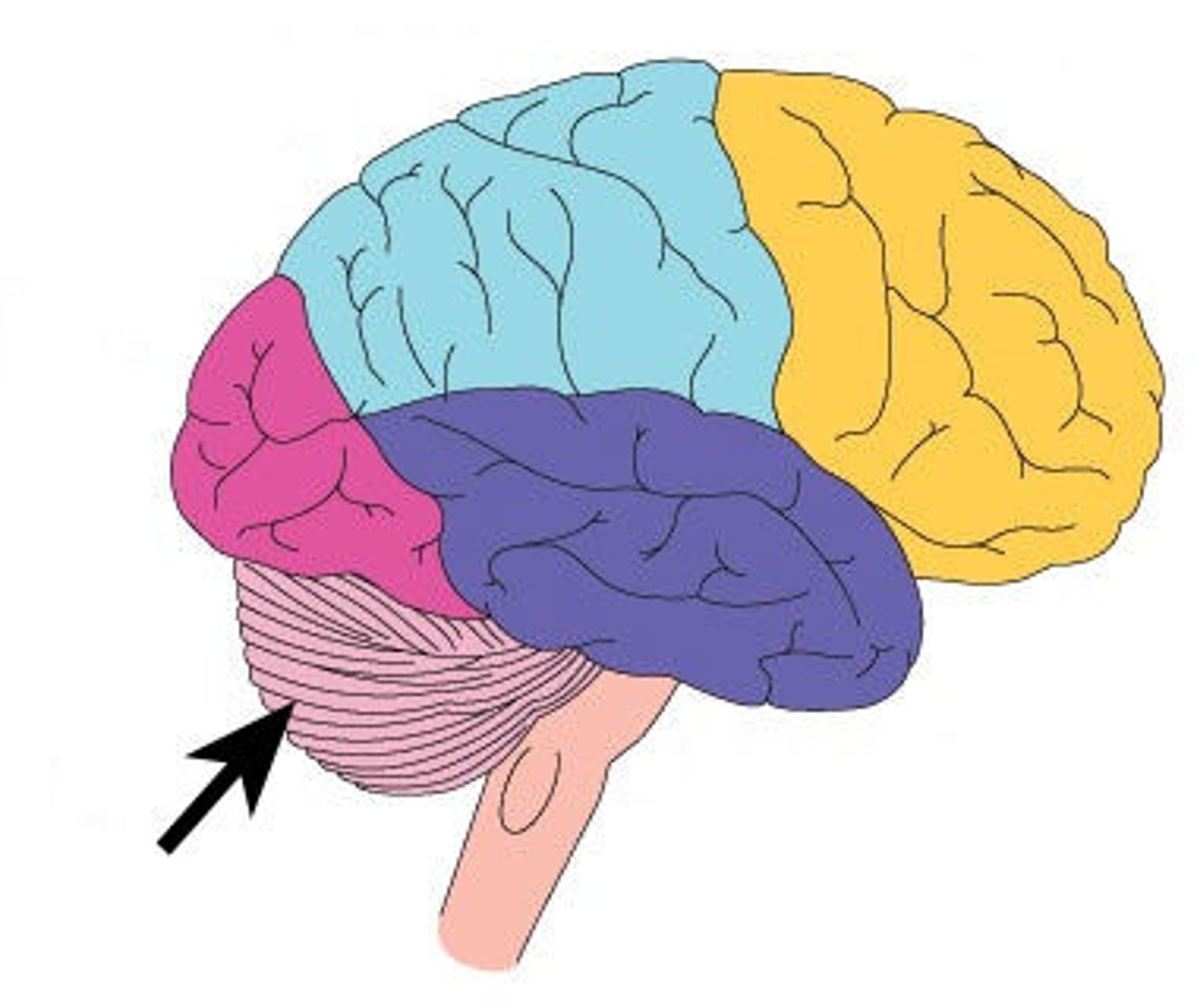
Cerebellum
> coordinates complex somatic motor patterns
> adjusts output of other somatic motor centres in brain and spinal cord
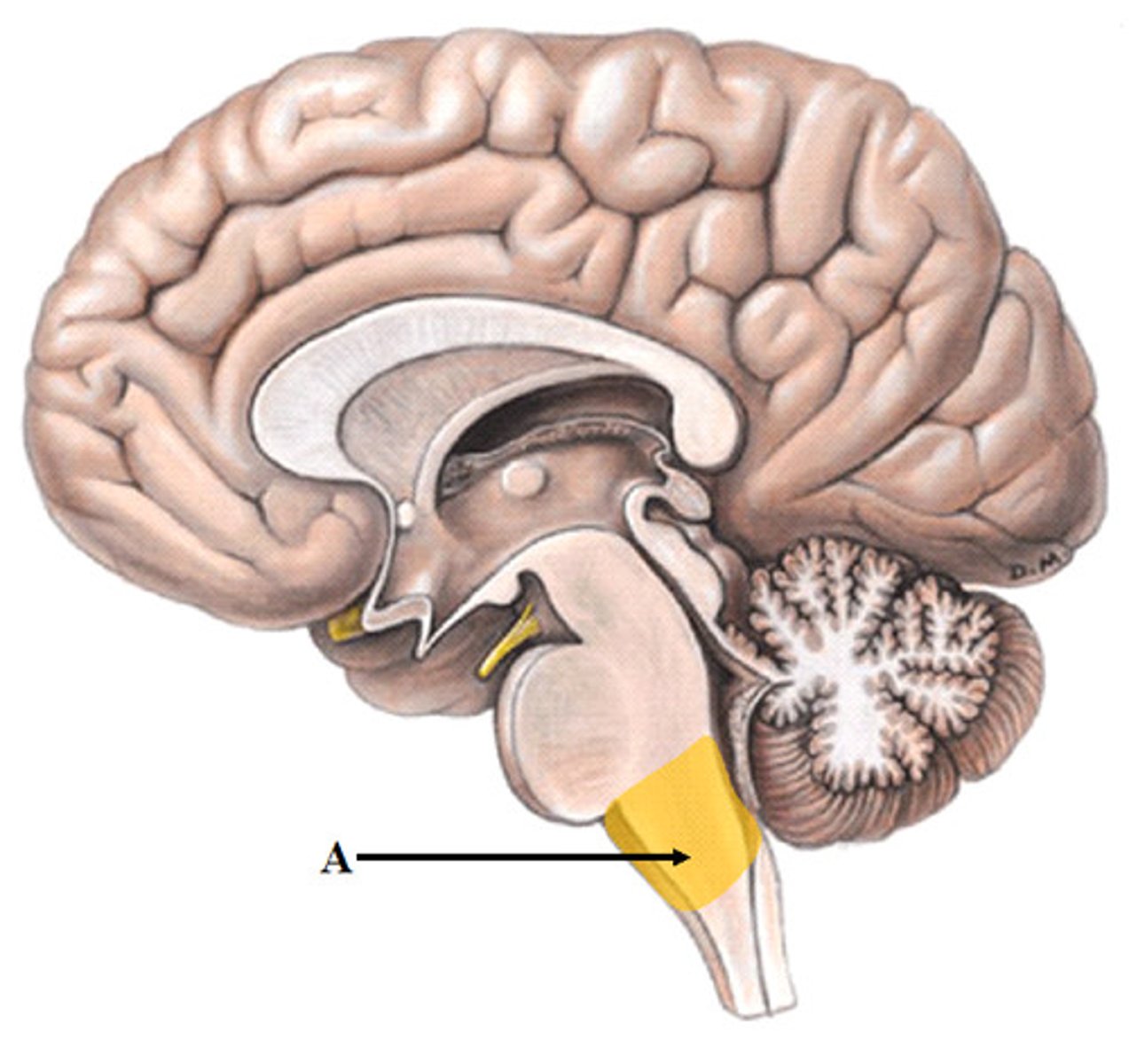
Medulla oblongata
> relays sensory info to thalamus and to other portions of brain stem
> autonomic centres for regulation of visceral function (cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities)
Pons
> relays sensory info to cerebellum and thalamus
> subconscious somatic and visceral motor centres
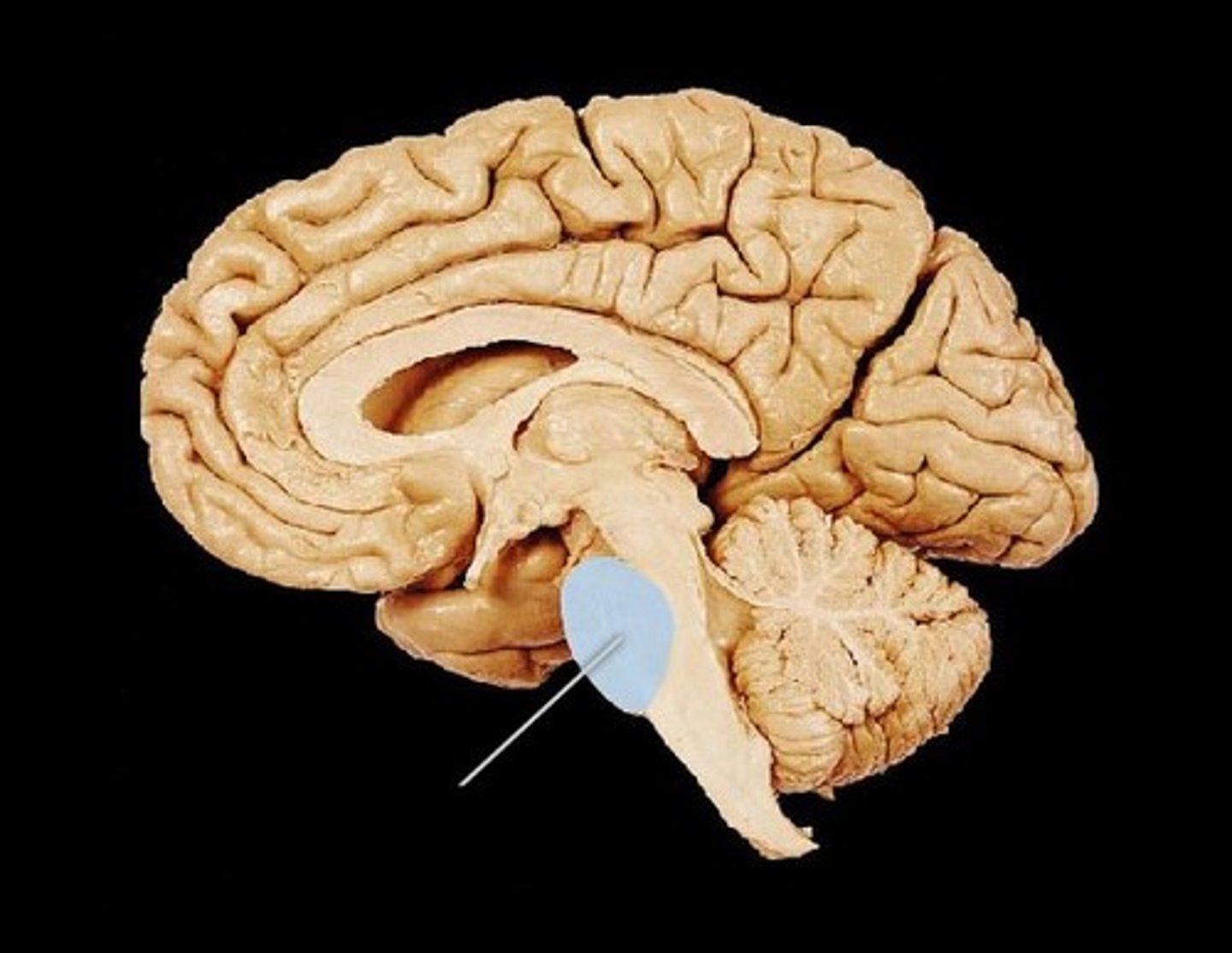
Mesencephalon
> processing of visual and auditory data
> generation of reflexive somatic motor responses
> maintenance of consciousness
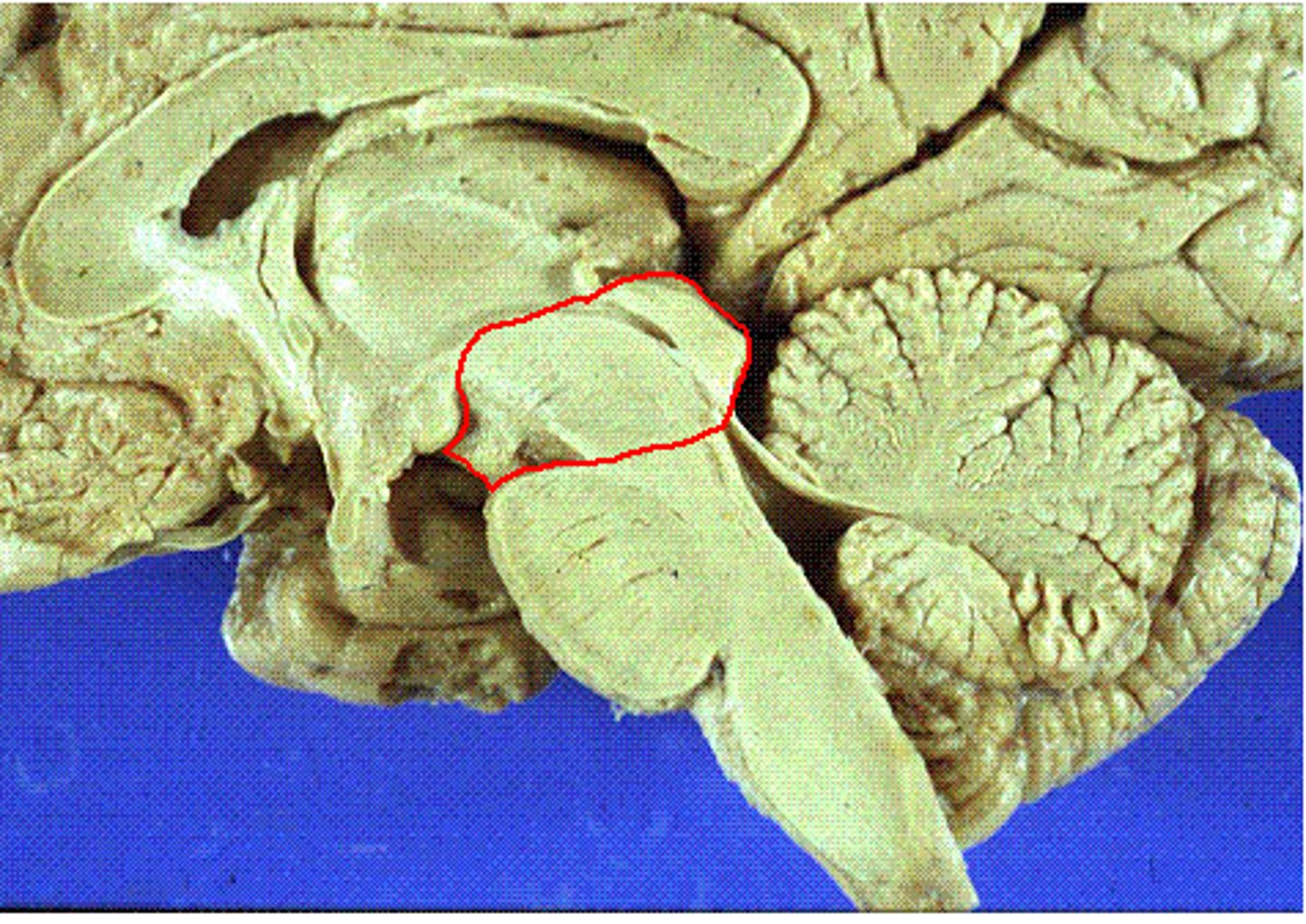
Diencephalon (2 parts)
1. thalamus
> relay and processing centres for sensory info
2. hypothalamus
> centres controlling emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production
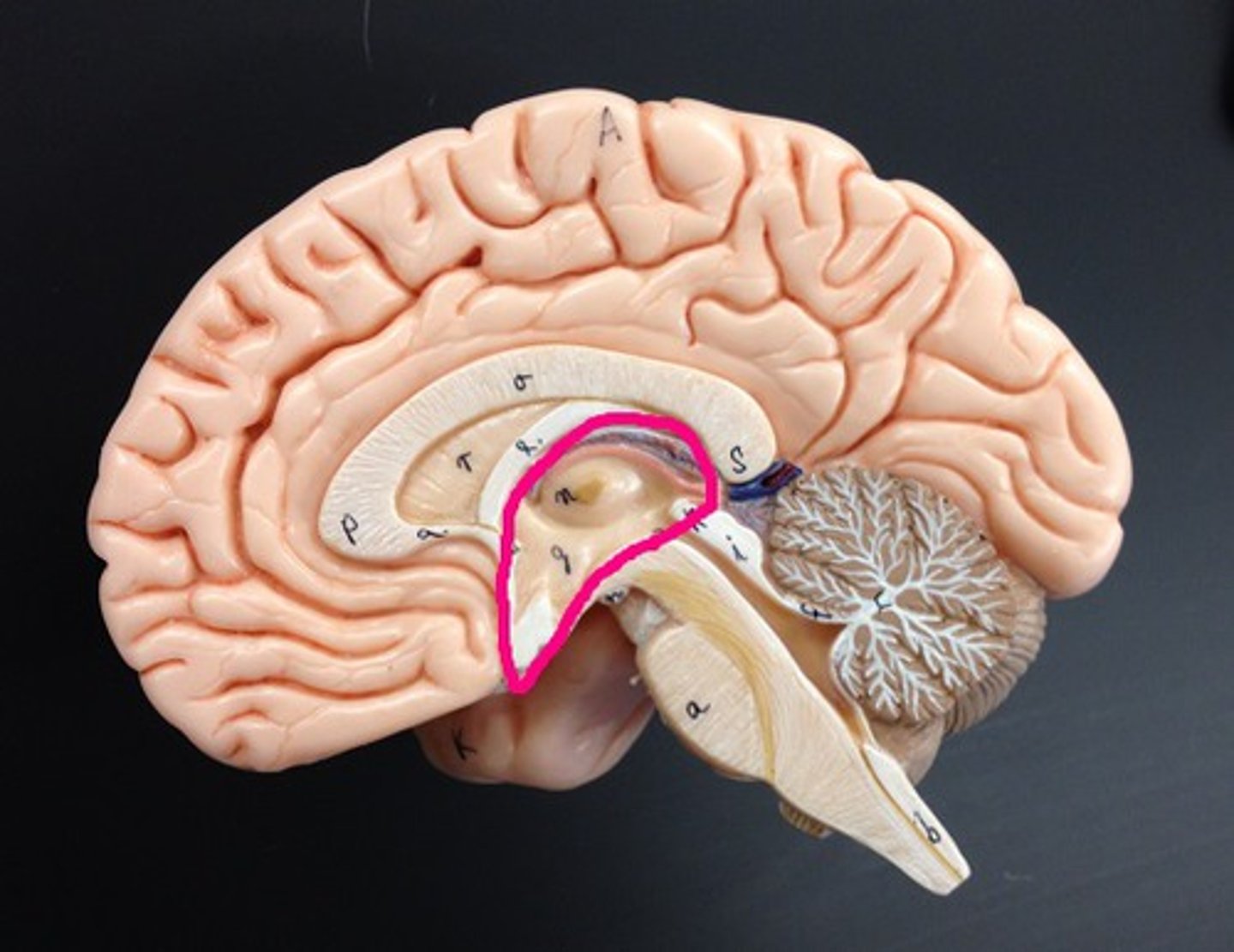
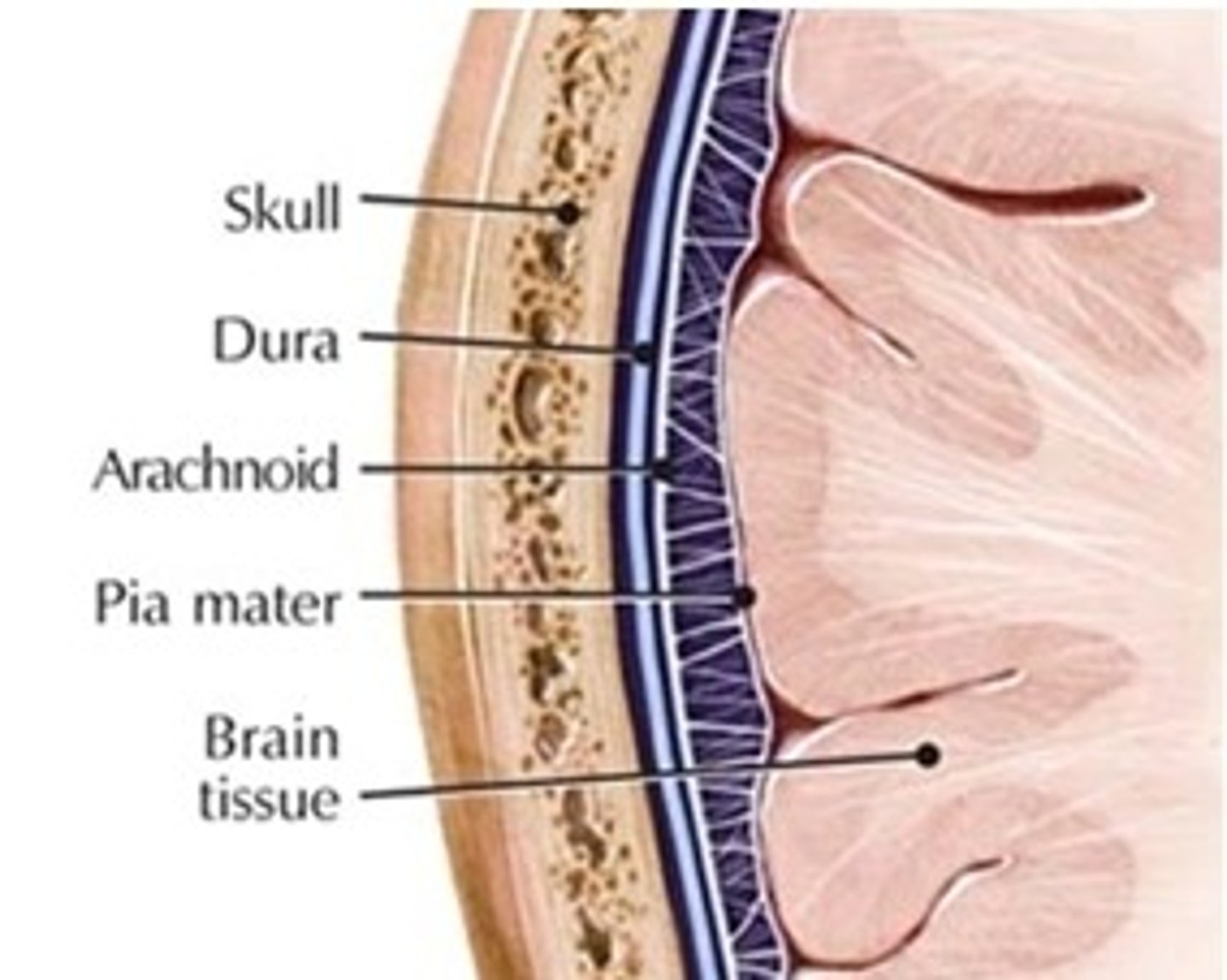
Meninges
> 3 layers of brain that protects CNS
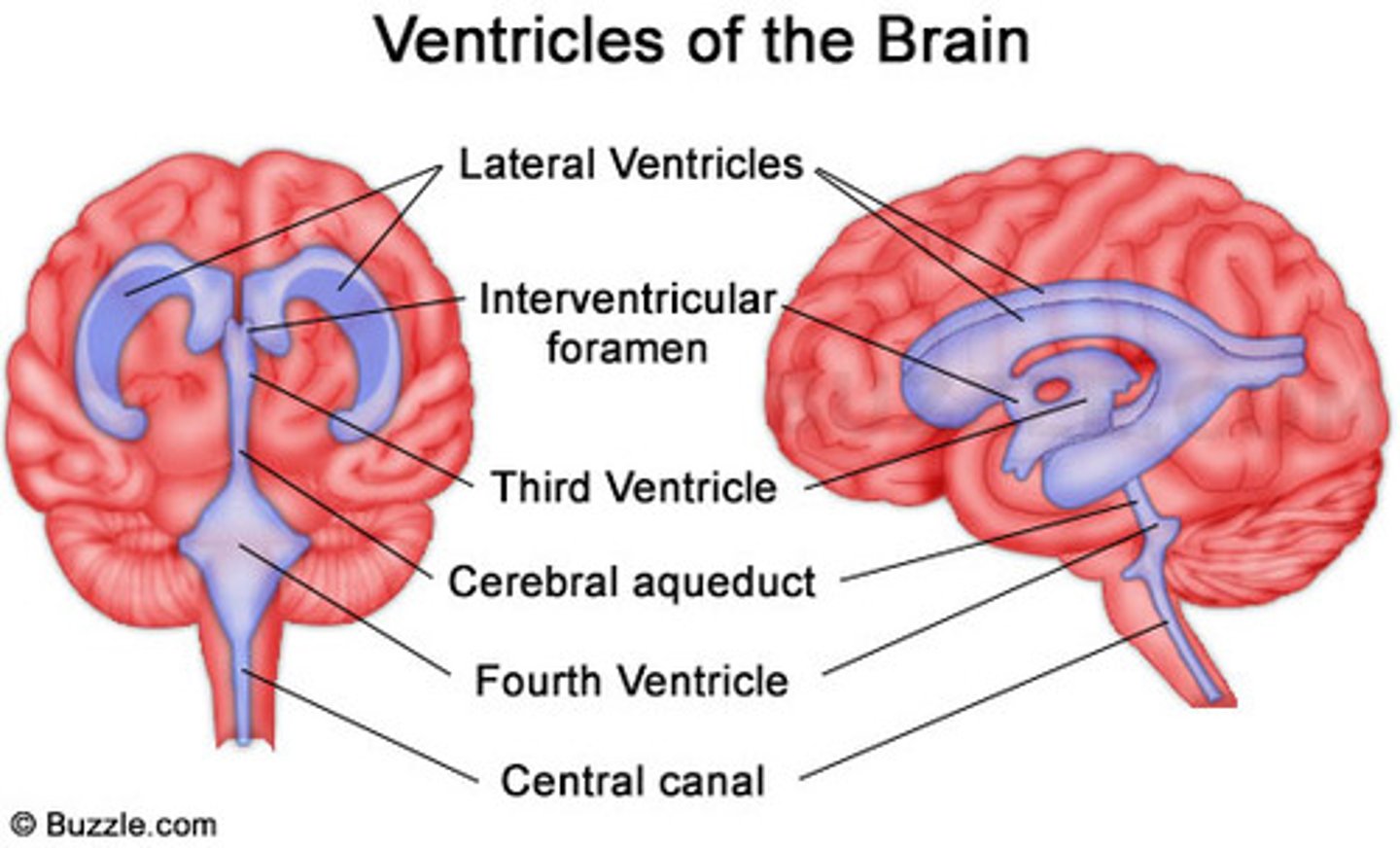
Ventricles of brain
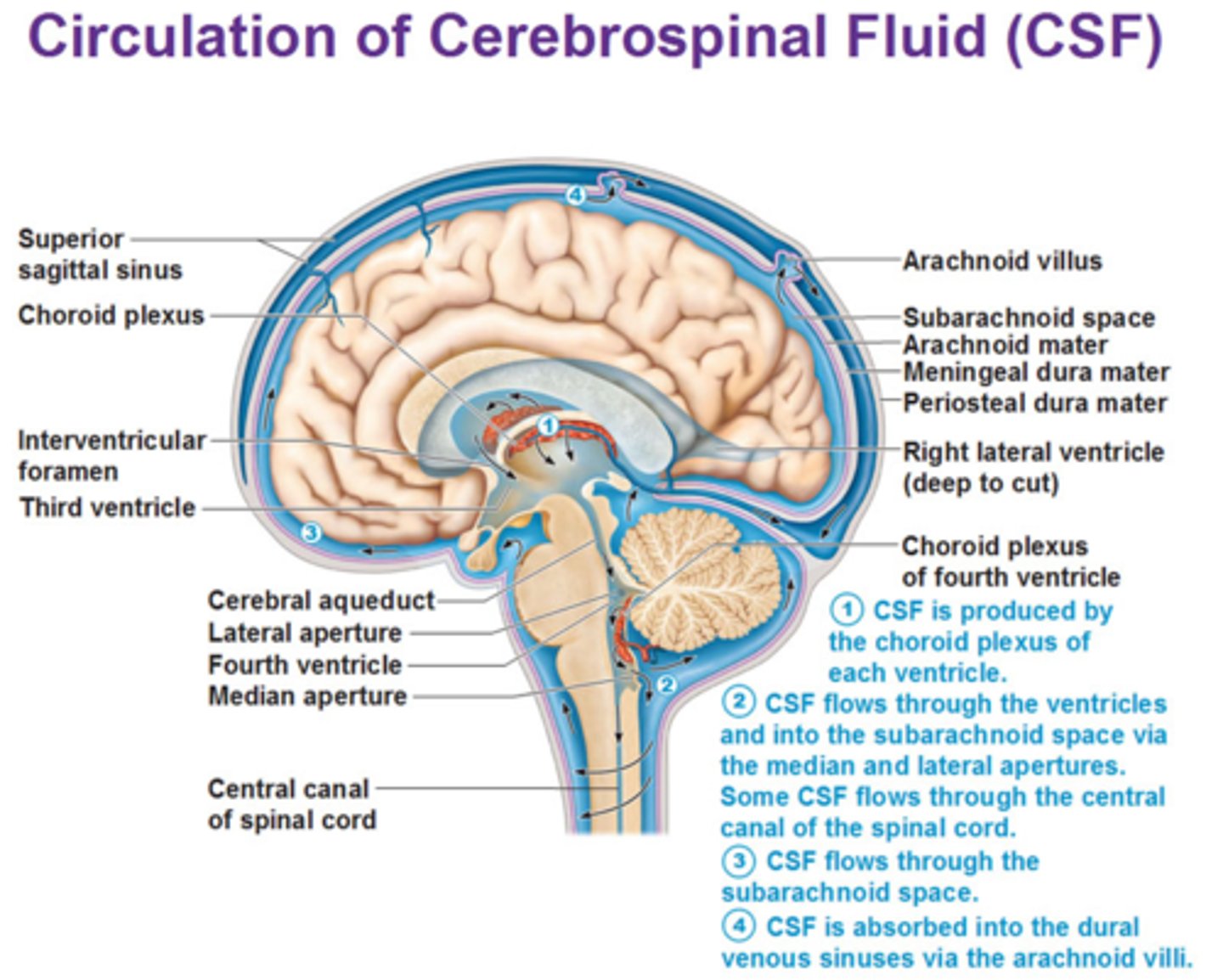
Circulation of CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
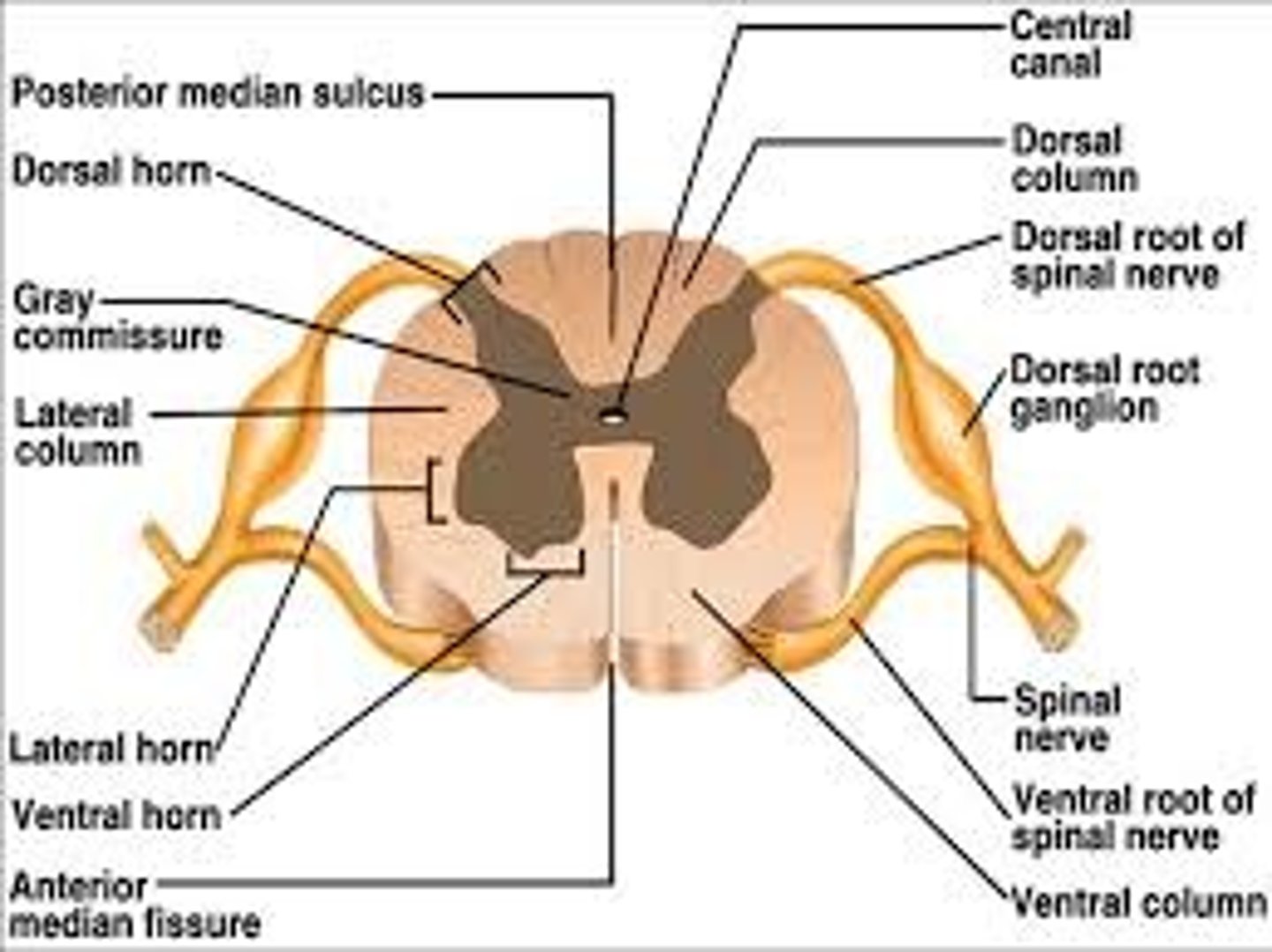
Spinal cord (basic)
> suspended in vertebral canal surrounded by meninges and CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
> continuous with medulla oblongata and extends to border of 1st lumbar vertebra
> nervous tissue link between brain and rest of body
Spinal cord (detailed)
> composed of grey matter in centre surrounded by white matter
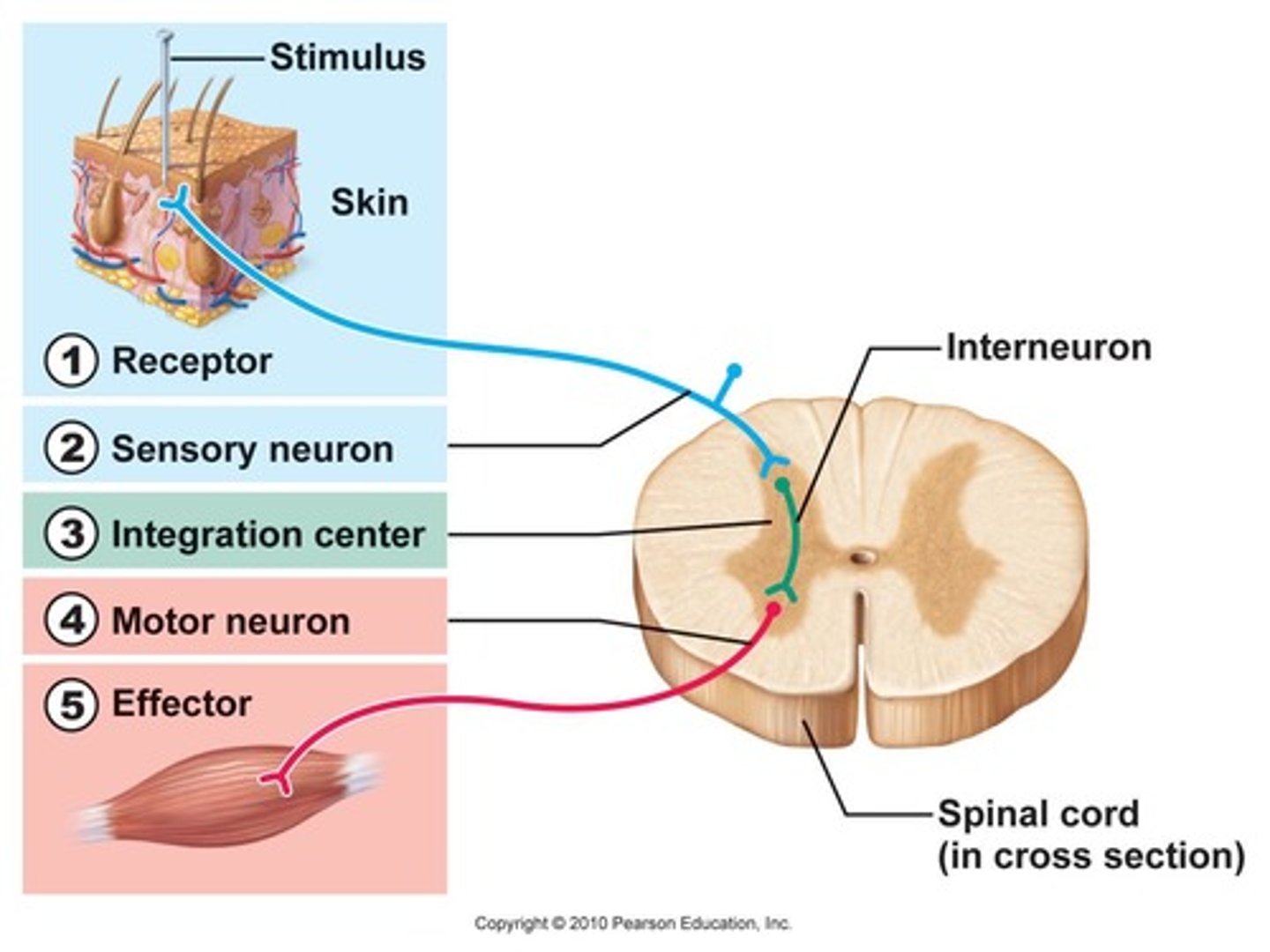
> receptors in skin send info to spinal cord through spinal nerves. Cell bodies for these neurons in dorsal horn
Reflex arc
What are the 2 parts to the PNS?
1. sensory-somatic NS
> 31 pairs of spinal nerves
> 12 pairs of cranial nerves
2. autonomic NS
> sympathetic
> parasympathetic
PNS
> most nerves composed of sensory fibres that convey afferent impulses from sensory organs to brain
> motor nerve fibres convey efferent impulses from brain to effector organs e.g. skeletal muscles, smooth muscles and glands
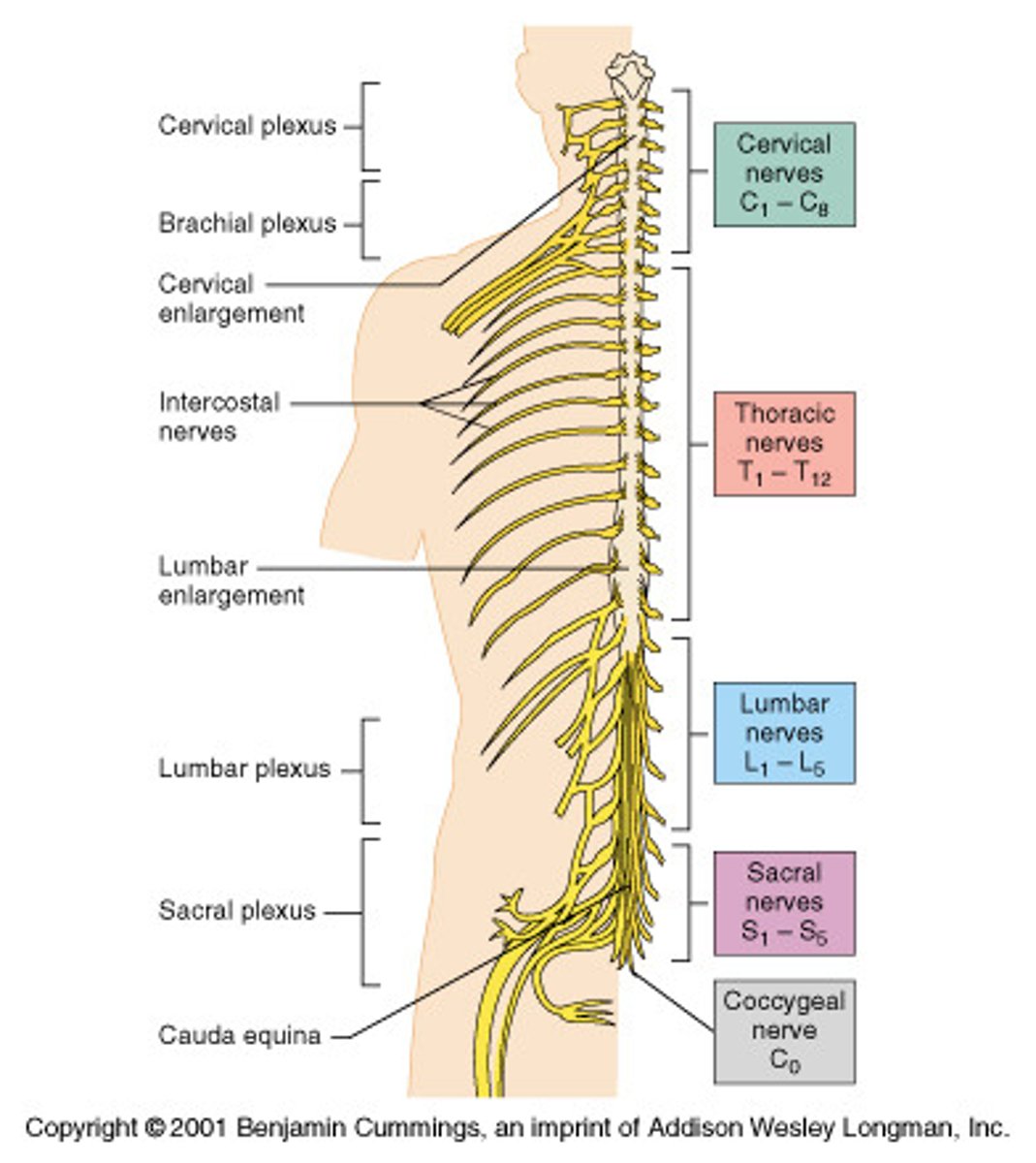
Spinal nerves
> 8 cervical
> 12 thoracic
> 5 lumbar
> 5 sacral
> 1 coccygeal
How do the spinal nerves work?
> leave vertebral canal by passing through invertebral foramen, small openings in each vertebra
> each nerve is a mixed nerve
> after emerging from foramen, divide into branches or rami
> form large masses of nerves or plexuses where they group together
> 5 plexuses formed on each side of vertebral column
5 plexuses that form on each side of vertebral column
> cervical plexuses
> brachial plexuses
> lumbar plexuses
> sacral plexuses
> coccygeal plexuses
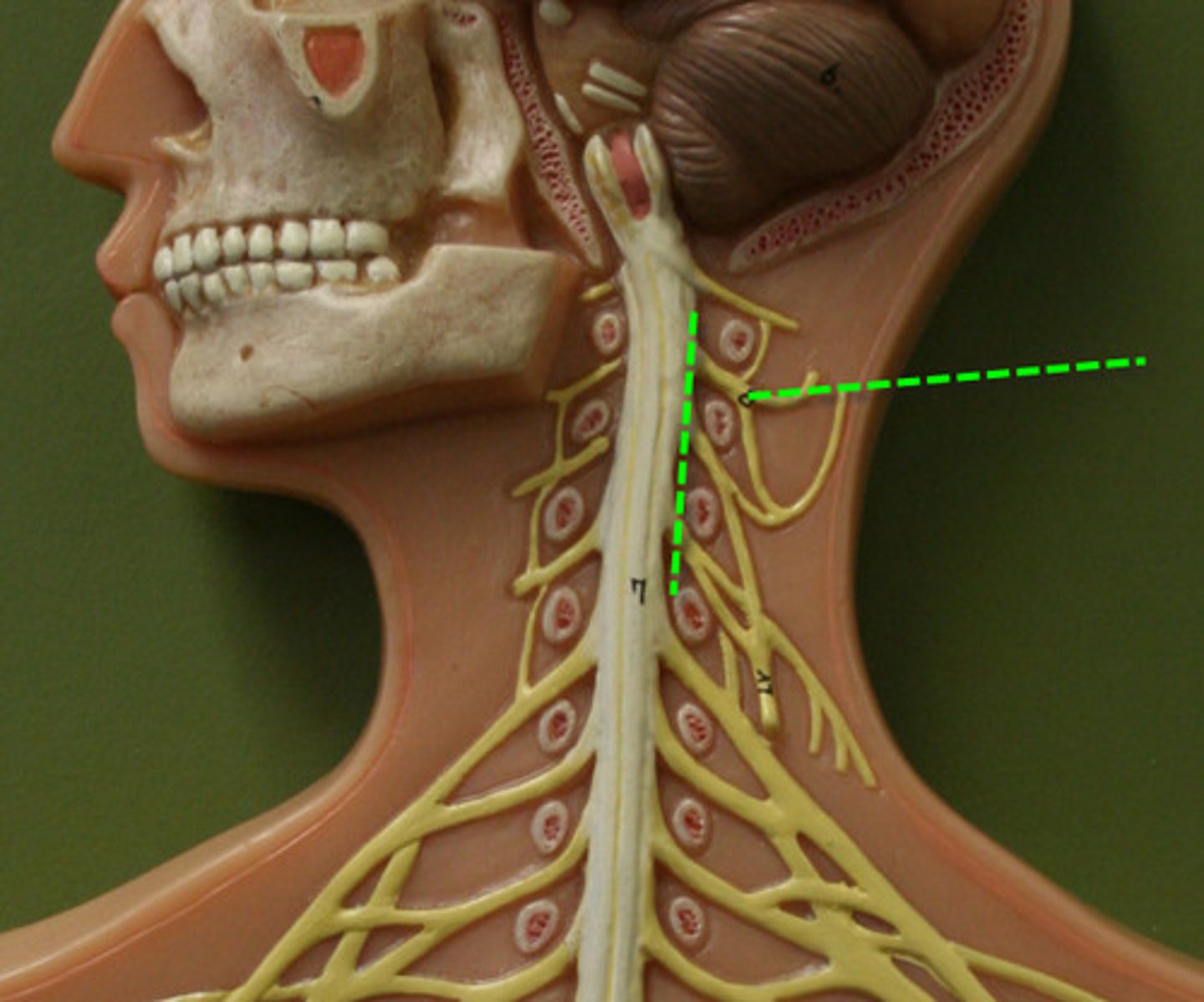
Cervical plexus
> supply structures at back and side of head and skin of front of neck to level of sternum
> supply muscles of neck e.g. trapezius
> phrenic nerve passes through thoracic cavity to supply diaphragm
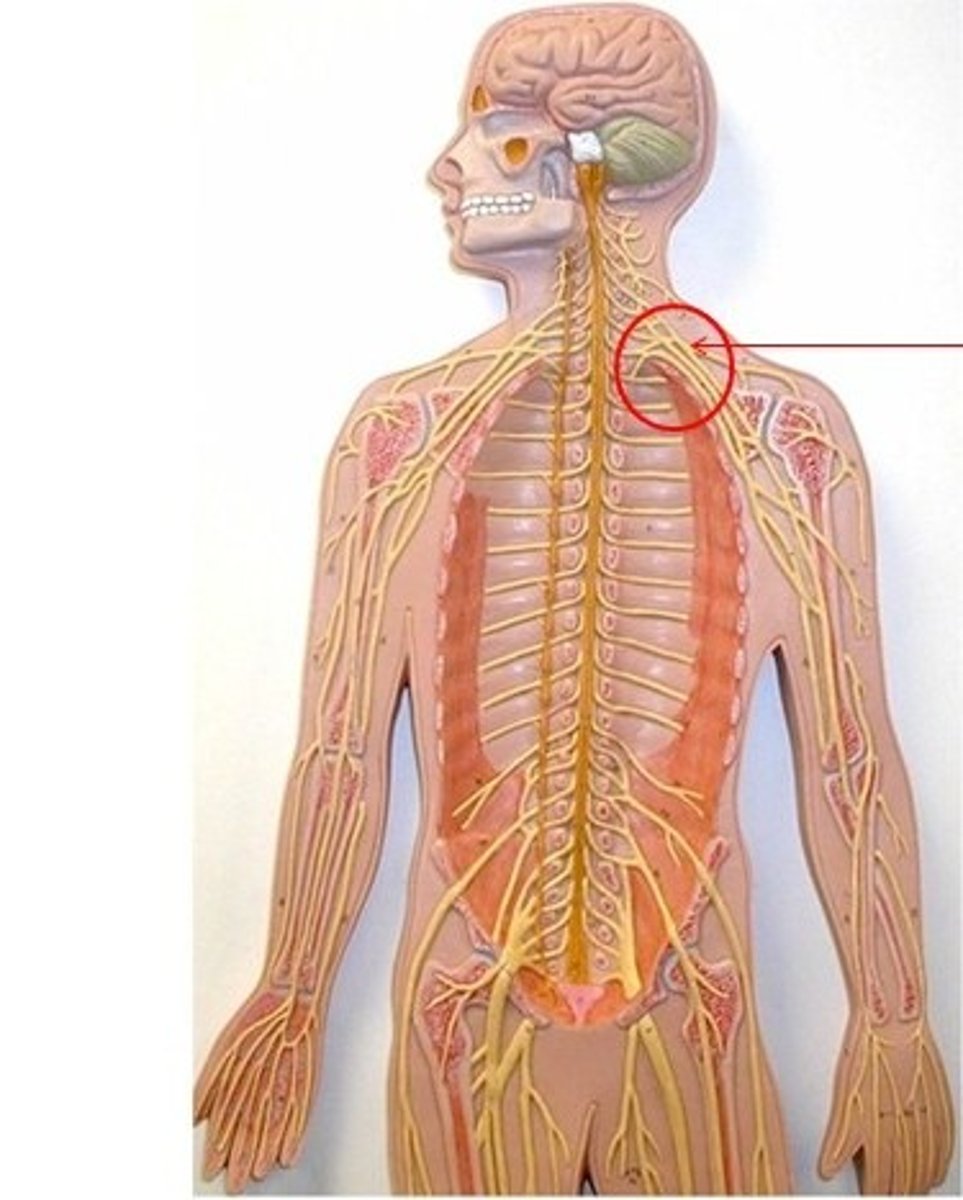
Brachial plexus
supply skin and muscles of upper limbs and some chest muscle e.g. radial nerve, ulnar nerve
Lumbar plexus
> supply muscles and skin in lower abdomen, all aspects of thighs and inguinal regions
> e.g. femoral nerve
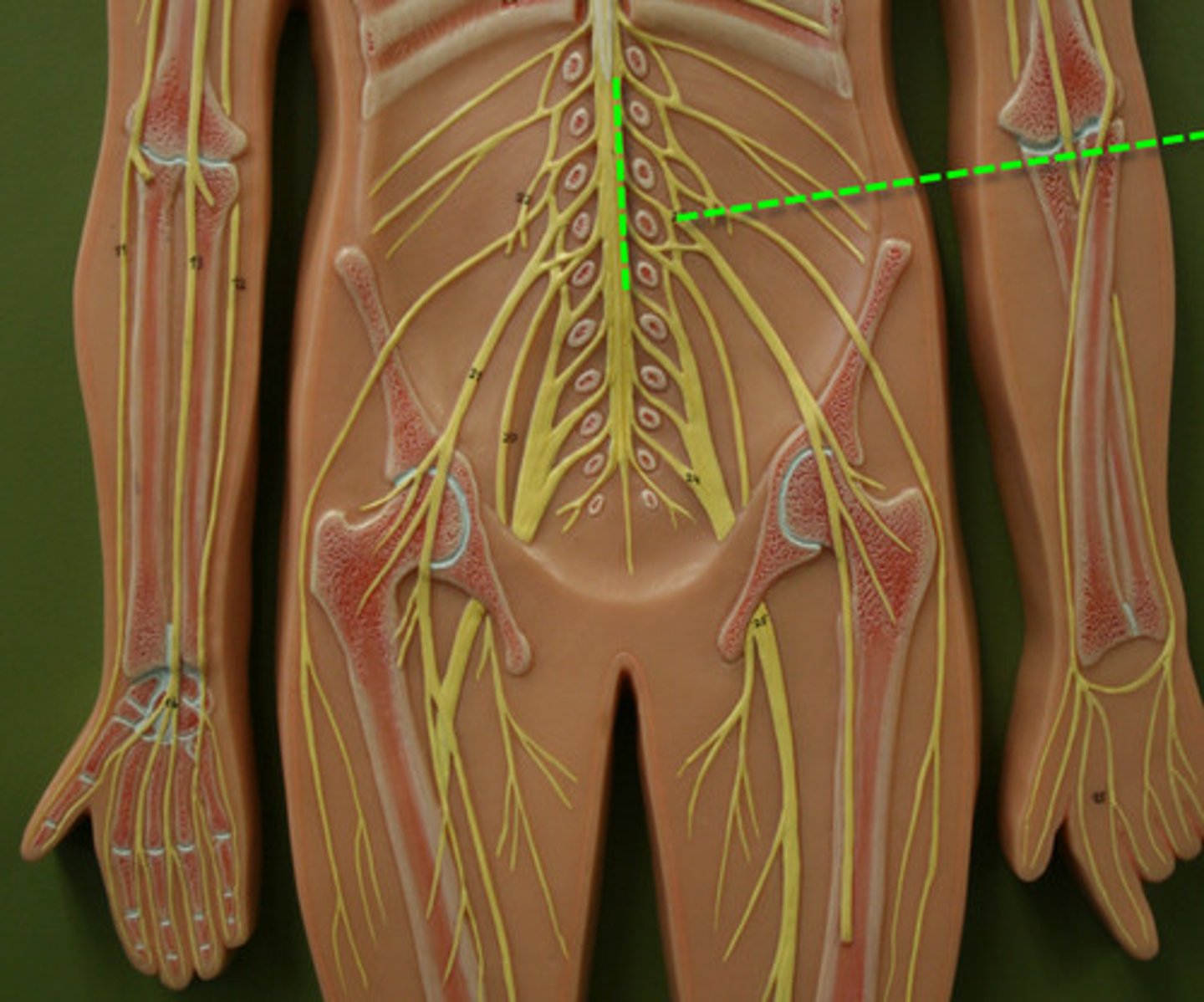
Sacral plexus
> supply muscles and skin of pelvic floor, muscles around hip joint and pelvic organs
> e.g. sciatic nerve
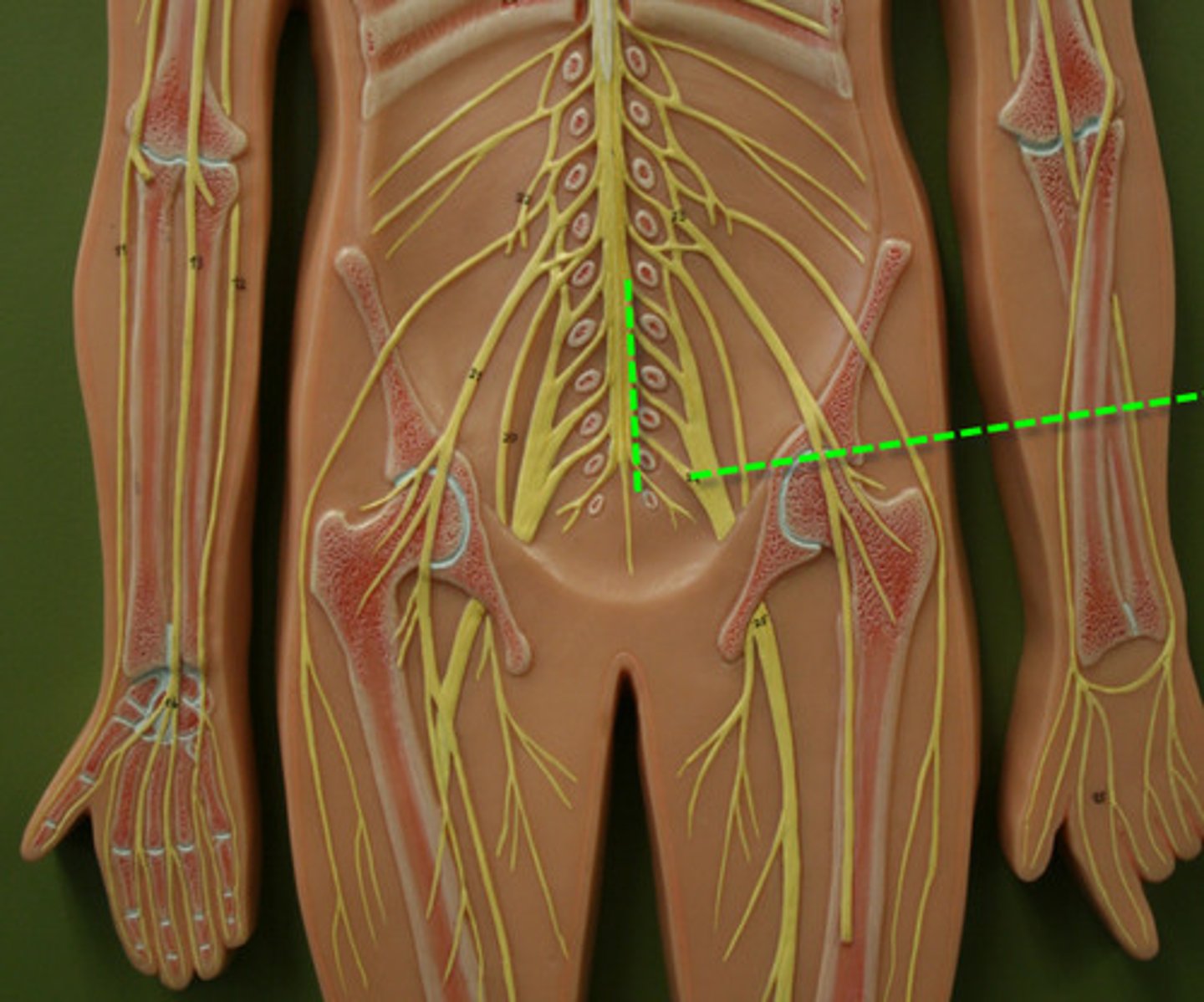
Coccygeal plexus
> very small
> supply skin around coccyx and anal area
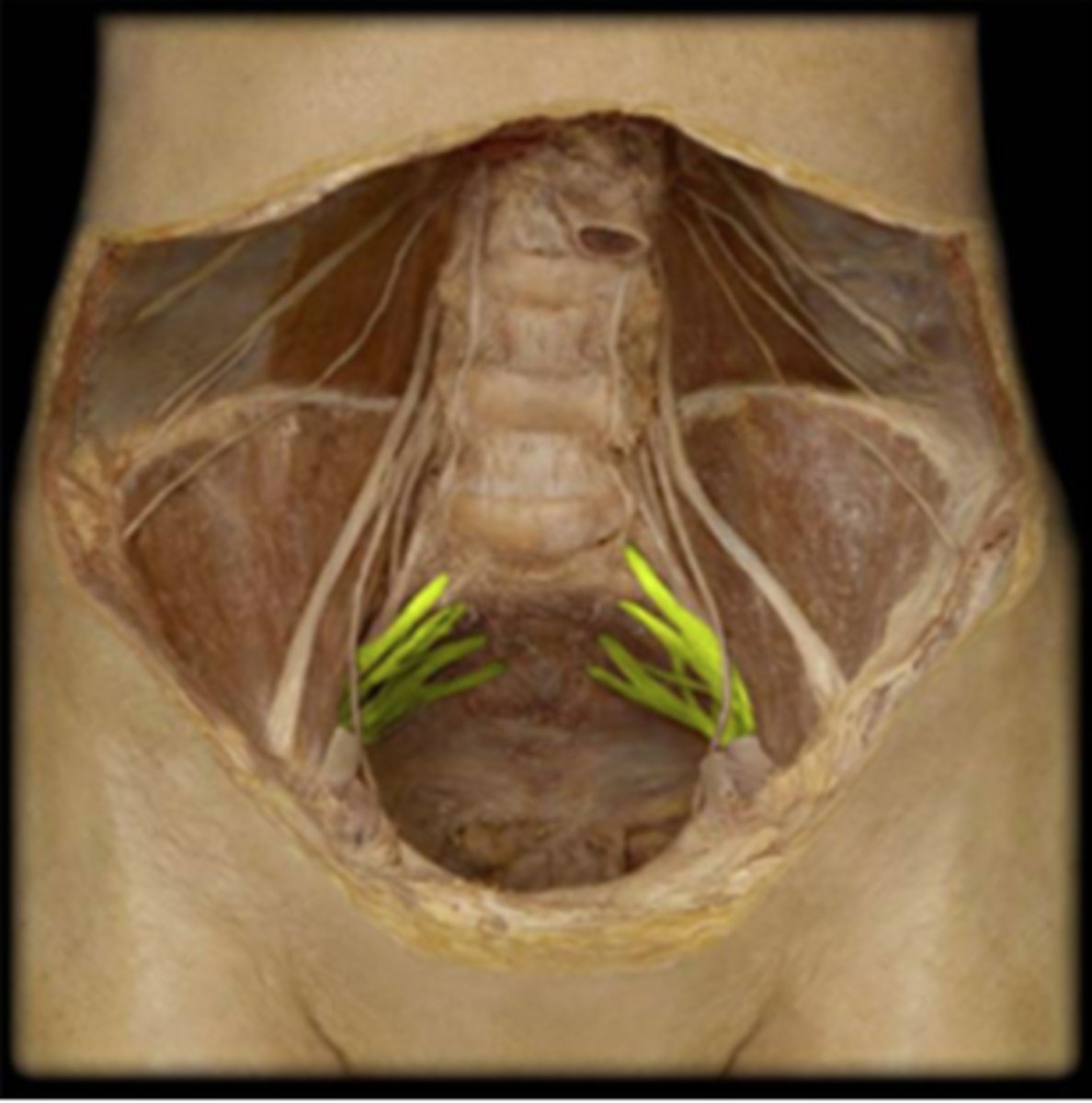
Plexus anatomy
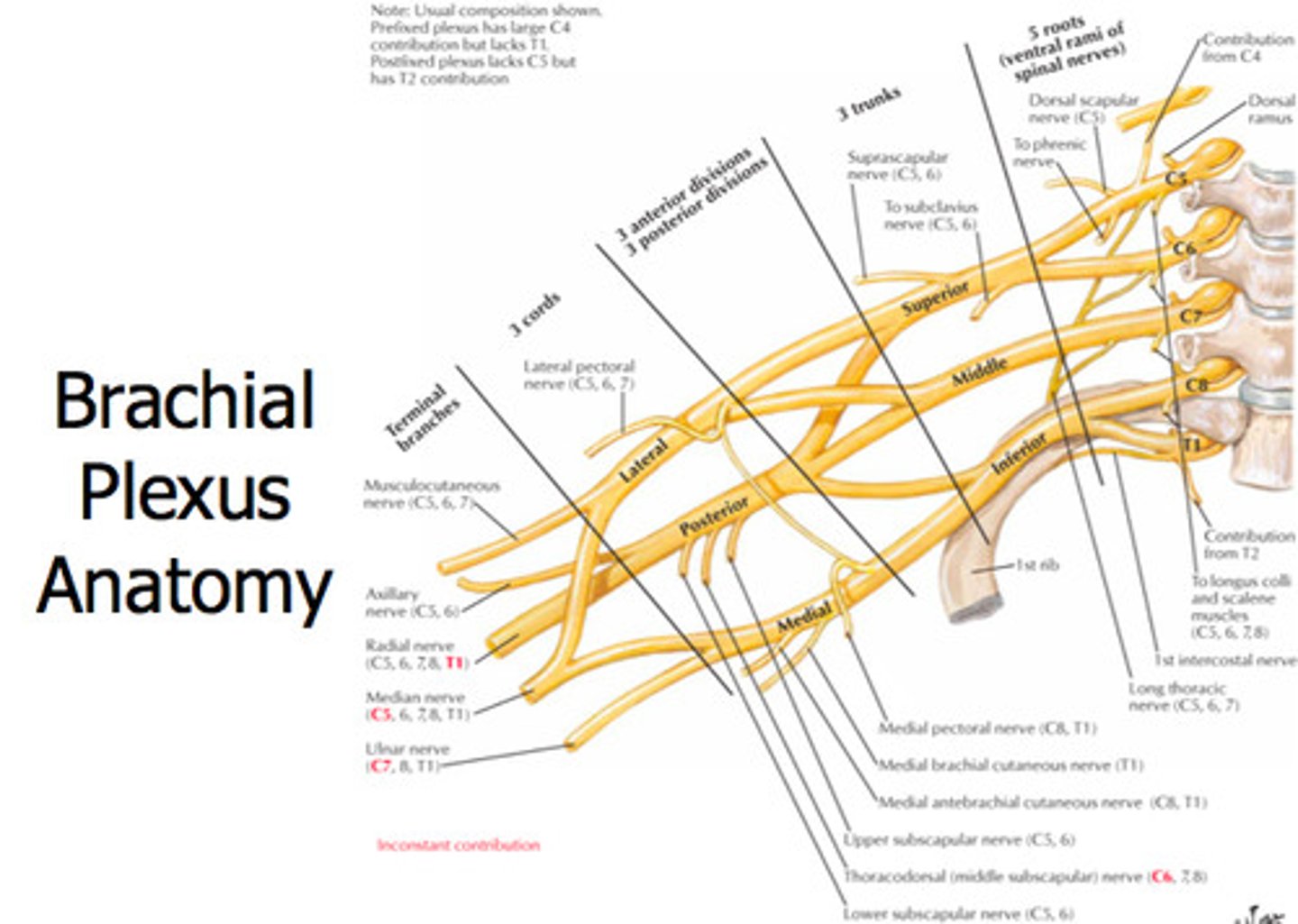
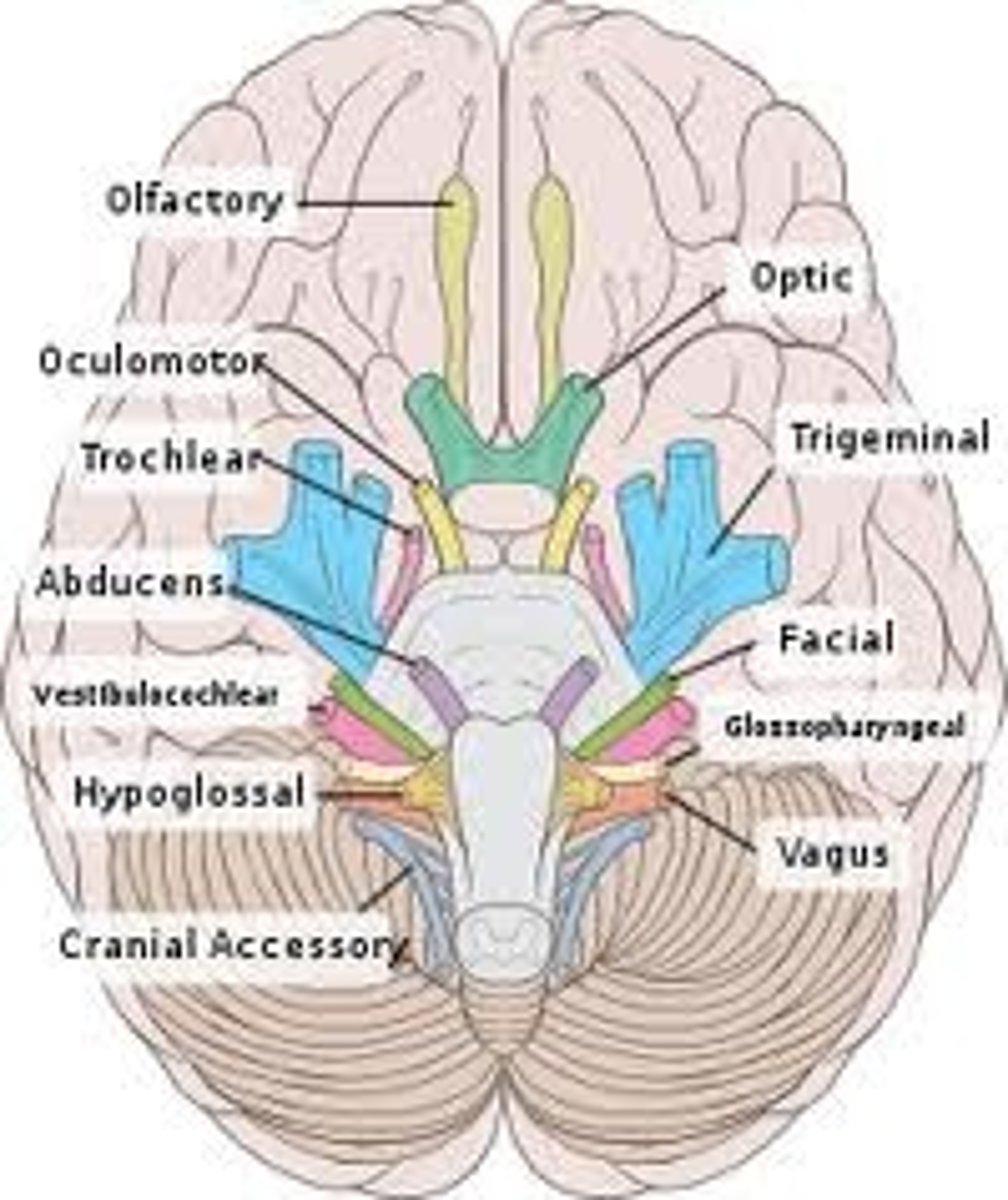
12 cranial nerves
1. olfacotry: sensory
2. optic: sensory
3. oculomotor: motor
4. trochlear: motor
5. trigeminal: mixed
6. abducens: motor
7. facial: mixed
8. vestibulocochlear (auditory) sensory
9. glossopharyngeal: mixed
10. vagus: mixed
11. accessory: motor
12. hypoglossal: motor
ANS
> controls automatic functions of body
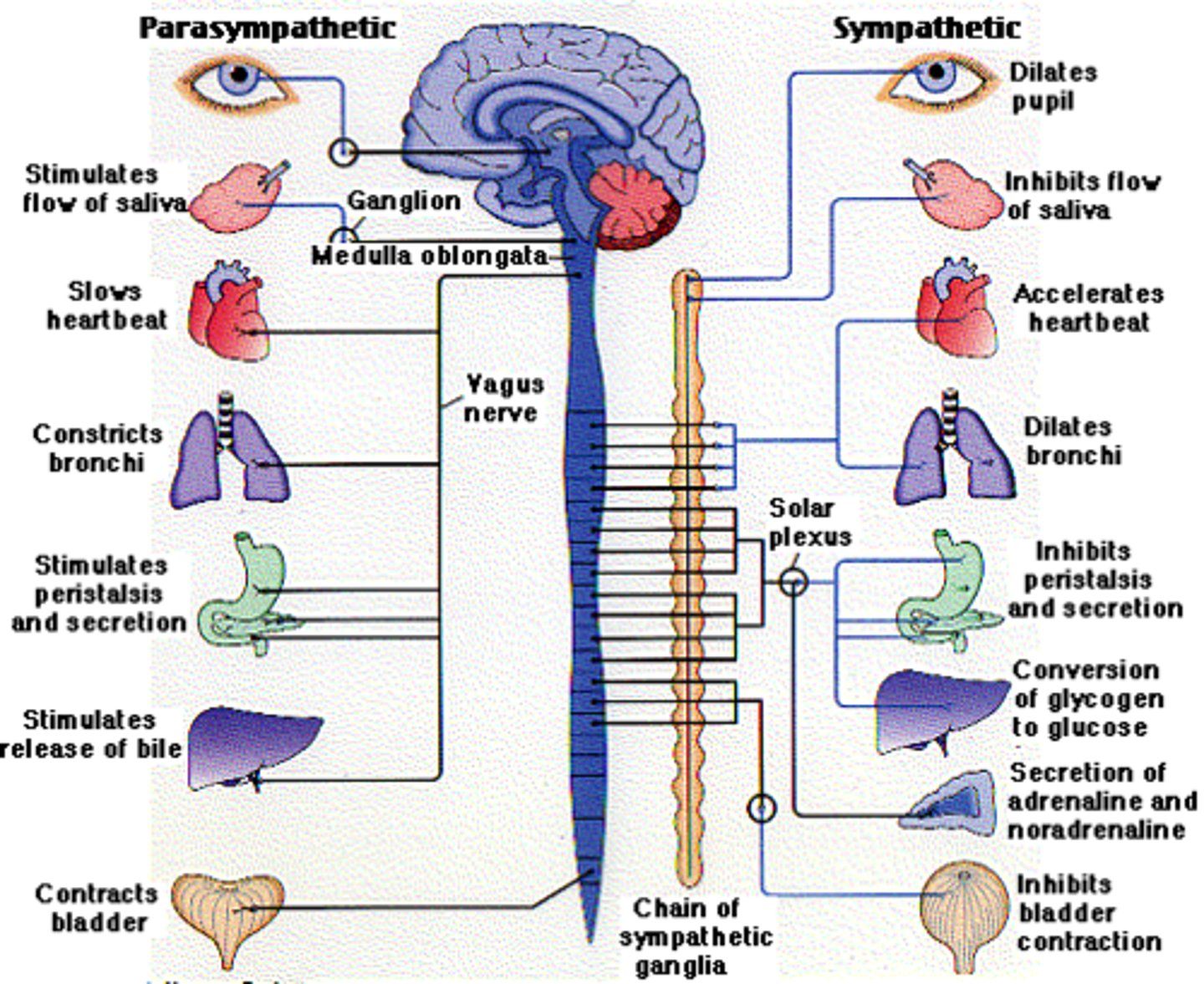
Components of the ANS
> smooth muscle
> cardiac muscle
> glands
> sympathetic NS
> parasympathetic NS
> these normally work in opposing manner, enabling or restoring balance of involuntary functions
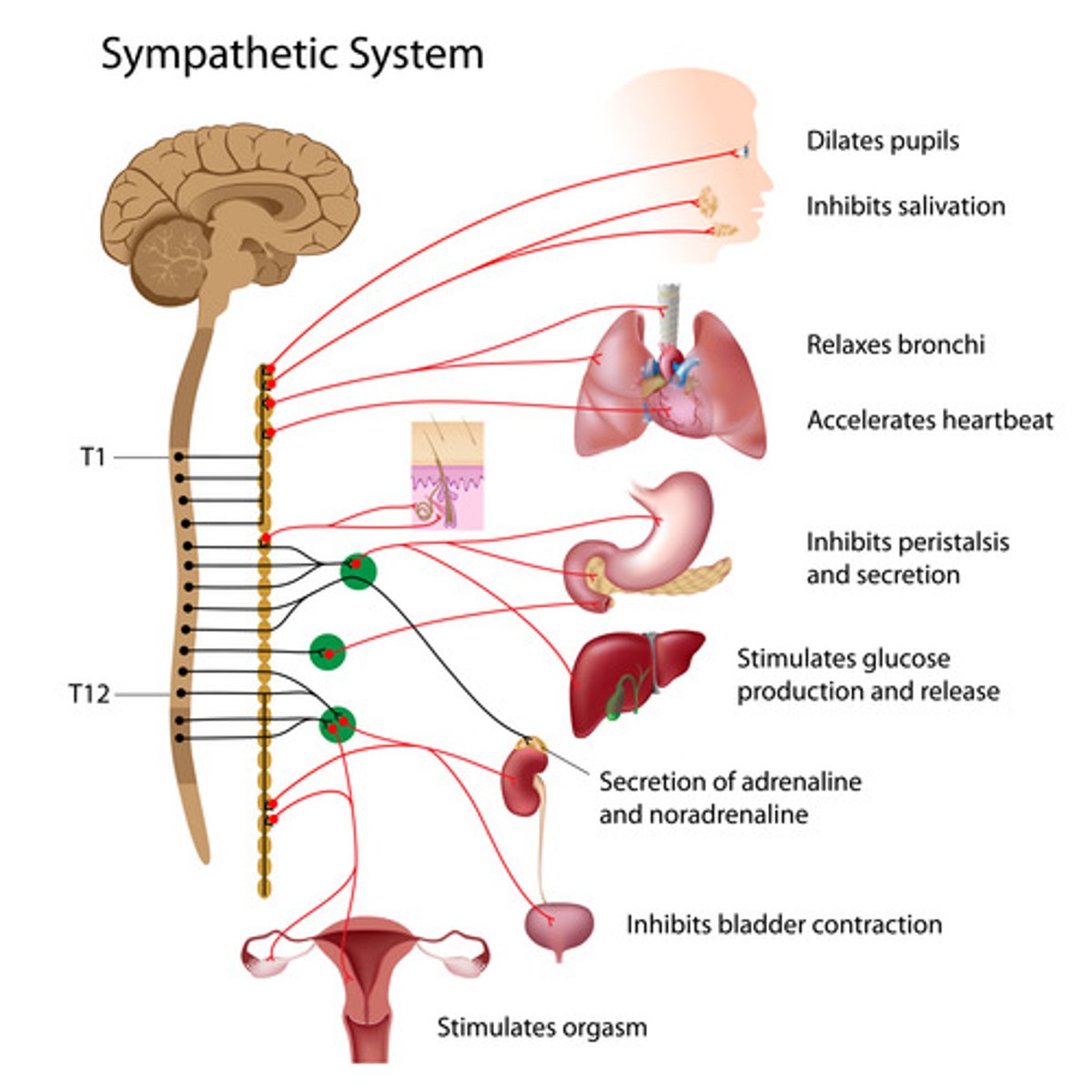
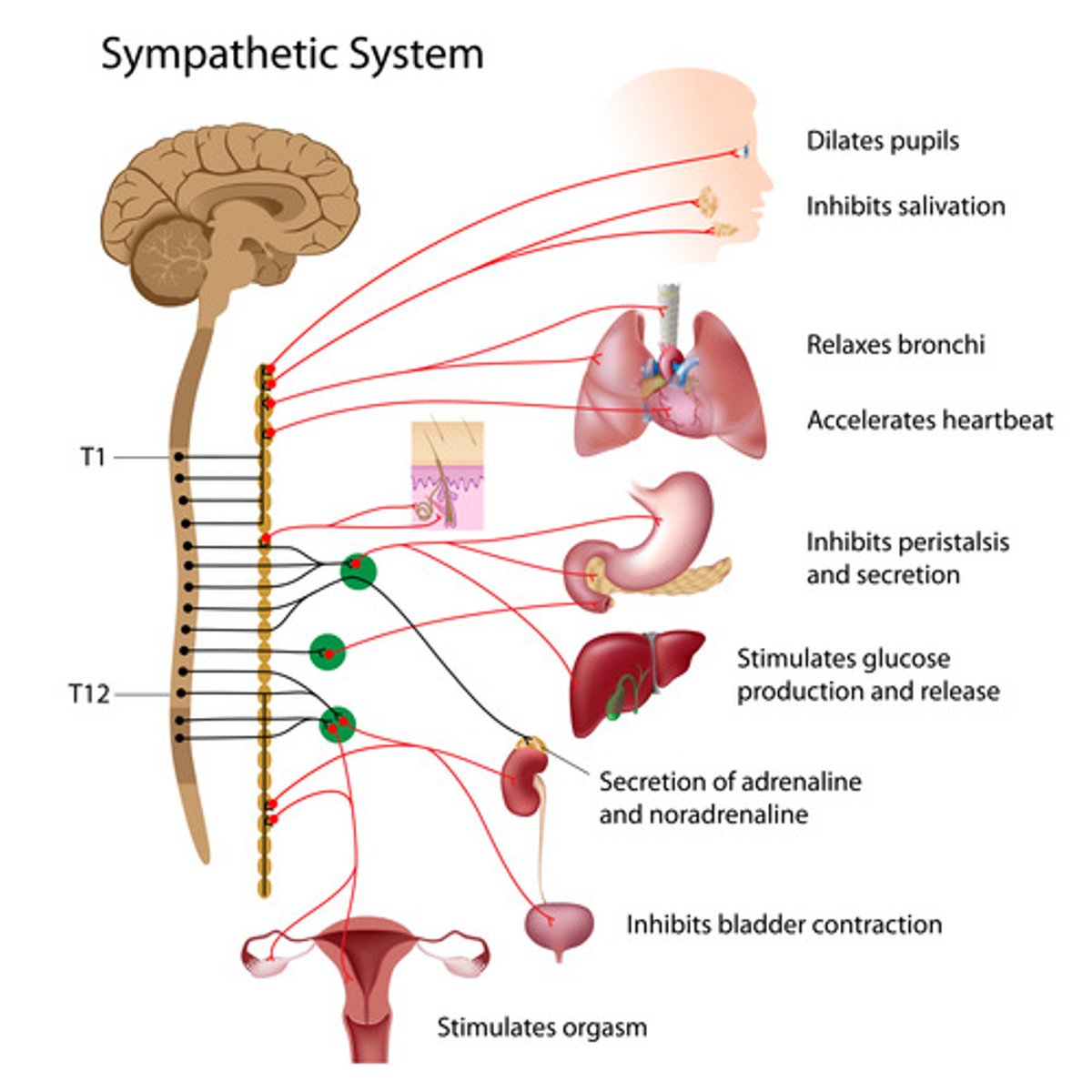
Sympathetic NS
> excitement or stress
> range of emotions
> adrenal glands secrete hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline
> BP increases
> tachycardia
> digestion slows
> originates in preganglionic neuron in grey matter of spinal cord
> neurotransmitter here is acetylcholine
> synapses with post ganglionic neuron which terminates in organ or tissue supplied
> neurotransmitter here is noradrenaline
> exception is sweat glands where post ganglionic neuron uses acetylcholine
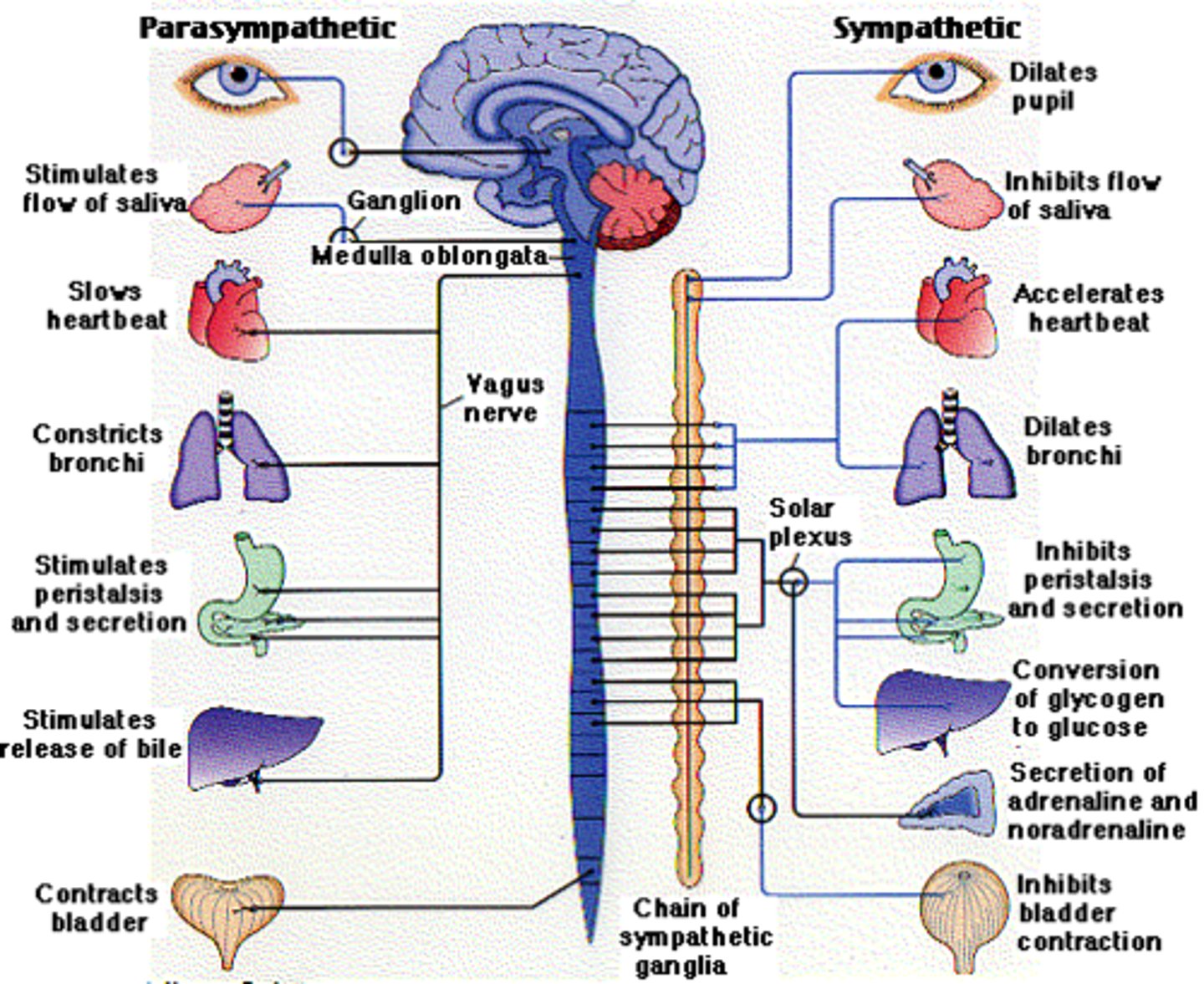
Sympathetic NS
> slows down body processes except digestion and absorption of food and GU function
> allows restoration to occur quietly and peacefully
> BP decreases
> heart beats slower
> digestion can start
> preganglionic neurons located in spinal cord and medulla - cranial nerves III (oculomotor), VII (facial), IX (glossopharyngeal), and X (vagus)
> synapse, using acetylcholine, with postganglionic neurons which project to target organs using acetylcholine again as neurotransmitter