envirochem test prep - organic geochemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Contaminants
________ that are found in coal are primarily sulphur due to sulphur being present in salt water swamps due to bacteria in the swamp that converted sulphate in saltwater to pyrite (FeS2) which became a part of the coal.
2
New cards
HM
________ is a class of substances that are produced and reside in soil and water.
3
New cards
Biomarkers
________ are organic molecules that are derived from living matter but are resistant to degradation.
4
New cards
Sterane
They are fully saturated (carbons bonded to 4 other things and all bonds are taken) (terpenes contain double bonds, terpanes contain single bonds) ________ is a terpane that is derived from steroids or sterols via diagenesis and catagenesis breakdown Hopane (C30H48) is a triterpene that originates from bacteria There are over 150 naturally occurring hopanoids.
5
New cards
Degradation
________ pathway- The degradative pathway hypotheses that the formation of HM occurs from modification of plant biopolymers through ________.
6
New cards
Coal
________ was formed over 300 million years ago due to dead plant matter that fell into swampy water.
7
New cards
Monomethyl tin
________ (CH3 Sn3+) is more toxic to aquatic biota than inorganic tin because it can cross cell membranes.
8
New cards
Petroleum
________ comes from OM that is deposited on seabed which are buried by sediments which are then broken down and transformed over millions of years.
9
New cards
Components of petroleum
________ are separated through fractional distillation and it is the boiling point of each fraction that allows this separation to occur.
10
New cards
Humic material
________ (HM) is made up of decayed organic material of plant or microbial origin.
11
New cards
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
In order to analyse biomarkers, ________ is used to separate compounds through two phases: Stationary phase (column) a stationary phase which is coated with material that interacts whatever compound we are looking for and it slows it down, giving a chance to separate out into fractions Mobile gas phase (He gas- inert and does not react with the compounds) and that carries that through the system and is heated.
12
New cards
Biomarkers
________ are formed by organic material that dies and undergoes anaerobic diagenesis, which turns organic matter into kerogen (we do this by losing oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur)
13
New cards
Biomarkers
________ are used for characterising oil by looking at the molecules present.
14
New cards
As we move along the pathway of humin → humic acid → fulvic acid we have decreasing
molecular weight (breaking down molecules), carbon and nitrogen content, degree of polymerisation (related to weight, breaking down), intensity of colour
15
New cards
Cap rock
Impermeable rock to prevent fluids and gas escaping upward
16
New cards
what is natural organic matter
Natural sources of organic matter are those derived mainly from plant or microbial residues. Examples include things such as the degradation of plant and animal matter as well as microorganisms and fungi found in soil.
17
New cards
what is anthropogenic organic matter
organic matter that has come from human activity and can include point and non-point sources. An example of a point source would be discharge pipes, while a non point source would be sediment runoff from farmland.
18
New cards
define total carbon
The sum of all carbon-containing compounds in a sample, including both organic and inorganic carbon.
19
New cards
What subcategories can total carbon (TC) be divided into
Subcategories of Total Carbon (TC): Organic Carbon (OC) and Inorganic Carbon (IC). OC comes from living organisms, while IC comes from non-living sources like rocks and minerals. this can further be broken down into particulates, dissolved, particulate organic carbon, and dissolved organic carbon
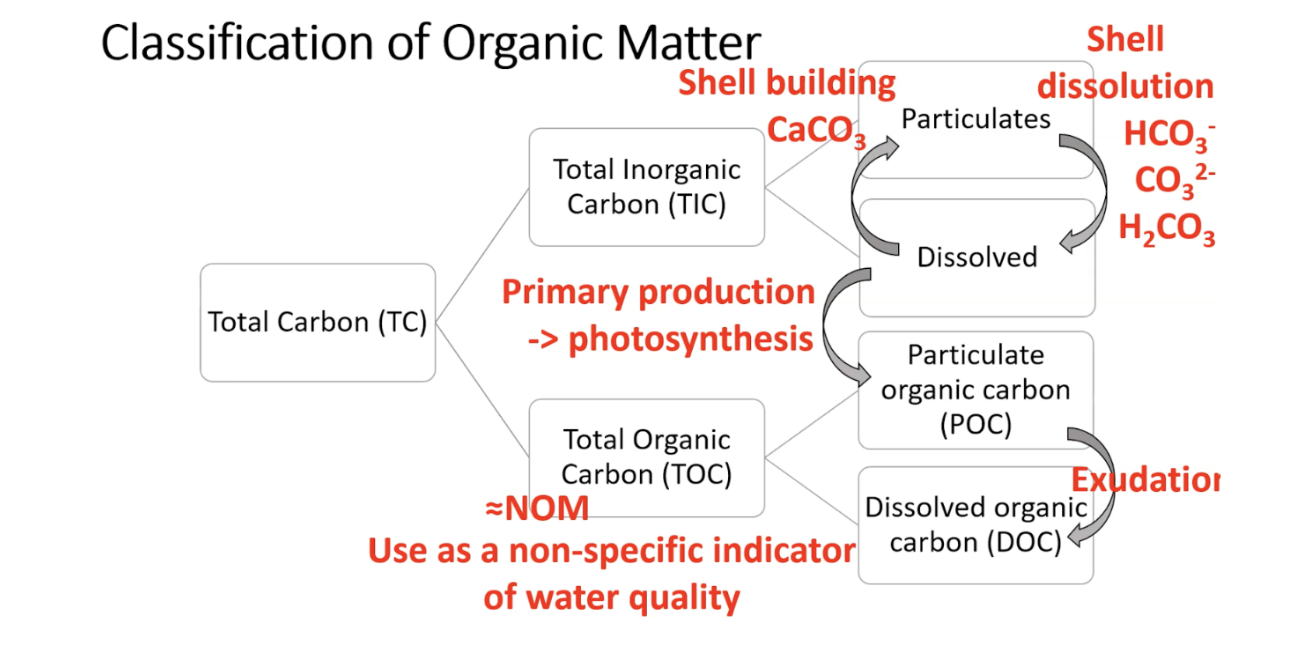
20
New cards
3 main environmental issues related to aqueous organic matter:
1. Toxicity of specific organic compounds - e.g pesticides and their breakdown products
2. Reaction with other aquatic species - Alkylation of metals by microbes e.g. Uses of organotin include in pesticides, preservatives of wood and antifouling paints. • Monomethyl tin (CH3 Sn3+) is more toxic to aquatic biota than inorganic tin because it can cross cell membranes.
3. Consumption of Oxygen - Non-living OM can be oxidised by oxygen and other oxidising agents in water Oxygen deprived water; anaerobic state - not enough o2 for living organisms to breathe.
Non living OM can also change the chemistry of the water as organic matter + o2 in water creates carbon dioxide which then reacts with water to form carbonic acid, and then dissociate further into carbonate and H+, making the water more acidic, harming aquatic life
21
New cards
what is humic material
HM is a class of substances that are produced and reside in soil and water.
22
New cards
what is humic material made up of
decayed organic material of plant or microbial origin.
23
New cards
subcategories of humic material
Humin (Hu) •Humic acid (HA) •Fulvic acid (FA)
24
New cards
two main theories hypothesise the formation of Humic Material by two main pathways:
1. Degradation pathway - The degradative pathway hypotheses that the formation of HM occurs from the modification of plant biopolymers through degradation. This theory proposes that labile macromolecules (e.g. carbohydrates and proteins) are degraded and lost. While biopolymers (e.g. lignin, macromolecules) are modified to produce the high molecular mass humin, then oxidised to produce the smaller components. Plant biopolymers → humin → humic acid → fulvic acid → small molecule
2. Synthetic pathway - The synthetic pathway hypotheses that plant biopolymers are first broken into small molecules then re-polymerised to form humic material. Individual molecules cannot be identified in humic material, So it is subdivided into 3 categories for operational purposes: •Humin (Hu) •Humic acid (HA) •Fulvic acid (FA) Plant biopolymers → small molecule → fulvic acid → humic acid → humin
25
New cards
humic material structure contains many ____
functional groups
26
New cards
What are the general chemical changes that take place as you move from HM to Fulvic acid?
Decreasing : molecular weight (breaking down molecules), carbon and nitrogen content, degree of polymerisation (related to weight, breaking down), intensity of colour. However, we also have increasing: oxygen, and degree of solubility (because molecules smaller, easier to dissolve)
27
New cards
The interactions of Humic Material are dependent on the ____
environment
28
New cards
Explain how coal was formed
Coal was formed over 300 million years ago due to dead plant matter that fell into swampy water. Anaerobic conditions caused the plant matter to not decompose and over time it was buried and built up. Overall, pressure, heat, and time converted the organic matter into coal. This process is called coalification.
29
New cards
what contaminants are found in coal
primarily sulphur due to sulphur being present in salt water swamps due to bacteria in the swamp that converted sulphate in saltwater to pyrite (FeS2 ) which became a part of the coal. There is also some mercury in coal present due to its affinity for sulphur.
30
New cards
how is low sulphur coal made
Low sulphur coal was formed in freshwater swamps
31
New cards
where does petroleum come from
Petroleum comes from OM that is deposited on seabed which is buried by sediments which are then broken down and transformed over millions of years. There are special conditions that are required to form petroleum. All seven conditions need to exist in one place, hence why petroleum is only found in certain areas of the world
32
New cards
what are the 7 conditions required to form petroleum
1. Source rock with a High organic content (marine organisms) - would come from marine organisms because most petroleum reserves found from old oceans
2. Rapid burial to create a reducing environment - anoxic conditions (no O2) as we don’t want organisms to degrade
3. Overburden pressure – created by burial to depths of \~7-15 km -> helps in maturation process
4. Structure (e.g Anticline trap) - fold structure with an arch of non-porous rock overlying reservoir rock to trap oil and gas
5. Cap rock – Impermeable rock to prevent fluids and gas escaping upward
6. Reservoir rock – a porous permeable rock where petroleum and natural gas are found - has to move upwards as it forms and needs rock porous to hold oil and fluids need to be able to move from one rock to another - so important where capping layer occurs
7. Movement easiness from the source rock to the reservoir rock
33
New cards
How are components of petroleum separated and what property allows this separation to occur
Components of petroleum are separated through fractional distillation and it is the boiling point of each fraction that allows this separation to occur
34
New cards
If there is an oil spill at sea what will happen to the different fractions
Light fractions will evaporate and heavy fractions will float/sit on top of the water
35
New cards
what are biomarkers
rganic molecules that are derived from living matter but are resistant to degradation.
36
New cards
how are biomarkers formed
by organic material that dies and undergoes anaerobic diagenesis, which turns organic matter into kerogen (we do this by losing oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur ). With increasing temp and pressure we push kerogen into oil (biomarker) through catagenesis.
37
New cards
what are some important features of biomarkers
need to be resistant to degradation, need to be easily identifiable in low concentrations, need to have various concentrations
38
New cards
what are biomarkers used for
differentiation and correlation of oils to oil spills, allowing for identification of contamination (e.g if there was an oil spill) and allows for the monitoring of its breakdown for its relation to the environment and environmental effects.
39
New cards
What technique is used to analyse biomarkers
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry is used to separate compounds through two phases: Stationary phase (column) a stationary phase which is coated with material that interacts whatever compound we are looking for and it slows it down, giving a chance to separate out into fractions
40
New cards
how are biomarker compounds identified in gcms
The compounds can be identified based on their retention time.