Valvular Regurgitation - Aortic Insufficiency
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Definition: AI
• The backflow of blood through the aortic valve during diastole
AI can be
acute or chronic
• Murmur: AI (3)
When heard
sounds like
how does it sound for severe AI
Which intercostal space
o Diastolic, blowing, decrescendo
o May be holodiastolic in severe aortic regurgitation
o Heard in the third intercostal space
INDIRECT SIGNS OF AI
EPSS
AMVL Diastle fluttering
AI jet hitting AMVL
AMVL Reverse doming
AI Hits MV into LA!
will cause MV in shorts to look weird
when to do valsalva (LVOT)
DO VALSALVA WHEN LVOT IS >1.5 m/s
This will evaluate whether its dynamic or not
why does AI cause diastolic BP to be low
because the blood is just falling out through the aortic valve
severe AI
Quadracusp aortic valve-clover

severe AI
STEEP
GET A DOC!
DONT LET THEM LEAVE
SPIKE IS DURING DIASTOLE
Severe AI murmur AKA
Austin Flint murmur BOARD QUESTION
Etiology (causes) AI (2)
Leaflet Abnormalities (changes in leaflet flexibility and shape)
Aortic Root Abnormalities
Leaflet Abnormalities (changes in leaflet flexibility and shape) (6)
causes (etiology)
o Rheumatic heart disease
o Bicuspid aortic valve
o Calcific valve disease
o Myxomatous valve disease
▪ Sagging or slipping of one or both of the leaflets in diastole
▪ Leaflets are thickened and redundant on two-dimensional echo
o Endocarditis
o Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis
• Aortic Root Abnormalities (4)
causes (etiology)
o Systemic hypertension
▪ Causes dilation of the aortic annulus
o Dissection
▪ Valve leaflets may be normal or flail leaflet
▪ Annular dilation causing leaflet displacement (altered geometry)
o Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm
▪ Dilation of the annulus and sinuses of Valsalva
o Trauma (acute)
o Marfan syndrome
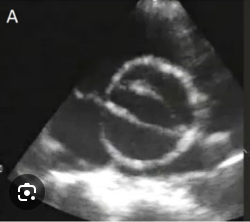
bicuspid aortic valve- most common way it happens
football
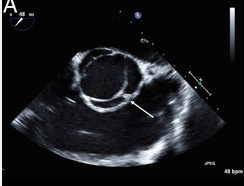
this type of bicuspid aortic valve is less common
football
Myxomatous valve disease
▪ Sagging or slipping of one or both of the leaflets in diastole
▪ Leaflets are thickened and redundant on two-dimensional echo
o Systemic hypertension leads to
▪ Causes dilation of the aortic annulus
o Dissection leads to (3)
▪ Valve leaflets may be normal
▪ Annular dilation causing leaflet displacement o Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm
▪ Dilation of the annulus and sinuses of Valsalva
Segments of the proximal aorta: (4)
• Left ventricular outflow tract
• Sinus of valsalva
• Sinotubular junction
• Ascending aorta
Left Ventricular Response (due to chronic volume overload) (5)
• Progressive dilation of the left ventricle
• Left ventricular function is normal, not hyperdynamic
• Increased sphericity
• Initially, systolic function remains normal
• Systolic dysfunction will develop over time due to the significant chronic volume overload
Indirect Signs of Aortic Regurgitation (4)
• Increased E-point septal separation (EPSS)
• High-frequency fluttering of the anterior mitral leaflet
• Reverse doming of the anterior mitral leaflet
• Jet lesion on the septum or mitral valve
Two-Dimensional evaluation of AoV
WHAT SETTINGS
WHAT VIEWS
• Obtain careful, high resolution imaging focusing on the aortic valve in both harmonics and fundamental modes in the parasternal long axis view and short axis view
o Use magnification (zoom)
Mitral valve m-mode
o Fine diastolic flutter of the anterior mitral valve leaflet o Diastolic damping of the anterior mitral valve leaflet with decreased D-E amplitude and increased Epoint septal separation
• Left ventricle m-mode
o Volume overload pattern
o Dilatation
o Determine parameters carefully; especially the end-systolic dimension, fractional shortening, ejection fraction
Color Doppler Evaluation (3)
• Parasternal Long-Axis View
o Jet Height/Width: Assess the color Doppler height/width of the aortic valve in relation to the left ventricular outflow tract for central jets
o Extent of Jet: in relation to the left ventricular area
o Vena Contracta Width:
o Vena Contracta Width:
▪ Parasternal long axis view
▪ Magnify/zoom
▪ Measure the narrowest segment of the regurgitant signal
▪ A vena contracta width less than 0.3 cm indicates mild regurgitation
▪ A vena contracta width greater than 0.6 cm indicates severe regurgitation
color doppler evaluation
• Parasternal Short-Axis View
jet area
PSAX
o Jet Area :
▪ A central color Doppler jet that takes up less than 25% of the aortic valve indicates mild aortic regurgitation
▪ A central color Doppler jet ≥ 65% of the aortic valve indicates severe aortic regurgitation
Color doppler evaluation
Apical Views - Color Doppler Jet Mapping
extent of jet and jet area
eccentric or central
o Extent of Jet and Jet Area: (2)
▪ How far back does the jet travel into the left ventricle?
▪ How much area of the LV does the jet involve?
o Eccentric or central
▪ eccentric jet implies aortic valve prolapse
▪ central jet implies aortic root dilatation or restricted valve motion
SPECTRAL DOPPLER OF AoV EVALUATES
PHT (CW)
AORTIC FLOW REVERSAL
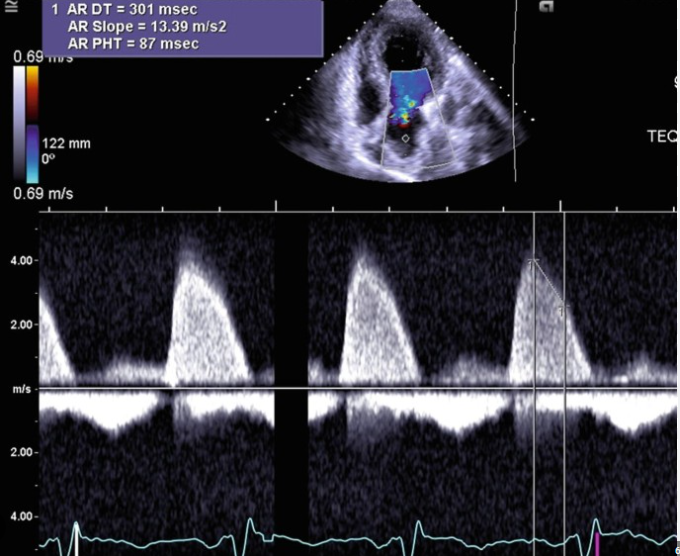
Pressure Half-Time by Continuous-Wave Doppler
AoV
o To assess aortic insufficiency severity
o Apical four-chamber or apical long axis view (three-chamber view)
o Obtain complete Doppler spectral waveform (3 – 5 meters per second)
o If velocity is low – probably not getting complete waveform
o Obtain pressure half-time on complete waveforms only
o Mild (flat) = greater than 500 milliseconds
o Severe (steep) = less than 200 milliseconds
o Assess the density of the spectral Doppler signal
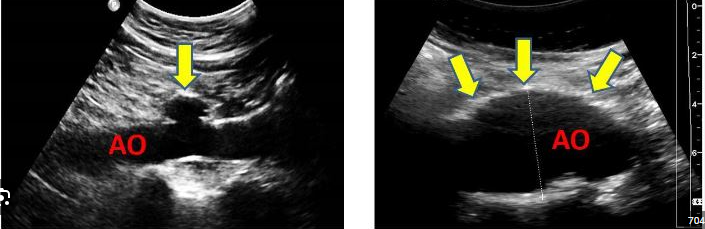
Aortic Flow Reversal
o Pulsed-wave Doppler of the proximal descending aorta in the suprasternal notch view examining for retrograde flow
▪ Retrograde flow indicates moderate to severe aortic regurgitation
o Pulsed-wave Doppler of the descending aorta in the subcostal view examining for retrograde flow
▪ Retrograde flow indicates severe aortic regurgitation
o Velocity greater than 0.6 m/s, VTI greater than 15 cm, or end-diastolic velocity greater than 20 cm/s may indicate significant aortic regurgitation
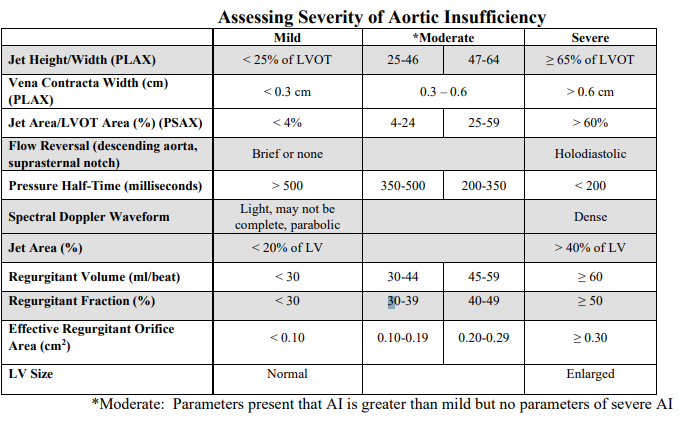
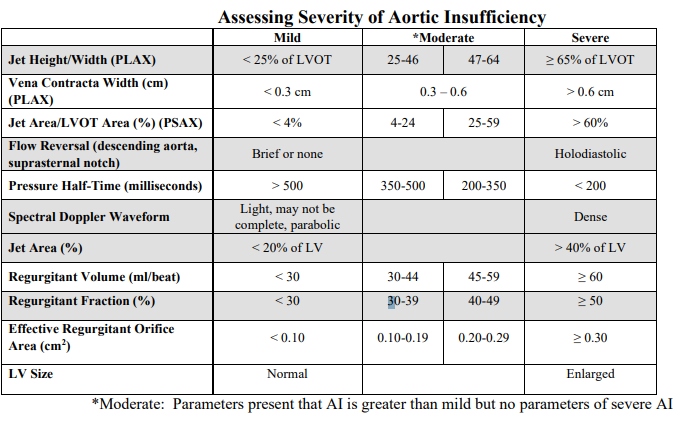
Mild AI
Jet height/width
vena contracta
PHT
Spectral doppler waveform
flow reversal
jet area
regurgitant oriface area
LV size
• Jet height/width (LVOT) <25%
• Vena contracta width less than 0.3 centimeters
• Pressure half-time greater than 500 milliseconds
• Light or incomplete density of the spectral Doppler waveform
• Only brief or no diastolic flow reversal in the descending aorta
• Jet area less than 20% of the left ventricle
• Regurgitant orifice area less than 0.10 cm2
• Normal left ventricular size
Severe AI
Jet height/width
vena contracta
PHT
Spectral doppler waveform
flow reversal
jet area
regurgitant oriface area
LV size
• Jet height/width (LVOT) ≥ 65%
• Vena contracta width greater than 0.6 centimeters
• Pressure half-time less than 200 milliseconds
• Holodiastolic flow reversal is seen in the descending aorta (supraternal window)
• Jet area greater than 40% of the left ventricle
• Regurgitant orifice area ≥ 0.30 cm2
• Dense spectral Doppler signal
• Left ventricular enlargement
AI PHT
mild
moderate
moderatley severe
severe
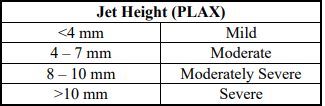
jet height (PLAX)
mild
moderate
moderatley severe
severe
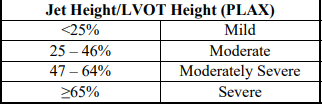
Jet height / LVOT Height (PLAX)
mild
moderate
moderatley severe
severe
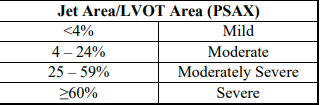
Jet area / LVOT area (PSAX)
mild
moderate
moderatley severe
severe
Vena contracta width (cm) (PLAX)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
< 0.3 cm
moderate
0.3 - 0.6 cm
severe
> 0.6 cm
Jet area / LVOT area (%) (PSAX)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
<4%
moderate
4 - 24%
25 - 59%
severe
>60%
Flow reversal (descending aorta, suprasternal notch)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
brief or none
moderate
severe
holodiastolic
AO PHT (ms)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
>500 ms
moderate
500 - 350 ms
350 - 200 ms
severe
< 200 ms
Spectral doppler waveform
mild
moderate
severe
mild
Light, may not be complete, parabolic
moderate
severe
Dense
AI Jet area
mild
moderate
severe
mild
< 20% of LV
moderate
severe
> 40% of LV
Regurgitation volume (mL/beat)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
<30 mL/beat
moderate
30 - 44 mL/beat
45 - 59 mL/beat
severe
≥ 60 mL/beat
Regurgitaion fraction (%)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
< 30%
moderate
30 - 39%
40 - 49%
severe
≥ 50%
Effective Regurgitant oriface area (cm²)
mild
moderate
severe
mild
< 0.10 cm²
moderate
0.10 - 0.19 cm²
0.20 - 0.29 cm²
severe
≥ 0.30 cm²
LV Size
mild
moderate
severe
mild
normal
moderate
severe
Enlarged