Physics I Module of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse: Lesson 11: Capacitors and Magnetism (Pro)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Lesson 11: Capacitors and Magnetism
Lesson 11: Capacitors and Magnetism
What equation can be used to calculate the total Capacitance for the Equivalent Capacitor when you have capacitors in series?
1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2.... + 1/Cn
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
You have three capacitors in series (C1 = 2.6 F, C2 = 7.4 F, C3 = 2.2 F) and connected to a battery (V = 13.3 V). What is the voltage across C3?
(A) 3.12
(B) 6.05
(C) 13.24
(D) 19.44
(B) 6.05
1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3
1/Ceq = 1/2.6 + 1/7.4 + 1/2.2
1/Ceq = approx. 1 (actual: .974)
Ceq = approx. 1 (actual: 1.03)
Ceq = Q / V
1.03 = Q / 13.3
Q = approx. 13.3 (actual: 13.7)
C3 = Q / V3
2.2 = 13.3 / V3
V3 = approx. 6 (actual: 6.05)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Explain why the charge on all the capacitors in series must be equal to each other?
This is because for each electron that moves from one plate to another plate, it will cause a chain reaction, resulting in one electron building up on each plate.
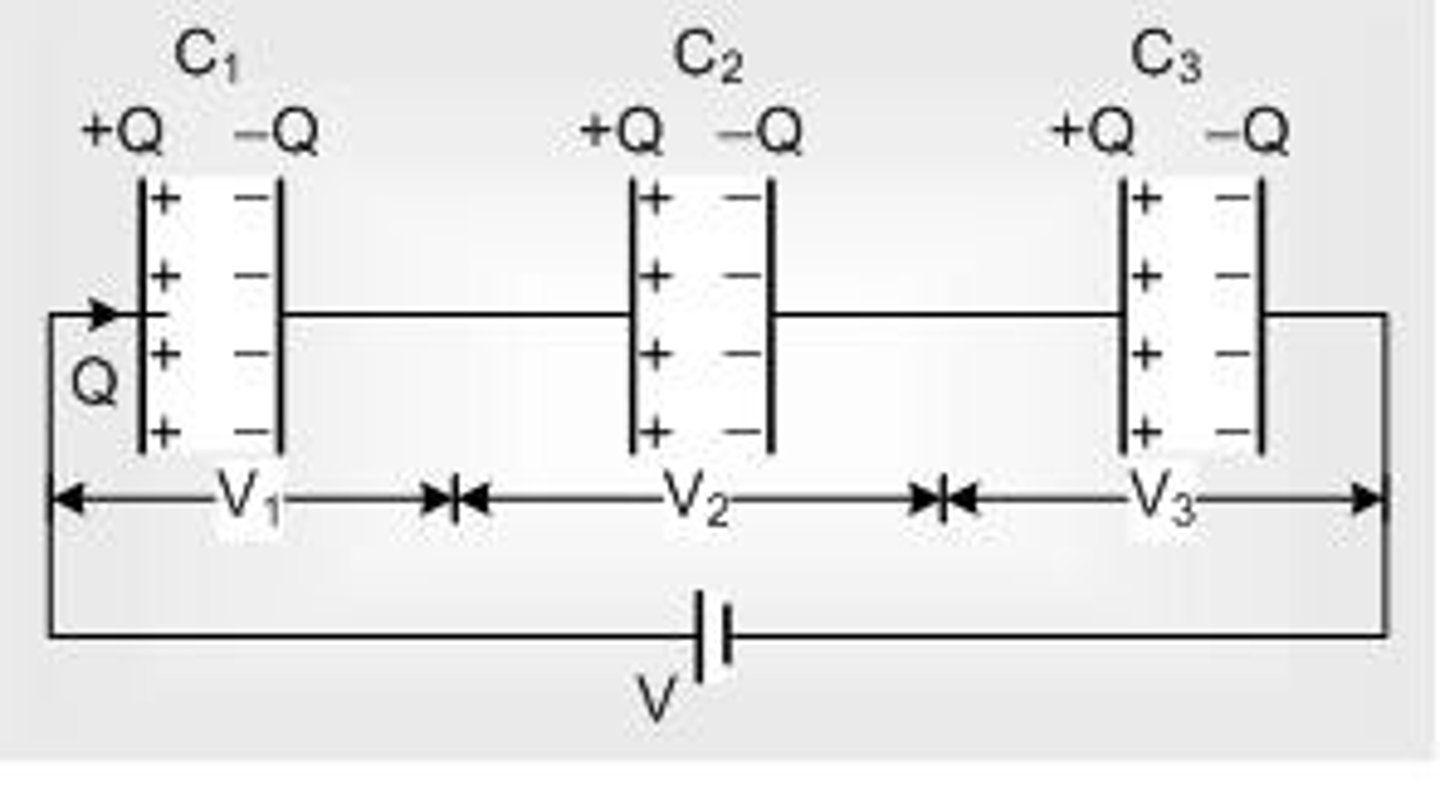
CRB Recall the equation for the charge on a Capacitor. What happens to the Capacitance if the Charge is doubled?
(A) The Capacitance Quadruples
(B) The Capacitance Doubles
(C) The Capacitance stays the same
(D) The Capacitance is cut in half
(C) The Capacitance stays the same
The equation for charge on a Capacitor is Q = CV. Capacitance is constant for a given Capacitor, so if charge doubles, then the voltage would double.
Why is the Equivalent capacitance less than the capacitance for each individual capacitor when in series?
Think about it as if you were to add the distances together. This would decrease the overall capacitance.
What equation can be used to calculate the total Capacitance for the Equivalent Capacitor when you have capacitors in parallel?
Ceq = C1 + C2... + Cn
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
You have three capacitors in parallel (C1 = 2.6 F, C2 = 7.4 F, C3 = 2.2 F) and connected to a battery (V = 13.3 V). What is the voltage across C3?
(A) 2.56
(B) 7.09
(C) 13.30
(D) 21.34
(C) 13.30
The voltage across each capacitor is exactly the same in a parallel configuration.
Why is the voltage across each capacitor exactly the same for each capacitor in a parallel configuration?
The voltage across each capacitor is exactly the same as the overall voltage because each capacitor is directly linked to the battery and every spot along a wire that isn't interrupted by either a resistor or a capacitor will have the exact same voltage in it.
Explain why the equivalent capacitance in the case of a parallel arrangement is equal to the sum of the individual capacitors' capacitances.
Think about it as if their area is simply combined together. This would increase the capacitance accordingly.
You have three capacitors in parallel (C1 = 2.6 F, C2 = 7.4 F, C3 = 2.2 F) and connected to a battery (V = 13.3 V). What is the charge on a plate of C3?
(A) 12.27
(B) 18.79
(C) 29.26
(D) 48.30
(C) 29.26
C3 = Q3 / V
2.2 = Q3 / 13.3
Q3 = approx. 30 (actual: 29.26)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB Which of the following are the main purposes for a Capacitor on the MCAT?
I. Creating uniform Electric Fields
II. Regulating the movement of Charges within a Circuit
III. Storing Electrical Potential Energy
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(C) I and III only
The main purposes of a Capacitor on the MCAT are to create Uniform Electric Fields and Storing EPE.
CRB Write out the Ed's Formula, which relates the Voltage to the uniform Electric Field to the Voltage of a Capacitor?
V = E x d
V = Voltage (V)
E = Electric field (V/m)
d = distance between the parallel plates (m)
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB Write out the equation for the Electrical Potential Energy stored by a Capacitor.
PE = 1/2QV
PE = Potential Energy stored by Capacitor
Q = Charge
V = Voltage difference between the two plates of a capacitor
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
What is a Dielectric? Why do we place Dielectrics between capacitor plates?
A Dielectric is a non-conducting (insulating) material. We place them between capacitor plates to prevent them from touching, which if they did touch, they would no longer store charge but rather just be part of the circuit, allowing charge to flow through them.
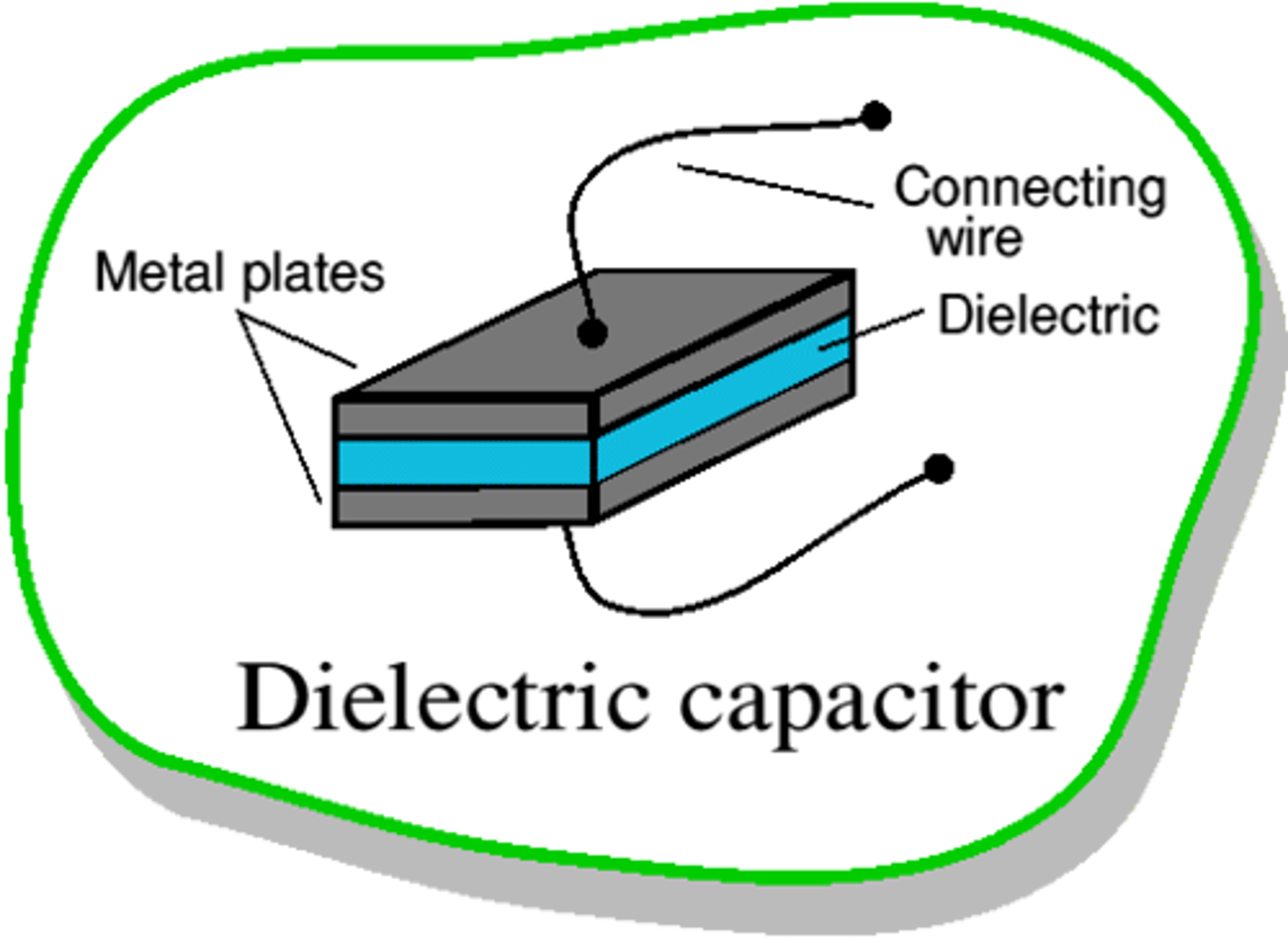
When a capacitor is charged up and then disconnected from a battery, adding a dielectric will:
I. Increase the voltage
II. Increase the charge
III. Increase the capacitance
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) II and III Only
(B) III Only
A dielectric will increase the capacitance of a capacitor, which will allow more charge to build up on the capacitor. It will not affect the charge, but will actually decrease the voltage. This is because the induced polarization within the dielectric will effectively cancel out the charges on the plates, making the voltage difference between the two plates smaller.
When a capacitor remains connected to a battery, adding a dielectric will:
I. Increase the voltage
II. Increase the charge
III. Increase the capacitance
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) II and III Only
(D) II and III Only
A dielectric will increase the capacitance of a capacitor, which will allow more charge to build up on the capacitor. This is because the induced polarization within the dielectric will effectively cancel out the charges on the plates, making the voltage difference between the two plates smaller. The battery will then add more charge to the plates in order to once again make the voltages equal, leaving the voltage unchanged while increasing the number of charges on each plate.
What equation do you use to calculate the new Capacitance of a capacitor upon addition of a dielectric?
C' = kC
C' = New Capacitance
C = Capacitance without Dielectric
k = Dielectric Constant
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
True or False? There are rare dielectric materials with Dielectric Constants less than 1 due to their weak ability to insulate.
False. Dielectric materials are defined to be non-conducting materials. As such, their Dielectric Constant must always be greater than 1.
You add regular paper (k = 3.6) between two capacitor plates of a capacitor (C = 25.8) without removing the battery (V = 14.9). What will the charge be on a capacitor plate after addition of the paper?
(A) 1.38
(B) 13.8
(C) 138
(D) 1380
(D) 1380
C' = kC
C' = (3.6) (25.8)
C' = approx. 90 (92.88)
C = Q / V
92.88 = Q / 14.9
Q = approx. 1500 (1383.9)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
The north pole of a magnet would be attracted to the north or south pole of another magnet?
The north pole of a magnet would be attracted to the south pole of another magnet.
True or False? When you cut a magnet in half, you end up with a north magnet and a south magnet.
False. All magnets have both a north and south pole. Cutting a magnet in half would simply give you two smaller magnets, both having their own north and south pole.
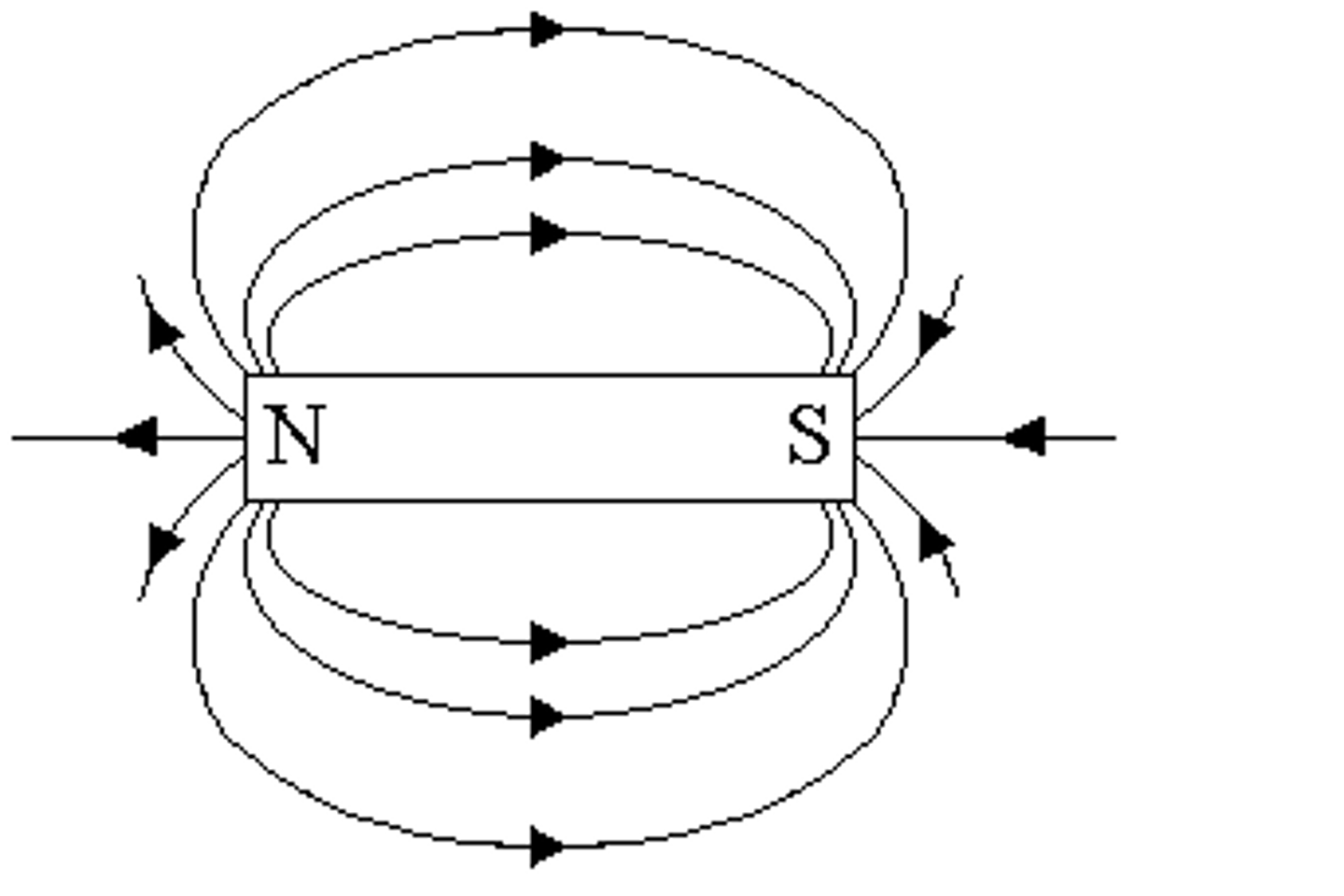
Draw the magnetic field lines coming out of a simple bar magnet.
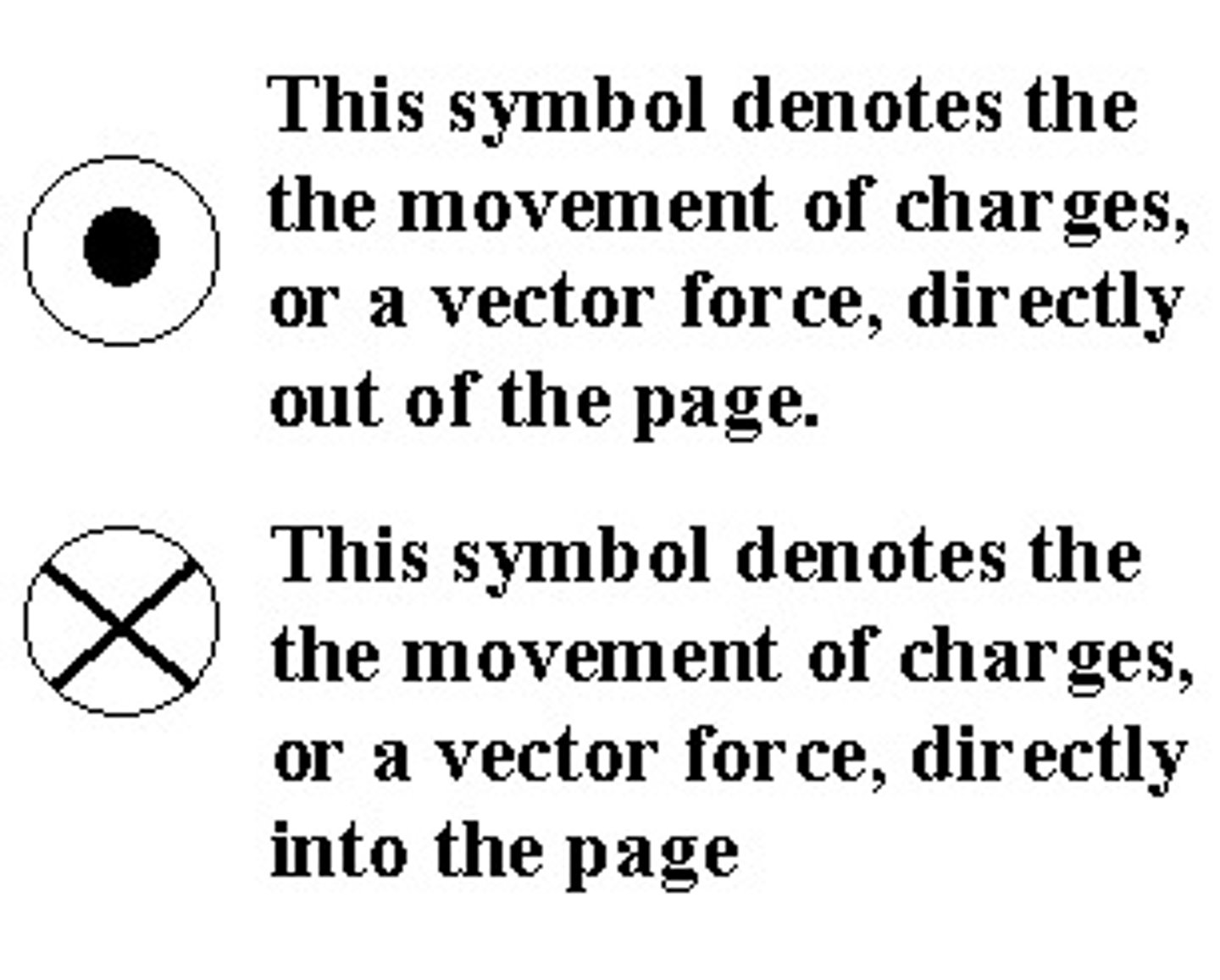
CRB Fill in the blanks: To signify that the magnetic field is moving out of the plane of the page, a _________ is drawn; when the magnetic field is moving into the plane of the page, a __________ is drawn.
(A) Square, Circle
(B) Circle, Square
(C) Circle, X
(D) X, Circle
(C) Circle, X
To signify that the magnetic field is moving out of the plane of the page, a Circle is drawn; when the magnetic field is moving into the plane of the page, an X is drawn.
CRB Which of the following is not one of the three major categories of materials based on magnetism?
(A) Ferromagnetic
(B) Quasimagnetic
(C) Diamagnetic
(D) Paramagnetic
(B) Quasimagnetic
The three main categories of materials based on magnetism are Ferromagnetic, Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic
CRB Which of the following classes of materials is known for having no unpaired electrons and will be weakly repelled by a magnet?
(A) Ferromagnetic
(B) Quasimagnetic
(C) Diamagnetic
(D) Paramagnetic
(C) Diamagnetic
Diamagnetic materials are known for having no unpaired electrons and will be weakly repelled by a magnet
CRB Which of the following classes of materials is known for having unpaired electrons and will be weakly magnetized by an external magnetic field, but will not remain magnetized long after that magnetic field is removed?
(A) Ferromagnetic
(B) Quasimagnetic
(C) Diamagnetic
(D) Paramagnetic
(D) Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic materials are known for having unpaired electrons and will be weakly magnetized by an external magnetic field, but will not remain magnetized long after that magnetic field is removed.
CRB Which of the following classes of materials is known for having unpaired electrons and will be strongly magnetized when an external magnetic field is applied or under certain temperatures, and can have mostly aligned magnetic dipoles even after the external magnetic field is removed?
(A) Ferromagnetic
(B) Quasimagnetic
(C) Diamagnetic
(D) Paramagnetic
(A) Ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetic materials are known for having unpaired electrons and will be strongly magnetized when an external magnetic field is applied or under certain temperatures, and can have mostly aligned magnetic dipoles even after the external magnetic field is removed.
CRB Which of the following is not one of the most common ferromagnetic materials?
(A) Zinc
(B) Iron
(C) Nickel
(D) Cobalt
(A) Zinc
The three most common ferromagnetic materials are Iron, Nickel and Cobalt.
What equation will allow you to calculate the Magnetic Force on a moving charge in a magnetic field?
F = qvBsinθ
F = Magnetic Force
q = Charge
v = Velocity of the charge
B = Magnetic flux density
θ = angle between the magnetic field and the velocity of the charge
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
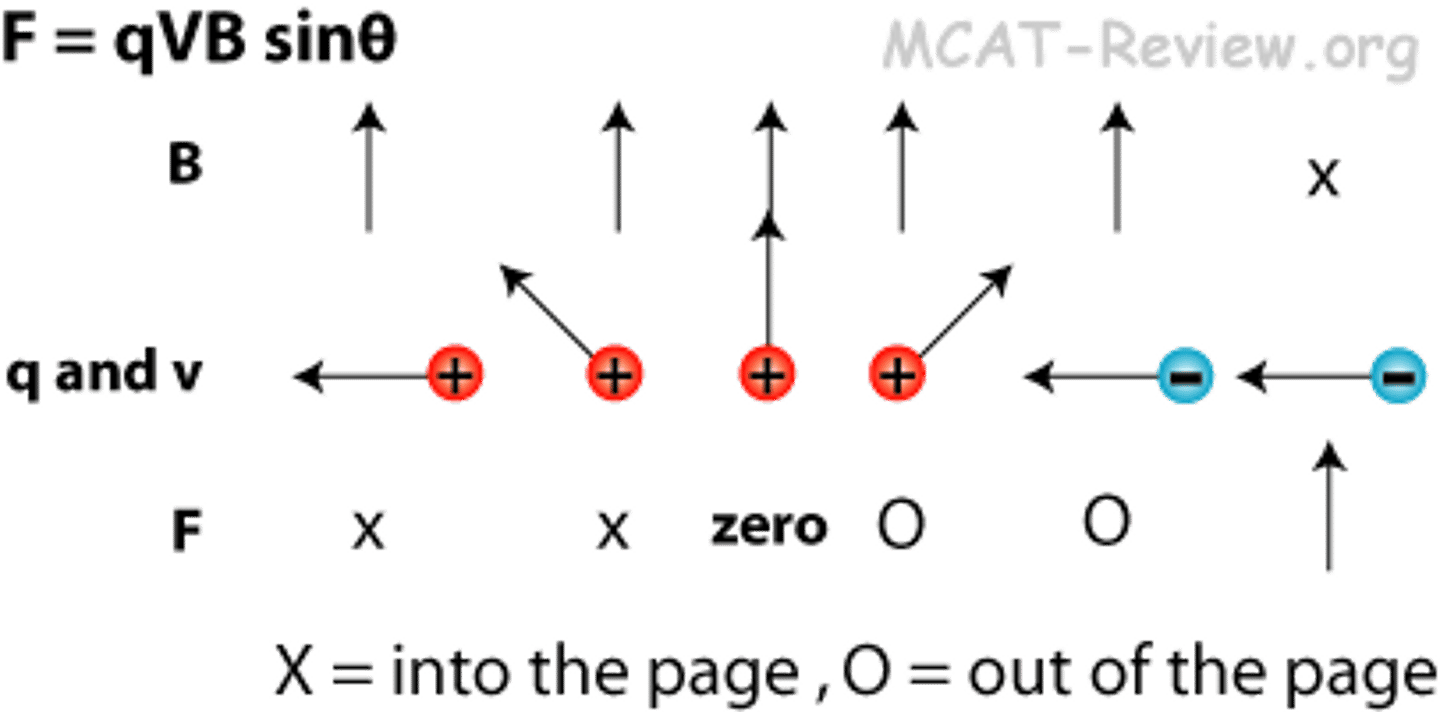
A proton (q = 1.602⋅10^-19 C) is travelling through a magnetic field (B = .27 T) at an angle of 47° with a velocity of 4.5⋅10^7 m/s. What is the Magnetic Force acting on this proton?
(A) 1.42⋅10^-12
(B) 6.78⋅10^-13
(C) 9.22⋅10^-14
(D) 3.09⋅10^-15
(A) 1.42⋅10^-12
F = qvBsinθ
F = (1.602⋅10^-19) (4.5⋅10^7)(.27)sin47°
F = (1.602⋅10^-19) (4.5⋅10^7)(.27)(approx. √2/2 or .7 (actual: .731))
F = approx. 1.5⋅10^-12 (actual: 1.423⋅10^-12)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB True or false? If the charged particle has no outside forces acting on it, then it will never create a magnetic field.
False. If the charge has no outside forces acting on it AND its initial velocity is 0, then it will never create a magnetic field.
Having no outside forces act on the charge just means it won't accelerate, not that it will have no velocity.
CRB Which of the following statements about Magnetic Field's units are correct?
I.The SI unit for magnetic field strength is the Gauss.
II. Teslas are quite large, with 1 T = 10^4 Gauss
III. One Tesla is equal to 1 N s / (m C) [Newton second per meter Coulomb].
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
Each of the following statements are true:
I.The SI unit for magnetic field strength is the Tesla.
II. Teslas are quite large, with 1 T = 10^4 Gauss
III. One Tesla is equal to 1 N s / (m C) [Newton second per meter Coulomb].
Your professor makes an analogy comparing centripetal force to magnetic force. How are these two concepts related?
When magnetic force acts on a charge, it causes it to change directions in a way that makes it go in a circle.
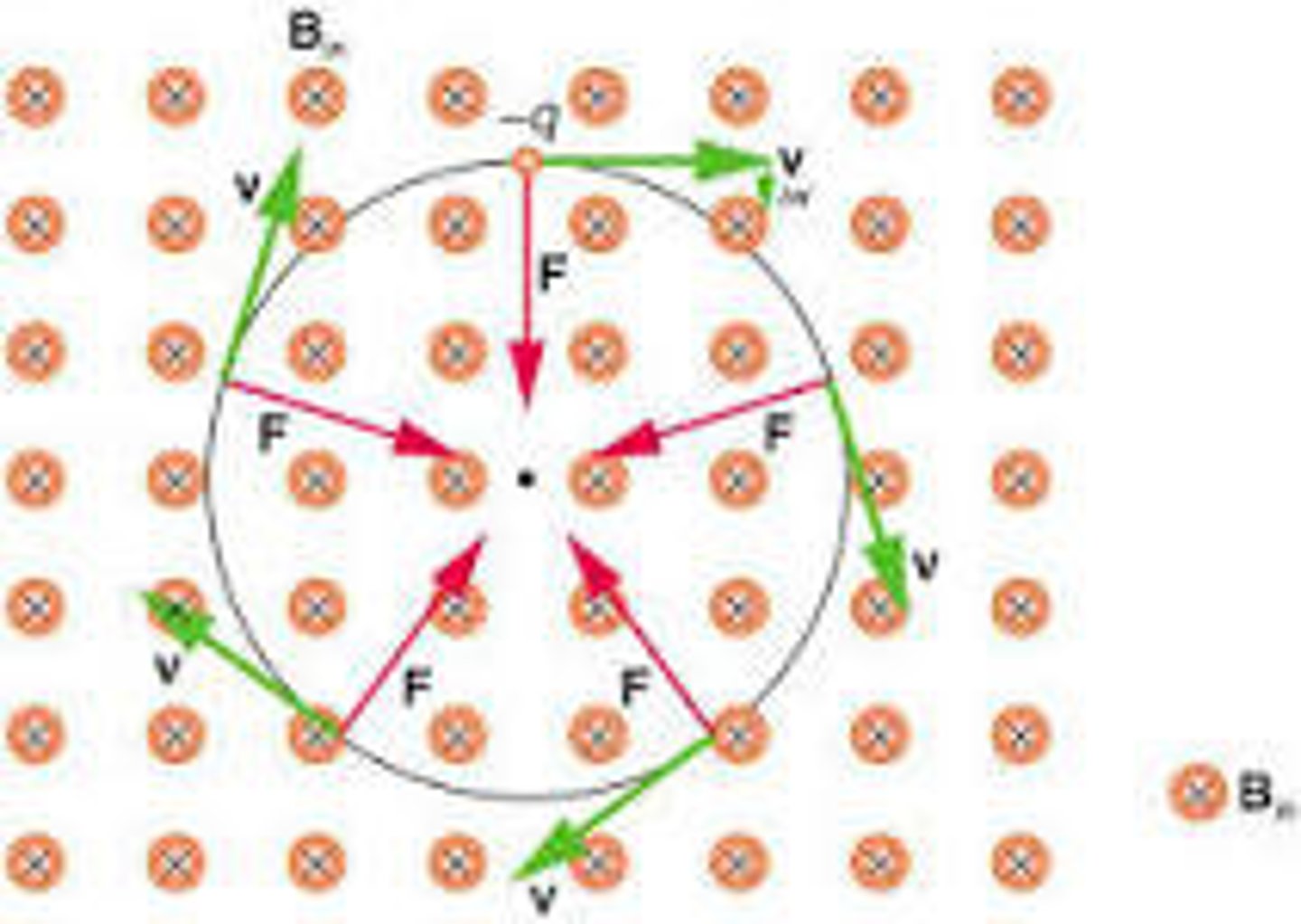
CRB True or false? If an outside magnetic field is perpendicular to the velocity of a charged particle, then that magnetic field does no work on that charged particle.
False. If an outside magnetic field is parallel to the velocity of a charged particle, then that magnetic field does no work on that charged particle.
The proton (1.67⋅10^-27 kg) in the most recent practice problem was acted on by a force of 1.42⋅10^-12 N and had a velocity of 4.5⋅10^7 m/s. What is the radius of the circle that this proton is moving in?
(A) 4.56⋅10^-2
(B) 2.41⋅10^-1
(C) 2.38⋅10^0
(D) 8.76⋅10^1
(C) 2.38⋅10^0
Fm = Fc = m (v^2 / r)
1.42⋅10^-12 = 1.67⋅10^-27 ((4.5⋅10^7)^2 / r)
1.42⋅10^-12 = 1.67⋅10^-27 (approx. 2⋅10^15 (actual: 2.025⋅10^15) / r)
1.42⋅10^-12 = (approx. 3⋅10^-12 (actual: 3.38⋅10^-12)) (r)
r = approx. 2 (actual: 2.38)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB After the previous few lessons, you realize that there are usually both magnetic and electrostatic forces acting on charged particles. Which of the following is the Sum of these forces?
(A) Newton's Force
(B) Electrostatic-Magnetic Force
(C) Tesla-Coulumb Force
(D) Lorentz Force
(D) Lorentz Force
The Lorentz Force is the resultant of the Magnetic and Electrostatic forces' vectors.