Art History Exam #2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
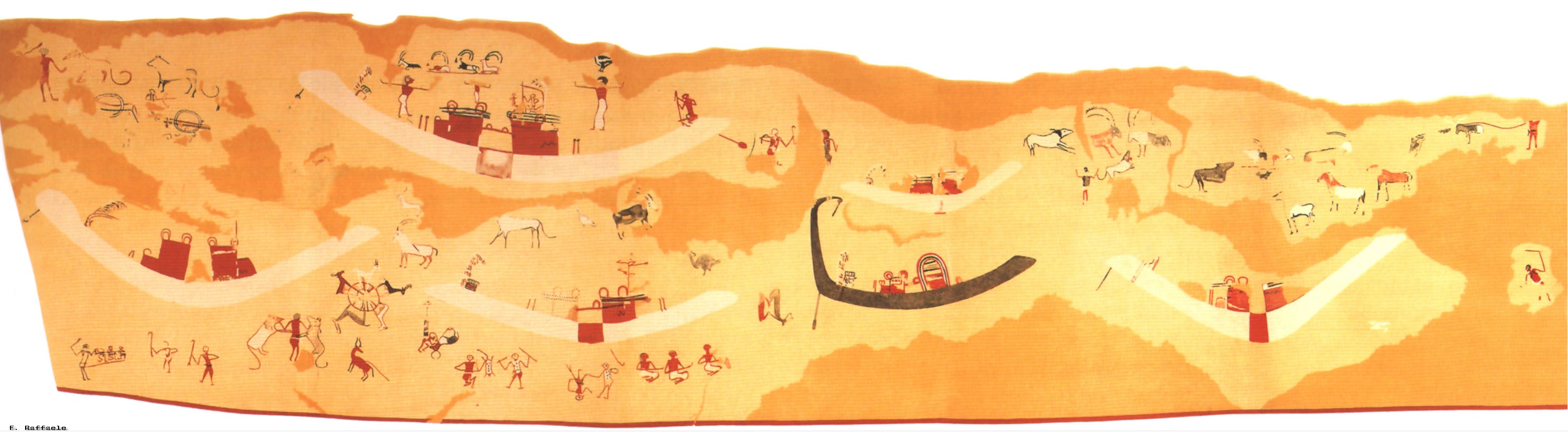

Tomb Painting, Hierakonpolis, c. 3500
Heraldic Composition
Kohl
Galean and soot, likely a ceremonial palette or offering to Horus

The Palette of Narmer, Hierakonpolis, Early Dynastic period, c.2900 BCE, green schist, 25'“ h

Mastaba Tomb
an ancient Egyptian structure of mud-brick or stone with sloping sides erected over a subterranean tomb-chamber

Serdab
chamber that contained a Ks statue to receive offerings and prayers

Stepped Pyramid of Djoser
Saqqara, Egypt, 204’ tall, limestone
Builder of Stepped Pyramid of Djoser
Imhotep, 2600 BCE

The Great Pyramids
Giza, Old Kingdom, Egypt, c.2600-2500 BCE

Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut*
New Kingdom, Egypt, c. 1500 BCE

Akhenaten and His Family*
New Kingdom, Egypt, c. 1400 BCE
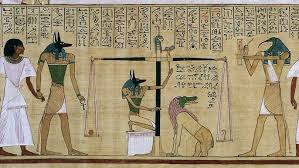
Judgement of Hunefer Before Osiris
New Kingdom, Egypt, c. 1300 BCE

Figure of a Woman*
Cyclades, c. 2600-2400 BCE

Bull Leaping*
Minoan, c. 1700-1500 BCE

Palace of Knossos
Minoan, c. 1700-1500 BCE

Lion Gate
Mycenaean, C.1300 BCE

Treasury of Atreus
Mycenaean, c. 1300-1200 BCE


Peplos Kore*
Archaic Greece, c. 500 BCE

(Riace) Warrior
Classical Greece, c.500 BCE

Kallikrates and Iktinos*
Parthenon, Classical Greece, c. 450 BCE

Lacoon and His Sons
Hellenistic Greece, 1st c BCE or 1st c. CE

Master Sculptor Vulca, Apollo*
Etruscan, 500 BCE

Burial Chamber, Tomb of the Reliefs*
Etruscan, Italy, 3rd c. BCE

Sarcophagus
A stone coffin, often decorated with inscriptions and reliefs, used to house and protect a mummified body.
Hieroglyphs
The formal writing system of ancient Egypt, using pictorial symbols to represent sounds, words, or ideas.
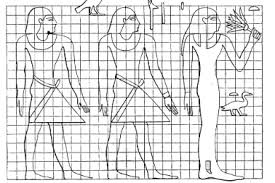
Canon of Proportions
A set of ideal mathematical ratios used by Egyptian artists to create consistent, standardized human figures—ensuring uniform body proportions in art.

Nemes Headdress
A striped head cloth worn by pharaohs, draping over the shoulders and tied at the back, symbolizing royal authority.

Composite Pose
A conventional artistic style showing the human body from multiple viewpoints at once—typically the head and legs in profile, but the torso frontally.

Stepped Pyramid
A pyramid made of several mastaba-like layers stacked on top of each other; the earliest large-scale stone construction in Egypt
True Pyramid
A pyramid with smooth, angled sides that converge to a point at the top
Ka
The spiritual life force or soul in Egyptian belief, which continued to live after death and required offerings and a preserved body.
Ka Statue
A sculptural representation of the deceased that served as a physical dwelling place for the ka if the body was destroyed.
Necropolis
Literally “city of the dead”; a large burial ground or cemetery complex associated with ancient Egyptian cities.

Ashlar Masonry
A type of building construction using precisely cut, squared stone blocks laid in even courses without mortar.

Rock-Cut Temple
A temple carved directly into natural rock formations or cliffs rather than built as a freestanding structure.
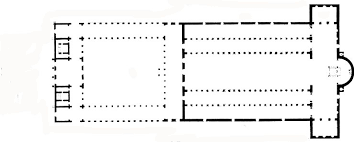
Axial Plan
An architectural layout organized along a straight central line, leading from the entrance through successive spaces toward a sanctuary.

Hypostyle Hall
A large hall filled with columns supporting a roof, common in Egyptian temples.

Pylon
A monumental gateway to an Egyptian temple, characterized by massive sloping walls and a central doorway.
Books of the Dead
A collection of funerary texts containing spells, prayers, and instructions to help the deceased navigate the afterlife.
Ankh
An ancient Egyptian symbol shaped like a cross with a loop at the top, representing life and immortality.


Cyclopean Masonry
A style of construction using massive, irregular limestone boulders fitted together without mortar

Rhyton
A ceremonial drinking or pouring vessel, often shaped like an animal or human head, used in ritual libations.
Repousse
A metalworking technique in which a design is hammered into relief from the reverse side of a metal sheet.
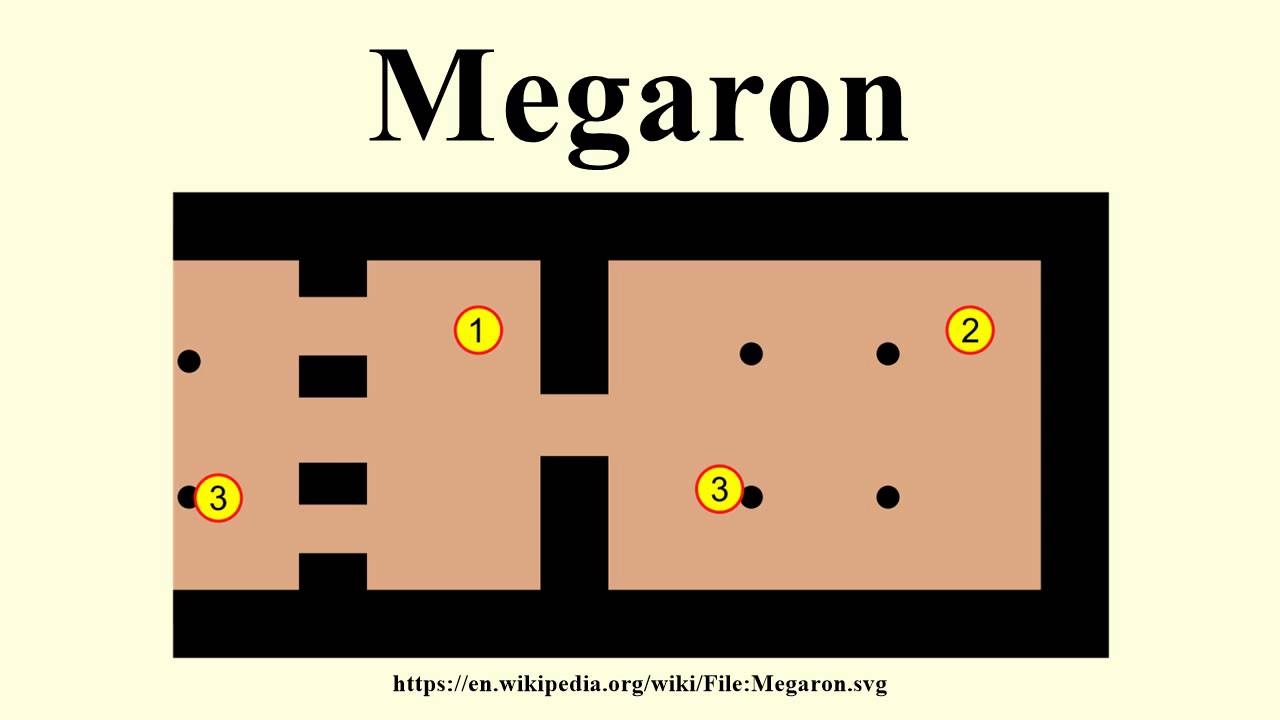
Megaron
The main hall or throne room in a Mycenaean palace, featuring a rectangular layout, a central hearth, four columns, and a front porch with columns.
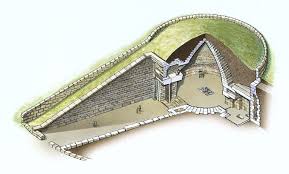
Tholos (or Beehive Tomb)
A circular underground tomb built with corbeled stone layers that form a high domed roof, resembling a beehive in shape.

Corbeled Vault
An arch-like structure created by overlapping layers of stone that gradually project inward until they meet at the top, forming a vault or dome without true arches.

Black-Figure Ceramics
A style of Greek pottery decoration where figures were painted in black slip on a red clay background, then details were incised to reveal the red beneath.

Red-Figure Ceramics
the background was painted black and the figures were left in red, allowing for greater detail and naturalism with painted lines.

Caryatids
Sculpted female figures used as architectural supports in place of columns or pillars
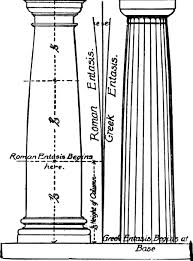
Entasis
A slight convex curve in the shaft of a column, designed to correct the optical illusion of concavity and make the column appear straight and more dynamic.

The “Canon” of Polykleitos
A set of ideal mathematical proportions for the human body developed by the sculptor Polykleitos, emphasizing balance, symmetry, and harmony.
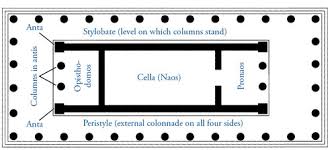
Cella (or Naos)
The main interior chamber of a Greek temple that housed the cult statue of the deity.
Portico
A covered entrance or porch supported by columns, leading to the entrance of a building.
Colonnade
A row of columns supporting a roof, entablature, or arcade—commonly seen around temples or courtyards.
Archaic Smile
A slight, closed-mouth smile seen on sculptures from the Archaic period of Greek art, used to suggest that the subject was alive and well.
Kouros
A free-standing statue of a nude young man, representing idealized youth and athleticism.
Kore
A free-standing statue of a clothed young woman, often serving as a votive offering to a goddess.
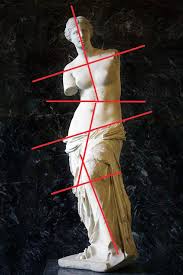
Contrapposto
A pose in sculpture where the figure stands with weight on one leg, causing a natural shift in the hips and shoulders

Agora
The central public space in ancient Greek cities, used as a marketplace, gathering place, and civic center for political and social life.
What happened to the Etruscans?
The Etruscan civilization gradually declined as Rome rose in power.
What was Etruscan political structure like?
organized into independent city-states, each ruled by a king or powerful aristocratic families.
Describe Etruscan religious practices.
Highly ritualistic and focused on interpreting divine will through omens, augury, and haruspicy. They believed gods influenced every aspect of life, and these beliefs strongly shaped early Roman religion.
Where was the sculpture on an Etruscan temple located?
Temple sculptures were on the roof, especially along the ridgepole, and often made of painted terra cotta.
Terra Cotta
A type of baked clay used by the Etruscans for sculpture, architectural decoration, and sarcophagi because it was lighter and cheaper than stone.
Who ruled Rome before the Romans
Etruscan kings
In Cycladic civilization what tool was used to carve marble figures?
emery
Where are Cycladic marble figures usually found?
burial sites (graves), often placed with the deceased. Their purpose is uncertain; possibly religious, funerary, or symbolic.
Why did the Minoan civilization flourish economically?
Maritime trade and Natural resources
What ened the Minoan civilization?
A massive volcanic eruption, which caused tsunamis and destruction on Crete. Later, Mycenaean invasions likely finished their collapse.
What was the written language of the Minoans?
Linear A, an undeciphered script, and hieroglyphic symbols.
Why is the Mycenaean culture considered to be more militaristic than the Minoan
They built fortified citadels, produced weapons and armor, and depicted warriors and battles in art.
What are the stylistic features of the Amarna Period in Egypt?
A more naturalistic and relaxed artistic style. Figures had elongated heads and necks, soft, curving bodies, and intimate, family-oriented scenes.
What are the key characteristics of the Geometric Period (c. 900–700 BCE)?
Art featured abstract, geometric designs and stylized human and animal figures on pottery.
What defines the Orientalizing Period (c. 700–600 BCE)?
Greek art began showing influences from the Near East and Egypt, including floral patterns, mythic animals, and more detailed human forms.
What are the key features of the Archaic Period (c. 600–480 BCE)?
Art became more naturalistic but still stylized. Kouros and Kore figures were common, featuring the Archaic smile. Temples became more elaborate, and black-figure pottery dominated.
What defines the Classical Period (c. 480–323 BCE)?
Art emphasized idealized human forms, proportion, and balance. Contrapposto became common, and architecture like the Parthenon represented harmony and order.
What are the key traits of the Hellenistic Period (c. 323–31 BCE)?
Art became dramatic, emotional, and dynamic, with twisting poses and intense expression. Artists focused on individuality and realism rather than ideal perfection.
What are the three main Classical Orders in Greek architecture?
Doric Order, Ionic Order, Corinthian Order
What is the function of the entablature in Greek architecture?
the horizontal structure supported by columns, divided into the architrave (bottom), frieze (middle), and cornice (top).
How did the transition from Etruscan to Roman rule affect Roman culture?
Rome adopted many Etruscan artistic and religious traditions, but developed a new political identity centered on the Republic and civic duty