Antisemitic policies 1933 - 1945
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anti-Semitic policies under the Nazi Regime
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Boycott of Jewish Shops and Businesses
1st April 1933
What was the Boycott of Jewish shops and businesses
Aimed to target places of business, but also applied to Jewish professionals (e.g. Lawyers, Doctors)
Enforced by the SA, who aimed to deter those not participating in the boycott from attempting to enter Jewish places of business
Law for the Restoration of the Civil Service
Excluded Jews and the “Politically Unreliable” (e.g. communists) from being able to work in the civil service (unsuccessful as there was no objective or definition on how to define a person as Jewish)
Not comprehensive as Hindenburg prevented the law from applying to German Jews who served in WW1 or had fathers killed in the war.
When was the Law for restoration of the civil service introduced
7th April 1933
Law against Overcrowding of German Schools and Universities
April 1933
Restrictions on the no. of Jewish Children who could attend state schools and universities, by promoting the idea that Aryan students were more deserving that children who could become ‘enemies of Germany’ and that well-educated Jews were a threat to Germany
Exclusion of German Jews from the press - The Reich Press Law
October 1933
The Reich Press Law allowed the censorship and banning of publications that disputed with the Nazi Regime, by silencing the large no. of Jewish journalists, editors and publishers
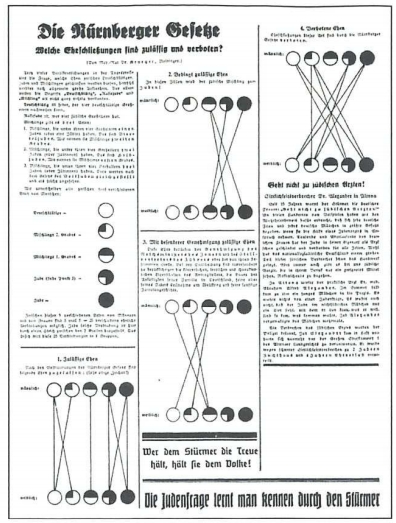
The Nuremberg Laws
15th September 1935
extension of the antisemitic legislature, named after their announcement at a Nuremberg Party Rally in 1935, the laws included;
The Reich Citizenship Law
The Law for the Protection of German Blood and Honour
Allowed for easier enforcement of anti-semetism by Gestapo, Judges and Civil servants
The Reich Citizenship Law
as part of the Nuremberg Laws.
German citizens can only be classed as such, if they had purely ‘German blood’ → stripping Jews and other ‘non-Aryans' were classified as subjects and had fewer rights than true citizens
When was the Reich Citizenship Law introduced
15th September 1935
The Law for the Protection of German Blood and Honour
Outlawed marriage between Aryans and Non-Aryans and marriage or sexual relations between German citizens and Jews.
Later amended to cover any physical contact between Jews and Aryans; with allegations resulting in convictions and Aryan Women being encouraged to leave Jewish husbands
Impact from the decree for the protection of German Blood and Honour
First Supplementary Decree on the Reich Citizenship Law
November 1935
Law defining what constituted as a ‘full Jew' or a ‘half Jew’.
The law was hard to interpret, due to the definition being based on the number of Jewish grandparents had, but many had converted to Christianity, making many of the classifications arbitrary or inconsistent.
1936, Berlin Olympics
A major event used by the Nazi regime to showcase Aryan supremacy and promote Nazi propaganda, with VERY limited participation from Jewish athletes.
The games were used to distract from the regime's antisemitic policies and present a positive image of Germany to the world - to kerb international reactions
Banning ability for optional name changes, for Jewish people
5th Jan 1938
Anchluss with Austria
March 1938
Unification with Austria, was a ‘bloodless victory' as German troops were welcomed by Austrians;
This allowed the Nazis to become ambitious in their foreign policy and adopt more radical policies overall.
Registration of Jewish Assest over 5000 marks
26 April 1938
The Decree for the Reporting of Jewish-Owned Property, required Jews submit detailed accounts of their property and assets valued over 5000 marks.
Part of the broader plan to economically disenfranchise Jews, making it easier for confiscation of assets and wealth. Failure to comply could result in imprisonment.
ALL Jewish people forced to chage their names
17 August 1938
Men to ‘Israel’, Women to ‘Sarah'; aimed at furthering the exclusion and identification of Jews in society. This policy was part of a larger set of antisemitic measures implemented by the Nazi regime.
Jewish passports stamped with a large ‘J’
5 October 1938
Used as a method of separtating and identifying Jewish people from the rest of the German population
De-certification of Jewish Doctors in Germany
30th September 1938
Jews forbidden to visit theatres, etc.
November 1938
Alienating and separating Jewish people from the general German public
Reichkristallnacht
9 - 10 November 1938
Instigated by Nazi leadership, over the murder of Ernest Vom Rath in Paris on 9th November, by a Polish-Jew
Jewish homes and businesses were looted and vandalised
Synagogues were arsoned
Thousands of jews were arrested, beaten and killed
The radical actions were supported by the German Public
Expulsion of all Jewish pupils from schools
November 1938
Compulsory sale of all Jewish business
December 1938
Introduction of rationing, excluding Jewish people
August 1939
German Invasion of Poland
1st September 1939
triggered World War II, essentially marking the beginning of full racial war against Jewish people and other targeted groups.
Einsatzgruppen
September 1939
7000 killed within the first month
Ghettoisation of Jews in Poland
September 1939
Euthanasia Programme organised by Hitler
October 1939
Jews in occupied Poland made to wear Star of David
November 1939
First Ghetto established in Lodz, Poland
February 1940
German invasion of Western Europe
April 1940
Madagascar Plan
1940
Establishment of the Warsaw Ghetto in Poland
October 1940
Jews Excluded from wartime rationing
October 1940
Einsatzgruppen ordered to kill Jewish sympathisers and communist commissars
July 1941
Jews in Germany compelled to wear the Star of David
December 1941
Wansee Conference
January 1942
meeting where Nazi officials discussed the implementation of the "Final Solution" to exterminate the Jewish population.
Round up of Jewish people from France
occurred in July 1942 during the Vel' d'Hiv Roundup, where thousands were arrested and deported to concentration camps.
Auschwitz
May 1943
German Jews began to be deported
June 1943
Hungary Jewish sent to Auschwitz
May 1944
Auschwitz destroyed
November 1944
Liberation of Auschwitz
January 1945