Ch. 16 Static Electricity
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Give an example of polarization
small particles that are charged that remain on an item (comb that attaches to paper)
When does static electricity charge
at rest
True or False: like charges repel and opposite charges attract
true
Can electric charge be conserved?
Yes, cannot be created/destroyed
Do charges move after they are placed?
No
in electrostatic charge, charges do not move once placed
What are ways that charges can be separated?
objects can be rubbed
think of tape example
Differentiate insulators and conductors
Insulators
Charges do NOT move
Conductors
charges are free to move
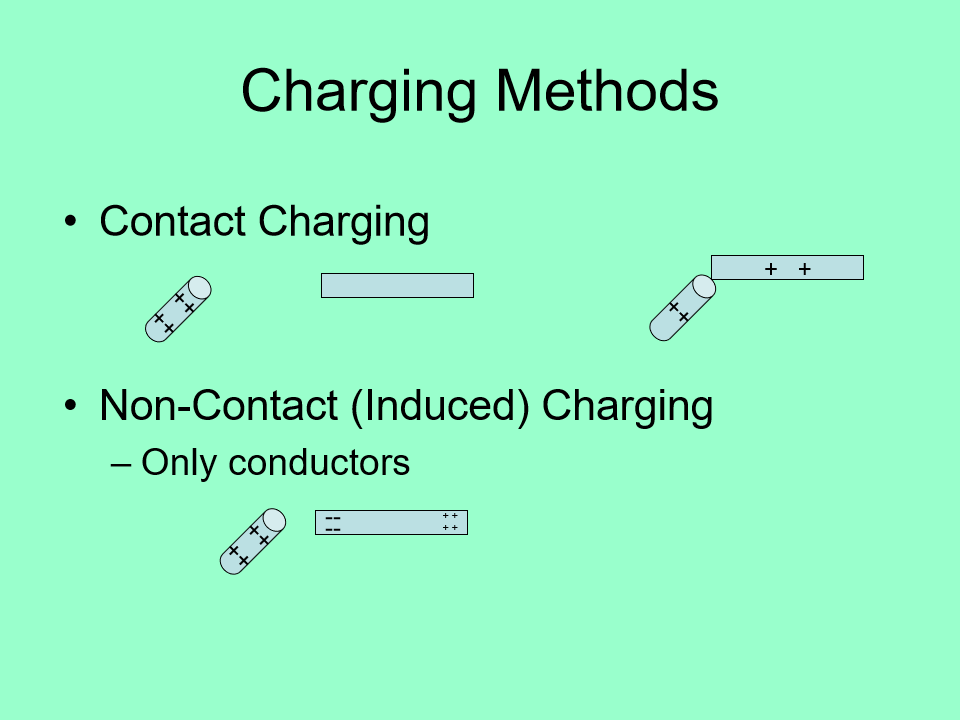
What are some methods on how to charge?
contact charging
non-contact (induced) charging
only in conductors (opp. charges attract)
ex: electroscope
What term refers to when something can absorb/release a large # of e- without changing its charge appreciable
give example!
Ground
ex: earth
What is Coulomb’s law? Explain what each variable is
k = constant
Q1, Q2 = charges
r = distance between 2 charges
If finding magnitude, ignore the signs of the charges
What law applies to Coulomb’s Law?
Newtons 3rd Law (every rxn, has equal/opposite rxn)
vector quantities
signs of charges are imp
G = constant (replace k)
What do you do if there are more than 2 charges?
find the vector sum of all forces acting on it
What is the electric field?
extends outward from (inward to) every charge and permeates all space
electric field’s physical effect exert a force on a charge (q) so force created by charge
In an electric field, which way do positives and negatives direct?
Positives face outward
negatives face inward
What do field lines have to do with charges?
all charges want to move along them
# of field lines is proportional to magnitude of charge
What happens when the field lines are closer together?
the electric field is stronger
If there were an electric field inside a conductor, what would the charge be? how about in parallel lines?
E inside conductor = 0
it is “protected” → (think of a cage man)
in parallel lines, there would be no E (zero)
At what angle are electric field lines always set in respect to the surface?
at 90 degrees
Explain how electric fields apply in DNA replication
when there are random collisions inside the cell, A =T attract and G=C attract
NO other combos
Explain how electric fields apply in photocopy machine
drum + charged
image focused on drum
black areas stay charged and attract toner particles
image transfers to paper
sealed with heat
What is an electric flux?
amount of something coming out of a surface depending on angle/surface area
like water flow, electric, field
When is flux positive and negative?
Flux = positive (less than 90 deg)
Flux = negative (more than 90 deg)
What does Gauss’s Law state for a closed surface?
it is the total flux through a closed surface depending on the charge enclosed
How does Gauss’s Law work for a sphere?
Outside of the sphere (r>r0)
use equation to find E
inside of the sphere (r<r0)
E = 0