Immune system
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
What are the three lines of defense in the immune system?
Physical and chemical barriers, innate immune system, and adaptive immune system.
Give examples of physical and chemical barriers in the first line of defense.
Skin, mucous membranes, tears, stomach acid
List characteristics of the innate immune system.
Nonspecific, present at birth, and fast response.
List characteristics of the adaptive immune system.
Specific, slow to activate, and memory-based.
Describe the nature of the innate immune response.
Immediate and general.
Describe the nature of the adaptive immune response.
Delayed, specific, and remembers past infections.
What does it mean by the innate immune response is non-specific?
Responds to patterns (PAMPs).
What allows the innate immune system to be inducible?
Scale response through cytokines.
Does the innate immune system have memory?
Same response every time.
How does the innate immune system trigger adaptive immunity?
Antigen presentation.
Which immune cells are located in the blood and tissues?
Neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells.
What is the function of the lymphatic system in the context of immunity?
Adaptive system activation.
What does every cell use to signal infection?
MHC I.
Where is mucosal immunity located?
Lungs, gut, urogenital tract.
How are exogenous pathogens detected?
TLRs on the membrane.
How are endogenous pathogens detected?
TLRs in endosomes.
On what are Exogenous pathogens presented?
MHC Class II.
On what are Endogenous pathogens presented?
MHC Class I.
What are PAMPs?
Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns.
What are TLRs?
Toll-Like Receptors.
Which cells are involved in phagocytosis?
Neutrophils, Macrophages, Dendritic cells, and B cells.
What is distinctive about Neutrophils function?
First responders, die after phagocytosis (form pus).
What is distinctive about Macrophages function?
Eat and signal adaptive system.
What is distinctive about Dendritic Cells function?
Eat and migrate to lymph nodes.
What is distinctive about B Cells function?
Eat and present antigen (adaptive role).
What are the steps of phagocytosis?
Detect PAMP with TLR, engulf into phagosome, fuse with lysosome to form phagolysosome, digest pathogen into antigens, and release cytokines.
Which cells are professional APCs?
Macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells.
What are the steps of MHC II antigen presentation?
Pathogen digested in phagolysosome, antigens loaded into MHC II, and MHC II-antigen complex displayed to T helper cells.
What do natural killer (NK) cells do?
Patrol for abnormal or infected host cells and recognize changes in MHC I expression.
How do NK cells kill their target cells?
Apoptosis.
What do interferons (IFN-α and IFN-β) do?
Produced by infected host cells and protect neighboring cells.
How do AVPs stop viral replication?
Disable ribosomes.
What are the steps of MHC I antigen presentation?
Viral proteins broken into peptides, peptides enter ER, loaded into MHC I, and MHC I-antigen complex displayed.
What triggers inflammation?
Tissue damage, infection, TLR activation, complement fragments, mast cells, eosinophils, basophils.
What do cytokines do during inflammation?
Vasodilation, increased permeability, chemotaxis, margination, and diapedesis.
What are the signs of inflammation?
Heat, redness, swelling, and pain.
How do Corticosteroids work?
Block cytokine production → reduce inflammation.
When are Corticosteroids best used?
Best for autoimmune diseases, not ideal for infections.
What is a Cytokine Storm?
Massive cytokine release → dangerous inflammation.
What happens during a Cytokine Storm in COVID-19?
Vessels leak fluid into lungs → low oxygen saturation, respiratory failure.
What antigens does MHC I present?
Endogenous antigens (viruses).
What antigens does MHC II present?
Exogenous antigens (bacteria).
Where is MHC I found?
All nucleated cells.
Where is MHC II found?
Professional APCs only.
What does MHC I activate?
Cytotoxic T cells.
What does MHC II activate?
Helper T cells.
Adaptive Immune System
The specific, slower, but highly targeted part of your immune defense that adapts and 'remembers' pathogens for faster responses during reinfection.
Lymphocytes
Cells involved in adaptive immunity; include T cells and B cells.
Antigen
A molecule that is recognized as foreign by the immune system.
T Cell Receptors (TCR)
Found on T cells; bind antigens only when presented on MHC.
B Cell Receptors (BCR)
Found on B cells; can bind free-floating antigen without MHC.
Helper T Cells (CD4+)
T cells that contain CD4 protein, recognize MHC II + antigen, and differentiate into Th1 or Th2 cells.
Th1 Cells
Activate cytotoxic T cells.
Th2 Cells
Activate B cells.
Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8+)
T cells that contain CD8 protein, recognize MHC I + antigen, and kill infected host cells using perforin and granzyme.
Transmembrane Region (TCR)
Anchors the TCR in the cell membrane.
Constant Region (TCR)
The part of the TCR that is the same in all TCRs.
Variable Region (TCR)
The antigen-binding site of the TCR, unique for each T cell.
MHC
Major Histocompatibility Complex; presents antigens to T cells.
MHC Class I
Found on all nucleated cells; presents endogenous (intracellular) antigens; recognized by CD8+ cytotoxic T cells.
MHC Class II
Found only on professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs); presents exogenous (extracellular) antigens; recognized by CD4+ helper T cells.
Clonal Expansion (T Cells)
Process where activated CD8+ cells replicate to form effector cytotoxic T cells and memory T cells.
Perforin
Makes pores in the infected cell.
Granzyme
Triggers apoptosis in the infected cell.
B Cell Activation Signal 1
Binds antigen and presents on MHC II.
B Cell Activation Signal 2
Th2 cell binds TCR ↔ MHC II + antigen and CD40L ↔ CD40 for B cell activation.
Plasma Cells
Produce antibodies.
Antibody Structure
Y-shaped proteins with variable regions (arms) for antigen-binding and a constant region (stem) that determines class and function.
Neutralization (Antibody Function)
Block binding sites on toxins/viruses.
Agglutination (Antibody Function)
Clump pathogens together for easier removal.
Opsonization (Antibody Function)
Coat pathogen to enhance phagocytosis.
Complement (Antibody Function)
Trigger complement cascade → cell lysis and inflammation.
ADCC (Antibody Function)
Attract NK cells to kill antibody-coated cells.
IgM
First antibody made, good at complement, agglutination, neutralization.
IgG
Antibody found in blood/tissues, complement, ADCC, opsonization.
IgA
Antibody found in mucous membranes, tears, milk; does not cause inflammation.
IgE
Antibody involved in allergy, parasitic worm defense.
Affinity Maturation
Small mutations introduced into variable region during clonal expansion that can increase or decrease affinity.
What is the skin's role as a physical barrier?
A thick, waterproof layer of cells that is difficult for microbes to breach.
What role do secretions like tears and saliva play in defense?
Constant flushing of surfaces, making it harder for bacteria to attach; saliva swallowed goes into stomach acid.
What is the benefit of having a normal microbiome?
Microbial antagonism.
What are the two main goals of the innate immune system?
To eliminate or kill any invading pathogen and to alert the adaptive immune system that it might be needed.
What are two key characteristics of the innate immune system?
They are nonspecific and inducible.
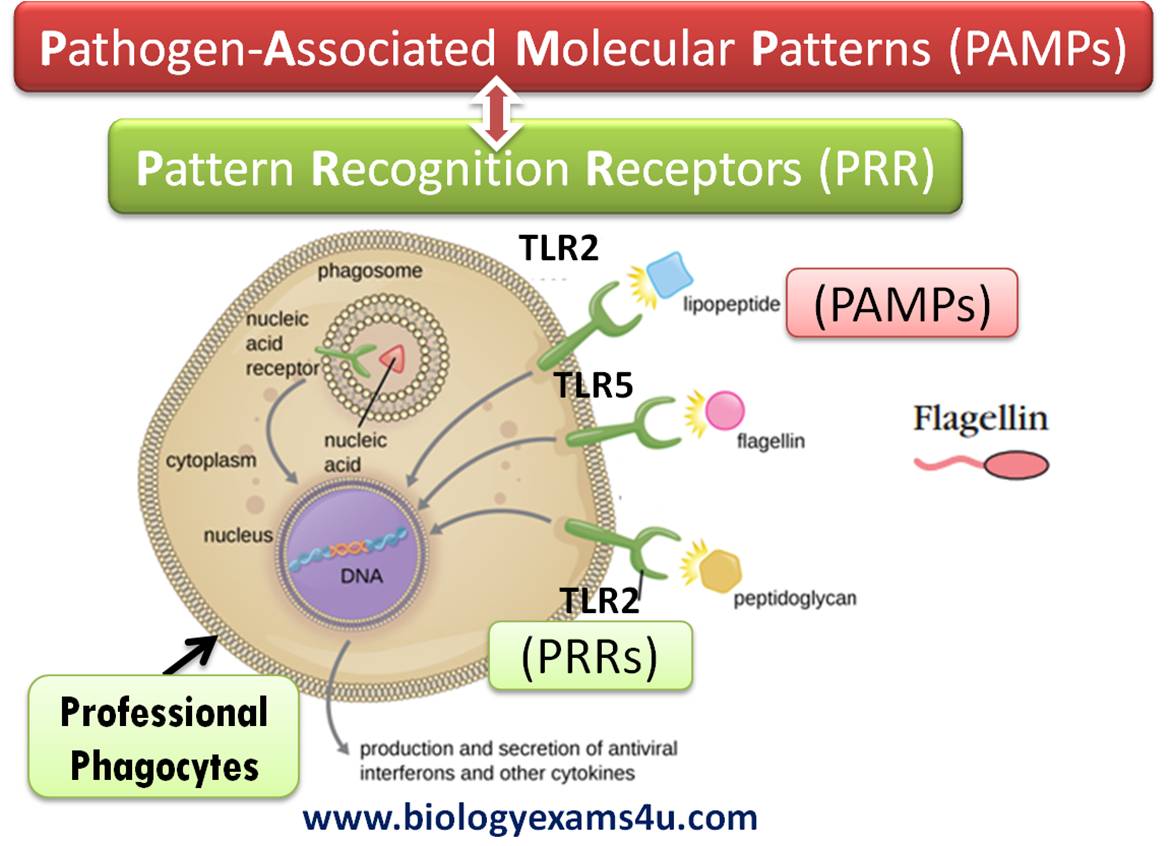
What are PAMPs?
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; common molecules or motifs on classes of microbes, like peptidoglycan.
How do immune cells communicate?
Immune cells release cytokines to communicate with other immune cells.
Why is it critical for phagocytes to differentiate between self and non-self?
They must be able to tell the difference between self and non-self to prevent autoimmunity and damage to the body's own cells.
What characteristics can phagocytes look for to identify pathogens?
Structures or molecules found exclusively on bacterial cells, fungi, or viruses, but not in human cells.
How do innate immune cells recognize PAMPs?
By using Toll-like Receptors (TLRs).
What is the innate immune system meant to do?
To kill any invading pathogen and to alert the adaptive immune system that it might be needed
What patrols for and finds foreign bodies within the body.
The pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), patrol the interstitial space, sensing any foreign material that may enter the body.
Give three specific characteristics the immune system can look for within a cell.
Peptidoglycan, LPS, and mycolic acid
Name three structures a phagocyte can check for when determining what is self and what is not.
Plasmids, bacterial DNA, double stranded RNA
How does the phagocytosis reaction begin?
Toll-like receptors bind to the PAMP on the surface of a microbe triggering that response.
What does pus consist of.
Neutrophils die at site of infection and that accumulation is pus.
Besides phagocytosis, what power do macrophages and dendritic cells have in addition to it?
An antigen presentation.
What are the two professional antigen presenting cells?
Macrophages and dendritic cells.
Is phagocytosis the goal of a natural killer cell?
Releases poisons.
What results from cellular toll like receptors.
Trigger the production of interferon.
What is the outcome disparity from stimulating intracellular and extracellular toll like receptors triggers?
Extracellular toll like receptors trigger phagocytosis. Cellular toll like receptors trigger the production of these molecules called interferon.
What is the topic of the last homework?
The last homework assignment is about vaccines.