HSCI Chapter 3
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are basic cellular functions?
Cell metabolism (Catabolic and Anabolic), maintaining shape and integrity, dispose of waste, and cell reproduction.
What are key features of a general cell structure?
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm (Cytosol, organelles, and cytoskeleton), and nucleus
Plasma Membrane Structure
Phospholipid bilayer with membrane proteins, cholesterol, and glycolipids/proteins. 2 layers of phospholipid molecules. Hydrophilic head - Pointed both inside and outside of cell. Hydrophobic tail - Keeps water from getting in or out.
Plasma Membrane Functions
Physical barrier, selective permeability, communication, and cell recognition
Integral Proteins
Hydrophobic areas interact with lipid tails and hydrophilic areas interact with water. Function as transport proteins
Peripheral Proteins
Enzymes, cell to cell communication, structural support. Only on one side of the membrane. Inside or out.
Leaky Channel Proteins
Integral protein. Facilitated diffusion. A tunnel that allows substances to enter or exit the cell. Always open. Anything with a charge (ion) can enter.
Gated Channel Protein
Integral protein. Facilitated diffusion.Tunnel that allows substances to enter or exit the cell. Closed by a gate. Opened by a chemical binding to the channel or a voltage change. Anything with a charge (ion) can enter.
Carrier Protein
Integral protein. Closed until the substance binds to the protein. Changes the protein’s shape to allow the substance to pass through. Only open one direction at a time. Small polar molecules (amino acids and glucose) can pass through.
Glycocalyx
Glycolipid/protein. Carbohydrate attached to a lipid or a protein. Important for cell recognition and the immune system. Extracellular, attached to the plasma membrane.
Cholesterol
Stabilized plasma membrane fluidity. Makes sure it isn’t too tight or loose. Resists temperature changes. Embedded in plasma membrane with slight extracellular portion.
Passive Transport
Movement of solutes from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentrations (Between extracellular and intracellular fluids). Diffusion (simple and facilitated) and osmosis.
Diffusion rate is dependent on…
Steepness of gradient, temperature (High temp = faster), distance molecules must move (Closer = faster), surface area (larger = faster), molecule size (smaller = faster)
Simple Diffusion
Diffusion dependent on concentration gradient only. Used by nonpolar solutes (Ex. O2, CO2, lipids)
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion dependent on transport proteins and concentration gradients. Used by charged or polar solutes (Ex. Ions - Cl- and Ca2+, Glucose). Carrier and channel proteins used.
Osmosis
Movement of water across plasma membrane. Through lipid bilayer on its own or through an aquaporin. Needs a water molecule concentration gradient (High water to low water). High water concentration = Low solute concentration
Tonicity
Ability of an extracellular solution to make water move in or out of a cell via osmosis. Iso, hypo, and hyper tonic concentrations.
Isotonic
Same concentration of solution in the extracellular and intracellular fluid
Hypotonic
More solute/less water molecules in the intracellular fluid. Water flows into the cell. (ECF < ICF). Swollen red blood cell.
Hypertonic
Less solute/more water molecules in the intracellular fluid. Water moves out of the cell. (ECF > ICF). Crenated red blood cell (Shriveled up)
What are the three types of active transport and what are the universal processes of all three?
Primary, secondary, and vesicular. They all require energy to function.
Primary Active Transport
Transport where solutes are pumped from low to high concentration using ATP directly. Ex. Calcium, hydrogen, Na+/K+ pumps
How does ATP give energy?
Hydrolysis of phosphate bonds in the ATP molecule release energy that change the shape of the transport protein pump.
Na+/K+ Pump
Type of primary active transport. Pushes against the concentration gradient. 3 Na+ pumped out for every 2 K+ ions pumped in. Uses 40% of the body’s ATP. Essential for electrochemical gradients.
Na+ is primarily where in the cell?
Outside
K+ is primarily where in the cell?
Inside the cell
Cl- is primarily where in the cell?
Outside
Ca2+ is primarily where in the cell?
Outside
Proteins are primarily where in the cell?
Inside
Secondary Active Transport
Required energy comes indirectly from ATP made during primary. Can’t happen without primary because glucose hitches a ride on the Na+ gradient.
Uniport Transport Protein
One substance is moved one way (in or out of the cell)
Symport Transport Protein
2+ substances moved in the same direction (in or out of the cell)
Antiport Transport Protein
2+ substances moved in opposite directions (in and out of the cell)
Vesicular Transport
Used for large polar macromolecules. Moved in and out of the cell in a vesicle.
Vesicle
Membranous enclosed sacs that envelop large polar macromolecules. Require ATP. Don’t require concentration gradients
Endocytosis
Bring into cell
Exocytosis
Bring out of the cell
Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
Difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane when the cell is at rest. Determined by the ion/molecule charges. Inside of the cell is negatively charged compared to the outside.
What are the conditions for establishing RMP?
Unequal distribution of ions/molecules (positive/negative charges) across the plasma membrane
What are the conditions to maintain RMP?
Selective permeability (Keeping negatively charged proteins trapped) and Na+/K+ pumps to keep the concentration gradient maintained
Cytosol
Gel like substance in a cell that supports organelles
Non Membranous Organelles
Organelles that are freeballing in the cytosol.
Non Membranous Organelles Examples
Cytoskeleton, Ribosomes, and Centrosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of tubes and cisterns that accounts for half of the cells membranes. 2 kinds, smooth and rough.
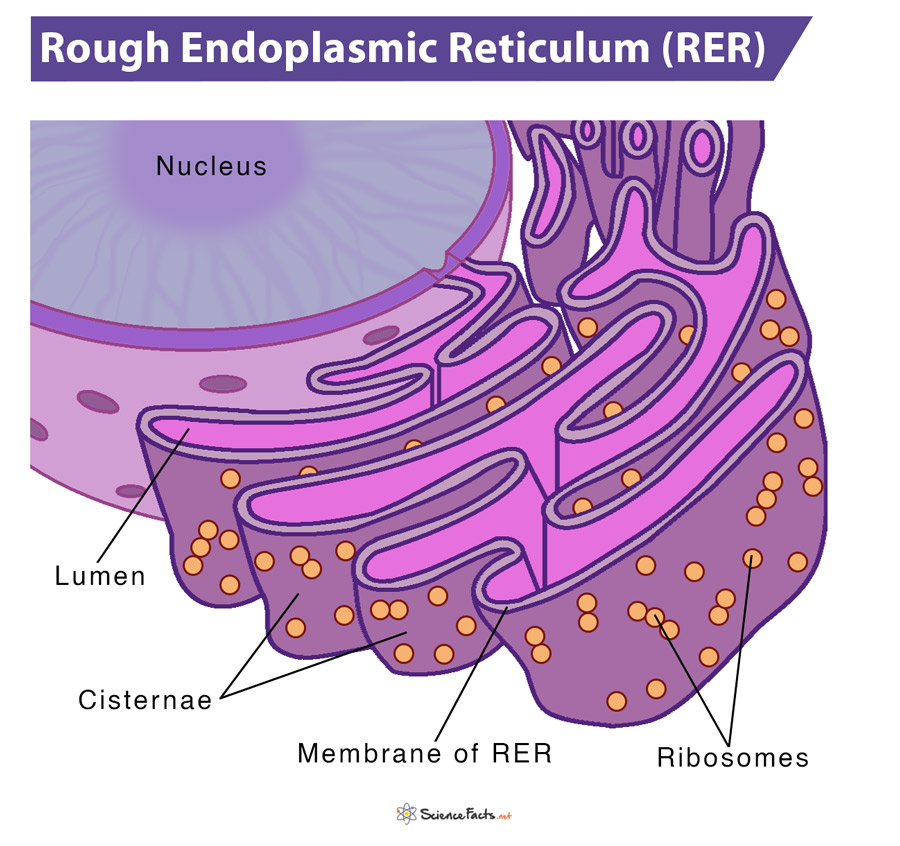
Rough ER
Contains ribosomes, interconnected cisterns, and is continuous with the nuclear envelope. The ribosomes manufacture all proteins secreted from cells (Ex. Immune and liver cells). Form the integral proteins and phospholipids used in the cell membrane.
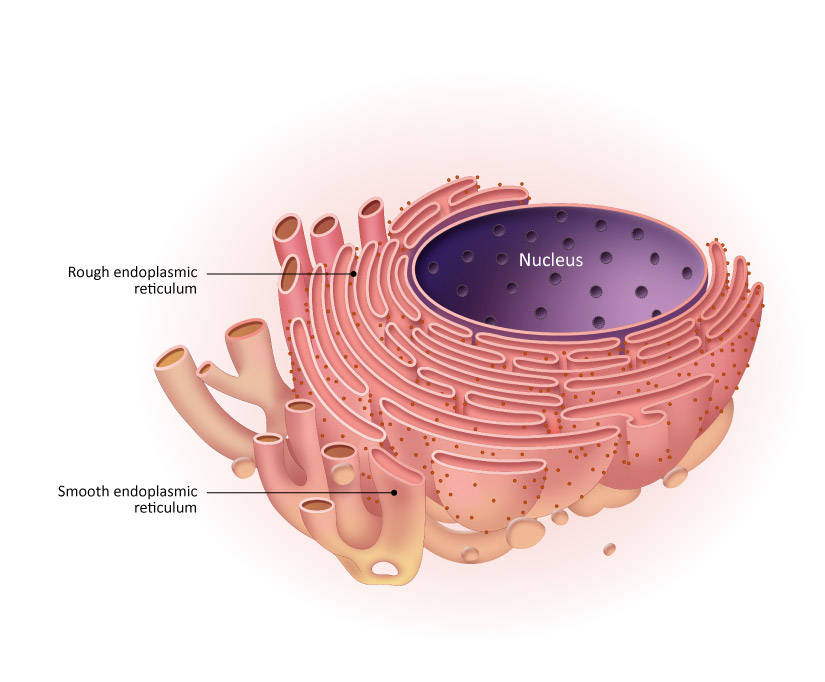
Smooth ER
Continuous with the rough ER and is made up of looping tubules. No ribosomes. Metabolizes lipids, synthesizes steroid based hormones, detoxifies drugs, breaks down glycogen, and stores calcium ions.
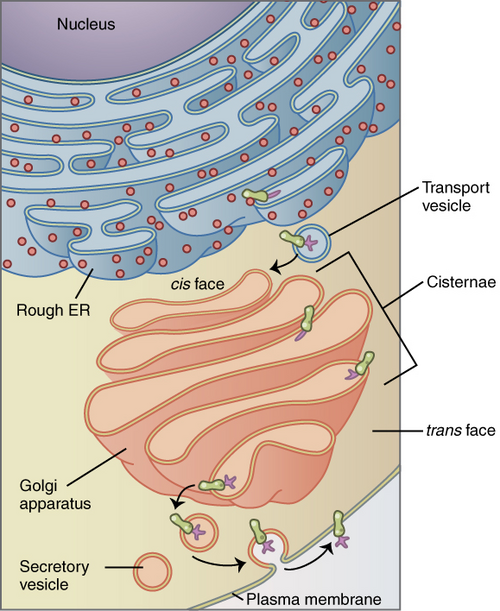
Golgi Apparatus
Stacked, flattened cisterns. Not connected to the nucleus. Modifies, concentrates, and packages proteins and lipids made in the ER. Forms vesicles for the exocytosis of proteins and lipids.
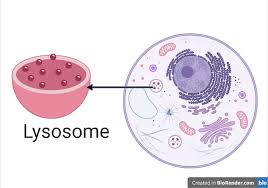
Lysosomes
Spherical membranous bags that contain digestive enzymes. Digest foreign substances, non functional organelles, and injured/damaged cells. Also aids in metabolism.
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs that are slightly larger than ribosomes. Contain detoxifying substances. They oxidize toxins into hydrogen peroxide and help breakdown fatty acids.
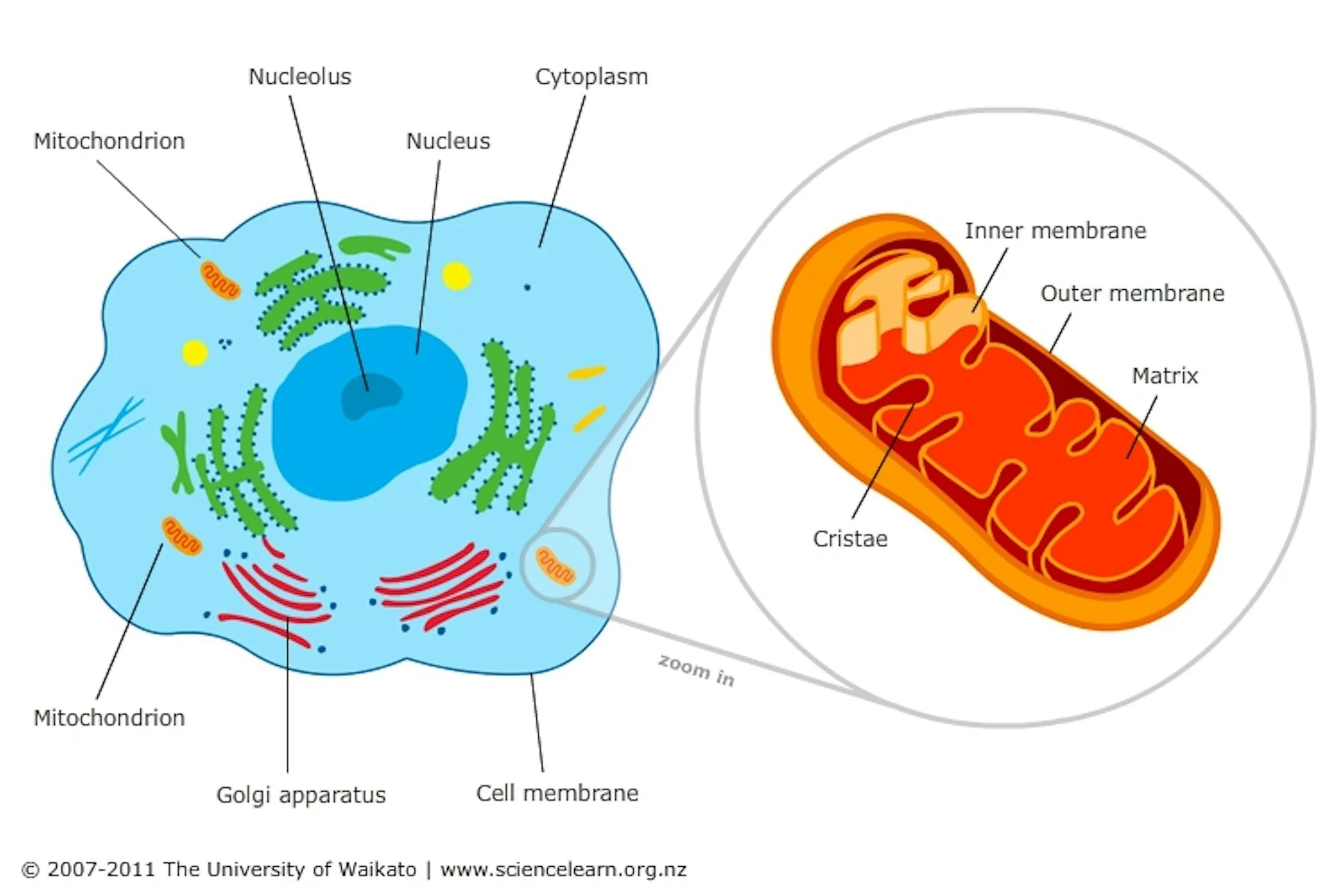
Mitochondria
Contains a double layer membrane. Outer layer contains large channels with openings that allow substances in and out of the cell. Inner layer has multiple folds (cristae) that’s embedded with membrane proteins. Inner layer executes the cells main function, the creation of ATP through cellular respiration.
Nucleus
Made up of the nuclear envelope (With the nuclear pores which allow substances in and out), the nucleolus (makes ribosomes), and the chromatin (condensed chromosomes). It directs the activities of other cellular components and participates in ribosome and genetic synthesis. Has it’s own DNA. Not every cell will have a nucleus.
Ribosomes
Tiny granular organelles with large and small subunits. Composed of ribosomal proteins and RNA. Bound to the rough ER or free in the cytoplasm. Synthesizes proteins.
Microvilli
Short and thick finger like extensions on the outside of a cell. Increase surface area allowing for greater absorption.
Cilia
Thin and long hair like projections on the outside of a cell. Move substance across and away from a cell.
Flagella
Single long extension that propels a whole cell. Ex. Sperm
Name the intracellular junctions
Tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions.
Tight Junctions
Hold cells tightly together to stop molecules from moving between cells.
Desmosomes
Zips cells together (Looks like a zipper). Resists mechanical stress and keeps cells together.
Gap Junctions
Look like butterfly stitches. Small pores within protein channels that aid electrical signal cell to cell communication.