242 Lab 1: Reduction of Camphor
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
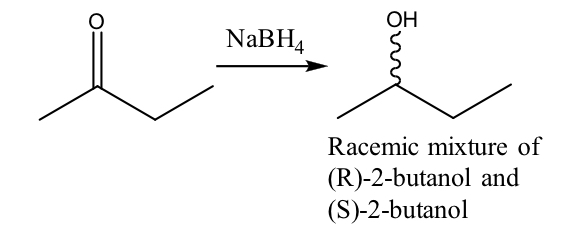
What stereochemistry is produced when ketones are reduced?
ketones are flat so they generally give both stereoisomers of an alcohol
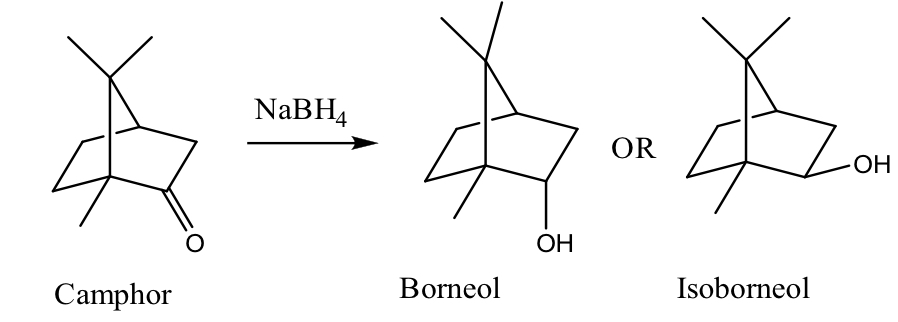
what are the possible products of camphor and NaBH4?
diastereomers of one another, new chiral center
why is sodium borohydride attractive for use?
ease of handling, does not react as violently with water so it can be used in alcohol based solvents, used in excess to avoid losing too much
mechanism of NaBH4 reduction?
delivery of a hydride at the electrophilic carbon of the ketone four times to generate a tetraalkoxycarbon compound, this can then be decomposed, at elevated temperatures
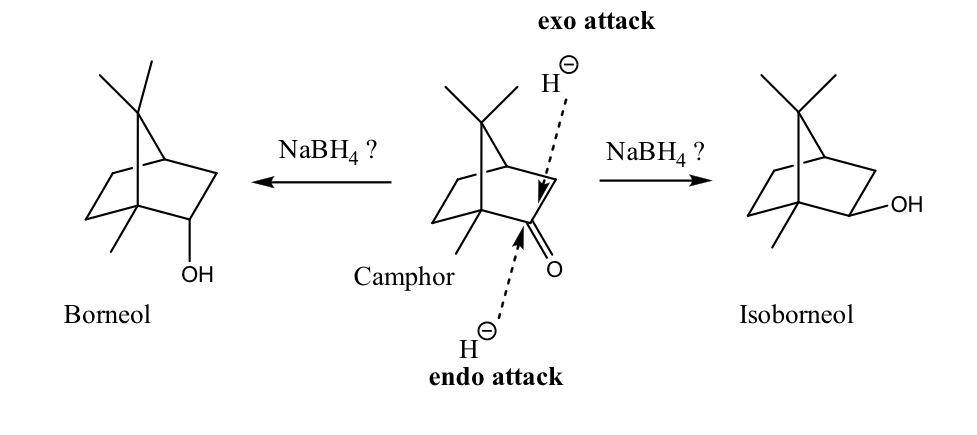
what are the different attacks a hydride can do on camphor?
endo or exo attack
what is the safety information?
NaBH4 reacts vigorously with water & releases H2 gas, avoid mixing with aqueous solns, acetone and methanol are highly flammable
procedure
dissolve camphor in methanol and stir @ room temp, add NaBH4 in 2 portions, heat until boiling, continue heating 5 min then cool to room temp
procedure for isolation of borneol and isoborneol
cool rxn in ice bath, add cold H2O, white solid appears, collect on buchner funnel, filter and allow dry for 5 min
procedure for purification and characterization
rinse product off paper w/ hexanes, fully dissolve product, dry over Na2SO4, decant, evaporate hexanes soln w/ air, and take mp
how to normalize GC spectra?
remove unwanted peaks, renormalize remaining peaks by added wanted peaks areas dividing each peak area by the total area
what analysis techniques were used?
NMR, GC-MS
borneol vs isoborneol H-C-O nmr shift
borneol: 4 ppm, isoborneol: 3.6 ppm
what was the major product according to NMR and GCMS?
NMR: isoborneol because of 3.6 peak
GCMS: largest % due to summary sheet
why did the reaction show this selectivity?
the hydride will attack the less hindered side of camphor
does the reaction favor an endo or exo attack?
endo attack
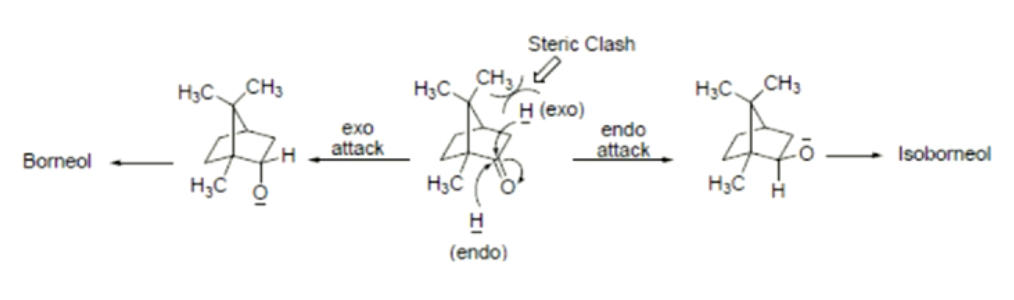
what kind of reaction is this?
irreversible reaction, under kinetic control so whichever one has the more stable TS will be the major product
why don’t we need a reflux condenser for this reaction?
the reaction is over so quickly that barely any solvent will have boiled away
what would tell us if camphor was transformed into borneol + isoborneol?
mp, IR (above 1500 cm^-1), NMR (3-5 ppm), NMR (below 3 ppm) (absence of CH next to C=O at 2.5 ppm), MS (molecular ion peak)
which of these would tell us if the major product was borneol or isoborneol?
NMR (between 3-5 ppm), MS (fragmentation pattern) if computer assistance
why were the webmo chemical shifts for the OH peak different than the literature values?
webmo doesn’t take into account intermolecular interactions, only looking at a single molecule so it doesn’t show the deshielding of the OH peak accurately, not representing the H bond strength
camphor has ___ chiral centers and borneol has ___ chiral centers.
camphor has 2 chiral centers and borneol has 3 chiral centers
borneol and camphor are ______ of each other.
not isomers
why is water not a suitable solvent?
the NaBH4 would decompose in H2O so no reaction would occur and camphor is not soluble in H2O so no reaction would occur