Year 8 Science - PHYSICS
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the 4 types of potential (stored) energy?
Gravitational
Elastic
Chemical
Nuclear
What are the 5 other types of kinetic energy?
Kinetic
Heat
Thermal
Sound
Light
What are waves?
A wave is able to transmit energy from one place to another without moving any matter over this distance.
What are the two types of waves?
Transverse
Longitudinal
What is the best known example of longitudinal waves?
sound
Sounds Travel at Different Speeds:
The higher the temperature…
the faster the particles of the medium will move and the faster the particles will carry the sound.
How do we calculate energy efficiency?
useful output energy/total input energy
What are the three ways of energy transfer?
conduction, convection and radiation
In what medium does conduction occur?
in solids
In what medium does convection occur?
in fluids (liquids and gases)
In what medium does radiation occur?
in empty space
What is conduction?
The transfer of heat energy as a result of neighbouring vibrating particles.
What substance has high thermal conductivity?
metals and fluids
What substance has low thermal conductivity?
plastics
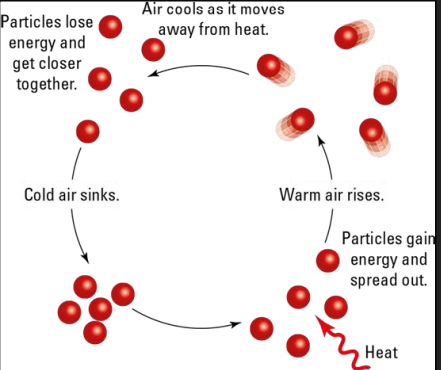
What is convection?
The transfer of heat energy by the movement of particles from one region to another in liquids and gases. Cycle of these are called convection currrents.
How do you reduce convection?
By stopping the free flow of fluids.
What is a similarity between conduction and convection?
Both involve particles gaining kinetic energy.
What is radiation?
Heat that is transferred without the presence of particles at all, as electromagnetic radiation. The energy is carried by infrared waves.
Radiation:
The hotter an object is…
the more radiation it emits.
Energy transfers and transformations are never 100% efficient. Some energy isalways wasted in the process of transfer or transformation usually as…
heat energy.
What is a conductor?
A material that allows the flow of electricity through it with very little resistance.
energy
Kinetic energy
Light energy
Electrical energy
Thermal (heat) energy
Sound energy
Potential energy
Gravitational energy
Elastic energy
Chemical energy
How do we measure energy?
Joules (J) or Kilojules (KJ)
1 KJ = 1000 J
What is the law of Conservation
That energy can never be created or destroyed. Energy is conserved or kept as it is converted from one form to another.
what is energy transfer?
Energy transfer is when energy is relocated from one form to another. E.g. Kinetic energy being transferred from a persons foot to the ball.
What is energy transformation?
When energy changed form. E.g Electrical energy turning into sound energy
What is energy efficiency