METEROLOGY EXAM 3 ALRDICH MIZZOU
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Definition of fronts
Transition zones between air of different densities
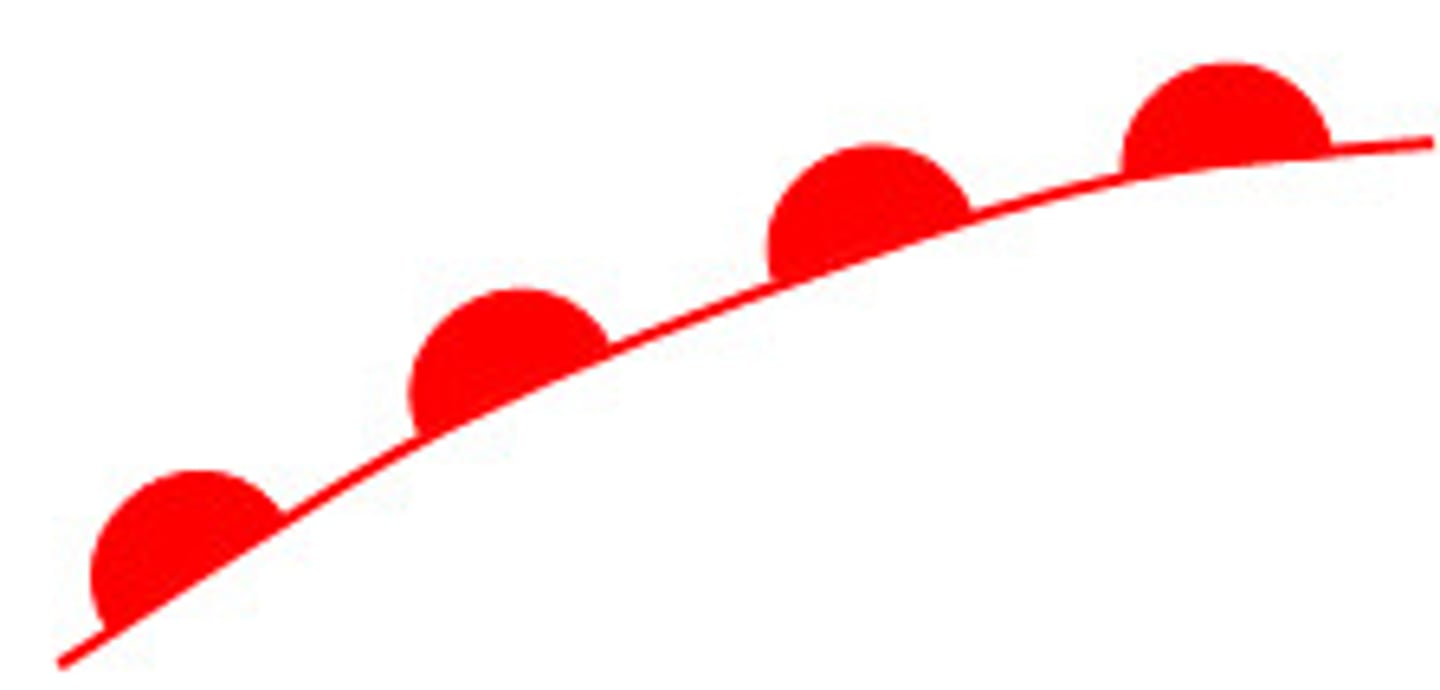
Warm Fronts
red ovals pointing in the direction of warm air advancing, light rain
IMAGE: warm fronts
most warm at inner center

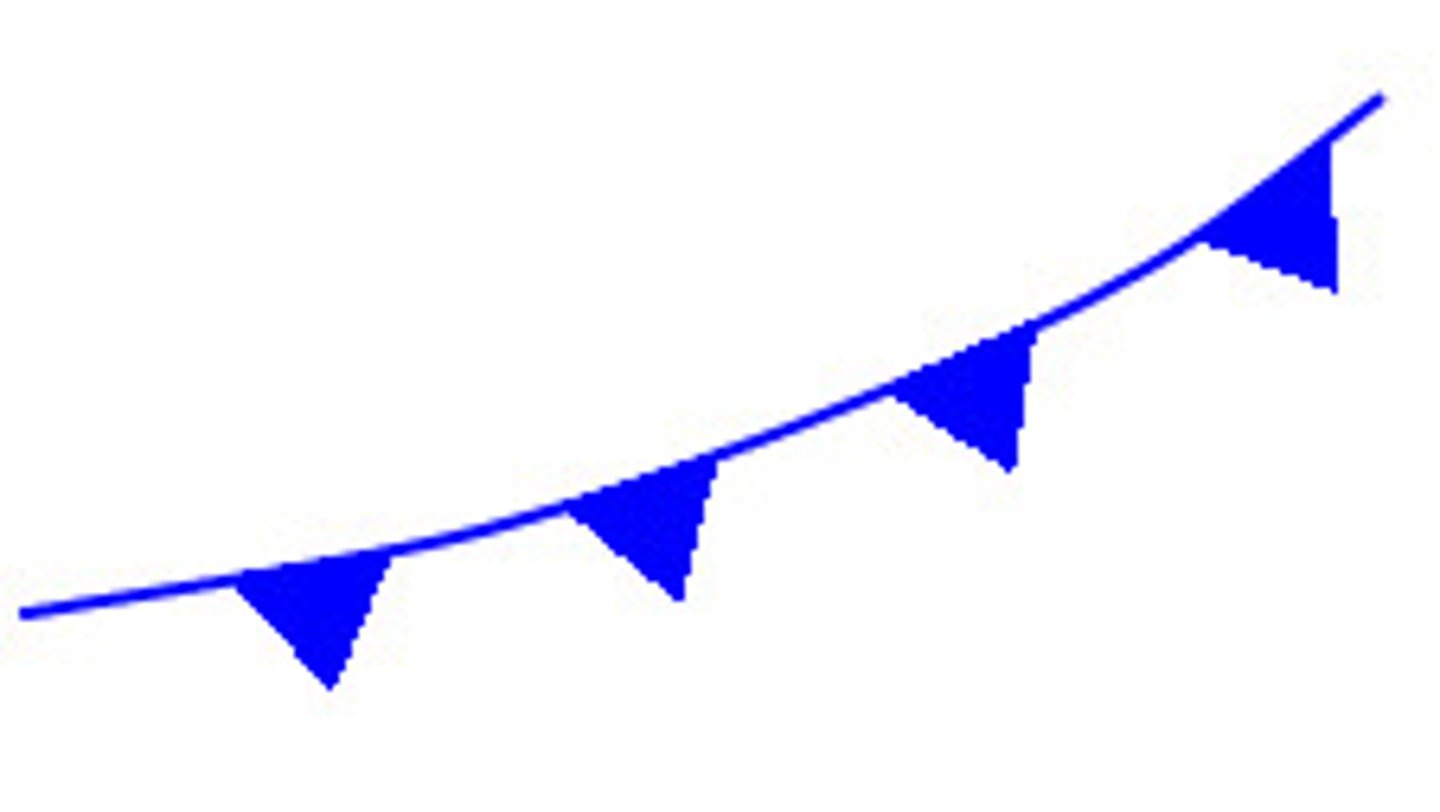
Cold Fronts
blue triangles pointing in the direction cold air is advancing, active weather along the cold front
IMAGE: cold fronts
coldest on the center of the line

Stationary Front
red and blue, essentially no movement, difference in air masses (north and south of front)
IMAGE: Stationary Front
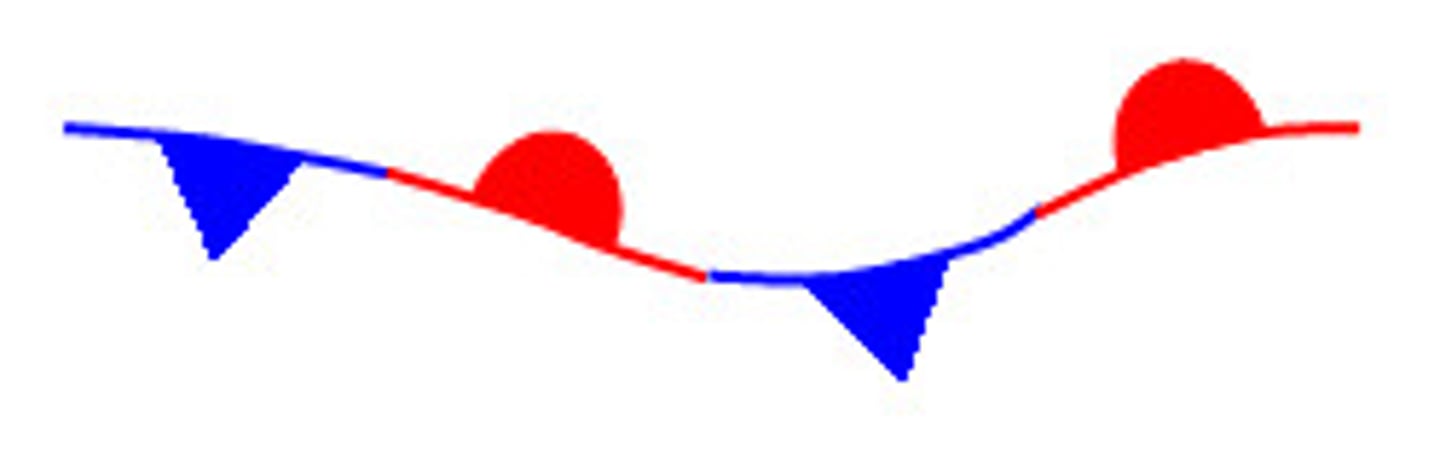
Occluded Front
Purple drawn in alternating "pips" (pointing parts) where cold and warm air collide, attatched to STRONG low-pressure systems
IMAGE: Occluded Front
colder within circle, warmer on outside

Dryline Front
yellow tight "pips", separates dry and moist air
IMAGE: Dryline Front
lol sorry no image was available but tight half circles on outer edge
Frontogenesis definition
an increase in temperature contrast across a front can cause it to strengthen
Frontolysis definition
as the temperature contrast across a front lessens, the front will weaken and dissipate
REGION: Continental Polar (cP) and Continental Arctic (cA)
forms over ice and snow covered regions of Alaska and Canada and moves cold air south to Central US
WEATHER: Continental Polar (cP) and Continental Arctic (cA)
cold air moving south, but as it moves south it warms. cP air moving over Gulf of Mexico gains moisture and becomes maritime.
REGION: Maritime Polar (mP)
forms over cold waters like the North Atlantic or Pacific and moved inland over the Pacific Northwest (Washington/Oregon)
WEATHER: Maritime Polar (mP)
causes major winter storms, precipitation to west coast, moisture to New England storms
REGION: Maritime Tropical (mT)
warm moist air from sub-tropical Pacific, Gulf of Mexico and other south atlantic areas. moves inland
WEATHER: Maritime Tropical (mT)
warm, moist and unstable weather
REGION: Continental Tropic (cP)
hot and dry air masses originate over the deserts of Mexico
WEATHER: Continental Tropic (cP)
hot and very dry
What is a jetstream?
fast flowing air currents found in the atmosphere around 36,00 ft (just under tropopause)
How is the jetstream separated?
north is cold, stormy and wet weather (trough). south is warm, calm weather (ridge)
Subtropical jetsream
"southern jetstream", around latitutde 30
Polar jetstream
"northern jetstream", around latitude 30 and 60
Low Level Jetstreams (LLJ)
close earth's surface, forms over central plains. strongest at night, weakest at midday
What is a high pressure system?
clockwise wind flow, pushes air away, weather is fair and settled
What is a low pressure system?
counter clockwise wind flow, brings air in, inclement weather
What is the general circulation of the atmosphere
wind, movement of air around the planet
Where are the midlatitudes?
30-60 (middle of the world)
Why is weather so changeable?
Because wind blows jet stream around and changes weather
WHERE: Hadley Cell
0 to 30
WHAT: Hadley Cell
surface winds North to South and turning right by Coriolis, starts at equator with warm rising air
MOTION: Hadley Cell
heat up, direct, cold down
WHERE: Ferrell Cell
30 to 60
WHAT: Ferrell Cell
surface winds move south to north and turn right, large air contrast, air sinks over subtropical high
MOTION: Ferrell Cell
cold down, indirect, heat up
WHERE: Polar Cell
60 to 90
WHAT: Polar Cell
surface winds north to south and turn right, sinks at polar high because dense and cold. meets air from subtropical high and rises
ITCZ: Inter Tropical Convergance Zone
belt of low pressure close to equator where trade wints of north and south hemispheres meet
El Nino:
WARM, ocean current in Pacific around Christmas
La Nina:
COOL
Land and Sea Breezes
- a type of thermal circulation
- uneven heating rates of land vs. water create mesoscale coastal winds
- caused by temperature difference
Land breeze
wind blows from high pressure water to low land during NIGHT
Sea Breeze
wind blows from high pressure water to low land during the DAY
Monsoons
seasonally driven change in wind direction caus eby high pressure on land, wind blows from land to water
Wet Monsoon
summer, wind blows from sea to land
Dry Monsson
winter, wind blows from land to see
Wind direction
the direction from which the wind is blowing
Wind vane
spins on a post until arrow points into the wind (direction only)
Barometer
measures air pressure
Anemometer
cups on a poll and spins around faster in stronger wind (speed only)
Pilot Balloon (Weather Balloon)
instrument that takes in temperature, humidity, pressure and wind, radisonde
Radiosonde
instrument package on a weather balloon to measure air pressure, humidity, temperature, wind speed, and wind direction of the upper atmosphere
Planetary
longwaves in westerlies, 10,000 km or large, weeks or longer
Synoptic
high and low pressure systems and hurricanes, 500-2,000 km, days to weeks
Mesoscale
fronts and thunderstorms (severe weather), few-500 km
Microscale
tornados and smaller winds, less than 1 km, minutes to hours
PBL (planetary boundary layer)
microscale and mesoscale, atmospheric boundary and friction layer, SURFACE FRICTION
PGF: Pressure Gradient Force
makes wind move due to change in air pressure, measured by isobars, moving high pressure to low pressure
Coriolis Force
makes wind move due to rotation of the earth, causes wind to deflect to the right of intended path
Friction Force
reduces wind and Coriolis Force
Air will always flow from areas of ____ pressure to areas of ____ pressure
high, low
Equation of State
demonstrates that pressure, temperature, and density are related