Econ Chapter 5 Elasticity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
elasticity
measure of how much one economic variable responds to changes in another economic variable
price elasticity of demand/supply
the responsiveness of the quantity demanded/supplied to a change in price
price elasticity formula
% in quantity demanded or supplied
% change in price
elastic demand or supply
when % change in quantity is GREATER than the % change in price
inelastic demand or supply
when the % change in quantity is LESS than the % change in price
unitary elastic demand or supply
when the % change in quantity EQUALS the % change in price
midpoint formula
for price elasticity
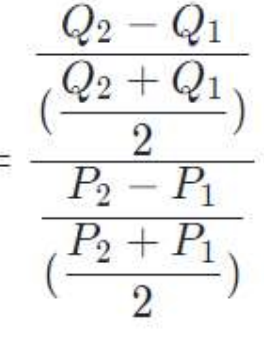
steeper slope
less elastic
flatter slope
more elastic
if a product has MORE substitutes available…
it will have MORE elastic demand
if a product has LESS substitutes available…
it will have LESS elastic demand
the MORE time passes…
the MORE elastic demand for a product becomes
the demand curve for a LUXURY is…
MORE elastic than the demand curve for a NECESSITY
the MORE narrowly a market is defined…
the MORE elastic demand will be
perfectly inelastic demand/supply
when the quantity is completely unresponsive to price and price elasticity = 0
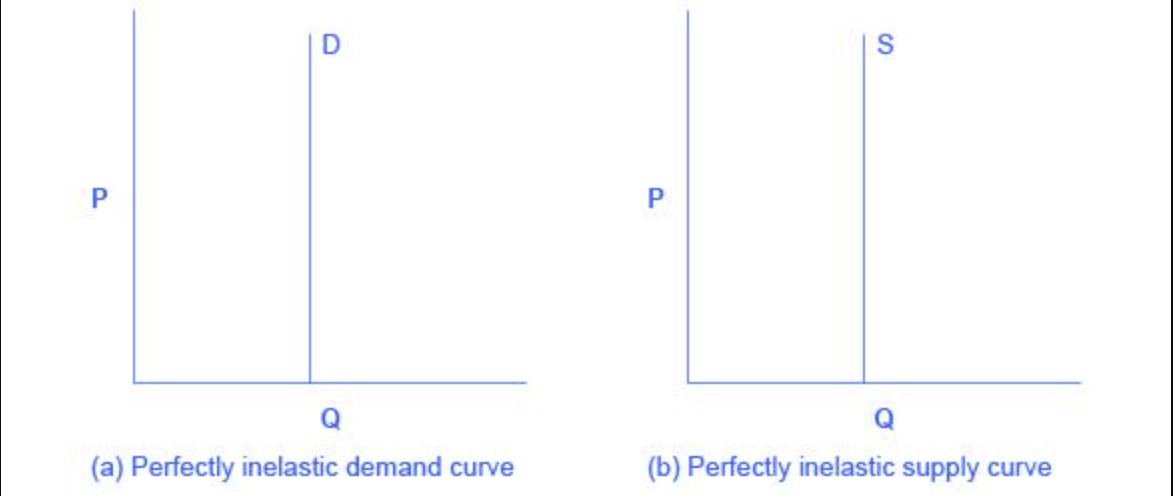
perfectly elastic demand/supply
when quantity is infinitely responsive to price, and the price elasticity = infinity
constant unitary elasticity
when a price change of 1% results in a quantity change of 1%
total revenue
total amount of funds received by a seller of a good or service (Total revenue = Price x Quantity)
excise tax
a wedge between the price paid by consumers and the price received by producers
when demand is more elastic than supply…
the tax incidence on consumers is lower than producers
when supply is more elastic than demand…
the tax incidence on consumers is larger than producers
cross-price elasticity
the % change in quantity demanded of one good divided by the % change in the price of another good
income elasticity
% change in quantity demanded divided by % change in income
if products are substitutes…
the cross price elasticity will be positive
if products are complements…
the cross price elasticity will be negative
if products are unrelated…
the cross price elasticity will be 0
if income elasticity is positive but LESS than 1…
then the good is normal and a necessity
if income elasticity is positive and MORE than 1…
the the good is normal and a luxury
if income elasticity is negative…
then the good is inferior