biology topic 7
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
joints
structures where bones and muscles connect to allow movement
tendons
join muscles to bone
white fibrous tissue
made of bundles of collagen fibres
strong but inelastic
ligaments
hold bones to bones in correct alignment while allowing movement
yellow elastic tissue
high elasticity
cartilage
tissue at ends of bones
hard flexible tissue
can be compressed
good shock absorber
protects bones from eroding
how is movement brought about?
antagonistic pairs of muscles that work in opposite directions - flexor and extensor muscles
synovial joints
most common type of joint - have synovial fluid and a surrounding synovial capsule e.g. hip, knee and ankle
fibrous joints
bones connected by fibrous connective tissue - fixed, non-moving e.g. in skull
cartilaginous joints
bones connected by cartilage - have more movement than fibrous joints but less than synovial e.g. between vertebrae
smooth muscle
non-striated, spindle shaped, uninuclear fibres
in walls of internal organs
involuntary
cardiac muscle
striated, branched, uninuclear fibres
walls of heart
involuntary
skeletal muscle
straited, tubular, multinuclear fibres
attached to skeleton
voluntary
myocyte
muscle cell
muscle cells
multinucleate
large
cytoplasm mainly made up of myofibrils
myofibrils
bundles of myofilaments
myofilaments
long repeated chains of contractile units called sarcomeres - made of actin and myosin filaments
actin
thin filament - many monomers with myosin binding sites - covered by tropomyosin and troponin
myosin
think filament - 2 globular heads with ATP and actin binding sites with a tail
sliding filament theory
the actin filaments move between myosin filaments, shortening the length of the sarcomere
relaxed state of actin
in absence of Ca2+ tropomyosin blocks myosin binding site on actin filament
muscle contraction process
nerve impulse causes Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ binds to troponin which pulls tropomyosin away from myosin binding site
myosin head attaches to actin forming a crossbridge
powerstroke initiated - myosin head pivots and bends, pulling the actin
ADP is released - myosin remains attached to actin
ATP binds to myosin head - crossbridge detaches
myosin ATPase hydrolyses ATP so myosin is ready to bind again
types of muscle fibres
fast twitch and slow twitch
twitch
a single muscle contraction that occurs in response to a single nerve impulse - all or nothing
summation
if a second nerve impulse occurs before relaxation is complete, the contraction of other muscle fibres is added, increasing overall contraction strength
slow twitch muscle fibres
slow, sustained, can remain contracted for long time
maintaining posture and steady movement
mostly aerobic respiration
precise control is possible
rich blood supply and high myoglobin content
fast twitch muscle fibres
fast contraction speed
sudden and quick movement
mostly anaerobic respiration
low blood supply and little to no myoglobin
no precise control
myoglobin
present in muscle cells
similar to haemoglobin - acts as an O2 store
has a higher affinity for O2 - will attract away from haemoglobin
how can you change your muscle fibre composition?
exercise - can alter the type and size of fibres
genetics - some people born with higher proportion of slow/fast twitch muscle fibres - better at some sports
phosphorylation
adding a phosphate to a molecule
redox reactions
reactions that involve both oxidation and reduction
hydrolysis
splitting a molecule using water
metabolic pathway
a series of small reactions
active transport
process that requires ATP
respiration
process that creates ATP
eukaryotic
have a true nucleus
catabolic reactions
breaking larger molecules into smaller ones
cristae
folds in mitochondria
photolysis
splitting a molecule using light
anabolic reaction
combining smaller molecules to make bigger ones
why do we need respiration?
muscle contraction
active transport
anabolism (making macromolecules)
warmth
steps of respiration
glycolysis
link reaction
Krebs cycle
electron transport chain
substrate level phosphorylation
production of ATP by transfer of P from a phosphorylated substrate
glycolysis
splitting glucose - in cytoplasm
steps of glycolysis
glucose —> 2x GALP using 2x ATP
2x GALP —> 2x pyruvate
second part produces 4x ATP and 2x NADH
equation for glycolysis
glucose + 2 ADP + 2 P + 2 NAD+ —> 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH
equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O
equation for anaerobic respiration
C6H12O6 —> 2 C3H6O3
link reaction
in matrix of mitochondria
steps of link reaction
pyruvate has CO2 removes
NAD+ —> NADH
pyruvate has CoA added to form acetyl CoA
equation for link reaction
2 pyruvate + 2 NAD+ —> 2 acetyl CoA + 2 NADH + 2 CO2
Krebs cycle
in matrix of mitochondria
also called citric acid cycle
Krebs cycle process
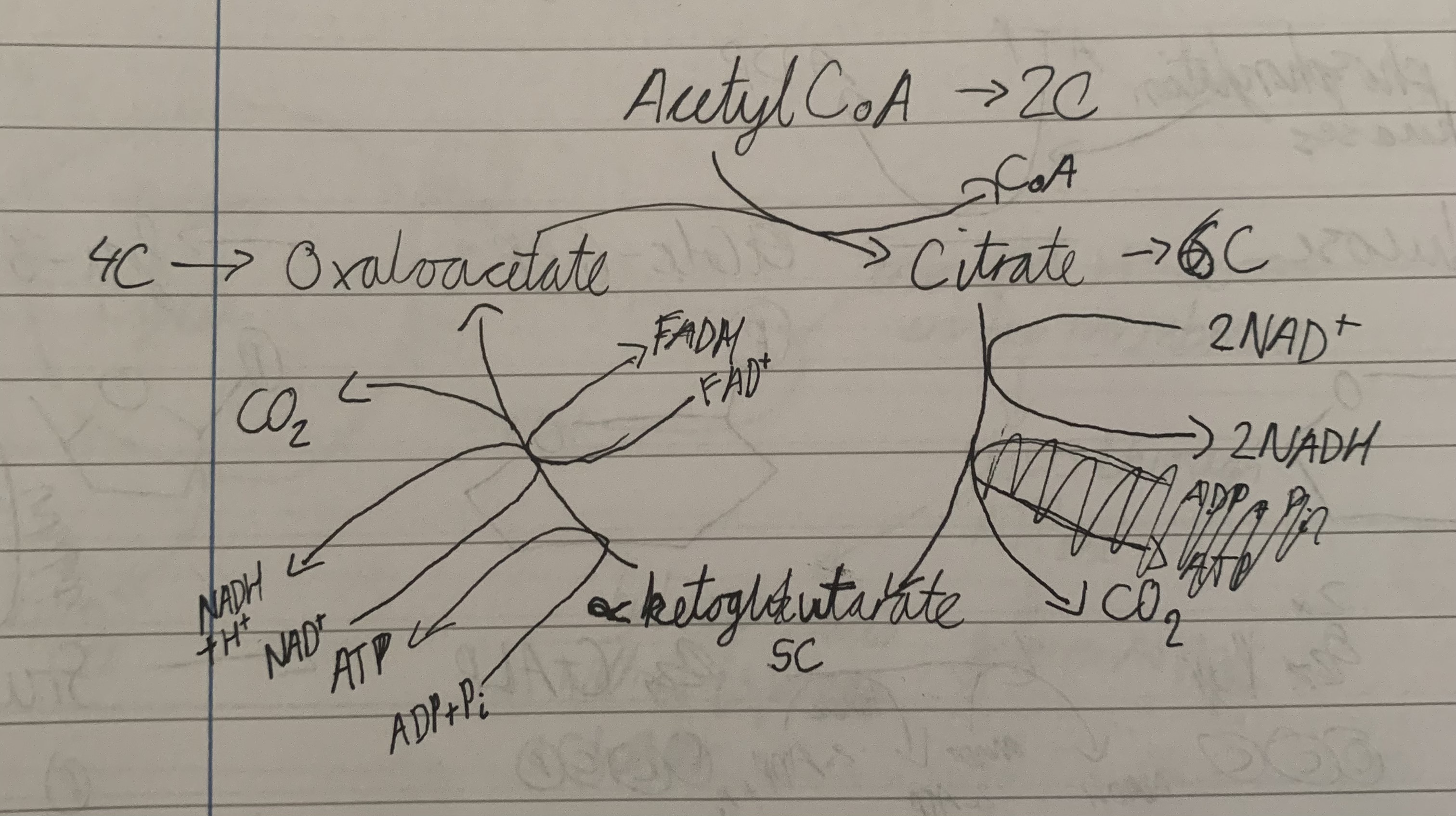
Krebs cycle equation
2 acetyl CoA + 6 AND+ + 2 ADP + 2 P + 2 FAD —> 4 CO2 + 6 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 FADH2
NADH
coenzyme
functions as a reducing agent carrying hydrogen
reduced form - NADH
FAD
coenzyme
functions as a reducing agent carrying hydrogen
reduced form - FADH2
electron transport chain
electron transport and chemiosmosis
on inner membrane of mitochondria
electron transport in ETC
respiratory enzyme complexes transport electrons (in a series of redox reactions) and pump H+ out of the matrix
the final electron acceptor in O2 leading to the production of H2O
chemiosmosis and oxidative phosphorylation in ETC
the resulting electrochemical H+ gradient is used by ATP synthase to make ATP
electron transport chain diagram
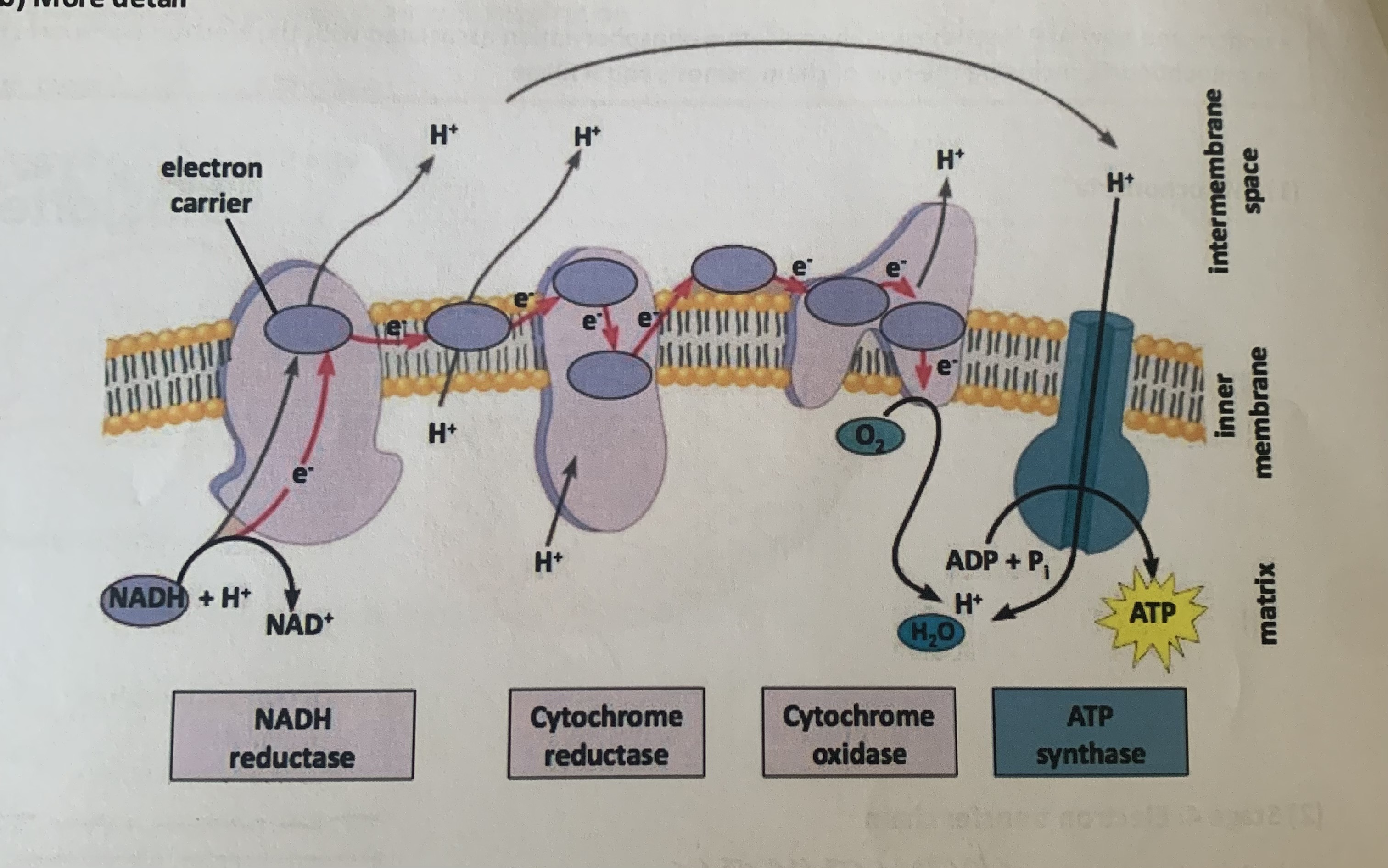
chemiosmosis
movement of H+ across a selectively permeable membrane during respiration down their electrochemical gradient
oxidative phosphorylation
production of ATP in a process where energy is released in the ETC, the energy is used to establish the H+ gradient which power ATP synthase
ETC equation
10 NADH + 10 H+ + 2 FADH2 + 34 ADP + 34 P + 6 O2 —> 10 NAD+ + 2 FAD + 34 ATP + 6 H2O
why is the maximum yield of ATP not achieved?
leaky membranes
energy cost for transporting pyruvate and ADP into mitochondria
what factors affect the rate of respiration?
pH
temperature
enzyme concentration
substrate concentration
what are the advantages of respiration being enzyme controlled?
controlled release of energy
prevents cell form overheating
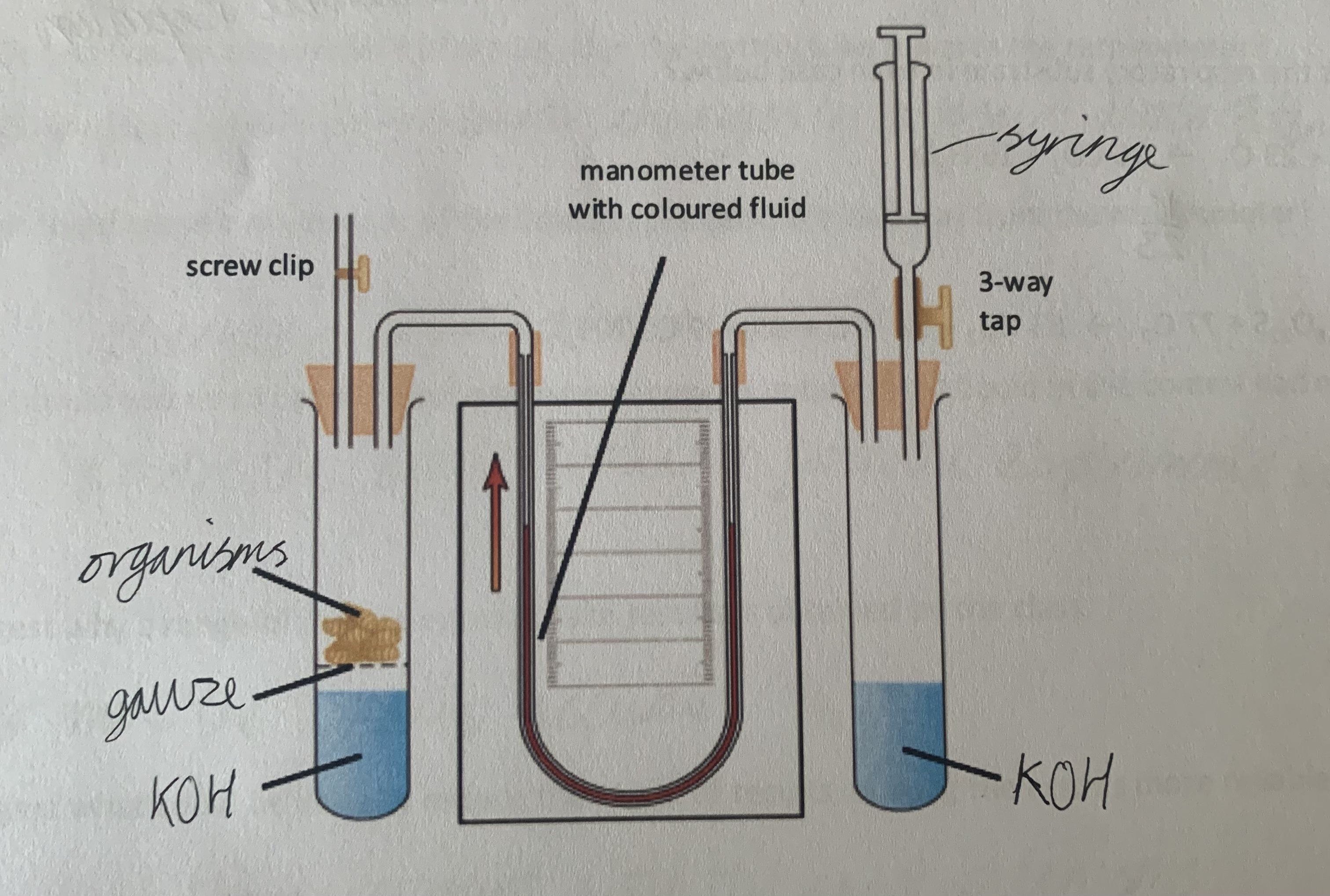
respirometer
used to measure the rate of respiration by measuring the rate of oxygen consumption
equation of anaerobic respiration
C6H12O6 —> 2 lactate(lactic acid) + 2ATP
stage 1 of anaerobic respiration
glycolysis to form 2 pyruvate
stage 2 of anaerobic respiration
lactic fermentation - pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid by oxidising NADH + H+ , happens in cytoplasm
what are the downsides of anaerobic respiration?
low energy yield
build up of lactic acid
what is the problem with lactic acid?
low pH - affects enzym activity
how do cells get rid of lactic acid?
resynthesized to pyruvate, then transported through Krebs cycle etc.
Excessive post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC)
oxygen uptake greater than normal in recovery period after exercise to break down lactic acid - oxygen debt
what is oxygen needed for in oxygen debt?
breakdown of lactic acid via Krebs cycle
transport of lactic acid to liver to resynthesise glucose
reoxygenation of myoglobin
increased metabolism
energy to allow increased breathing and heart rate
gluconeogenesis
synthesis of glucose
where does energy come from at the beginning of exercise?
as ATP is used, it is immediately regenerated from phosphocreatine stored in muscles which give Pi to ADP
how long does the PC store last?
can generate ATP for about 6-10 seconds
how are PC levels restored?
creatine gets Pi from ATP when we are at rest
what are the three energy systems?
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
ATP-PC
what does the ability to do prolonged strenuous exercise depend on?
genetics
gender
fitness
ratio of fast to slow twitch muscle fibres
aerobic capacity
ability to consume oxygen
factors that affect aerobic capacity
breathing efficiency
cardiac output
efficiency of oxygen use in muscles
VO2
aerobic capacity - volume O2 consumption per minute
VO2 max
maximal aerobic capacity during intense exercise
effect of training on aerobic capacity
increased vital capacity
increased capillarisation of lungs
increased stroke volume of heart
increased cardiac output
increased red blood cell production
increased capillarisation of muscles
lower fat : muscle ratio
increased number and size of mitochondria
cardiac output
the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one minute
equation for cardiac output
cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
why does cardiac output increase during exercise?
to deliver oxygen to muscles and remove carbon dioxide at a higher rate
stroke volume
volume of blood pumped out of the left ventricle per contraction
why does stroke volume increase during exercise?
greater force of contraction and larger venous return
venous return
the volume of blood returning to heart in vena cava
heart rate
the number of left ventricle contraction per minute
ECG
graphic record of electrical activity during the cardiac cycle
control of heart rate
cardiovascular control centre in medulla receives impulses
impulses form CO2 chemoreceptors and baroreceptors in vena cava, aorta and carotid artery
sends impulses down sympathetic(accelerator) or parasympathetic(decelerator) nerves
tidal volume
volume of air breathed in and out at each breath at rest
vital capacity
maximum volume of air that can be breathed in and out
inspiratory reserve volume
maximum volume of air that can be inhaled beyond tidal
expiratory reserve volume
maximum volume of air that can be exhaled beyond tidal
reserve volume
volume of air remaining in lungs after maximal exhalation
total lung capacity
volume of lungs at maximal inhalation
minute ventilation
volume of air taken into lungs in one minute