Visual Fields
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1. What are visual field defects commonly referred to as?
A) Blind spots
B) Scotomas
C) Glaucomas
D) Retinopathies
B) Scotomas
On average;
the monocular visual field extends nasally about __ degrees, temporally about __ degrees, superiorly about __ degrees, and inferiorly about __ degrees.
60 degree nasally
90-110 degree temporally
60 superiorly
70 inferiorlly
Blind spot 15 degree temporally
In bitemporal hemianopia, there is a loss of which visual field?
A) Nasal visual field in both eyes
B) Temporal visual field in both eyes
C) Upper visual field
D) Lower visual field
B) Temporal visual field in both eyes
What does "homonymous hemianopia" mean?
Visual field defects in both eyes are on the ______ side of vision.
Same
Explanation: Homonymous hemianopia refers to visual field defects that affect the same side in both eyes.
An altitudinal defect is a visual field defect that respects the __________ midline and involves two quadrants of either superior or inferior visual fields.
Horizontal
What is quadrantanopia?
Quadrantanopia is the loss of one __________ of the visual field.
Answer: Quarter
Explanation: Quadrantanopia refers to a type of visual field defect where one quarter of the visual field is lost, which can be classified as bitemporal, binasal, or homonymous.
Complete visual field loss is defined as the _______ loss of visual field in a specific area.
Total
Incomplete visual field loss involves a ________ reduction in vision within a specific area.
Partial
Congruity describes how ________ the visual field defect is between two eyes.
Symmetrical
Congruity in visual field defects refers to how similar the defects are in shape, size, location, and density between the two eyes.
A __ defect is identical in both eyes
An __ defect indicates asymmetry and can suggest a compressive lesion.
Congruous
Incongruous
The more congruous the visual field defect, the __ the lesion is along the visual pathway.
Further
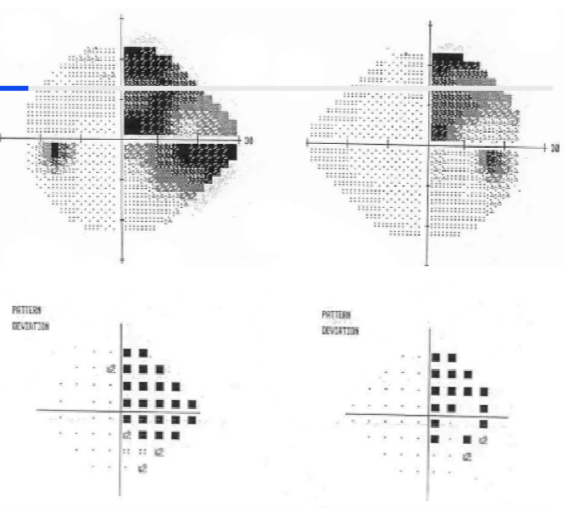
__ __ incomplete __ hemianopia
Incongruous right incomplete homonymous hemianopia
What is macular sparing in the context of visual field defects?
Macular sparing refers to the preservation of central vision (from the macula and fovea) in the presence of a visual field defect, such as a hemianopia or quadrantanopia.
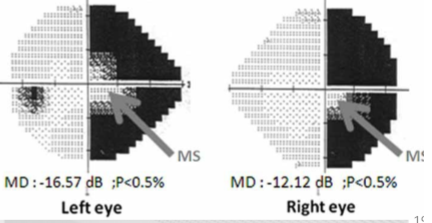
Macular sparing is often associated with injuries to which part of the brain?
The occipital lobe.
Explanation: It is commonly linked to injuries or lesions in the occipital lobe.
The spared area in macular sparing must include at least how many degrees to be confirmed clinically?
At least 3 degrees.
Explanation: This is necessary for clinical confirmation of macular sparing.
What are the primary reasons for macular sparing to occur?
Extensive blood supply to the occipital lobe.
Large representation of the macula in the occipital lobe ("cortical magnification").
Explanation: These factors help protect central vision despite surrounding visual field defects.
What are arcuate defects?
Arcuate defects are curves or arc-shaped visual field losses.
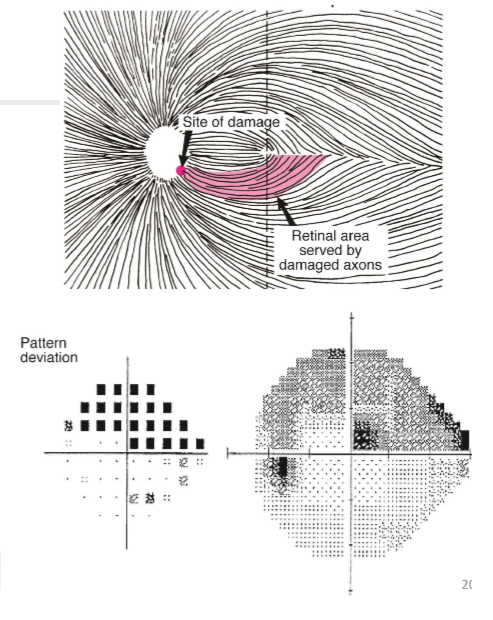
How do arcuate defects typically manifest in visual fields?
They can extend to the blind spot and often end abruptly at the nasal horizontal meridian at the horizontal retinal raphe.
In the context of glaucoma, what is significant about arcuate defects?
Arcuate defects are often one of the first areas of decline in glaucoma, making them crucial for early detection and diagnosis.
A nasal step is a defect in the visual field that sits on the ________ meridian but does not ________ it.
horizontal; cross
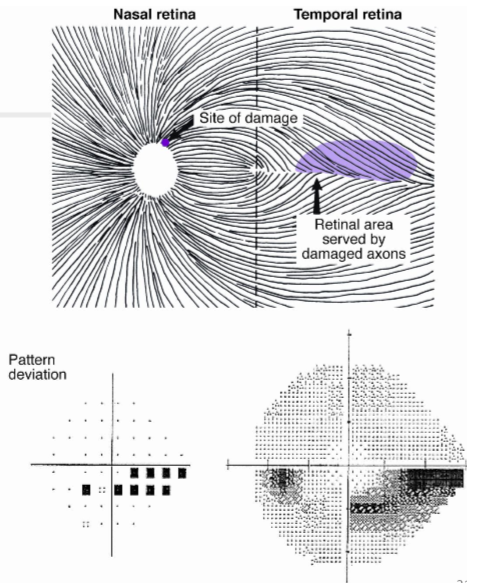
A nasal step can be ________ or ________.
superior; inferior
A nasal step often precedes an ________ defect in glaucoma.
arcuate
Nasal steps correspond anatomically to the nerve fibre axons from the area ________ to the macula.
temporal
A paracentral scotoma is an island of field loss located within ________ of fixation.
10 degrees
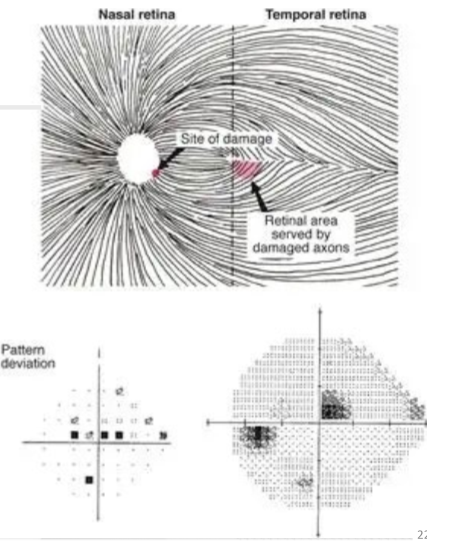
Paracentral scotoma is caused by loss of nerve fibres from the ________ or ________ retina.
inferotemporal; superotemporal
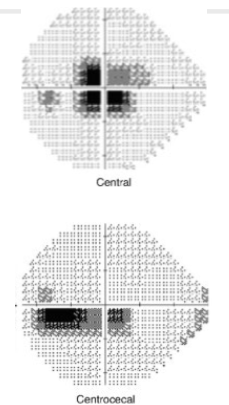
A centrocecal scotoma extends from central vision to the ________.
blind spot
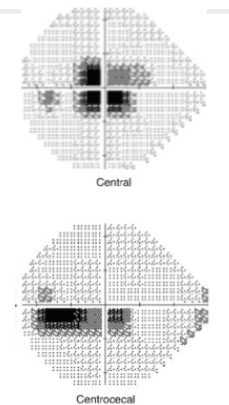
The main difference between central and centrocecal scotomas is that the former involves only the area of fixation, while the latter extends to the ________.
blind spot
Sensitivity loss in visual field assessments is reported as or __ (total loss of sensitivity).
relative; absolute
Relative scotomas refer to areas of visual field loss where perception is ________.
diminished
Absolute scotomas refer to areas of visual field loss where perception is ________.
completely lost
Modern visual field assessments shine light of different intensities at different points on the retina to identify where light is ________ and at what ________.
detected; intensity
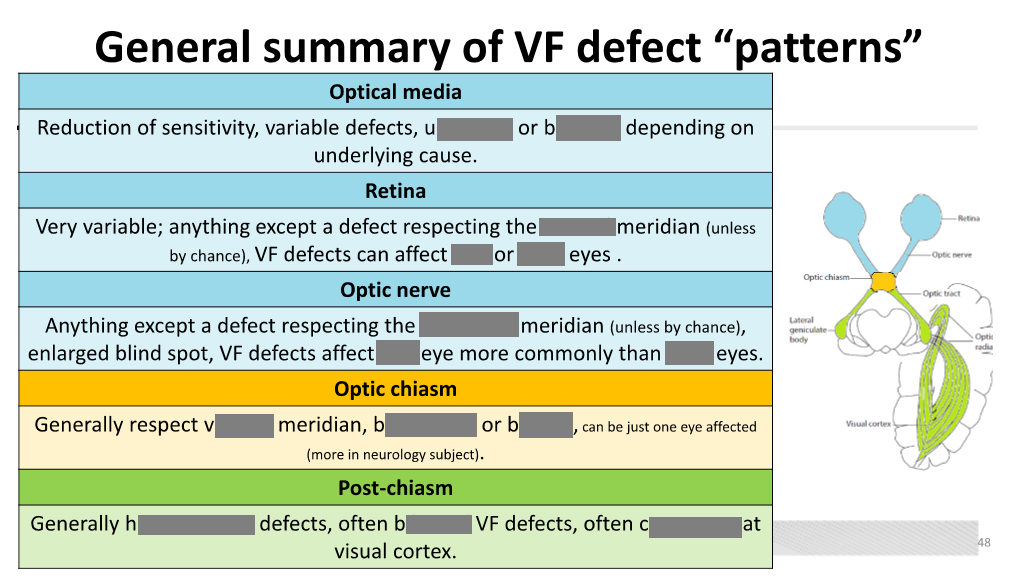
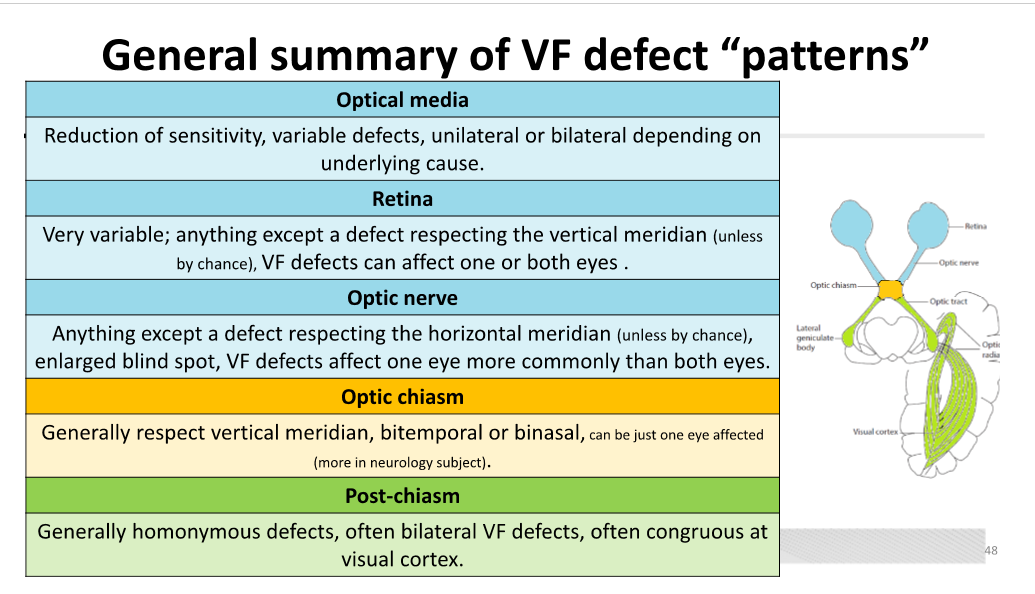
Unilateral visual field defects are located ________.
pre-chiasm
Bitemporal (or binasal) defects are typically located at the ________.
chiasm
Homonymous visual field defects are located ________.
post-chiasm
Glaucoma can cause visual field defects such as ________, ________, and ________.
nasal step; arcuate defects; tunnel vision
Swelling of the optic nerve can lead to an ________ and can cause generalized constriction of ________.
enlarged blind spot; visual field (VF)
Compression of the optic nerve can be caused by ________, ________, and ________.
tumors; TED; gliomas
Vascular abnormalities at the optic nerve can cause ________ vision loss and may present with various findings such as ________ and ________.
sudden; arcuate scotomas; central scotomas
Retinal degeneration, such as ________, can cause central scotomas of varying density.
macular degeneration
Retinal dystrophy can lead to generalized constriction of the ________.
visual field
In retinal infection or inflammation, the visual field defect is located according to the position of the ________ on the retina.
pathological lesion
Retinal tumors can cause that correlate to the __ of the retina involved by the tumor.
scotomas, area
Vascular abnormalities at the chiasm often arise from the ________.
internal carotid artery
Lesions at the chiasm are most commonly caused by ________ and ________.
pituitary adenomas; vascular abnormalities
Lesions at the chiasm can cause compression of the ________.
optic chiasm
Aneurysms or dilations of blood vessels can lead to ________ at the chiasm.
compression
It is common for field loss at the optic tract to be ________.
Homonymous
Lesions at the optic radiations can cause visual field defects due to the segregation of ________ and ________ fibers.
inferior; superior
Visual field defects of isolated optic radiation bundles take the form of ________.
quadrantanopias
Static Perimetry
Definition: Varying intensities of lights are used to determine visual sensitivity thresholds at different locations within the ____.
Outcome: Produces a quantified point-by-point ____ of vision.
Visual, Hill
Kinetic Perimetry
Definition: Moving stimuli of predetermined light sensitivities are moved from non-seeing to ____ areas.
Outcome: Creates a “____” line map of the field of vision.
Seeing, Geographic
The Humphrey Visual Field Analyser (HVFA) primarily conducts _____ visual field assessments.
Static
The HVFA can assess up to _____ degrees in screening mode.
160
The Goldmann perimeter is _____ operated.
manually
Goldmann perimetry is very good for assessing patients with _____ conditions.
neurological
Octopus perimetry is a _____ version of the Goldmann perimeter.
computerized
The primary delivery of stimulus in Octopus perimetry is _____, similar to HVFA.
static
The Bjerrum Screen is used to manually map visual fields. It mainly involves _____ testing, but static testing can also be applied. The Bjerrum Screen can only assess _____ of visual field.
kinetic
30-35 degrees
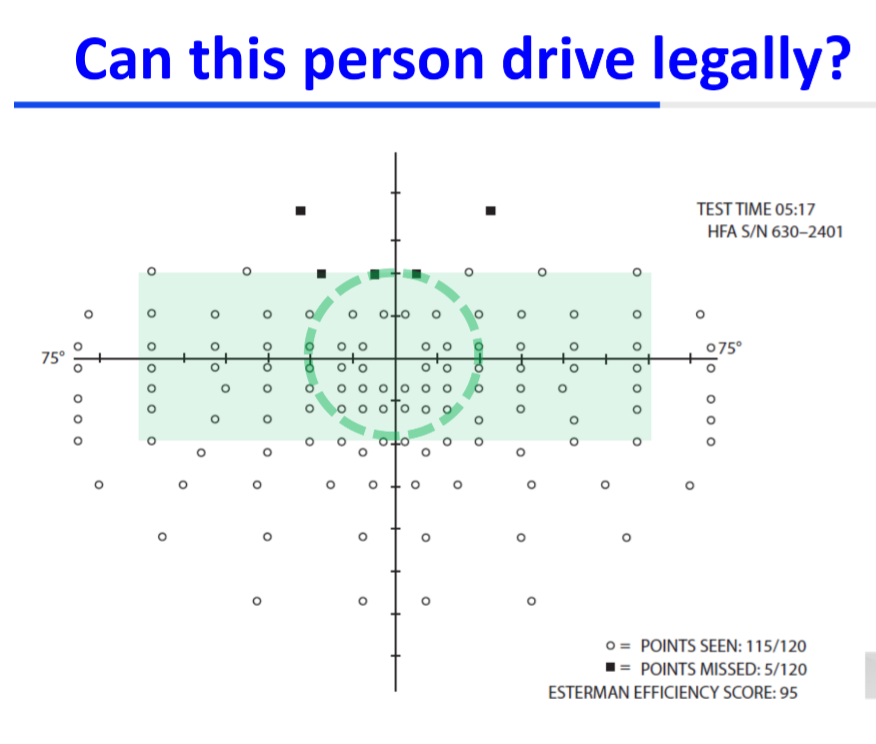
Visual field defects impair the ability to detect driving hazards compared to participants' normal performances.
__ visual field defects have been found to have more impact than _____ defects.
superior, inferior
By law, an adequate field of _____ vision is required for safe driving.
A driver must have at least _____° of horizontal visual field (60° left and right).
The vertical field must be at least _____° (20° up and down).
Within the central _____°, there must be no visual field defect.
binocular
120
40
20
An _____ visual field assessment can be conducted using a HVFA, Octopus, or Goldmann.
Esterman
The _____ Esterman test is suitable for monocular drivers.
The _____ Esterman test is recommended for binoculary sighted drivers.
Monocular, Binocular