Module 4
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MKT 351
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Mere Exposure
Individuals develop a preference for certain products or brands simply because they are familiar with them. Frequent exposure can lead to increased liking and can influence purchasing decisions.
Purchase Involvment
Level of concern for the purchase process, triggered by the need to consider a particular purchase, temporary state influenced by the interaction of individual, product, and situational characteristics
Decision Making
Need recognition, search for information, evaluation of alternatives, choice/purchase decision, post purchase evaluation … Feedback
Nominal decision making
Low involvement, no alternative evaluation, minimal information search, no postpurchase evaluation
limited decision making
Moderate involvement, some alternative evaluation, information search, and post purchase evaluation.
Extended decision making
High involvement, extensive information search, thorough evaluation of alternatives, and significant post-purchase evaluation. (relative external search)
Habitual Decision Making
also nominal, do not seek information at all, related to brand loyalty and repeat purchases
Do decision making processes always led to consumer choice or purchases
No, decision-making processes do not always lead to consumer choice or purchases due to factors like indecision, external influences, or changing preferences.
Rational Decision-Making perspective
refers to a structured or systematic process of making choices based on logical reasoning, evaluation of alternatives, and expected outcomes.
experimental decision-making perspective
Focuses on hedonic value or variety seeking behavior. Consumers seek new products as a response to boredom or to satisfy a perceived need for change. Based on the effect, or feeling attached to a product or behavior.
Behavioral Influence decision making perspective
Mainly influenced by the physical environment, store layouts, design, point of purchase displays
Problem recognition
disparity between their current and desired state, the gap must be substantial Ac
active problem
one consumer is aware of or will become aware that a problem exists and is motivated to find a solution.
inactive problem
which the consumer is not aware of and must be convince they have the problem, and the brand can fix it
Five primary sources of information available to consumers
A memory of past searches, personal experiences, and low- involvement learning.
Personal sources, such as friends, family, and others.
Independent sources, such as magazines, consumer groups, social media influencers, and government agencies.
Marketing sources, such as sales personnel, company websites and social media, and advertising.
Experiential sources, such as inspection or product trial.
Inept set
avoided alternatives, which a consumer considers unacceptable or unworthy based on prior experience or negative perceptions.
Inert set
neutral alternatives in awareness set that you have no feelings or are indifferent to
Three ways to use consistent messaging
Use the same value proposition
Use similar calls to action
Use the same design elements
affective choices
tend to be more holistic brand not defined by rational evaluation, focusing instead on the emotional connection to the brand.
two types of attributes
perceptual which is visually apparent and recognizable (size, shape, color, etc.) and underlying which is not readily apparent can only be learn through experiences
Conjunctive Rule
establishes minimum required performance for each evaluative criterion. Eliminate the choice that falls under the cut-off
1- poor, 5- good
minimum req- 3 for different performances like price
disjunctive rule
The option selected surpasses a relatively high cut-off point on at least one attribute, needs to reach the score of ten
need at least one to reach the best performance on a single attribute
Only focusing on ONE attribute
Lexicographic rule
Choose the option that scores the highest on the more important attributes
Rate which attribute is more important, gas mileage is the most important. Choose honda.
Only focusing on one criteria
compensatory decision making rule
The brand that rates the highest on the sum of the consumer’s judgements of the relevant evaluative criteria.
Weight each attribute.
You are accounting into all of the factors will be chosen.
service product
paying for other persons efforts and work
Differences between goods and services
intangibility, heterogeneity (individual and unique), simultaneously production and consumption, perishability (cant bring home)
Derived Services
the function of physical goods, becomes a part of the service. ie a razor or gaming council
service environments
Ambient conditions (noise music oder)
Space function (layout equipment)
Signs/symbols
facilitator
Servicescapes can make it easier or more difficult for customers to accomplish their goals. Improve the service experience.
socializer
help customers and employees understand their expected roles
differentiator
unique/aesthetically pleasing design, more functional features than competitors, that sets a product apart in the market.
Showrooming effect
the phenomenon of consumers visiting a B&M store, examine the products, but then buying online to obtain lower prices.
Webrooming Effect
is a shopping trend where customers research products online and then buy them in a physical store.
Percived Risk
Social cost, financial cost, time, effort, physical cost
Post Purchase dissonance
occurs when a consumer has doubts or anxiety regarding the wisdom of a purchase made and is a function of the following:
The degree of commitment or irrevocability of the decision
The importance of the decision to the consumer
The difficulty of choosing among the alternatives
The individual’s tendency to experience anxiety
Brand Laziness
Low involvement and low processing effort: a natural inertia toward a brand based on familiarity and convenience
Problem solving
High involvement and processing effort ; deliberated effort to collect info and carefully evaluate a variety of brands
Variety Seeking
Choosing new alternatives over more familiar/recently purchased ones
Brand Loyalty
intrinsic commitment to a brand based on specific benefits and values offered, self-concept enhanced
problem recognition
when consumers recognize a disparity between their current state and their desired state
Active Problem
A problem that a consumer is currently aware of and is actively seeking to resolve through purchases or other means.
Inactive Problem
A problem that consumers are not currently aware of, which may influence their decisions once recognized.
Churn
refers to turnover in a firms customer base.
Base of 100 customers, 20 leave each year and 20 new ones become customers. You have a churn rate of 20%
Consumption guilt
when negative emotions or guilt feelings are aroused by the use of a product or a service
Net promoter score
an indirect word of mouth measure of true attitudinal loyalty.
It gauges customer satisfaction and their likelihood to recommend a product or service to others.
(promoters, passively satisfied, detractors)
NPS = (% promoters - % detractors)
omni-channel shoppers
Consumers who engage with a brand across multiple channels, such as online and offline, to make purchases.
switching cost
The costs that a consumer incurs as a result of changing brands or suppliers. Switching costs can include time, money, and effort involved in making the transition.
use innovativeness
a consumer using a product in a new way
relationship marketing
an attempt to devlop an ongoing expanding exchange relationship within a firms customers’.
Three types of decision making
nominal, limited, and extended
evoked set
alternatives given consideration to
Awareness set
Evoked, inert and inept
Maintenance Strategy
The brand is purchased habitually by the target market, the marketers strategy is to maintain that behavior.
This strategy focuses on reinforcing customer loyalty and ensuring consistent repurchase patterns to sustain market presence.
Disrupt Strategy
challenge and alter existing consumer behaviors and preferences, aiming to capture market share from competitors by introducing innovative solutions or products.
Preference strategy
aims to create a strong brand preference among consumers, differentiating the product from competitors through unique benefits or emotional connections.
What are the three types of consumer choices
affective choice, attitude-based choice, and attribute-based choice.
attitude-based choice
consumers evaluate options based on their overall feelings or attitudes towards a brand, rather than specific attributes or features.
attribute based choice
consumers assess options based on specific product attributes or features, comparing them to make a decision.
affective choice
consumers make decisions based on their emotional responses or feelings about the options available, often prioritizing personal sentiments over logical analysis.
surrogate indicator
used to stand for or indicate another attribute
that consumers may use when they lack direct information about a product's quality or performance.
Expectancy Disconfirmation Theory
consumers form expectations about a product's performance and that satisfaction results from the comparison between their expectations and the actual performance.
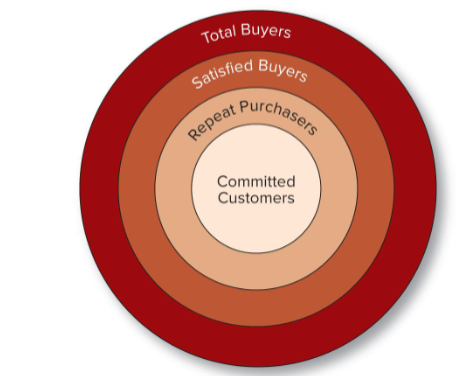
Creating Committed customer is increasing the focus of marketing strategy
Total buyers, satisfied buyers, to repeat purchasers, to committed customers. Costs more to obtain newer customers, satisfaction = profit
evaluative criteria
comparison of brands on one or more attributes
includes the various dimensions, features, or benefits a consumer looks for in response to a specific problem