Geographical Concepts - Yr9
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is spicess
space, place, interconnection, change, environment, sustainability, scale
Space
Is an abstract idea, it is a continuous 3-D area without meaning .
Involves:
Location - where things are located
Spatial distribution - the shapes and patterns in which things are arranged
Organisation - how and why things are arranged and managed by people
Interconnection
The idea that there us a link between all people places and environment.
change
the degree to which a place, is modified over time.
time to better understand a place, an environment, a spatial pattern or a geographical problem.
sustainability
maintaining the capacity of the environment to support our lives and those of other living creatures.
environmental, social and economic criteria to judge the wisest use of resources.
scale
relationship between the size of an area on a map and the actual size of an area on the Earth’s surface.
distance
The length of space between two locations
distribution
arrangement of features or objects on the Earth’s surface.
PQE is used to describe it
movement
change in location of a phenomenon.
It also describes how people and ideas in one place make contact with people from another place; for example, by plane, the internet etc.
region
definable area containing one (usually more) characteristics that distinguish it from surrounding areas.
Regions can be defined by physical characteristics such as mountain ranges, politically by official decisions about boundaries and names; for example, Bayside City Council.
spatial association
the degree to which two or more phenomena are similarly distributed or arranged on the Earth’s surface.
Place
A specific location with meaning and significance:
Name of a place - Name a place that starts with the same letter as your first name.
Location - Absolute (e.g. an address or latitude and longitude) and Relative (the distance and direction from another place).
Landmarks - Name a landmark on each continent.
Regions (e.g. the Yarra Valley)
Sense of place (e.g. home)
Spiritual significance (eg. ancient indigenous sites where rituals take place)
Property (e.g. The Emporium)
A specific environment (e.g. rainforest, desert)
Environment
All physical and biological aspects that influence life
What must Maps include
Border – a box around the map to clearly show its extent
Orientation – a compass direction
Legend – the key to what the symbols and colours on the map stand for
Title – a clear indication of what the map is about or its theme
Scale – indicates distances on the map compared with the actual area being shown
Source – where possible the information used to make the map
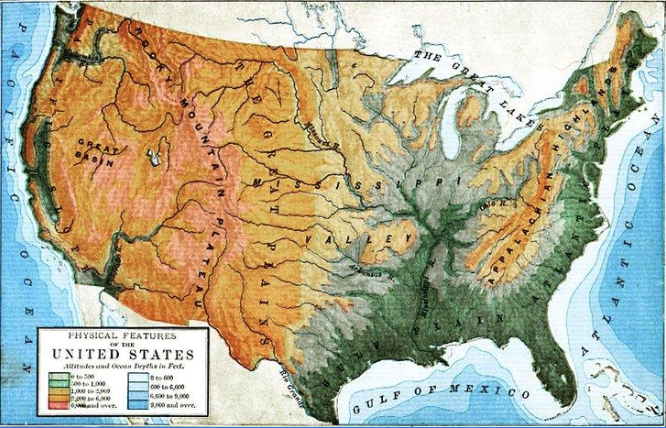
Physical Maps
display the physical features of a place, including land and water features such as mountains, plains, rivers, and oceans.
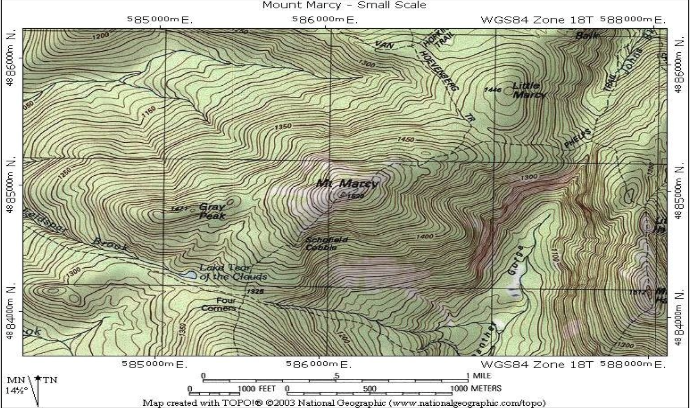
Topographic Maps
used to show elevation
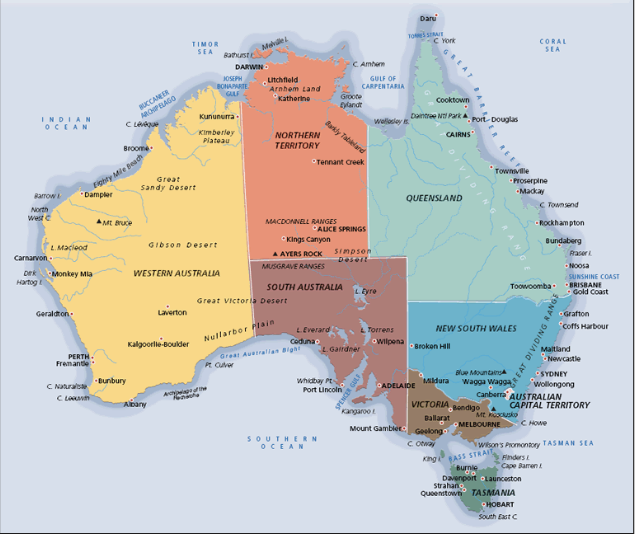
Political
display artificial boundaries such as state or national borders, as well as cities and sometimes bodies of water.
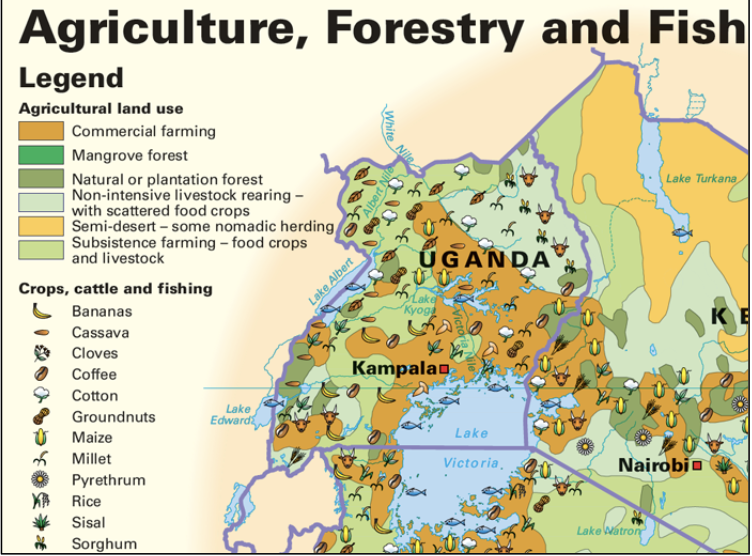
Thematic
Map has a particular theme, symbols, picture, and colours are used to represent what is being mapped.
Process
Physical and human forces work in combination to form and transform the world.
eg:
erosion, hydrological (water) cycle, migration or urbanisation.
What are Grid References, Eastings, and Northings?
Grid references are a method to locate things on maps. The vertical lines on the map are called eastings, and the horizontal lines are call northings. Eastings are numbered towards the East, and northings are number towards North.