Econ Chapter 8
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
When is market is perfectly competitive?
if all the firms in that market act as price takers
Price takers:
Firms that must accept the market price because they are too small to influence it.
Competition increases the ____ of ____ demand for each seller’s output
elasticity; residual
Residual demand:
the part of market demand that is left over for one firm after all other firms have supplied their amount.
In summary, increased competition in terms of demand means:
More elastic residual demand
Very competitive markets in terms of demand means:
residual demand is almost perfectly elastic
A market is perfectly competitive if all the firms in that market act as ______
Perfectly competitive markets in terms of demand means:
A market is perfectly competitive if all the firms in that market act as price takers
Residual demand is perfectly elastic
Perfectly elastic residual demand means firms must sell at:
Market price
If demand ↓, what happens to price and where does each firm move? What does the demand curve and MR curve look like?
price ↓ and firm moves down MC
D gets smaller and flatter —> same thing happens to MR because when demand goes down, price and quantity go down

If demand ↑, what happens to price and where does each firm move?
price ↑ and firm moves up its MC
As more firms join the market, what does the demand curve look like?
Curve gets flatter and flatter until looks horizontal (more elastic)
(these demand curves are not the demand for the entire market, just the demand for each individual firm)
ex: demand for tomatoes are not perfectly elastic, but tomatoes for a specific vendor are perfectly elastic because there’s so many similar vendors around them
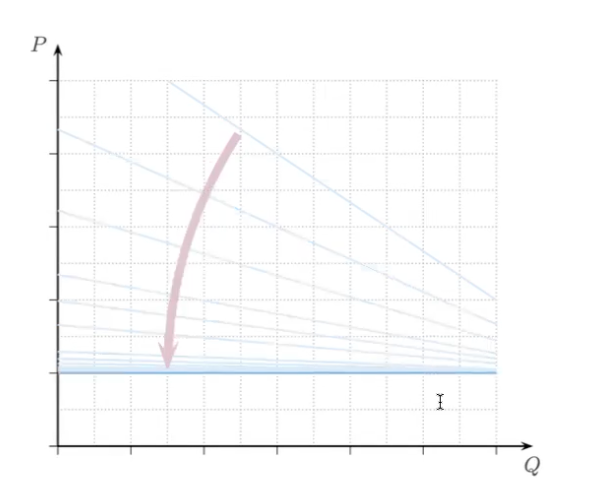
Competitive firms cannot influence _____
market price
Because they cant influence market price, they can only do these 2 things:
take price as given
only choose how much to produce
Marginal revenue = what 2 things?
Marginal revenue = demand = price
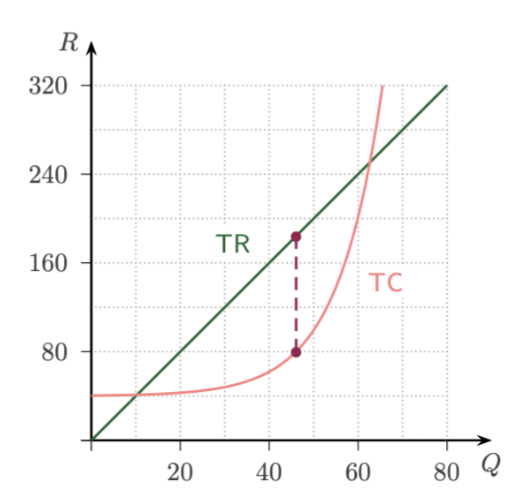
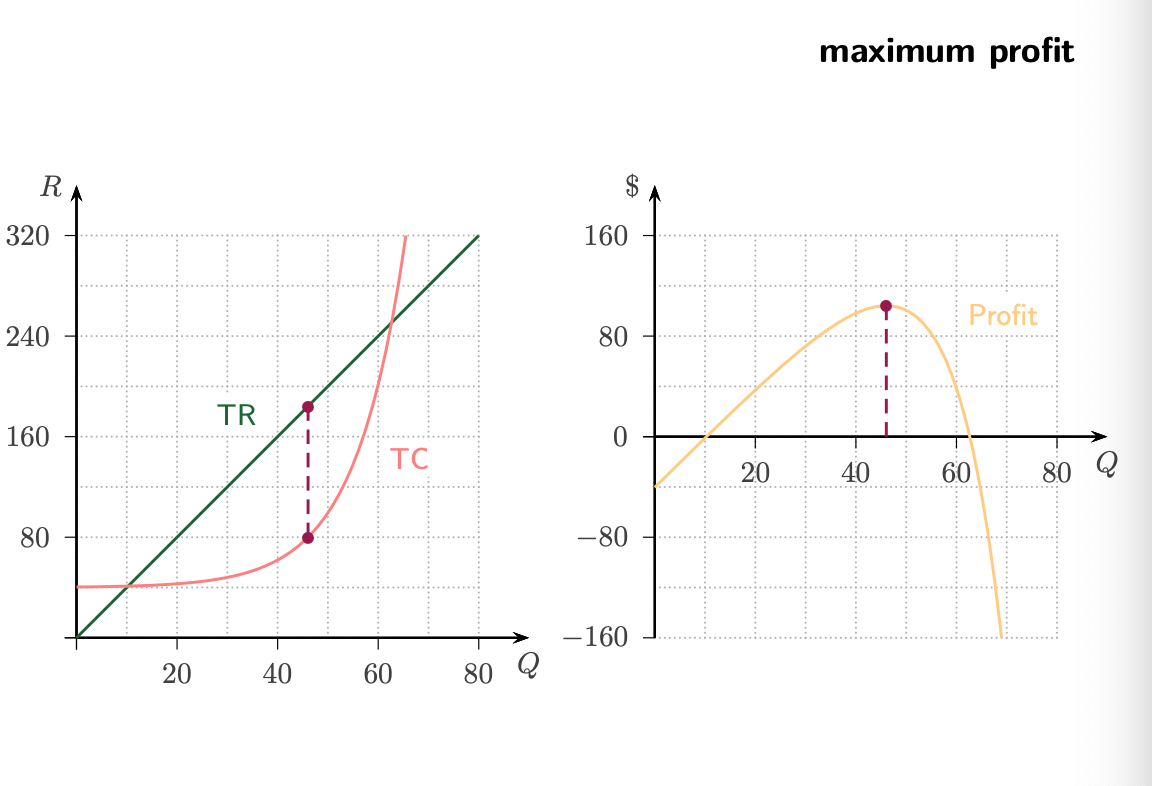
How to make a profit graph from TR and TC? How to find maximum profit?
If a firm in a competitive market produces a positive quantity, the optimal output solves what?
MC = P
Firms are still monopolists of their own output but the difference is:
their residual demand is perfectly elastic
Where is the optimal price?
where D=MC
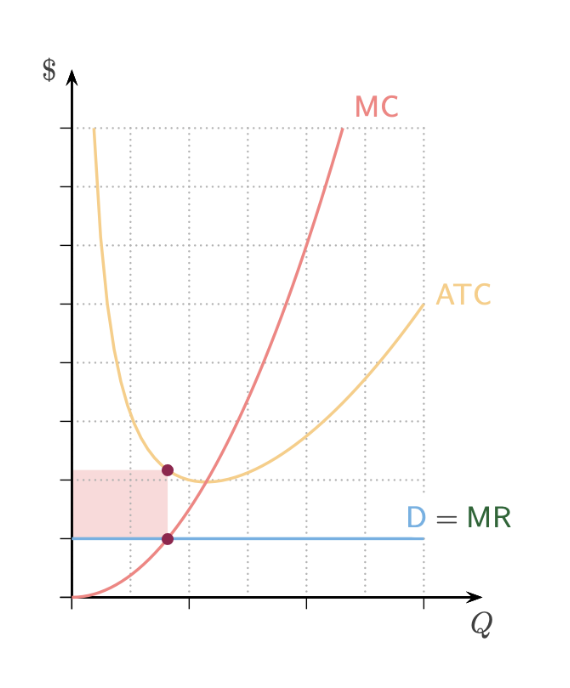
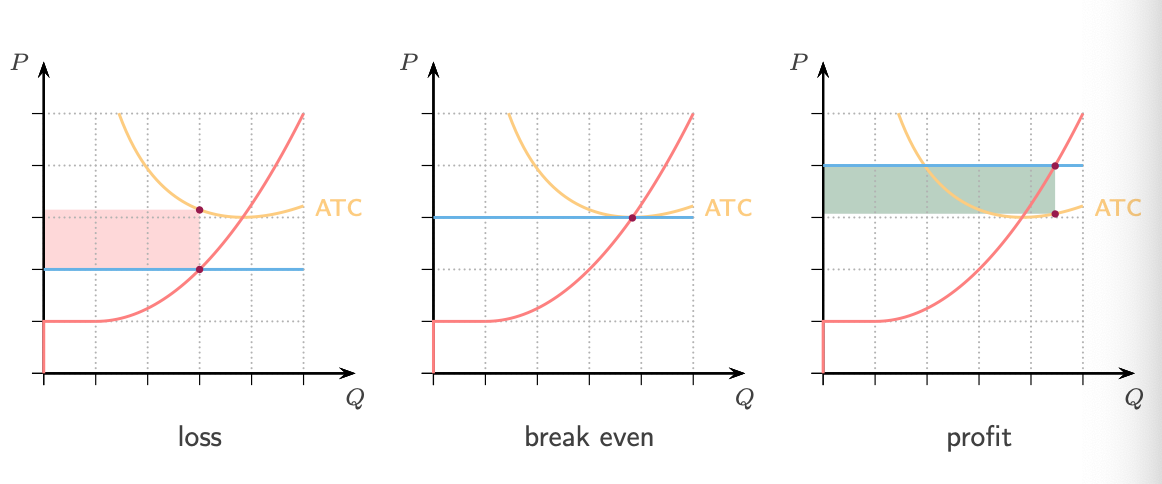
What happens when P > ATC? What type of signal is it? What happens to price? What happens to profit?
If P > ATC → profit → entry signal → lower prices → lower profit
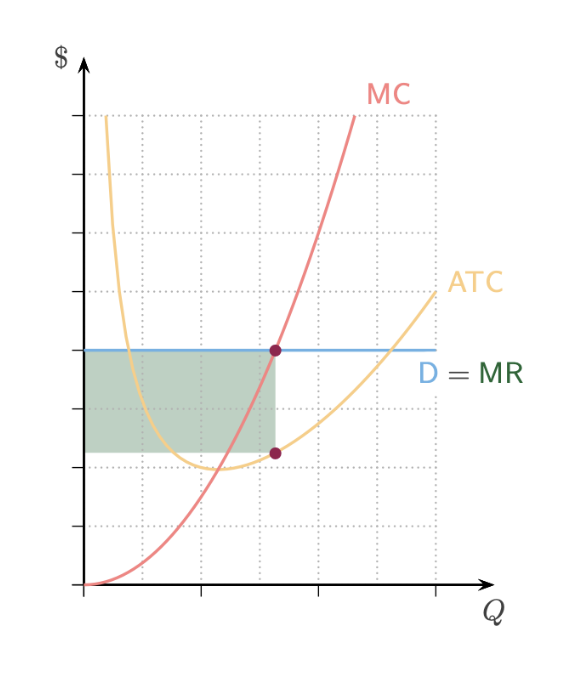
What happens when P = ATC? What type of signal is it? What happens to price? What happens to profit?
If P = ATC → break even → no change → same price and profit (zero)
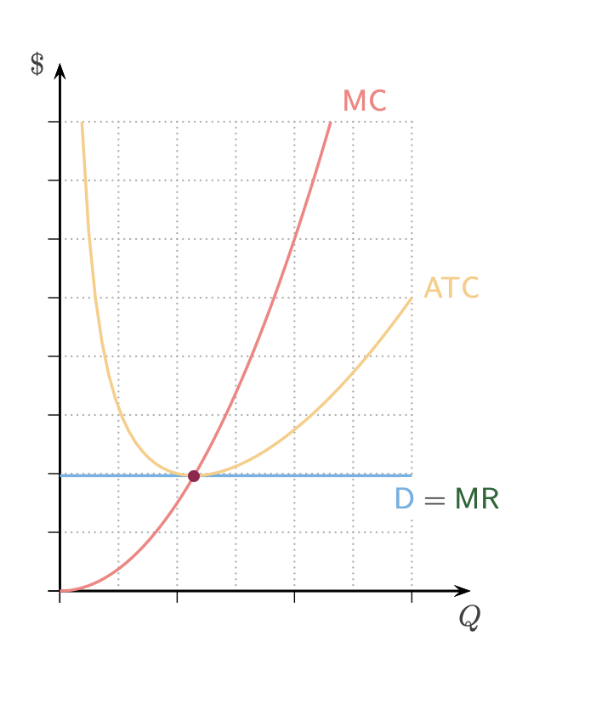
What happens when P < ATC? What type of signal is it? What happens to price? What happens to profit?
If P < ATC → loss → exit signal → higher prices → higher profit
The individual supply function of a firm in a competitive market corresponds to the ____ curve above the ____ curve
MC curve above the AVC curve
Red curve = MC
Blue = price (P)
Red curve = Supply
Blue = market demand (D)

Production is only worth it when?
When P > min AVC
What happens when P < min AVC instead?
Temporary shutdown
Where is the exact shutdown point? What does that mean in terms of loss>
where AVC is minimum; at that price, indifferent between producing and shutting down; loss = TFC
Why do competitive equilibrium profits approach zero in the long run?
Because of free entry and an unlimited number of potential entrants
Break-even point determines what two things?
long run price
&
MC = ATC
Minimum efficient scale determines _____
number of firms
Economic profit ______ accounting profit
doesn’t equal
Zero economic profit (normal profit only) ≈ ______
same accounting profit across industries
Short run market supply curve shows the quantity supplied by:
What happens if all firms are identical?
all the firms in the market at each price
if all firms are identical, multiply by number of firms
A short run partial competitive equilibrium for a competitive market consists of what 2 things?
an equilibrium price P
an equilibrium quantity Q
(they must be equal to each other)
Where is Allocative efficiency?
where P=MC
Why is MR Curve always Below Demand curve?
To sell more, the monopolist must lower the price on all units, not just the extra unit.
So marginal revenue falls faster than price.
Compare P and Q with Perfect competition vs Monopoly
Perfect competition: Low P, high Q —> efficient
Monopoly: High P, low Q —> creates deadweight loss
What is deadweight loss?
Lost trades that would benefit society but dont happen under monopoly