Atoms and Molecules
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Matter
anything that had mass and takes up space
Atom
the smallest unit of matter
How does an atom absorb energy, and what does it do?
It absorbs energy in the form of heat, light, or sound, and it then vibrates and then releases the energy
Why do atoms tend to release as much energy as possible:?
The less energy an atom has, the more stable it is.
Element
any substance that cannot be bokren down into any simpler substance
Periodic Table
a categorized and organized table of all 118 elements, invents by Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleyer
Atomic Number
the number of protons in an element define its position within the Periodic Table of Elements
Chemical Symbol
each element on the Periodic Table is assigned a symbol usually made up of one or two letters.
Period
each row in the Periodic Table
Group/Family
each column in the Periodic Table
Subatomic Particle
a substance that is smaller than an atom
What are the three subatomic particles?
protons, neutrons, and electrons
What charge do protons hold?
a positive charge
What charge do electrons hold?
a negative charge
How do particles act together?
Particles with the same electric charge repel each other away, particles with opposite charges are attracted to each other
What charge do neutrons possess?
Neutrons do not possess a charge, yet they still play a key roles within an atom’s structure
What is the center of an atom called and what are they composed of?
The center of an atom is called a nucleus, and they are primarily composed of protons and neutrons
How do protons affect a nucleus?
They give the nucleus a positive charge.
How does the positive charge of a nucleus affect electrons?
The positive charge within the nucleus from protons cause the electrons to orbit around the nucleus.
Isotope
atoms that have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons
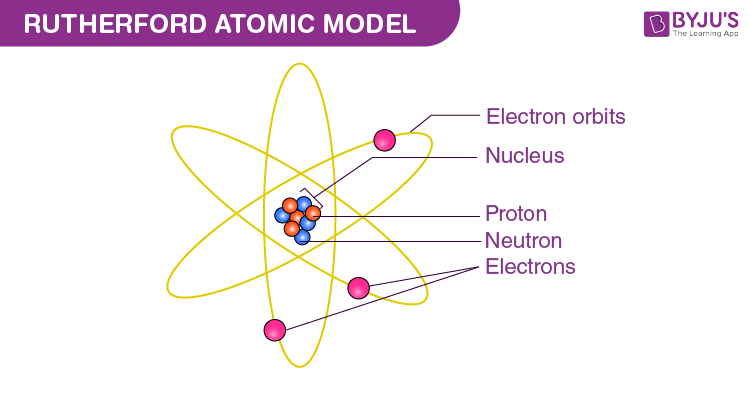
Rutherford Atomic Model
A model curated by Ernest Rutherford that is historically imporant, but not the most common amongst science fields.
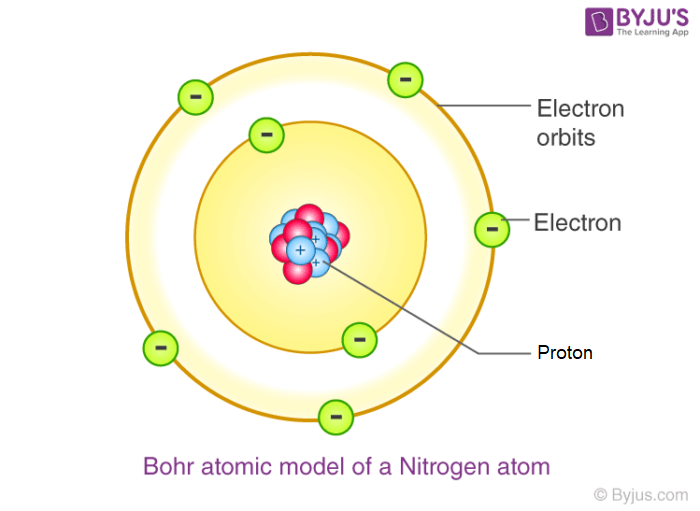
Bohr Model
The most common model that represent atoms and their electron shells and is based on orbiting electrons.
Electron Shell
electrons move outside the nucleus in various shells, which are basically rings of energy levels.
What is the relationship between electrons and level shells?
The greater the energy of an electron, the higher level shell it will then occupy.
What are electron orbits similar to and in what ways?
The electron orbits are similar to our solar system. The electrons that orbit the nucleus is similar to the planets of our solar system orbiting around the Sun.
Core Electrons
the electrons in the shells closest to the nucleus
have the strongest attractive force to the positively charged nucleus, making them the most stable shell
Valence Electron
electrons in the shells that are farthest away from the nucleus
have the largest orbits
What are the characteristics of a valence electron’s stability?
They are more unstable than core electrons and have the highest energy levels, making them the least stable level. Because they are the least stable, they are also more likely to break away from the influence of the nucleus.
What is the maximum number of valence electrons in any orbit dependent on?
It is dependent on how small the orbit is, and there can be more than one valence electron within a shell.
What is the correlation between the proximity of a shell and the amount of electrons?
The closer the shell is to the nucleus, the fewer electrons there are, due to the negative charge of each electron.
Hypothetically, what would happen if there were tens of electrons packed into one shell?
They would repel each other and cause the energy of the whole atom to increase, rendering the atom very unstable.
What are the maximum amount of electrons in each shell?
Two electrons in the shell closest to the nucleus, eight electrons in the next, and the third has a maximum of eighteen.
Why do electrons first occupy the shells closest to the nucleus before occupying other levels?
Due the atom’s preference for stable levels of energy and because the shells represent the lowest energy states availible to the electrons in the atom
Although an atom usually prefers to be at its lowest energy state so that it can maintain its stability, what are the two exceptions?
energy is added to the atom and/or an atom’s valence electron shell is not completely filled to the max.
Because valence electrons contain higher energy than other electrons, what happens when an electron shell is filled?
all electrons in that shell behave similarly to core electrons, increasing the atoms’ stability and lowering its energy.
What does an incomplete valence electron shell cause?
They typically cause the attractive force from the positively charged nucleus to spill out of the atom.
What happens as a result in order to combat the nucleus spills?
Electrons from outside of the shells will move into the leaks to plug them. completing the valence shell.
Atomic Bonding
the process where atoms interact with other atoms to lower their energy. Atoms with incomplete valence electron shells tend to participate in this process, essentially taking electrons from other atoms to achieve a full valence shell.
Covalent Bonding
atoms essentially share a pair of electrons, and then the shared pairs of electrons can fill the outermost energy shells of the bonded atom.
Molecules
a group of atoms bonded together
How many atoms with other atoms bond with in order to maintain low energy?
Atoms will bond with as many other atoms as needed to achieve stability and low energy.
Compound
the combination of two or more different atoms
What is the difference between molecules and compounds?
Molecules can be made up of differing elements or the same elements, while a compound must be made up of different atoms. So, atoms make up molecules, and molecules make up compounds, but not all compounds are molecules.
Diatonic
some elements that exist as molecules composed of two of the same atom
i.e Oxygen (O2) and Hydrogen (H2)